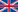
Allied Warships
HMS Ark Royal (91)
Aircraft Carrier of the Ark Royal class

HMS Ark Royal in sinking condition
| Navy | The Royal Navy |
| Type | Aircraft Carrier |
| Class | Ark Royal |
| Pennant | 91 |
| Built by | Cammell Laird Shipyard (Birkenhead, U.K.) |
| Ordered | 17 Apr 1935 |
| Laid down | 16 Sep 1935 |
| Launched | 13 Apr 1937 |
| Commissioned | 16 Dec 1938 |
| Lost | 13 Nov 1941 |
| Loss position | 36° 03'N, 4° 45'W |
| History | At 1637 hours on 13 November 1941 the German submarine U-81 fired a spread of four torpedoes at the British battleship HMS Malaya in Force H and heard two detonations after 6 minutes 6 seconds and 7 minutes 43 seconds. In fact one torpedo hit HMS Ark Royal (Capt. Loben Edward Harold Maund, CBE, RN) amidships, which sank under tow by the British tug HMS Thames with almost all of her aircraft about 25 nautical miles east of Gibraltar, in position 36°03'N, 04°45'W, at 0813 hours on 14 November 1941. The carrier was returning from Operation Perpetual. On 10 November, the carrier had left Gibraltar together with the British carrier HMS Argus to ferry 37 Hurricane fighters to Malta under escort by the Force H, formed by HMS Malaya, HMS Hermione and seven destroyers [see events below for a full account of this operation and her sinking.] Hit by U-boat |
| U-boat Attack | See our U-boat attack entry for the HMS Ark Royal |
Commands listed for HMS Ark Royal (91)
Please note that we're still working on this section
and that we only list Commanding Officers for the duration of the Second World War.
| Commander | From | To | |
| 1 | Capt. Arthur John Power, RN | 17 Jan 1938 | 20 Apr 1940 |
| 2 | Capt. Cedric Swinton Holland, RN | 20 Apr 1940 | 18 Apr 1941 |
| 3 | Capt. Loben Edward Harold Maund, RN | 19 Apr 1941 | 13 Nov 1941 |
You can help improve our commands section
Click here to Submit events/comments/updates for this vessel.
Please use this if you spot mistakes or want to improve this ships page.
Notable events involving Ark Royal include:
The page of HMS Ark Royal was created in March 2022.
This page was last updated in April 2024.
[Note: information regarding operations by the Fleet Air Arm (FAA) aircraft of HMS Ark Royal is not complete on this page. Further research from first hand sources, read original documents from the National Archives, will have to be undertaken in the future.]
31 Aug 1939
Around 1800A/31, the Home Fleet departed Scapa Flow to patrol between Scotland, Iceland and Norway for returning German merchant vessels.
Ships that participated in this patrol were; battleships HMS Nelson (Capt. G.J.A. Miles, RN, flying the flag of Admiral J.M. Forbes, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Rodney (Capt. E.N. Syfret, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), light cruisers HMS Aurora (Capt. G.B. Middleton, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral R.H.C. Hallifax, RN), HMS Sheffield (Capt. E. de F. Renouf, CVO, RN), HMS Belfast (Capt. G.A. Scott, DSC, RN) (from the 18th Cruiser Squadron), HMS Effingham (Capt. J.M. Howson, RN), HMS Cardiff (Capt. P.K. Enright, RN), HMS Dunedin (Capt. C.E. Lambe, CVO, RN), HMS Emerald (Capt. A.W.S. Agar, VC, DSO, RN) (from the 12th Cruiser Squadron), HMS Caledon (Capt. C.P. Clark, RN), HMS Calypso (Capt. N.J.W. William-Powlett, DSC, RN), HMS Diomede (Commodore E.B.C. Dicken, OBE, DSC, RN), HMS Dragon (Capt. R.G. Bowes-Lyon, MVO, RN) (from the 7th Cruiser Squadron. These ships were escorted by destroyers from the 8th Destroyer Flotilla; HMS Faulknor (Capt. C.S. Daniel, RN), HMS Fame (Cdr. P.N. Walter, RN), HMS Fearless (Cdr. K.L. Harkness, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, RN), HMS Foresight (Lt.Cdr. G.T. Lambert, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Fortune (Cdr. E.A. Gibbs, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. P.H. Hadow, RN) and HMS Fury (Cdr. G.F. Burghard, RN).
To patrol off the Skagerrak was the battlecruiser squadron which was made up of the battlecruisers HMS Hood (Capt. I.G. Glennie, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral W.J. Whitworth, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Repulse (Capt. E.J. Spooner, DSO, RN) which were escorted by destroyers from the 6th Destroyer Flotilla; HMS Somali (Capt. R.S.G. Nicholson, DSC, RN), HMS Ashanti (Cdr. W.G. Davis, RN), HMS Bedouin (Cdr. J.A. McCoy, RN), HMS Eskimo (Cdr. St. J.A. Micklethwait, RN), HMS Mashona (Cdr. P.V. McLaughlin, RN), HMS Matabele (Cdr. G.K. Whitmy-Smith, RN), HMS Punjabi (Cdr. J.T. Lean, RN) and HMS Tartar (Capt. G.H. Warner, DSC, RN). These ships departed Scapa Flow around the same time.
Some of the ships had already been at sea for exercises.
The bulk of the Fleet returned to Scapa Flow in the morning of September 6th.
Most of the cruisers had acted independently to inspect shipping. HMS Caledon, HMS Calypso, HMS Cardiff and HMS Dunedin returned to Scapa Flow in the early morning of September 5th.
HMS Aurora and HMS Sheffield returned to Scapa Flow in the evening of September 5th.
HMS Belfast returned to Scapa Flow on the 6th after having joined other ships for exercises on the 5th.
HMS Diomede, HMS Dragon, HMS Effingham and HMS Emerald returned to Scapa Flow in the morning of the 7th.
Most of the destroyer had to return to Scapa Flow once to refuel, HMS Somali and HMS Ashanti were at Scapa Flow between 0100/2 and 0400/2.
HMS Faulknor, HMS Fearless, HMS Firedrake, HMS Fortune and HMS Foxhound were at Scapa Flow between 1000A/3 and 1530A/3.
HMS Bedouin, HMS Eskimo, HMS Punjabi and HMS Tartar were at Scapa Flow between 1100A/3 and 1600A/3.
HMS Fame was detached at 2359A/3 to go to the aid of the torpedoed liner Athenia but she was not needed to pick up survivors and proceeded to the Clyde arriving in the moring of the 5th having carried out an A/S sweep en-route.
HMS Matabele was detached to Scapa Flow at 1130/5. Around 2030A/5, she grounded near the boom and damaged her propellers.
HMS Foresight, HMS Forester, HMS Fury and HMS Mashona did not refuel before they returned with the Fleet in the morning of the 6th. (1)
7 Sep 1939
Around 0730A/7 the battleships HMS Nelson (Capt. G.J.A. Miles, RN, flying the flag of Admiral J.M. Forbes, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Rodney (Capt. E.N. Syfret, RN), battlecruiser HMS Repulse (Capt. E.J. Spooner, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), light cruisers HMS Aurora (Capt. G.B. Middleton, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral R.H.C. Hallifax, RN), HMS Sheffield (Capt. E. de F. Renouf, CVO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. C.S. Daniel, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, RN), HMS Foresight (Lt.Cdr. G.T. Lambert, RN), HMS Fortune (Cdr. E.A. Gibbs, RN), HMS Fury (Cdr. G.F. Burghard, RN), HMS Ashanti (Cdr. W.G. Davis, RN), HMS Bedouin (Cdr. J.A. McCoy, RN), HMS Mashona (Cdr. P.V. McLaughlin, RN), HMS Punjabi (Cdr. J.T. Lean, RN), HMS Somali (Capt. R.S.G. Nicholson, DSC, RN) and HMS Tartar (Capt. G.H. Warner, DSC, RN) departed Scapa Flow to operate off the Norwegian coast as far north as 63°00'N to intercept German shipping.
They returned to Scapa Flow in the evening of the 10th having sighted no German ships. Visibility had been bad throughout.
11 Sep 1939
A/S operations by HMS Ark Royal in the Western Approaches.
11 September 1939.
At 2030A/11, a submarine hunting group, made up of the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) departed Scapa Flow for an A/S patrol in the Western Approaches. She is escorted by the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. C.S. Daniel, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. P.H. Hadow, RN) and HMS Eskimo (Cdr. St. J.A. Micklethwait, RN).
12 September 1939.
At 0625A/12, seven Swordfish aircraft were flown off for an all round A/S sweep. Around 0700A/12, one of these spotted a surfaced submarine and attacked it. This was the German submarine U-37 whih reported hearing two explosions but these were not close. At 0720A/12, HMS Faulknor and HMS Firedrake were detached to hunt this submarine but they could not make contact and rejoined HMS Ark Royal around 0945A/12.
The aircraft returned around 0845A/12.
At 1200A/12, HMS Ark Royal was in position 59°34'N, 10°31'W. Around 1307A/12, course was altered to the south-east.
At 1600A/12, Nine Swordfish were flown off for an all round A/S sweep. One of the aircraft returned at 1620A/12 with engine trouble.
Around 1800A/12, the remaining eight Swordfish returned to HMS Ark Royal.
13 September 1939.
At 0638A/13, HMS Ark Royal started flying off ten Swordfish aircraft for an all round A/S search. These aircraft returned around 1000A/13.
At 0741A/13, an aircraft reported a submarine about 40 miles south of HMS Ark Royal. Bombs were dropped and a direct hit was claimed on the submarine which was reported to be diving at that time. [was this perhaps U-39 ?].
Around 0807A/13, A strike force of three aircraft was launched to attack the reported submarine but they failed to find it as did HMS Foxhound and HMS Eskimo which had been detached around the same time.
HMS Foxhound and HMS Eskimo rejoined HMS Ark Royal around 1430A/13. The aircraft had returned around 1108A/13.
At 1200A/13, HMS Ark Royal was in position 56°45'N, 14°19'W.
Around 1308A/13, eight Swordfish were launched for an A/S search. They returned around 1500A/13.
Around 1533A/13, three aircraft were flown off. They returned around 1715A/13.
Around 1653A/13, seven aircraft were flown off for an A/S sweep. They returned around 1940A/13.
14 September 1939.
Around 0630A/14, the destroyers HMS Tartar (Capt. G.H. Warner, DSC, RN), HMS Bedouin (Cdr. J.A. McCoy, RN) and HMS Punjabi (Cdr. J.T. Lean, RN) joined HMS Ark Royal.
Around the same time HMS Ark Royal launched 14 Swordfish for an A/S search. These aircraft returned around 0935 hours shortly after 16 aircraft for a new A/S search had been launched.
At 1200A/13, HMS Ark Royal was in position 58°13'N, 11°22'W.
At 1223A/14, the merchant vessel Fanad Head (British, 5200 GRT, built 1917) was attacked by the German submarine U-30 in position 56°43'N, 15°21'W. They managed to send a signal that they were being attacked.
Around 1240A/14, Vice-Admiral Wells was informed of the Fanad Head being attacked. So HMS Tartar and HMS Punjabi were detached to the position of the attack at 32 knots.
Around 1345A/14, the aircraft that had been launched around 0935A/14 were landed on.
Around 1312A/24, HMS Bedouin and HMS Eskimo were detached to join HMS Tartar and HMS Punjabi but HMS Eskimo was later recalled to rejoin the carrier so HMS Bedouin went on and joined HMS Tartar and HMS Punjabi around 2155A/24.
At 1440A/24, HMS Ark Royal launched three Skua's armed with bombs to search for the attacking submarine. They were sent because they had a longer range then the Swordfish aircraft.
Around 1511A/14, HMS Ark Royal was missed by two torpedoes fired a few minutes before by the German submarine U-39. HMS Faulknor, HMS Firedrake and HMS Foxhound then attacked the submarine with depth charges. The submarine was forced to surface and was then taken under fire by the destroyers. The submarine sank shortly afterwards in position 58°32'N, 11°49'W, the destroyers picked up it's entire crew of 44.
At 1540A/14, one of Ark Royal's Skua's sighted a merchant vessel which turned out to be the Fanad Head and on closing it was seen the a U-boat was laying alongside. The aircraft immediately attacked from low altitude but as the bombs hit the water the aircraft was heavily damaged, caught fire and then crashed.
The attack was seen by one of the other Skua's. On the Fanad Head port bow they sighted an oil patch with a black object in the center of it. They thought this was the conning tower of a submarine and started an attack and they dropped all their bombs in two runs. It was later thought that the object they had sighted was the wreck of the crashed Skua. The Skua, now out of bombs, strafed U-30 after she surfaced due to a dinghy still being tied to her. After the rope was cut, the submarine quickly submerged again. As the aircraft was now low on fuel she had to return to HMS Ark Royal on which she landed on around 1825A/14.
The third Skua was on it's way back to HMS Ark Royal when a ship was spotted in the distance. They closed and then sighted a submarine appearing from the merchant ship. An attack was started just like the first Skua had done and the third Skua also dropped it's bombs from to low and sustained damage. She too crashed.
After the aircraft crashed U-30 surfaced again to toke off her boarding party from the Fanad Head. She then moved off to launch a torpedo and finish off the merchant vessel.
In the meantime, after the report from the second Skua came in, around 1650A/14, HMS Ark Royal launched a strike force. Five of these aircraft attacked the submarine shortly after it had finished off the merchant vessel. The strike force returned to HMS Ark Royal around 1958A/14. Around the same time HMS Tartar and HMS Punjabi arrived in the area of the sinking and HMS Tartar picked up the crew of the Fanad Head. They then searched the area but could not make contact on the submarine.
Around 2000A/14, HMS Faulknor, HMS Firedrake and HMS Foxhound returned from their hunt and sinking of U-39. HMS Eskimo then parted company to join the three other Tribal-class destroyers.
15 September 1939.
The Tribal-class destroyers did not rejoin HMS Ark Royal but conducted an A/S sweep.
At 0635A/15, Swordfish aircraft were launched by HMS Ark Royal for an A/S search. A/S patrols were maintained throughout the day.
Around 1800A/15, HMS Faulknor, HMS Forester and HMS Foxhound were detached shortly after HMS Fury (Cdr. G.F. Burghard, RN) and HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN) had joined the carrier.
Around 1830A/15, HMS Fearless (Cdr. K.L. Harkness, RN) and HMS Fortune (Cdr. E.A. Gibbs, RN) also joined the screen of the carrier.
16 September 1939.
Around 0710A/16, Swordfish aircraft were launched by HMS Ark Royal for an A/S search. again A/S patrols were maintained throughout the day but nothing was seen.
Around 1200A/16, HMS Tartar, HMS Bedouin and HMS Punjabi joined HMS Ark Royal and her four escorting destroyers.
17 September 1939.
Around 0715A/17, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Tartar, HMS Bedouin and HMS Punjabi, HMS Fearless, HMS Forester, HMS Fortune and HMS Fury arrived at Loch Ewe. (2)
17 Sep 1939
A/S operations by HMS Ark Royal in the Western Approaches.
17 September 1939.
Around 1415A/17, the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Fearless (Cdr. K.L. Harkness, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Fortune (Cdr. E.A. Gibbs, RN) and HMS Fury (Cdr. G.F. Burghard, RN) departed Loch Ewe for more A/S operations in the Western Approaches. Course was set to proceed southwards through the Minches.
Around 1600A/17, HMS Ark Royal launched six Swordfish for an A/S search. They returned around 1915A/17.
Around 1800A/17, HMS Forester was detached to join the destroyers HMS Somali (Capt. R.S.G. Nicholson, DSC, RN) and HMS Matabele (Cdr. G.K. Whitmy-Smith, RN) which were also on passage to the area having also departed Loch Ewe around 1415A/17 but were already further to the south. HMS Forester joined them around 0015A/18.
18 September 1939.
Around 0600A/18, HMS Ark Royal launched six aircraft for an A/S search. A/S patrol were maintained throughout the day.
Around mid-afternoon HMS Ark Royal is ordered to return to Loch Ewe.
Around 1550A/18, HMS Somali, HMS Matabele and HMS Forester joined HMS Ark Royal.
At 2040A/18, HMS Somali and HMS Matabele were detached to act on a submarine attack report.
19 September 1939.
Around 0615A/19, HMS Ark Royal launched six aircraft for an A/S search. They returned around 0915A/19.
Around 0945A/19, HMS Ark Royal arrived at Loch Ewe escorted by HMS Fearless, HMS Forester, HMS Fortune and HMS Fury. Immediately after arriving the destroyer departed again. (3)
20 Sep 1939
Battleships HMS Nelson (Capt. G.J.A. Miles, RN, flying the flag of Admiral J.M. Forbes, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Rodney (Capt. E.N. Syfret, RN), battlecruisers HMS Hood (Capt. I.G. Glennie, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral W.J. Whitworth, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Repulse (Capt. E.J. Spooner, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, RN), HMS Fortune (Cdr. E.A. Gibbs, RN), HMS Punjabi (Cdr. J.T. Lean, RN) and HMS Tartar (Capt. G.H. Warner, DSC, RN) departed Loch Ewe in the evening for Scapa Flow. They were joined by the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. C.S. Daniel, RN), HMS Fearless (Cdr. K.L. Harkness, RN), HMS Foresight (Lt.Cdr. G.T. Lambert, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. P.H. Hadow, RN) and HMS Fury (Cdr. G.F. Burghard, RN) which had departed Scapa Flow earlier, most likely for an A/S sweep and then to join the escort.
This force arrived at Scapa Flow in the morning of the 21st but not before four more destroyers; HMS Bedouin (Cdr. J.A. McCoy, RN), HMS Eskimo (Cdr. St. J.A. Micklethwait, RN), HMS Mashona (Cdr. P.V. McLaughlin, RN) and HMS Matabele (Cdr. G.K. Whitmy-Smith, RN) had joined the escort.
22 Sep 1939
Operation SK.
To conduct an operation against German shipping off the Norwegian coast the light cruiser HMS Aurora (Capt. G.B. Middleton, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral R.H.C. Hallifax, RN) and the destroyers HMS Tartar (Capt. G.H. Warner, DSC, RN), HMS Punjabi (Cdr. J.T. Lean, RN), HMS Eskimo (Cdr. St. J.A. Micklethwait, RN) and HMS Bedouin (Cdr. J.A. McCoy, RN) departed Scapa Flow around 0700A/22 as well as the light cruisers HMS Southampton (Capt. F.W.H. Jeans, CVO, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral G.F.B. Edward-Collins, CB, KCVO, RN), HMS Sheffield (Capt. E. de F. Renouf, CVO, RN), HMS Glasgow (Capt. F.H. Pegram, RN) and the destroyers HMS Jervis (Capt. P.J. Mack, RN), HMS Javelin (Cdr. A.F. Pugsley, RN) and HMS Jupiter (Lt.Cdr. D.B. Wyburd, RN) which had departed Rosyth around 0415A/22. HMS Jersey (Lt.Cdr. A.M. McKillop, RN), coming from the Chatham Dockyard, joined at sea.
To provide cover for this operation two forces were deployed from Scapa Flow. One force was made up of the battlecruisers HMS Hood (Capt. I.G. Glennie, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral W.J. Whitworth, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Repulse (Capt. E.J. Spooner, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Fame (Cdr. P.N. Walter, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, RN), HMS Foresight (Lt.Cdr. G.T. Lambert, RN) and HMS Fortune (Cdr. E.A. Gibbs, RN). They had departed Scapa Flow around 1000A/22.
The other force was made up of the battleships HMS Nelson (Capt. G.J.A. Miles, RN, flying the flag of Admiral J.M. Forbes, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Rodney (Capt. E.N. Syfret, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. C.S. Daniel, RN), HMS Fearless (Cdr. K.L. Harkness, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. P.H. Hadow, RN), HMS Somali (Capt. R.S.G. Nicholson, DSC, RN), HMS Mashona (Cdr. P.V. McLaughlin, RN) and HMS Matabele (Cdr. G.K. Whitmy-Smith, RN). Later the destroyers HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Fury (Cdr. G.F. Burghard, RN), HMS Esk (Lt.Cdr. R.J.H. Couch, RN) and HMS Express (Cdr. J.G. Bickford, RN) joined at sea. They had departed Scapa Flow around 1030A/22.
The raid was abandoned when HMS Javelin and HMS Jersey collided in position 57°09'N, 03°08'W at 2038A/22.
All forces returned to their port of departure on 23 September but not before HMS Hood reported an explosion at 1330A/23. The destroyers HMS Firedrake and HMS Fortune were detached to investigate but no contact was obtained. In fact this was indeed an attack by a German submarine; U-24 which reported to have made a failed torpedo attack at 1328A/23 on HMS Hood and two escorting destroyers.
25 Sep 1939
At 0510A/25 a radio message was received from the submarine HMS Spearfish (Lt. J.H. Eaden, RN) that she had been badly damaged by enemy warships and that she was unable to dive and was proceeding along the Danish coast try to make it back to the U.K.
Around 0730A/25 the light cruisers HMS Southampton (Capt. F.W.H. Jeans, CVO, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral G.F.B. Edward-Collins, CB, KCVO, RN) and HMS Glasgow (Capt. F.H. Pegram, RN) departed Rosyth and joined destroyers HMS Jervis (Capt. P.J. Mack, RN) and HMS Jupiter (Lt.Cdr. D.B. Wyburd, RN) near May Island shortly after 0900 hours. They were to operate off the Norwegian coast at 60°N to closely cover the retreat of the damaged submarine. with the destroyers HMS Somali (Capt. R.S.G. Nicholson, DSC, RN), HMS Eskimo (Cdr. St. J.A. Micklethwait, RN), HMS Mashona (Cdr. P.V. McLaughlin, RN) and HMS Matabele (Cdr. G.K. Whitmy-Smith, RN) which were already on patrol in that area.
The light cruisers HMS Aurora (Capt. G.B. Middleton, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral R.H.C. Hallifax, RN) and HMS Sheffield (Capt. E. de F. Renouf, CVO, RN) departed Scapa Flow and were ordered to proceed well into the approaches of the Skagerrak with the destroyers HMS Fame (Cdr. P.N. Walter, RN), and HMS Foresight (Lt.Cdr. G.T. Lambert, RN) which had been on the Fare Island patrol. These ships were to try to make contact with HMS Spearfish.
To provide more distant cover for the whole operation the battlecruisers HMS Hood (Capt. I.G. Glennie, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral W.J. Whitworth, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Repulse (Capt. E.J. Spooner, DSO, RN), heavy cruiser HMS Norfolk (Capt. A.G.B. Wilson, DSO, RN) and the destroyers (Capt. A.G.B. Wilson, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. C.S. Daniel, RN), HMS Fearless (Cdr. K.L. Harkness, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, RN), HMS Foresight (Lt.Cdr. G.T. Lambert, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Fortune (Cdr. E.A. Gibbs, RN) and HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. P.H. Hadow, RN) departed Scapa Flow.
[It is often stated that the light cruisers HMS Newcastle (Capt. J. Figgins, RN), HMS Edinburgh (Capt. F.C. Bradley, RN) also sailed with the 'Hood-Force' but this was not the case.]
Also from Scapa Flow sailed yet another cover force made up of the battleships HMS Nelson (Capt. G.J.A. Miles, RN, flying the flag of Admiral J.M. Forbes, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Rodney (Capt. E.N. Syfret, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Tartar (Capt. G.H. Warner, DSC, RN), HMS Punjabi (Cdr. J.T. Lean, RN), HMS Bedouin (Cdr. J.A. McCoy, RN) and HMS Fury (Cdr. G.F. Burghard, RN).
Around 0100A/26 the destroyers HMS Somali and HMS Eskimo made contact with HMS Spearfish which was then safely escorted to Rosyth despite German air attacks during which HMS Ark Royal was near missed and HMS Hood struck by a bomb which did not explode.
All ships returned to port late on the 26th or on the 27th September minus HMS Norfolk which was detached earlier to join the Northern Patrol being ordered to patrol in the Iceland-Faeroer gap.
1 Oct 1939
1 October 1939, an enemy raider reported in the South Atlantic and Indian Ocean. The chase of the German ‘pocket battleship’ Admiral Graf Spee
Movements of the German ‘pocket battleship’ Admiral Graf Spee 21 August 1939 – 13 December 1939.
Before the Second World War had started, on 21 August 1939, the German ‘pocked battleship’ Admiral Graf Spee departed Wilhelmshaven bound for the South Atlantic. On 1 September the Admiral Graf Spee was off the Canary Islands where she made rendes-vous with the supply ship Altmark and supplies were transferred.
On 11 September another rendes-vous was made with the Altmark in the South Atlantic. The Admiral Graf Spee had launched her Arado floatplane to scout in the area as supplies were transferred. The aircraft spotted the British heavy cruiser HMS Cumberland (Capt. W.H.G. Fallowfield, RN). The German ships then immediately parted company and cleared the area at high speed. Two days later, on the 13th, the ships again met and fueling was completed. The Admiral Graf Spee was still under orders to remain unseen.
On 20 September 1939 the Admiral Graf Spee and Altmark met again to fuel. On the 26th the Admiral Graf Spee was ordered to start raiding the British trade lanes. She then proceeded towards the Pernambuco area.
On 30 September 1939 the Admiral Graf Spee found her first victim, the British merchant vessel Clement (5050 GRT, built 1934) that was en-route from New York, U.S.A. to Bahia, Brasil. She then sank the ship in position 09°05’S, 34°05’W. The Admiral Graf Spee then proceeded eastwards and found three more victims between 5 and 10 October. On the 5th she captured the British merchant Newton Beech (4644 GRT, built 1925) in position 09°35’S, 06°30’W. This ship was en-route from Capetown to the U.K. via Freetown. On the 7th she sank the British merchant Ashlea (4222 GRT, built 1929) in position 09°52’S, 03°28’W. This ship was en-route from Durban to Falmouth. The crew of the Ashlea was transferred to the Newton Beech. The next day both crew were transferred to the Admiral Graf Spee and the Newton Beech was scuttled. On 10 October the Admiral Graf Spee captured the British merchant Huntsman (8196 GRT, built 1921) in position 08°30’S, 05°15’W. This ship was en-route from Calcutta to the U.K. On 15 October 1939 the Admiral Graf Spee met the Altmark again to receive supplies and fuel. On the 17th the crew of the Huntsman was transferred to the Altmark and the ship was scuttled in approximate position 16°S, 17°W. The next day the crews of the Newton Beech and Ashlea were also transferred to the Altmark and the German ships then parted company.
On 22 October 1939, the Admiral Graf Spee sank her next victim, the British merchant Trevanion (5299 GRT, built 1937) which was en-route from Port Pirie (Australia) to Swansea. This ship was sunk in position 19°40’S, 04°02’E. On 28 October 1939, near Tristan da Cunha, the Admiral Graf Spee once more refuelled from the Altmark. The Admiral Graf Spee then set course for the Indian Ocean.
On 15 November 1939 she sank the small British tanker Africa Shell (706 GRT, built 1939) in position 24°45’S, 35°00’E. This ship was in ballast and en-route from Quelimane (Portugese East Africa now called Mozambique) to Lourenco Marques (now Maputo, also in Portugese East Africa / Mozambique). Next day the Admiral Graf Spee stopped the Dutch merchant Mapia (7188 GRT, built 1923) but had to let her go as she was a neutral ship. The Admiral Graf Spee then set course to return to the South Atlantic where she met once more with the Altmark on 27 November 1939 and the next day she fuelled from her about 300 miles from Tristan da Cunha.
On 2 December 1939, the Admiral Graf Spee sank her largest victim, the British merchant Doric Star (10086 GRT, built 1921),in position 19°15’S, 05°05’E. This ship was en-route from Auckland, New Zealand to the U.K. The next morning the Admiral Graf Spee sank the British merchant Tairoa (7983 GRT, built 1920) in position 19°40’S, 04°02’E. This ship was en-route from Brisbane, Australia to London. On 6 December 1939 the Admiral Graf Spee refuelled once more from the Altmark. She then set course to the River Plate area where the British merchant traffic was the thickest. She was to sink more ships there and disrupt British shipping movements in that area before returning to Germany.
On 7 December 1939 the Admiral Graf Spee sank what was to be her last victim, the British merchant Streonshalh (3895 GRT, built 1928) in position 25°01’S, 27°50’W. This ship was en-route from Montevideo to Freetown and then onwards to the U.K.
Then in the morning of 13 December 1939, her smoke was sighted by three cruisers from the South America Division. More on this in the article ‘The Battle of the River Plate, 13 December 1939’.
British Dispositions in the South Atlantic / South America area
Shortly before the outbreak of the war the South America Division of the America and West Indies Station was transferred to the newly formed South Atlantic Station. The South America Division at that moment consisted of the heavy cruiser HMS Exeter (Capt. F.S. Bell, RN, flying the flag of Commodore H.H. Harwood, OBE, RN) and the light cruiser HMS Ajax (Capt. C.H.L. Woodhouse, RN). In late August 1939 HMS Exeter was at Devonport with her crew on foreign leave when she was recalled to South American waters. On 25 August 1939 she sailed from Devonport. HMS Exeter arrived at Freetown on 1 September 1939. Commodore Harwood then met the Commander-in-Chief South Atlantic Station, Vice-Admiral G. D’Oyly Lyon, CB, RN. Later the same day HMS Exeter sailed for Rio de Janeiro.
Meanwhile four destroyers from the 4th Destroyer Division, Mediterranean Fleet, the HMS Hotspur (Cdr. H.F.H. Layman, RN), HMS Havock (Lt.Cdr. R.E. Courage, RN), HMS Hyperion (Cdr. H.St.L. Nicholson, RN) and HMS Hunter (Lt.Cdr. L. de Villiers, RN) had left Gibraltar on 31 August 1939 for Freetown.
HMS Ajax was already on station off the coast of South America. Shortly after noon on 3 September she intercepted the German merchant vessel Olinda (4576 GRT, built 1927) in position 34°58’S, 53°32’W. This ship was en-route from Montivideo to Germany. As HMS Ajax had no prize crew available the ship was sunk by gunfire a few hours later. In the afternoon of the next day, the 4th, HMS Ajax intercepted another German ship, the Carl Fritzen (6594 GRT, built 1920) in position 33°22’S, 48°50’W. This ship was en-route from Rotterdam to Buenos Aires. This ship was also sunk with gunfire.
On 5 September two of the destroyers from the 4th Destroyer Division, HMS Hotspur and HMS Havock departed Freetown to join the South America Division. They were ordered to examine Trinidade Island on the way. On 8 September 1939 the heavy cruiser HMS Cumberland (Capt. W.H.G. Fallowfield, RN) departed Freetown to join the South America Division as well. This cruiser came from the Home Fleet and had arrived at Freetown on the 7th.
On 7 September 1939, HMS Exeter entered Rio de Janeiro where Commodore Harwood had a meeting with the Brazilian Secretary-General of Foreign Affairs and H.M. Ambassadors to Brazil and Argentine. HMS Exeter departed Rio de Janeiro the next day. Later that day Commodore Harwood was informed by the Admiralty that the German merchant ships General Artigas (11343 GRT, built 1923), Gloria (5896 GRT, built 1917) and Monte Pascoal (13870 GRT, built 1931) were assembling off the Patagonian coast. He decided to move both HMS Exeter and HMS Ajax south, and ordered the Ajax to meet him at 0800/9. They actually made rendezvous at 0700 hours. The Commodore considered it possible that the German merchant ships might embark German reservists and raid the Falkland Islands therefore he decided to sent HMS Ajax there. HMS Exeter proceeded to the Plate area to cover that important area.
On the evening of the 10th, Commodore Harwood was informed that the transportation of German reservists by the three German merchant ships was very unlikely but as it appeared probable that the German ships were converting themselves into armed raiders the Commodore decided to start short distance convoys from the Santos-Rio and Plate areas. He therefore ordered HMS Cumberland to refuel at Rio de Janeiro on her arrival there and to organize and run ‘out’ convoys in that area with HMS Havock as A/S escort. The convoys were to leave at dawn and be protected against submarines and surface raiders until dusk. The ships were then to be dispersed so that they would be far apart by dawn the next day. At the same time the Commodore ordered HMS Hotspur to join him in the Plate area after refuelling at Rio de Janeiro, so that similar convoys could be started from Montevideo. If one of the German ‘pocket battleships’ was to arrive of South America, HMS Cumberland was to abandon the convoy sheme and join HMS Exeter in the Plate area. Also on the 10th, Commodore Harwood was informed by the Admiralty that the German merchant Montevideo (6075 GRT, built 1936) was leaving Rio Grande do Sul for Florianopolis but decided not to intercept her as this would divert HMS Exeter 500 nautical miles from the Plate area.
On the night of 12 September 1939 the Commodore was informed by the British Naval Attaché, Buenos Aires, that a concentration of German reservists was taking place in southern Argentina with the Falklands as a possible objective. He therefore ordered HMS Ajax to remain in the Falklands till the situation cleared, and the Commodore then proceeded south of the Plate area to be closer to the Falklands himself and yet remain in easy reach of the Plate area. During the next few days HMS Exeter intercepted several British and neutral vessels.
In view of a report that the German merchant vessels Porto Alegré (6105 GRT, built 1936) and Monte Olivia (13750 GRT, built 1925) were leaving Santos on 15 September 1939 Commodore Harwood decided to start the short distance convoys from Montevideo as soon as possible. HMS Cumberland had meanwhile arranged a twelve-hour convoy system from Santos. Ships from Rio de Janeiro for Freetown would sail at dawn on odd numbered days, and ships for the south on even numbered days with HMS Havock as anti-submarine escort and HMS Cumberland in distant support. HMS Cumberland left Rio de Janeiro on 16 September and during the next eight days sighted 15 British and neutral ships while on patrol.
On 17 September 1939, HMS Hotspur joined HMS Exeter in the Plate area. HMS Exeter then made a visit to Montevideo and resumed her patrol off the Plate area on the 20th. Fuelling was done from the oiler RFA Olwen (6470 GRT, built 1917, Master B. Tunnard) in the mouth of the River Plate. Soon after leaving Montevideo on 20 September Commodore Harwood learned from the British Naval Attaché, Buenos Aires, that the local German authorities were endeavoring to inform German ships at sea that the British merchant Lafonia (1872 GRT, built 1911) was on her way to the Falklands with British reservists for the Falkland Islands defence force. It was also reported that on 17 September an unknown warship had passed Punta Arenas eastwards. In view of these reports and of other pointing out that German merchant ships in southern waters were being outfitted as armed raiders the Commodore ordered HMS Hotsput to escort the Laofona to Port Stanley. As the volume of trade in the Plate area was greater than in the Rio de Janeiro – Santos area, HMS Havock was ordered to proceed southwards to the Plate area.
The first local convoy outward from Montevideo sailed on 22 September 1939. It consisted of the British merchant ships Sussex (11062 GRT, built 1937), Roxby (4252 GRT, built 1923), El Ciervo (5841 GRT, built 1923) in addition to the earlier mentioned Lafonia, and was escorted by HMS Hotspur. HMS Exeter met this convoy during the forenoon and covered it throughout the day. At dusk the merchant ships were dispersed on prearranged courses while HMS Exeter remained within supporting distance and HMS Hotspur escorted the Lafonia to Port Stanley.
On 24 September 1939, Vice-Admiral Lyon (C-in-C, South Atlantic) and Commodore Harwood learned from the Naval Attaché, Buenos Aires, that ‘according to a reliable source’ arrangements had been made for a number of German ships and a submarine to meet near Ascension on 28 September 1939. HMS Cumberland was ordered to proceed there and HMS Ajax was ordered to leave the Falklands and take up her place in the Rio de Janeiro area. HMS Neptune (Capt. J.A.V. Morse, DSO, RN) was also ordered to proceed to the area off Ascension with the destroyers HMS Hyperion and HMS Hunter which departed Freetown on the 25th. No German ships were however encountered off Ascension and all ships then proceeded to Freetown where they arrived on 2 October 1939 with HMS Cumberland low on fuel.
While HMS Cumberland left the station to search for the German ships, HMS Exeter and HMS Ajax were sweeping of the Plate and Rio de Janeiro – Santos area respectively. On 27 September 1939, HMS Havock escorted a convoy made up of the British merchants Miguel de Larrinaga (5231 GRT, built 1924), Pilar de Larringa (7352 GRT, built 1918) and Sarthe (5271 GRT, built 1920) out of the Plate area. The next day another convoy, made up of the British merchants Adellen (7984 GRT, built 1930), Cressdene (4270 GRT, built 1936), Holmbury (4566 GRT, built 1925), Lord Byron (4118 GRT, built 1934), Ramillies (4553 GRT, built 1927) and Waynegate (4260 GRT, built 1931) left the Plate area escorted by HMS Havock and with cover from HMS Exeter.
At daylight on 29 September 1939 HMS Ajax was off Rio de Janeiro ready to escort ships sailing northward. She sighted none until the early afternoon when she met the Almeda Star (12848 GRT, built 1926) and a few hours later the tanker San Ubaldo (5999 GRT, built 1921). That night several neutral steamers were sighted off Rio de Janeiro and the next day the British La Pampa (4149 GRT, built 1938) was met and escorted during daylight on her way to Santos. So far on the work of the South American Division during September 1939. The ships assigned to Commodore Harwood had been busy patrolling and escorting ships near the focal areas.
A surface raider reported, 1 October 1939.
When a report that the British merchant Clement had been sunk on 30 September 1939 by a surface raider off Pernambuco was received by the Admiralty in the afternoon of October 1st, the C-in-C, South Atlantic was informed that he should retain the 4th Destroyer Division and that his command would be reinforced by the cruisers HMS Norfolk (Capt. A.G.B. Wilson, DSO, RN), HMS Capetown (Capt. T.H. Back, RN), HMS Effingham (Capt. J.M. Howson, RN), HMS Emerald (Capt. A.W.S. Agar, VC, DSO, RN) and HMS Enterprise (Capt. H.J. Egerton, RN). Also the battleships HMS Resolution (Capt. C.H. Knox-Little, RN), HMS Revenge (Capt. E.R. Archer, RN) and the aircraft carrier HMS Hermes (Capt. F.E.P. Hutton, RN) were to proceed to either Jamaica or Freetown. These dispositions however never materialised being superseded on 5 October 1939 by a more general policy (the institution of hunting groups) which cancelled them.
The institution of hunting groups, 5 October 1939.
On 5 October 1939 the Admiralty formed five hunting groups in the Atlantic and Indian Ocean of sufficient strength to destroy any ‘pocket battleship’ or Hipper-class cruiser. These were; Force F; area: North America and West Indies. HMS Berwick (Capt. I.M. Palmer, DSC, RN), HMS York (Capt. R.H. Portal, DSC, RN), Force G; area: S.E. coast of South America. HMS Cumberland, HMS Exeter Force H; area: Cape of Good Hope, South Africa. HMS Sussex (Capt. A.R. Hammick, RN), HMS Shropshire (Capt. A.W.LaT. Bisset, RN), Force I; area: Ceylon. HMS Cornwall (Capt. C.F. Hamill, RN), HMS Dorsetshire (Capt. B.S.C. Martin, RN), HMS Eagle (Capt. A.R.M. Bridge, RN), Force K; area: Pernambuco, Brazil. HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN), Force L; area: Brest, France. Dunkerque (Capt. J.L. Nagadelle, replaced by Capt. M.J.M. Seguin on 16 October), Bearn (Capt. M.M.A. Lafargue, replaced by Capt. Y.E. Aubert on 7 October), Georges Leygues (Capt. R.L. Perot), Gloire (Capt. F.H.R. de Belot), Montcalm (Capt. P.J. Ronarc’h), Force M; area: Dakar, Senegal. Dupleix (Capt. L.L.M. Hameury), Foch (Capt. J. Mathieu), and Force N; area: West Indies. Strasbourg (Capt. J.F.E. Bouxin), HMS Hermes.
The institution of the hunting groups were not the only measures taken. The battleships HMS Resolution, HMS Revenge and the light cruisers HMS Emerald and HMS Enterprise were ordered to proceed to Halifax, Nova Scotia to escort homeward bound convoys. Light cruiser HMS Effingham was to join them later. The battleship HMS Ramillies (Capt. H.T. Baillie-Grohman, DSO, RN) left Gibraltar on 5 October for the same duty but was recalled the next day when the battleship HMS Malaya (Capt. I.B.B. Tower, DSC, RN) and the aircraft carrier HMS Glorious (Capt. G. D’Oyly-Hughes, DSO and Bar, DSC, RN) were ordered to leave the Mediterranean and proceed to the Indian Ocean where they formed an addition hunting group, Force J which was to operate in the Socotra area off the entrance to the Gulf of Aden.
Now back to the South Atlantic, on 9 October 1939 the C-in-C, South Atlantic had informed the Admiralty and Commodore Harwood that he intended to co-ordinate the movements of ‘Force G’, ‘Force H’ and ‘Force K’. As this would entail long periods of wireless silence in ‘Force G’ he proposed that Commodore Harwood should transfer his flag to HMS Ajax, leaving Capt. Fallowfield of HMS Cumberland in command of Force G. The Admiralty approved of this. Commodore Harwood stated that it was his intention to transfer his flag from HMS Exeter to HMS Ajax in the River Plate area on 27 October. He also stated that the endurance of HMS Exeter was only half the endurance of HMS Cumberland and that this would prove problematic when they were to operate together and he proposed that the Exeter would be relieved by another 10000 ton cruiser but for the moment no suitable cruiser was available to relieve her.
On 12 October 1939 the first of the hunting forces arrived on their station when HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal reached Freetown that morning coming from the U.K. They were soon followed by three more destroyers of the H-class coming from the Mediterranean; HMS Hardy (Capt. B.A. Warburton-Lee, RN), HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN) and HMS Hostile (Cdr. J.P. Wright, RN). On 13 October 1939 the cruisers HMS Sussex and HMS Shropshire arrived at Simonstown from the Mediterranean and one day later HMS Hermes arrived at Dakar from Plymouth.
The South America Division during the first half of October 1939.
When the news of an enemy raider in the South Atlantic reached the C-in-C at Freetown on 1 October 1939 he immediately suspended sailings from Pernambuco and Natal and he ordered HMS Havock and HMS Hotspur to escort British ships clear of the area. But next morning he cancelled these dispositions and ordered Commodore Harwood to concentrate HMS Exeter, HMS Ajax and the two destroyers off Rio de Janeiro. By this time, however, the raider was far away from the South American coast. On 3 October 1939 the Commodore signalled the C-in-C that he intened to concentrate the Exeter and Ajax off Rio and have the Hotspur to cover the Rio – Santos area and keep the Havock off the Plate but upon receiving the orders from the C-in-C to concentrate he ordered to destroyers to join the cruisers after fuelling but not later then 0800 hours on 4 October. Reports that the enemy raider was not a ‘pocket battleship’ however kept coming in and the Commodore decided that he could not leave the heavy traffic in the Plate area without some form of protection and he ordered HMS Havock to return there but when a report coming in from Bahia, Brazil confirmed that the Clement had been sunk by the ‘pocket battleship’ Admiral Scheer the Commodore once more ordered HMS Havock to join him. In the end HMS Ajax joined HMS Exeter at 1700/3, HMS Hotspur at 0500/4 and finally HMS Havock at 1300/4.
The Commodore was also informed by the Admiralty that the New Zealand cruiser HMS Achilles (New Zealand Division) (Capt. W.E. Parry, RN) would join his station coming from the west coast of South America. HMS Cumberland left Freetown at 1900/3 to join the Commodore in the Rio de Janeiro area as well.
Commodore Harwood’s policy against enemy raiders and a new raider report coming on on 5 October 1939.
Commodore Harwood had decided to keep his forces concentrated and as no new raider reports had come in to patrol the Rio de Janeiro area in accordance with the C-in-C, South Atlantic’s order. If he met a ‘pocket battleship’ he intended to shadow it until dusk. He would then close and attack in the dark hours. If, on the other hand, he made contact at night, his destroyers would at once close the enemy’s beam and attack her with torpedoes.
On 5 October 1939, the British merchant Martand (7967 GRT, built 1939) informed HMS Cumberland that a German armed raider had attacked an unknown ship, this unknown ship was in fact the Newton Beech that was attacked about 900 nautical miles away. This information was not acted upon by the Commanding Officer of the Cumberland. The Captain of the Cumberland assumed the raider report would have been intercepted by other ships and passed on to the C-in-C, South Atlantic. He considered it was important to keep radio silence and decided against breaking it. The Admiralty however later was of the opinion that the report should have been passed on to the Commander-in-Chief.
By 5 October 1939, the Exeter, Ajax, Havock and Hotspur were concentrated in the Rio de Janeiro area ready to engage the raider if she came south from the Pernambuco area. HMS Achilles was on her way round Cape Horn.
When HMS Ajax visited Rio de Janeiro on 7 October 1939, Commodore Harwood directed her to suggest to the Consular Shipping Advisers there, and at Santos, that, owning to the small volume of shipping leaving these ports, the local convoy systems, which had been instituted on 22 September against armed merchant raiders, should be suspended, and Allied merchant ships be routed independently.
The Commodore intended to meet HMS Cumberland at 1700/8, but at 1600/7 he received a message from the Consular Shipping Adviser at Rio de Janeiro in which he desired an escort for a 13 knot convoy that was to sail at 0430/8 and that had received much local publicity. The Commodore thought that this publicity might draw the enemy raider to the area and he therefore took his entire force back towards Rio de Janeiro and sent HMS Hotspur ahead to make contact with the convoy, while keeping his other ships in support. The convoy consisted of the British merchants Highland Chieftain (14131 GRT, built 1929), Nariva (8723 GRT, built 1920) and the French merchant Alsina (8404 GRT, built 1922).
Meanwhile the Commodore had directed HMS Cumberland to meet him at dawn on October 9th. When the convoy was dispersed at 1800/8 the Exeter and Ajax steered to meet her while the Havock was detached to fuel at Rio de Janeiro. At 2200/8 HMS Ajax was detached. HMS Cumberland made rendezvous with HMS Exeter at 0500/9. They were ordered by the C-in-C, South Atlantic to make a sweep northwards but this could not be carried out as HMS Exeter was short of fuel. The Commodore therefore decided to make a sweep southwards towards the Plate area where HMS Exeter could refuel. He also decided to keep HMS Hotspur with the two cruisers as long as possible.
On 12 October 1939, Rio Grande do Sul reported that the German merchant Rio Grande (6062 GRT, built 1939) was about to sail. The Commodore at once ordered HMS Cumberland to proceed there and intercept. She arrived off Rio Grande do Sul at 1600/13 but on finding it all quiet in the harbour she shaped course for the Plate area at nightfall. Meanwhile the Commodore had ordered HMS Hotspur to fuel at Montevideo when HMS Havock left that port early on the 14th.
about this time RFA Olwen informed the Commodore the the German merchant Bahia Laura (8611 GRT, built 1918) was leaving Montevideo at 1000 next morning and might protest if HMS Havock sailed the same day. Instead, therefore, of entering Montevideo HMS Hotspur at once fueled from the Olwen and then remained out on patrol. The Bahia Laura however, showed no signs of leaving and at 0800/14, HMS Havock put to sea. At 1200 hours HMS Hotspur entered Montevideo. Later that day HMS Exeter and HMS Cumberland fueled from the Olwen in San Borombon Bay at the southern entrance to the Plate estuary. At 1430 hours they were joined by HMS Havock. Commodore Harwood then ordered her to patrol off Montevideo to watch the Bahia Laura. When HMS Exeter finished fueling she immediately put to sea. HMS Cumberland rejoined him next morning at 0700 hours. HMS Havock was then ordered to join the cruisers. On 16 October the commodore learned that the Bahia Laura had sailed at 1015 hours the previous day. By the time the signal reached him the German ship was far out at sea well past his patrol line. But as the whole area was enveloped in dense fog the Commodore decided against trying to catch her.
The South America Division during the second half of October 1939.
Meanwhile Commodore Harwood had informed the Commander-in-Chief, South Atlantic on 13 October that as HMS Exeter required certain minor repairs he proposed to proceed to the Falklands on the17th and then return to the Plate area on the 27th. The Commander-in-Chief replied that he preferred that HMS Exeter would stay in the Plate area till the Commodore would transfer his Broad Pendant to HMS Ajax on the 27th. As HMS Achilles was due in the Plate area on this day also, she and HMS Cumberland could then operate as ‘Force G’ during the Exeter’s absence. This would mean that there would be no cruiser in the Rio de Janeiro area until HMS Exeter would return from her repairs at the Falklands. The Commodore therefore ordered HMS Havock to sail on 21 October for a four day patrol in the Rio – Santos Area, where HMS Hotspur, which could remain at sea until 2 November, would relieve her. From that date until the relief of HMS Achilles there would be no warship in this area. The Commodore therefore asked the Commander-in-Chief to allow ‘Force G’ to operate in that area from 2 to 10 November. When HMS Hotspur joined the Exeter and Cumberland from Montevideo on 17 October the Commodore ordered her to patrol off Rio Grande do Sul to intercept the German ships Rio Grande and Montevideo if they would come out, and sent HMS Havock to patrol inshore with orders to anchor the night clear of the shipping route.
This proved to be the last duty of these two destroyers with the South America Division. On 20 October the Admiralty ordered their transfer to the West Indies. Three days later the Commodore sent them into Buenos Aires to refuel, and as the distance to Trinidad, 4000 miles, was at the limit of their endurance, also obtained permission to refuel them at Pernambuco. They both left Buenos Aires on the 25th and, bidding the Commodore farewell, proceeded northwards. They sailed from Pernambuco on 1 November but on the 3rd HMS Havock was diverted to Freetown with engine trouble. The two remaining destroyers of the 4th Division, HMS Hyperion and HMS Hunter, had left Freetown with convoy SL 6 on 23 October. Off Daker their escort duty was taken over by the French light cruiser Duguay-Trouin (Capt. J.M.C. Trolley de Prevaux). The destroyers then fueled at Dakar on the 27th and sailed for Trinidad early on the 28th.
Meanwhile HMS Cumberland had entered Montevideo at 0800/26. At 0900/26 HMS Achilles joined HMS Exeter in the Plate area and after fueling from RFA Olwen sailed to meet HMS Cumberland off Lobos the next day and then patrol with her as ‘Force G’ in the Rio – Santos area. The Olwen was now nearly out of fuel and filled up HMS Ajax ,which had arrived from the Rio area on the 26th, with her remaining fuel minus 500 tons for her passage to Trinidad. In the morning of 27 October, Commodore Harwood transferred his Broad Pendant to HMS Ajax and HMS Exeter then parted company to proceed to the Falklands for repairs.
Meanwhile the newly formed ‘Force H’ and ‘Force K’ were busy on the other side of the South Atlantic. ‘Force H’, made up of HMS Sussex and HMS Shropshire had reached the Cape on 13 October. As HMS Cumberland had not passed on the report of the Martland, no news on the raider had reached the Admiralty or the Commander-in-Chief since October 1st. On 14 October ‘Force H’ sailed to search for her along the Cape – Freetown route as far as the latitude of St. Helena. That day ’Force K’ (HMS Ark Royal and HMS Renown) left Freetown with HMS Neptune, HMS Hardy, HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN) and HMS Hereward (Lt.Cdr. C.W. Greening, RN) to search westwards towards St. Paul Rocks, the direction of their sweep being determined by the complete lack of any further raider information.
Finally a raider report on 22 October 1939, Sweeps by ‘Force H’ and ‘Force K’.
The three weeks old ‘mystery’ of the raiders whereabouts was partially solved on 22 October when the British merchant vessel Llanstephan Castle (11293 GRT, built 1914) intercepted a message from an unknown ship ‘Gunned in 16°S, 04°03’E’ at 1400 G.M.T. There was however no immediate confirmation of her report and the Commander-in-Chief ordered ‘Force H’ to sail after dark on the 27th to sail for the latitude of St. Helena. At noon on 31 October this Force was in 15°S, 02°51’E, the north-eastern limit of it’s patrol, when a Walrus aircraft failed to return to HMS Sussex from a reconnaissance flight. It was never found, though the two cruisers spend over three days searching for it. Being short of fuel they then returned to the Cape by the same route they had used outwards.
Sweep by ‘Force K’, 28 October – 6 November 1939.
To cover the northern end of the route from St. Helena onward, HMS Neptune and the destroyers HMS Hardy, HMS Hasty, HMS Hero and HMS Hereward had left Freetown on 28 October. HMS Neptune was to sweep independently from position 03°20’S, 01°10’W and then through 14°30’S, 16°50’W back to Freetown. On 30 October a report from Dakar stated that the German merchant Togo (5042 GRT, built 1938) had left the Congo on 26 October, that the German merchant Pionier (3254 GRT, built 1934) had sailed from Fernando Po (now called Bioko Island) on 28 October and that five German ships had left Lobito (Angola) the same day. When the Vice-Admiral, Aircraft Carriers, received this information her detached HMS Hardy and HMS Hasty to sweep north-westward for the Pioneer, while ‘Force K’ and the remaining two destroyers searched for her to the south-westward. Both searches were unsuccessful. Meanwhile a message from Lobito had stated that the five German ships that were stated to have left the harbour were still there. On 5 November the German merchant vessel Uhenfels (7603 GRT, built 1931), that had left Laurenco Marques (now called Maputo, Mozambique) on 16 October was sighted by an aircraft from HMS Ark Royal. Only energetic action from HMS Hereward saved her from being scuttled in position 06°02’N, 17°25’W. She was brought into Freetown on 7 November by HMS Herward, a few hours behind ‘Force K’.
’Force H’ and ‘Force G’, first half of November 1939.
The first half of November was relatively quiet on both sides of the South Atlantic At the start of the month ‘Force H’ and ‘Force K’ were still on the shipping lane between Sierra Leone and the Cape. On 3 November 1939 the Admiralty informed the Commander-in-Chief, South Atlantic that all German capital ships and cruisers were apparently in home waters. It appeared therefore that the pocket battleship, which was still thought to be the Admiral Scheer, had returned home and that the raider reported by the Llangstephan Castle on 22 October was nothing but an armed merchantman. Here was a good opportunity for resting the hunting groups and on 4 November the Admiralty issued orders that ‘Force G’ and ‘Force H’ should exchange areas. This exchange would not only give ‘Force G’ an opportunity of resting and refitting at the Cape, but would also provide Commodore Harwood with the hunting group of long endurance that he desired.
The Commander-in-Chief had planned that ‘Force H’ which had returned to the Cape on 7 November would then sweep towards Durban, arriving there on 16 November. However on the 11th they were ordered to sail for patrol in the Atlantic and on the evening of the 17th, while west of St. Helena, exchange patrol areas with ‘Force G’. The exchange of areas however did not take place as ‘Force G’ was delayed due to HMS Exeter being damaged while casting off from the oiler in heavy seas. Before the exchange now could take place it was cancelled.
South America Division, first half of November 1939.
After hoisting Commodore Harwood’s Broad on 27 October the HMS Ajax had swept the Plate focal area. When the Commodore received the signal of the Commander-in-Chief on the 5th regarding the changeover over patrol areas between ‘Force G’ and ‘Force H’, he ordered HMS Cumberland to proceed to the Plate at 20 knots to refuel. About this time a message reached him from Buenos Aires that the Argentinian Foreign Minister had drawn attention to cases of fueling in the Plate by HMS Exeter and HMS Ajax. Although the Argentinian Government had no apparent intention of raising the issue he decided to cut down the fuellings in the inshore waters of the Plate as much as possible. He therefore cancelled the fuelling of HMS Exeter, due to take place on 7 November from the oiler RFA Olynthus (6888 GRT, built 1918, Master L.N. Hill), which had relieved RFA Olwen. He ordered HMS Cumberland to fuel at Buenos Aires on 9 November. HMS Exeter which had arrived at the Falklands on 31 October for repairs, sailed again on 4 November to meet up with HMS Cumberland off the Plate on 10 November, but the Commodore ordered her to enter Mar del Plata for a 24-hour visit on the 9th. As this gave her some time at hand, he ordered her to cover the Plate while HMS Ajax visited Buenos Aires from 6 to 8 November during which the Commodore discussed the question of fuelling his ships in the River Plate Estuary with the Argentine naval authorities. During his visit to Buenos Aires, the Commodore discussed the matter of fuelling his ships of English Bank with the Argentinian Minister of Marine and his Chief of Naval Staff they both suggested that he should use San Borombon Bay which was most acceptable. He had in fact been using it for some time.
When HMS Ajax left Buenos Aires on 8 November she patrolled the Plate area. HMS Exeter arrived at Mar del Plata the next day but fuel could not be obtained there. She was ordered to fuel from RFA Olynthus in San Borombon Bay on the 10th and then meet up with HMS Cumberland off Lobos Island at 0600/11. On the 10th HMS Ajax also fueled from RFA Olynthus as did HMS Exeter after her while HMS Ajax was at anchor close by. However weather quickly deteriorated and the Olynthus was forced to cast off, damaging the Exeter in doing so. Besides that she was still 600 tons short of fuel. As she could not reach the Cape without a full supply the sailing of ‘Force G’ to exchange areas with ‘Force H’ was delayed. The Exeter finally finished fuelling on the 13th and sailed with HMS Cumberland for Simonstown. Before the exchange of areas could be effected, however, a raider was reported in the Indian Ocean and the order was cancelled.
Another raider report, 16 November 1939.
On 16 November 1939 the Naval Officer-in-Charge, Simonstown, reported that the small British tanker Africa Shell ( GRT, built ) had been sunk off Lourenco Marques the previous day by a raider identified as a pocket battleship. After the usual conflicting reports from eye-widnesses during the next few days, however, it was doubtful how many raiders there were or whether they were pocket battleships or heavy cruisers.
The presence of an enemy heavy ship in the Mozambique Channel called for new dispositions. When the raider report reached the Admiralty on 17 November they immediately cancelled the exchange of areas between ‘Force G’ an ‘Force H’. ‘Force H’ was ordered to return to the Cape and ‘Force G’ was ordered to return to the east coast of South America. They also ordered the dispatch of ‘Force K’ towards the Cape with instructions to go on to Diego Suarez in Madagascar. That morning a report reached the Commander-in-Chief, South Atlantic that the German merchant vessels Windhuk (16662 GRT, built 1937) and Adolph Woermann (8577 GRT, built 1922) had left Lobito. He at once ordered ‘Force H’, which was at that moment west of St. Helena in the approximate latitute of Lobito to spend three days searching for them.
Next day, 18 November 1939, ‘Force K’ left Freetown together with HMS Neptune, HMS Hardy, HMS Hero and HMS Hostile to sweep west of St. Helena through position 16°30’S, 10°W and thence on to Diego Suarez. The destroyers parted company at 2300/18 to search for the German ships. On 20 November 1939, the Commander-in-Chief ordered ‘Force H’ to return to the Cape of nothing of the German merchant vessels had been sighted. HMS Sussex and HMS Shropshire did so on 23 November.
The Adolph Woermann had not escaped. Early on 21 November 1939, the British merchant Waimarama (12843 GRT, built 1938) reported her in position 12°24’S, 03°31’W. At 1127/21, ‘Force K’ (HMS Ark Royal and HMS Renown) was in position 05°55’S, 12°26’W, altered course to close, and HMS Neptune, which was still with them, went ahead at high speed. Shortly after 0800/22 she made contact with the Adolf Woermann in position 10°37’S, 05°11’W and went alongside. Despite efforts to save her the German vessel was scuttled and when HMS Neptune returned to Freetown on 25 November 1939 she had 162 German survivors on board.
’Force H’ and ‘Force K’, second half of November 1939.
As the search for the Adolf Woermann had taken ‘Force K’ nearly 200 miles to the eastward, the Vice-Admiral, Aircraft Carriers decided to proceed to the Cape by the route east of St. Helena to save fuel. In hindsight this might have saved Altmark for being intercepted as she was waiting for the Admiral Graf Spee in the area ‘Force K’ would have otherwise passed through. On 23 November 1939, the Commander-in-Chief, South Atlantic, ordered ‘Force H’ to sail from the Cape the next day and patrol the ‘diverse routes’ as far as 33°E until 28 November.
At the northern end of the South Atlantic station HMS Neptune, HMS Hardy, HMS Hero, HMS Hostile, HMS Hasty and the submarine HMS Clyde (Cdr. W.E. Banks, RN) had established a patrol between 22 and 25 November 1939 to intercept escaping German merchant ships or raiders. No ships were however sighted and they were recalled to Freetown on 30 November.
In the meantime the Admiralty had ordered, ‘Force H’ and ‘Force K’ to conducted a combined patrol on the meridian of 20°E. The two forces met early on 1 December. The plan, according to the Commander-in-Chief, appeared to be a good one in theory but was found unsuitable in practice that on account of local weather conditions. These permitted flying off aircraft from HMS Ark Royal only once in five or six days, so that the patrol could not be extended far enough to the south to intercept a raider bent on evasion. In fact, only once, on 2 December weather was suitable for flying off aircraft.
South America Division, second half of November 1939.
After HMS Cumberland and HMS Exeter (‘Force G’) had sailed from San Borombon Bay for Simonstown on 13 November 1939, HMS Ajax patrolled the Plate area and escorted the French Massilia ( GRT, built ) that was bound for Europe from Buenos Aeres with French reservists. After parting from the Massilia she closed Rio Grande do Sul and ascertained that the German merchant vessels Rio Grande and Montevideo were still there. For the next two days she patrolled the normal peace time shipping routes.
When the Admiralty cancelled the exchange of ereas between ‘Force G’ and ‘Force H’ on 17 November, Commodore Harwood sent ‘Force G’ to cover Rio de Janeiro. He ordered HMS Achilles to fuel off the Olynthus in the Plate area on 22 November and then relieve ‘Force G’ in the Rio area as HMS Exeter would need to refuel in the Plate area again on 26 November. HMS Cumberland was to remain with the Exeter to keep ‘Force G’ together so she could refuel from the Olynthus as well. They were then to patrol the Plate area so that HMS Ajax could visit the Falklands.
On 18 November the Commodore was informed that the German merchant Ussukuma ( GRT, built ) might sail from Bahia Blanca for Montevideo at any time. He at once ordered the Olynthus to watch for her between Manos and Cape San Antonio and took the Ajax south to the same vicinity.
On 22 November 1939 HMS Achilles heard the German merchant Lahn (8498 GRT, built 1927) calling Cerrito by wireless, and when HMS Ajax arrived half an hour later a search was carried out. It was insuccessful for both cruisers but both the Lahn and another German merchant the Tacoma (8268 GRT, built 1930) reached Montevideo safely during the forenoon.
HMS Ajax and HMS Achilles then both fuelled from the Olynthus at San Borombon Bay during the next afternoon. The Achilles the sailed for the Rio de Janeiro area. She had orders to move up to Pernambuco and show herself off Cabadello and Bahia as a number of German ships in Pernambuco were reported ready to sail to Cabadello to load cotton for Germany. She was to return at once to the Rio area if any raiders were reported in the South Atlantic.
HMS Ajax left the Plate area on 25 November 1939 and sent up a seaplane to reconnoitre Bahia Blanca. The Ussukuma showed no signs of sailing so HMS Ajax proceeded to the Falklands, arriving there on the 27th. By this time HMS Cumberland and HMS Exeter were in urgent need of refits after long periods at sea, and Commodore Harwood ordered the Exeter to proceed to the Falklands forthwith. She arrived at Port Stanley on 29 November 1939 and her defects were immediately taken in hand as far as local resources permitted.
8 December 1939 was the twenty-fifth anniversary of the Battle of the Falklands, and thinking the enemy might attempt to avenge the defeat, the Commodore ordered HMS Cumberland to patrol off the Falklands as of 7 December for two days after which she too was to enter Port Stanley for rest and refit.
French Forces at Dakar in November 1939.
During November them most important event at Dakar, where the French were maintaining a number of more or less regular patrols, was the reorganisation of ‘Force X’. On 1 November 1939 the large destroyer L’Audacieux (Cdr. L.M. Clatin) sailed from Dakar to the westward to 26°W and thence south-west to search for the German merchant Togo. She returned to Dakar on 4 November having sighted nothing. That day the French light cruiser Duguay-Trouin sailed to sweep round the Cape Verde Islands and then on to St. Paul Rocks. She returned to Dakar on 10 November. The old ‘Force X’, the Strasbourg (Capt. J.F.E. Bouxin), Algerie (Capt. L.H.M. Nouvel de la Fleche) and Dupleix (Capt. L.L.M. Hameury) sailed on 7 November to sweep west of the Cape Verde Islands. It returned to Dakar on 13 November 1939. Meanwhile French submarines based at Casablanca were maintaining a continuous patrol round the Canary Islands between 25°N and 30°N.
On 18 November a new ‘Force X’ was formed, now made up of the Dupleix and her sister ship Foch (Capt. J. Mathieu) and the British aircraft carrier HMS Hermes. On 21 November the Strasbourg, Algerie and the destroyers Le Terrible (Cdr. A.E.R. Bonneau) and Le Fantasque (Capt. P.A.B. Still) left Dakar to return to France. The next day the new ‘Force X’ sailed with the destroyers Milan (Cdr. M.A.H. Favier) and Cassard (Cdr. R.A.A. Braxmeyer) to cruiser towards 08°N, 30°W. That day L’Audacieux departed Dakar with a convoy for Casablanca.
On 25 November, the Duguay-Trouin sailed to patrol the parallel of 19°N, between 25° and 30°W. Two days later the British submarine HMS Severn (Lt.Cdr. B.W. Taylor, RN) docked at Dakar. On the 30th the Dupleix and Foch returned from patrol being followed the next day by HMS Hermes and her escorts Milan and Cassard.
Dispositions of South Atlantic Forces at the beginning of December 1939.
At the beginning of December 1939, HMS Ark Royal, still flying the flag of Vice-Admiral Aircraft Carriers, and HMS Renown (‘Force K’), were patrolling the meridian of 20°E, south of the Cape together with HMS Sussex and HMS Shropshire (‘Force H’) to intercept the raider reported in the Mozambique Channel on 15 November 1939.
In the north the light cruiser HMS Neptune with the destroyers HMS Hardy, HMS Hero, HMS Hostile and HMS Hasty and the submarine HMS Clyde were returning to Freetown after patrolling between there and Cape San Roque for escaping German merchant ships or raiders. The French cruiers Dupleix and Foch and the British carrier HMS Hermes (‘Force X’) and their two escorting destroyers Milan and Cassard were approaching Dakar. The French cruiser Duguay-Trouin was patrolling the parallel of 19°N, between 25° and 30°W. The British submarine Severn was refitting at Dakar. Across the South Atlantic, Commodore Harwood, in HMS Ajax was at Port Stanley as was HMS Exeter. HMS Cumberland was patrolling of the Plate area and HMS Achilles was off Rio de Janeiro.
Forces ‘H’ and ‘K’, 1 – 13 December 1939.
No further reports have been received of the raider which had sunk the Africa Shell off Laurenco Marques on 15 November and it seemed clear that she had either gone further into the Indian Ocean or doubled back into the South Atlantic by going well south of the Cape. On 2 December 1939 the Admiralty ordered ‘Force K’ and ‘Force H’ to their patrol line south of the Cape after refueling, and the Commander-in-Chief, South Atlantic at once ordered them to proceed for the Cape ports to fuel. That day a reconnaissance aircraft of the South African Air Force reported a suspicious ship south of Cape Point at noon. HMS Sussex intercepted her but her crew set her on fire. She proved to be the German merchant Watussi (9521 GRT, built 1928). She was eventually be HMS Renown. Her survivors were taken on board HMS Sussex and were landed at Simonstown.
No news of the missing raider had been coming in since 16 November but then the mistery shrouding her whereabouts was again partially solved. At 1530/2 a raidar signal ‘R.R.R., 19°15’S, 05°05’E, gunned battleship) reached the Commander-in-Chief, South Atlantic. It came from the British merchant Doric Star. As this signal placed the raider in the South Atlantic he immediately ordered to abandon the patrol south of the Cape and ordered ‘Force H’ to cover the trade routes between the Cape and the latitude of St. Helena at 20 knots on completion of fuelling. As it was too late for ‘Force K’ to reach the Freetown-Pernambuco area in time to intercept the rainder if she was to proceed to the North Atlantic he proposed the Admiralty that ‘Force K’, after fuelling should sweep direct from the Cape to position 20°S, 15°W. This was changed at the request of the Vice-Admiral, Aircraft Carriers to place his force in a more central position for proceeding to Freetown, to the Falklands or to Rio de Janeiro. At 1030/3 a report reached the Commander-in-Chief that the pocket battleship Admiral Scheer had been in 21°20’S, 03°10’E at 0500 hours, clearly indicating that the raider was moving westwards, clear of the Cape-Sierra Leone trade route. ‘Force H’ left Simonstown at 1700 that afternoon and ‘Force K’ sailed from Capetown at 0915/4.
The Commander-in-Chief estimated that if the enemy was proceeding northwards to the North Atlantic she would cross the Freetown-Pernambuco line between 9 and 10 December. He therefore arranged that ‘Force X’ should take HMS Neptune and her destroyers under her orders and patrol the parallel of 3°N between 31° and 38°W from 10 to 13 December. ‘Force K’ would meet HMS Neptune and the destroyers on the 14th and then return with them to Freetown to refuel. The destroyers of the 3rd Division of the 2nd Destroyer Flotilla (HMS Hardy, HMS Hostile and HMS Hero) left Freetown on 6 December with the oiler RFA Cherryleaf (5896 GRT, built 1917). They had orders to meet the Dupleix, Foch, HMS Hermes and their escorting destroyers Milan and Cassard and HMS Neptune in position 03°N, 31°W on 10 December. On 7 December ‘Force X’ left Dakar for the rendez-vous. That day the submarine HMS Clyde left Freetown to patrol between 03°N, 23°W and 03°N, 28°W and thence to 05°15’N, 23°W between 9 (PM) and 13 (AM) December.
On the evening of 8 December 1939 the German merchant ship Adolf Leonhardt (2989 GRT, built 1925) sailed from Lobito for South America. ‘Force H’ which was by then between St. Helena and the west coast of Africa, was at once ordered to intercept her. The Walrus from HMS Shropshire made contact at 0952 hours next morning and alighted alongside in position 13°S, 11°44’E. At 1250 hours HMS Shropshire arrived at that position but the German ship was scuttled by her crew and could not be saved. ‘Force H’ then returned to the Cape to refuel where they arrived on 14 December.
At 0800/11 the submarine HMS Severn left Freetown for Port Stanley. She was to protect the whaling industry in South Georgio and was to intercept hostile raiders or supply ships. The cruiser HMS Dorsetshire, which arrived at Simonstown from Colombo on the 9th to finally relieve HMS Exeter in the South America Division left Simonstown on 13 December for Port Stanley. She was to call at Tristan da Cunha on the way. On that day, 13 December 1939, was fought the action between the British South America Division and the German pocket battleship Admiral Graf Spee, known as the Battle of the River Plate.
The South America Division, 1 to 13 December 1939.
At the beginning of December 1939, HMS Ajax and HMS Exeter were at Port Stanley in the Falkland Islands. HMS Cumberland was off the River Plate and HMS Achilles was patrolling the Rio de Janeiro area. On 2 December HMS Ajax left Port Stanley for the Plate area. That evening the Commodore learned that the Doric Star had been sunk by a raider to the south-east of St. Helena. Two days later the Commander-in-Chief, South Atlantic informed him that HMS Dorsetshire would arrive at Port Stanley on 23 December to relieve HMS Exeter which was then to proceed to Simonstown for a much needed refit.
Early on 5 December the British Naval Attaché at Buenos Aires reported that the German merchant Ussukuma had left Bahia Blanca at 1900 hours the previous evening. The Commodore immediately ordered HMS Cumberland which was on the way south to the Falkland Islands to search for her. Meanwhile HMS Ajax turned south and closed the Argentinian coast in case the Ussukuma, which was known to be short of fuel, should attempt to reach Montevideo inside territorial waters. At 1910/5, HMS Ajax sighted her smoke to the north-north-east but the Germans managed to scuttle their ship and despite the efforts to save her she sank during the night. At 0615/6, HMS Cumberland came up and embarked the German survivors and made off for the Falklands. HMS Ajax then refuelled at San Borombon Bay from the Olynthus.
About the same time the Brazilian authorities asked that HMS Achilles should not refuel in any Brazilian port at an interval less then three months. The Commodore, therefore, ordered her to return south and refuel at Montevideo on 8 December. HMS Achilles then joined HMS Ajax at 1000/10 in position 35°11’S, 51°13’W, 230 miles west of English Bank. At 0600/12 they were joined by HMS Exeter in position 36°54’S, 53°39’W.
Ever since the beginning of the war Commodore Harwood’s cruisers had worked off the east coast of South America either single or in pairs. The concentration of these three cruisers off the River Plate on 12 December 1939 was, however, no mere matter of chance.
Concentration of British Force in the River Plate area, 12 December 1939.
When a pocket battleship was located in position 19°15’S, 05°05’E on 2 December by the sinking of the Doris Star, her position was over 3000 miles from any of the South America focal areas. The Commodore however recognised that her next objective might be the valuable shipping off the east coast of South America. He estimated that at a cruising speed of 15 knots the enemy could reach the Rio area on 12 December the Plate area on 13 December and the Falklands on 14 December. As the Plate area was by far the most important of these three focal areas he decided to concentrate all his available ships off the Plate on 12 December.
The three cruisers then proceeded together towards position 32°N, 47°W. That evening the Commodore informed the Captains of his cruisers that it was intention that if they met a pocket battleship to attack immediately, by day or by night. By they they would act as two units, the light cruisers were to operate together and HMS Exeter was to operate diverged to permit flank marking. By night the ships were to remain in company in open order.
At 0614/13 HMS Ajax sighted smoke bearing 324° in position 34°28’S, 49°05’W and Commodore Harwood then ordered HMS Exeter to investigate it.
What then followed can be read in the article ‘The battle of the River Plate, 13 December 1939’ which can be found on the pages of HMS Ajax, HMS Exeter and HMS Achilles. (4)
1 Oct 1939
Battleships HMS Nelson (Capt. G.J.A. Miles, RN, flying the flag of Admiral J.M. Forbes, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Rodney (Capt. E.N. Syfret, RN), battlecruisers HMS Hood (Capt. I.G. Glennie, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral W.J. Whitworth, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Repulse (Capt. E.J. Spooner, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Somali (Capt. R.S.G. Nicholson, DSC, RN), HMS Mashona (Cdr. P.V. McLaughlin, RN), HMS Matabele (Cdr. G.K. Whitmy-Smith, RN), HMS Ashanti (Cdr. W.G. Davis, RN), HMS Fame (Cdr. P.N. Walter, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, RN), HMS Foresight (Lt.Cdr. G.T. Lambert, RN) and HMS Fortune (Cdr. E.A. Gibbs, RN) departed Scapa Flow very late in the evening for Loch Ewe where they arrived around 0700A/2.
2 Oct 1939
Around 1800 hours HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN) departed Scapa Flow for Freetown. She is being escorted by the destroyers HMS Bedouin (Cdr. J.A. McCoy, RN) and HMS Tartar (Capt. G.H. Warner, DSC, RN).
Around 1900 hours HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) departed Loch Ewe to join HMS Renown at sea. She is being escorted by HMS Ashanti (Cdr. W.G. Davis, RN) and HMS Foresight (Lt.Cdr. G.T. Lambert, RN).
They made rendezvous around 2210/2.
The destroyers were detached at 2030/3. (5)
11 Oct 1939
Around 0600 hours, HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN) and HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), were joined by the destroyers HMS Hardy (Capt. B.A. Warburton-Lee, RN), HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN) and HMS Hostile (Cdr. J.P. Wright, RN), which came from Gibraltar. (6)
12 Oct 1939
HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Hardy (Capt. B.A. Warburton-Lee, RN), HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN) and HMS Hostile (Cdr. J.P. Wright, RN) arrived at Freetown. (5)
14 Oct 1939
The battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), light cruiser HMS Neptune (Capt. J.A.V. Morse, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Hardy (Capt. B.A. Warburton-Lee, RN), HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN) and HMS Hereward (Lt.Cdr. C.W. Greening, RN) departed Freetown to patrol towards the St. Paul's Rocks. (7)
23 Oct 1939
HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Neptune (Capt. J.A.V. Morse, DSO, RN), HMS Hardy (Capt. B.A. Warburton-Lee, RN), HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN) and HMS Hereward (Lt.Cdr. C.W. Greening, RN) returned to Freetown from patrol. (7)
28 Oct 1939
The battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), light cruiser HMS Neptune (Capt. J.A.V. Morse, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Hardy (Capt. B.A. Warburton-Lee, RN), HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN), HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN), HMS Hereward (Lt.Cdr. C.W. Greening, RN) and HMS Hostile (Cdr. J.P. Wright, RN) departed Freetown for a patrol towards Ascension.
HMS Neptune soon parted company to patrol independently towards position 03°20'S, 01°10'W and then towards 14°30'S, 16°50'W and then return to Freetown. (7)
31 Oct 1939
At 1600 hours, HMS Hardy (Capt. B.A. Warburton-Lee, RN) and HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN) parted company with HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN), HMS Hereward (Lt.Cdr. C.W. Greening, RN) and HMS Hostile (Cdr. J.P. Wright, RN).
HMS Hardy and HMS Hasty were to search for the German merchant vessel Pionier (3264 GRT, built 1934) which was reported to have departed from Fernando Pó (now called Bioko) at 2230 hours on 28 October. They were also ordered to return to Freetown on 3 November after their search.
During the day, HMS Hero, HMS Hostile and HMS Hereward were fuelled by HMS Renown. (8)
5 Nov 1939
An aircraft from HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) sighted the German merchant vessel Uhenfels (7603 GRT, built 1931), that had departed Laurenco Marques (now called Maputo, Mozambique) on 16 October. HMS Hereward (Lt.Cdr. C.W. Greening, RN) was detached to intercept and capture the German ship while HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Ark Royal, HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN), and HMS Hostile (Cdr. J.P. Wright, RN) continued their patrol and passage to Freetown.
The Germans tried to scuttle their ship, about 300 miles west-southwest of Freetown, to avoid capture but the boarding crew from HMS Hereward managed to save the ship which was then taken to Freetown. (7)
6 Nov 1939
HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN), and HMS Hostile (Cdr. J.P. Wright, RN) arrived at Freetown from patrol.
HMS Neptune (Capt. J.A.V. Morse, DSO, RN) returned at the same time from independent patrol, apparently having joined the Renown force shortly before arrival. (9)
14 Nov 1939
The battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Hardy (Capt. B.A. Warburton-Lee, RN), HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN), HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN) and HMS Hostile (Cdr. J.P. Wright, RN) departed Freetown to patrol to the south. (7)
16 Nov 1939
HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Hardy (Capt. B.A. Warburton-Lee, RN), HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN), HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN) and HMS Hostile (Cdr. J.P. Wright, RN) returned to Freetown having been recalled from patrol. (7)
18 Nov 1939
The battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), light cruiser HMS Neptune (Capt. J.A.V. Morse, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Hardy (Capt. B.A. Warburton-Lee, RN), HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN), HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN) and HMS Hostile (Cdr. J.P. Wright, RN) departed Freetown for Diego Suarez, Madagascar. (7)
20 Nov 1939
Around 2200Z/20, HMS Hardy (Capt. B.A. Warburton-Lee, RN), HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN), HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN) and HMS Hostile (Cdr. J.P. Wright, RN) parted company with HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) and HMS Neptune (Capt. J.A.V. Morse, DSO, RN).
The destroyers were to form part of a patrol line and conduct a search for German merchant vessels.
In order to intercept escaping German merchant ships or raiders a patrol line was to be established after parting company with force K by HMS Neptune and the destroyers as well as the submarine HMS Clyde (Cdr. W.E. Banks, RN).
The line was joining Freetown and Cape San Roque (in Brazil) and ships were to take up positions as follows; 1)The destroyers from dawn on 23 November, 230 mile length bearing 240° from position 04°00'N, 20°00'W. 2)HMS Clyde from the morning of 22 November, 150 miles bearing 060° from position 05°00'N, 20°00'W. 3)HMS Neptune was to sail from Freetown on 25 November, as she first had to land her German prisoners taken on 22 November, to prolong the patrol line for a further 300 miles 240° from the destroyers section. The RFA tanker Cheffyleaf (5896 GRT, built 1917) was to proceed up and down the line to provide fuel for the ships involved in the search.
To support these ships the aircraft carrier HMS Hermes (Capt. F.E.P. Hutton, RN), the French heavy cruisers Dupleix (Capt. L.L.M. Hameury), Foch (Capt. J. Mathieu) and the large destroyers Cassard (Cdr. R.A.A. Braxmeyer) and Milan (Cdr. M.A.H. Favier) (Force X) departed Dakar on 22 November. They were to patrol parallel to the British line 130 miles north-north-west of it and between 21°00'W and 28°00'W between 24 and 28 November. (9)
21 Nov 1939
HMS Neptune (Capt. J.A.V. Morse, DSO, RN) parted company with HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN) and HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) around noon to proceed ahead at high speed to the position where the German merchant vessel Adolph Woermann (8577 GRT, built 1922) had been reported by the British merchant vessel Waimarama (12843 GRT, built 1938).
After the German ship had been intercepted the following day, ' Force K ' set course to proceed to the Cape area via the east of St. Helena to conserve fuel. It had originally been intended to proceed to the West of St. Helena and to search the area for the German supply vessel Altmark. (7)
1 Dec 1939
Around 0630B/1, HMS Sussex (Capt. A.R. Hammick, RN) and
HMS Shropshire (Capt. A.W.LaT. Bisset, RN) (Force 'H') made rendezvous with HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN) and HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) (Force 'K'). (10)
3 Dec 1939
' Force K ', HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN) and HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), arrived at Capetown around 0700 hours. (7)
4 Dec 1939
' Force K ', HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN) and HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), departed Capetown around 0800 hours (zone -2) to proceed to position 28°00'S, 15°00'W. (7)
13 Dec 1939
' Force K ', HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN) and HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), was ordered to proceed to Freetown to refuel but early on the 14th this was changed and they were ordered to refuel at Rio de Janeiro instead. (7)
17 Dec 1939
In the morning, ' Force K ', HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN) and HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), arrived at Rio de Janeiro.
HMS Ark Royal completed fuelling at 1800 hours and immediately left for the Plate area followed around 0600/18 by HMS Renown.
HMS Neptune (Capt. J.A.V. Morse, DSO, RN) arrived in the afternoon, she departed Rio de Janeiro to join ' Force K ' after fuelling at 1230/18. Her fuelling had only commenced at 0500/18. (7)
18 Dec 1939
HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN) made rendezvous with HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) in the afternoon. Also the destroyers HMS Hardy (Capt. B.A. Warburton-Lee, RN), HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN) and HMS Hostile (Cdr. J.P. Wright, RN) joined around the same time. They then proceeded to patrol to search for the German supply vessel Altmark before proceeding to Freetown. (11)
20 Dec 1939
During the day, HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), refuelled the destroyers HMS Hardy (Capt. B.A. Warburton-Lee, RN), HMS Hostile (Cdr. J.P. Wright, RN) and HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN).
Early in the evening HMS Hardy and HMS Hostile parted company with HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) to patrol towards Bahia and then up the coast towards Pernambuco and then to proceed to a rendezvous position 00°00'N, 20°00'W at noon on 24 December where they were to meet the RFA tanker Cherryleaf and her escort, HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN) which came from Freetown. (12)
25 Dec 1939
HMS Hardy (Capt. B.A. Warburton-Lee, RN), HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN), HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN), HMS Hostile (Cdr. J.P. Wright, RN) and the RFA tanker Cherryleaf joined HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN) and HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN). All ships then set course for Freetown. (13)
27 Dec 1939
HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Hardy (Capt. B.A. Warburton-Lee, RN), HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN), HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN), HMS Hostile (Cdr. J.P. Wright, RN) and the RFA tanker Cherryleaf all arrived at Freetown in the morning. (7)
3 Jan 1940
HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Neptune (Capt. J.A.V. Morse, DSO, RN), HMS Hardy (Capt. B.A. Warburton-Lee, RN) and HMS Hostile (Cdr. J.P. Wright, RN) departed Freetown for Dakar. (14)
5 Jan 1940
HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Neptune (Capt. J.A.V. Morse, DSO, RN), HMS Hardy (Capt. B.A. Warburton-Lee, RN) and HMS Hostile (Cdr. J.P. Wright, RN) arrived at Dakar from Freetown. (14)
8 Jan 1940
Around 0930A/8, HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Neptune (Capt. J.A.V. Morse, DSO, RN), HMS Hardy (Capt. B.A. Warburton-Lee, RN) and HMS Hostile (Cdr. J.P. Wright, RN) departed Dakar. They were joined around 1600A/8 by HMS Dainty (Cdr. F.M. Walton, RN) which had departed Gibraltar on 4 January. (15)
9 Jan 1940
HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Neptune (Capt. J.A.V. Morse, DSO, RN), HMS Hardy (Capt. B.A. Warburton-Lee, RN), HMS Hostile (Cdr. J.P. Wright, RN) and HMS Dainty (Cdr. F.M. Walton, RN) were joined by HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN) and HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN).
HMS Hardy, HMS Hostile and HMS Dainty then parted company and set course for Freetown.
The other ships proceeded on patrol. (16)
11 Jan 1940
HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN) and HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN) parted company with HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) and HMS Neptune (Capt. J.A.V. Morse, DSO, RN). (17)
12 Jan 1940
HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN) and HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN) rejoined HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) and HMS Neptune (Capt. J.A.V. Morse, DSO, RN) near Ascension Island. The destroyers had fuelled there from the RFA tanker Cherryleaf (5896 GRT, built 1917). (17)
15 Jan 1940
HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Neptune (Capt. J.A.V. Morse, DSO, RN), HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN) and HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN) made rendezvous with HMS Ajax (Capt. C.H.L. Woodhouse, CB, RN).
Also on this day HMS Neptune fuelled from from the RFA tanker Cherryleaf (5896 GRT, built 1917).
In the evening the destroyers carried out dummy torpedo attacks on HMS Neptune. Apparently HMS Neptune and the destroyers were not in company with the capital ships and HMS Ajax.
They apparently rejoined these ships the following morning. Presumably after the exercises had been completed. (18)
16 Jan 1940
In the afternoon, HMS Neptune (Capt. J.A.V. Morse, DSO, RN), parted company with HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Ajax (Capt. C.H.L. Woodhouse, CB, RN), HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN) and HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN).
HMS Neptune then proceeded on patrol independently. (19)
19 Jan 1940
HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Ajax (Capt. C.H.L. Woodhouse, CB, RN), HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN) and HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN) arrived at Freetown. (17)
24 Jan 1940
HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Dainty (Cdr. F.M. Walton, RN) and HMS Diamond (Lt.Cdr. P.A. Cartwright, RN) departed Freetown to proceed to a rendez-vous position in which they were to join the damaged heavy cruiser HMS Exeter (Capt. F.S. Bell, CB, RN) and take over the escort from HMS Dorsetshire (Capt. B.C.S. Martin, RN) and HMS Shropshire (Capt. A.W.la T. Bisset, RN). (16)
29 Jan 1940
Around noon HMS Dorsetshire (Capt. B.C.S. Martin, RN) and HMS Shropshire (Capt. A.W.la T. Bisset, RN) turned over the damaged heavy cruiser HMS Exeter (Capt. F.S. Bell, CB, RN) to ships of 'Force K'; HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Dainty (Cdr. F.M. Walton, RN) and HMS Diamond (Lt.Cdr. P.A. Cartwright, RN) in approximate position 17°21'S, 24°56'W.
HMS Dorstershire and HMS Shropshire then proceeded on patrol in the South Atlantic still in company with each other. (20)
3 Feb 1940
HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Exeter (Capt. F.S. Bell, CB, RN), HMS Dainty (Cdr. F.M. Walton, RN) and HMS Diamond (Lt.Cdr. P.A. Cartwright, RN) arrived at Freetown. (21)
6 Feb 1940
HMS Exeter (Capt. F.S. Bell, CB, RN), and her escorts, HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Dainty (Cdr. M.S. Thomas, RN) and HMS Diamond (Lt.Cdr. P.A. Cartwright, RN) departed Freetown for Plymouth.
HMS Ark Royal and the destroyers parted company around 1800/9. Ark Royal was to proceed direct to the U.K. while the destroyers were to arrive at Dakar at 0900 (GMT) on the 11th.
Around dawn at 13 February 1940, HMS Renown and HMS Exeter were joined by HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN) and HMS Hero (Cdr. C.F. Tower, MVO, RN).
In the morning of the 14th the destroyers HMS Whitshed (Cdr. E.R. Conder, RN), HMS Vesper (Lt.Cdr. W.F.E. Hussey, DSC, RN) and HMS Acasta (Cdr. C.E. Glasfurd, RN) joined. This was before the other destroyers (see below) joined.
Around 1030/14 four more destroyers joined, HMS Hearty (Lt.Cdr. D.G.F.W. MacIntyre, RN), HMS Ardent (Lt.Cdr. J.F. Barker, RN), HMS Wren (Cdr. H.T. Armstrong, RN) and HMS Wolverine (Cdr. R.H. Craske, RN).
Around 1645/14, HMS Whitshed, HMS Vesper and HMS Acasta parted company when the merchant vessel Sultan Star was torpedoed and sunk on the horizon.
HMS Hero was detached, most likely on the 15th to Portsmouth where she was to refit.
HMS Renown, HMS Exeter, HMS Hasty, HMS Ardent, HMS Hearty, HMS Wren and HMS Wolverine arrived at Plymouth on the 15th. (21)
12 Feb 1940
The aircraft carrier, HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), which was on passage from Freetown to the U.K. was joined around 0925Z/12 by the destroyer HMS Antelope (Lt.Cdr. R.T. White, RN).
Around 1045A/12 the destroyers HMS Keith (Cdr.(Retd.) H.T.W. Pawsey, OBE, RN), HMS Veteran (Cdr. J.E. Broome, RN) and HMS Wakeful (Cdr. R.L. Fisher, RN) also joined.
HMS Ark Royal had been ordered to search the area for German merchant vessels which are thought to be present in the area having left Vigo, Spain to return to Germany. (22)
15 Feb 1940
HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Keith (Cdr.(Retd.) H.T.W. Pawsey, OBE, RN), HMS Antelope (Lt.Cdr. R.T. White, RN), HMS Veteran (Cdr. J.E. Broome, RN) and HMS Wakeful (Cdr. R.L. Fisher, RN) arrived at Portsmouth. (23)
19 Feb 1940
HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) is docked at the Portsmouth Dockyard. (23)
9 Mar 1940
HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) is undocked. (24)
17 Mar 1940
HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) conducted trials in Spithead. (24)
19 Mar 1940
Around 1500A/19, the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) departed Spithead for Portland Bay. She is being escorted by the destroyers HMS Isis (Cdr. J.C. Clouston, RN), HMS Arrow (Cdr. H.W. Williams, RN) and HMS Shikari (Lt.Cdr. H.N.A. Richardson, RN).
At 1603A/19, HMS Shikari parted company.
At 1640A/19, HMS Arrow and HMS Isis parted company.
At 1934A/19, HMS Ark Royal passed the boom into Portland Bay. (24)
20 Mar 1940
The aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) conducted flying exercises off Portland Bay. During the exercises the destroyer HMS Isis (Cdr. J.C. Clouston, RN) and two MA/SB's patrolled in the area. (24)
22 Mar 1940
At 1108A/22, the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) passed to boom to leave Portland Bay. She is to proceed to the Mediterranean for training her aircrews.
On departure from Portland she is escorted by the destroyers HMS Isis (Cdr. J.C. Clouston, RN) and HMS Imogen (Cdr. C.L. Firth, MVO, RN).
The destroyers parted company at 1749A/23. HMS Ark Royal then proceeded unescorted.
At 1203A/25, she was joined, in position 36°02'N, 09°36'W by the destroyer HMS Bulldog (Lt.Cdr. J.S.M. Richardson, RN) and about half an hour later by the destroyer HMS Active (Lt.Cdr. E.C.L. Turner, RN). These destroyers had departed Gibraltar on the 24th.
At 1747A/25, the destroyer HMAS Voyager (Lt.Cdr. J.C. Morrow, RAN) joined in approximate position 36°00'N, 07°50'W. HMS Active then parted company to make rendezvous with a merchant vessel coming from Freetown.
Around 1100A/28, HMS Ark Royal and her two escorting destroyers arrived at Malta. (25)
31 Mar 1940
The aircraft carriers HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) and HMS Glorious (Capt. G. D’Oyly-Hughes, DSO and Bar, DSC, RN) departed Malta for Alexandria. They were being escorted by the destroyers HMS Bulldog (Lt.Cdr. J.S.M. Richardson, RN), HMS Westcott (Lt.Cdr. W.F.R. Segrave, RN) and HMAS Voyager (Lt.Cdr. J.C. Morrow, RAN).
En-route flying exercises were conducted.
At 0800B/2, HMS Glorious and HMS Westcott parted company to remain at sea for further flying exercises.
Around 1530B/2, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Bulldog and HMAS Voyager arrived at Alexandria.
Around 1700B/4, HMS Glorious and HMS Westcott arrived at Alexandria. (26)
8 Apr 1940
Between 0920B/8 and 0945B/8, the aircraft carriers HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN) and HMS Glorious (Capt. G. D’Oyly-Hughes, DSO and Bar, DSC, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) [Vice-Admiral Wells had transferred his flag to Glorious for these exercises] departed Alexandria for flying exercises off Alexandria. At 0800B/8, the destroyers HMS Bulldog (Lt.Cdr. J.S.M. Richardson, RN) and HMS Westcott (Lt.Cdr. W.F.R. Segrave, RN) had departed Alexandria to escort the carriers.
Around 1700B/9, HMS Ark Royal and HMS Westcott returned to Alexandria.
Around 0200B/10, HMS Glorious and HMS Bulldog returned to Alexandria. (27)
10 Apr 1940
Around 0630B/10, the aircraft carriers HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) and HMS Glorious (Capt. G. D’Oyly-Hughes, DSO and Bar, DSC, RN) and the destroyers HMS Bulldog (Lt.Cdr. J.S.M. Richardson, RN) and HMS Westcott (Lt.Cdr. W.F.R. Segrave, RN) departed Alexandria for the U.K.
Around 1630B/11, off Malta, the destroyers HMAS Stuart (Cdr. H.M.L. Waller, RAN) and HMAS Waterhen (Lt.Cdr. J.H. Swain, RN) joined. HMS Bulldog and HMS Westcott then went to Malta to fuel.
Around 0715A/12, HMAS Waterhen was detached to return to Malta after HMS Bulldog and HMS Westcott had returned after fuelling from Malta.
Around 1900A/13, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Glorious, HMS Bulldog, HMS Westcott and HMAS Stuart arrived at Gibraltar. (28)
14 Apr 1940
Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN, transferred his flag from HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN) to HMS Glorious (Capt. G. D’Oyly-Hughes, DSO and Bar, DSC, RN).
HMS Glorious then departed Gibraltar for the U.K. escorted by the destroyers HMAS Stuart (Cdr. H.M.L. Waller, RAN), HMS Velox (Cdr.(Retd.) J.C. Colvill, RN) and HMS Watchman (Lt.Cdr. E.C.L. Day, RN). The destroyers were to escort the carrier until approximate position 41°30'N, 15°00'W.
On the 15th the destroyers parted company on reaching the pre-arranged position and set course to return to Gibraltar where they arrived on the 17th.
The carrier was later joined by the destroyers HMS Walker (Lt.Cdr. A.A. Tait, RN) and HMS Walpole (Lt.Cdr. H.G. Bowerman, RN).
HMS Glorious, HMS Walker and HMS Walpole arrived in the Clyde on 18 April 1940. (29)
16 Apr 1940
Around 0815A/16, the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN) departed Gibraltar for exercises off Alboran Island. She was escorted by the destroyers HMS Bulldog (Lt.Cdr. J.S.M. Richardson, RN) and HMS Westcott (Lt.Cdr. W.F.R. Segrave, RN).
During the exercises she was recalled to Gibraltar as she was to proceed to the U.K. with all despatch.
They arrived back at Gibraltar around 1800A/16.
After fuelling HMS Ark Royal departed Gibraltar for the U.K. around 2200A/16. She was escorted by the destroyers HMS Bulldog, HMS Westcott and HMS Vortigern (Lt.Cdr. R.S. Howlett, RN).
At 1720A/17, HMS Vortigern was detached.
At 1800A/17, HMS Bulldog and HMS Westcott were detached.
At 1951A/19, the destroyer HMS Saladin (Lt.Cdr. L.J. Dover, RN) joined.
Around 0830A/20, the destroyers HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN) and HMS Juno (Cdr. W.E. Wilson, RN) joined coming from the Clyde.
HMS Ark Royal, HMS Saladin, HMS Hasty and HMS Juno arrived at Greenock around 1900A/20.
Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN then hoisted his flag in HMS Ark Royal. Also Capt. C.S. Holland joined HMS Ark Royal. (28)
20 Apr 1940
Late in the evening, Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN, transferred his flag from HMS Glorious (Capt. G. D’Oyly-Hughes, DSO and Bar, DSC, RN) to HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN). (28)
22 Apr 1940
HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) departed Greeock around 0700A/22 for Scapa Flow. She was being escorted by HMS Mashona (Cdr. W.H. Selby, RN), HMS Sikh (Cdr. J.A. Giffard, RN) and HMS Juno (Cdr. W.E. Wilson, RN).
They arrived at Scapa Flow around 0800A/3. (30)
23 Apr 1940
Around 1330A/23, the aircraft carriers, HMS Ark Royal (Capt. A.J. Power, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) and HMS Glorious (Capt. G. D’Oyly-Hughes, DSO and Bar, DSC, RN) departed Scapa Flow for air operations of central Norway. On board HMS Ark Royal were 18 Skua's and 5 Rocs as well as 21 Swordfish. On board HMS Glorious were 18 Sea Gladiators and 11 Skua's. Also on board HMS Glorious were 18 RAF Gladiators which were to be flown off to Norway. The carriers were escorted by the heavy cruiser HMS Berwick (Capt. I.M. Palmer, DSC, RN), AA cruiser HMS Curlew (Capt. B.C.B. Brooke, RN) and the destroyers HMS Fearless (Cdr. K.L. Harkness, RN), HMS Fury (Cdr. E.W.B. Sim, RN), HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN), HMS Hereward (Lt.Cdr. C.W. Greening, RN), HMS Hyperion (Cdr. H.St.L. Nicolson, RN) and HMS Juno (Cdr. W.E. Wilson, RN).
In the evening HMS Glorious flew off the 18 RAF Gladiators to Norway which were to be used in the air defense of the Aandalsnes and Molde area.
On the 24th air operations were carried out over Aandalsnes. All aircraft returned safely to the aircraft carriers. Two Skuas crashed landed near the carriers on their return due to lack of fuel. Their crews were rescued by destroyers.
The carrier force then proceeded to an area between Namsos and Trondheim and at 0300A/25 the carriers flew off aircraft to attack the Vaernes airfield and other enemy military targets in the Trondheim area. Both carriers lost four aircraft, some of the crews were picked up by destroyers.
At 0725A/26 the destroyer screen parted company to proceed to Sullom Voe to refuel. They arrived at Sullom Voe at 2130A/26 and departed again 0400A/27 to rejoin the force at which they did around 1800A/27. They had been relieved at 0700A/26 by a group of destroyers coming from the Narvik area, these were; HMS Grenade (Cdr. R.C. Boyle, RN), HMS Fortune (Cdr. E.A. Gibbs, DSO, RN), HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St J. Morgan, RN), HMS Escort (Lt.Cdr. J. Bostock, RN), HMS Beagle (Lt.Cdr. R.H. Wright, RN) and HMS Volunteer (Lt.Cdr. N. Lanyon, RN).
During flying operations on the 26th two aircraft were lost.
During flying operations on the 27th also two aircraft were lost.
At 2100A/27, HMS Glorious parted company with the force and proceeded to Scapa Flow escorted by the destoyers HMS Hasty, HMS Grenade, HMS Fury, HMS Fortune, HMS Escort and HMS Encounter. They arrived at Scapa Flow at 1800A/28.
On the 28th, aircraft from HMS Ark Royal carried out another air raid on the Trondheim area. One aircraft was lost. During this raid the force was now made up of HMS Ark Royal, HMS Berwick, HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral M.L. Clarke, DSC, RN) (joined around 1200A/28), HMS Curlew (parted company around 1600A/28), HMS Fearless, HMS Hereward, HMS Hyperion and HMS Juno.
At 2100A/29, HMS Sheffield parted company.
At 0630A/30, HMS Glorious departed Scapa Flow to rejoin HMS Ark Royal at sea. Shortly after departure replacement aircraft were flown on. She was escorted by the destroyers HMS Beagle, HMS Antelope (Lt.Cdr. R.T. White, RN), HMS Acheron (Lt.Cdr. R.W.F. Northcott, RN) and HMS Volunteer. HMS Volunteer however developed defects and was soon detached to Sullom Voe arriving there at 2230A/30. Defects proved to be of such nature that she had to return to Scapa Flow for repairs. HMS Glorious and her remaining escorting destroyers joined the Ark Royal group around 1030/1.
At 0400A/30 HMS Juno was detached from the screen of HMS Ark Royal and proceeded to Sullum Voe with defects. At Sullom Voe ammunition was transferred to HMS Kimberley (Lt.Cdr. J.S.M. Richardson, RN) which then proceeded to take her place in the destroyer screen of HMS Ark Royal. HMS Juno then proceeded to Scapa Flow for repairs arriving there at 1800A/1.
Around 1100A/30, the battleship HMS Valiant (Capt. H.B. Rawlings, OBE, RN) and the destroyers HMS Fury, HMS Fortune HMS Escort and HMS Encounter joined coming from Scapa Flow which they had departed at 2100A/29.
Around 1820A/1, the force came under heavy German air attack but no damage was done.
At 2000A/1, Capt. Holland assumed command of HMS Ark Royal from Capt. Power while the ship was at sea.
At 2100A/1, HMS Hyperion and HMS Beagle were detached to Sullom Voe. HMS Hereward had already been detached around 1900A/1. HMS Hereward arrived at Sullom Voe at 1240A/2 followed aby HMS Hyperion at 2215A/2. HMS Beagle proceeded to Scapa Flow arriving there at 0630A/3.
HMS Ark Royal, HMS Glorious, HMS Valiant, HMS Berwick, HMS Acheron, HMS Antelope, HMS Encounter, HMS Escort, HMS Fearless, HMS Fortune, HMS Fury and HMS Kimberley arrived at Scapa Flow around 1030A/3. (31)
4 May 1940
Around 1600A/4, the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), AA cruiser, AA cruiser HMS Curlew (Capt. B.C.B. Brooke, RN) and the destroyers HMS Inglefield (Capt. P. Todd, RN), HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St J. Morgan, RN), HMS Mashona (Cdr. W.H. Selby, RN), HMS Sikh (Cdr. J.A. Giffard, RN), HMS Tartar (Cdr. L.P. Skipwith, RN) and HMS Jaguar (Lt.Cdr. J.F.W. Hine, RN) departed Scapa Flow for operations off Norway.
On the 6th, HMS Ark Royal flew of a Walrus to Harstad with the Staff Officer Operations onboard. He was to confer with Admiral of the Fleet W.H.D. Boyle (Lord Cork), GCB, GCVO, RN, the Flag Officer, Northern Norway.
In the afternoon of the 6th, HMS Ark Royal flew off six Skua's for a fighter patrol over Tjelsundet, Bogen and Harstad. One aircraft reported having sighted a submarine near the Andenes Lighthouse. Therefore an A/S patrol of three Swordfish was flown off but these sighted nothing.
At 0640A/7, HMS Encounter and HMS Jaguar were detached to fuel at Harstad. They returned at 2000A/7 at which time HMS Sikh and HMS Tartar were detached to fuel at Harstad.
On the 7th, flight operations were carried out by HMS Ark Royal, these included fighter patrols in the Narvik / Harstad area. Also the Walrus aircraft with the Staff Officer Operations returned to HMS Ark Royal. Two Swordfish aircraft carried out a photographic reconnaissance of the area east of Bogen.
HMS Sikh and HMS Tartar rejoined at 1054/8. Later that day, at 1737A/8, HMS Inglefield and HMS Mashona were sent to Harstad to fuel.
On the 8th, flight operations were carried out by HMS Ark Royal, these included the usual fighter patrols in the Narvik / Harstad area. In the afternoon Skua's damaged two enemy bombers and forced a enemy flying boat down. One of the Skua's was lost in this last engagement. The crew was safe and later returned to HMS Ark Royal. Also one Swordfish carried out a photographic reconnaissance of the east east of Bogen and the Herjangsfjord. In the afternoon two more Swordfish conducted an A/S patrol around the carrier force.
At 0902A/9, HMS Inglefield and HMS Mashona rejoined. At 1315A/9, HMS Jaguar was detached to Harstad. At 2253A/9, HMS Encounter was detached to Harstad.
On the 9th, flight operations were carried out by HMS Ark Royal. The flying operations started around 0800A/9 with a strike force of 9 Swordfish aircraft which were to to carry out an attack on the railway line at Nordalsbroen, Hundalen and Sildvik. They were followed by three Skua's which were to give fighter protection for this Swordfish strike force. Two more Skua's were then flown off for a defensive patrol. Three of the Swordfish had to return to HMS Ark Royal and one had to ditch and the crew was picked up by a destroyer. The remaining Swordfish successfully attacked railway infrastructure. One of the Skua's of the fighter cover for the Swordfish had to crash land due to engine problems. It's crew survived and managed to escape capture by the Germans. No flying was prossible for the remainder of the day due to the weather conditions.
At 0225/10, HMS Jaguar rejoined followed by HMS Encounter at 1703A/10 at which time HMS Sikh and HMS Tartar were detached for Harstad.
On the 10th, no flying was possible until early afternoon when 2 flights of three Skua's each were flown off for fighter patrols in the Narvik, area. Fighted patrols were maintained throughout the remainder of the day.
At 1355A/11, HMS Sikh and HMS Tartar rejoined and HMS Mashona and HMS Jaguar were detached with orders to proceed to Scapa Flow.
On the 11th, flying commenced around 1000 hours when three Skua's were flown off to provide fighter cover for Allied convoys. This fighter cover was maintained throughout the day.
On the 12th, flying commenced around 0400 hours with Skua's been again flown off for convoy fighter cover. These fighter patrols were discontinued around noon. In late afternoon aircraft were flown off for operations and fighter patrols in the Narvik area.
At 1304A/13, HMS Curlew and HMS Inglefield were detached to fuel at Harstad.
On the 13th, flying already started at 0215 hours when two Skua's were flown off for fighter patrol over Herjangsfjord. Also a Swordfish was flown off for reconnaissance duty for the Army. Fighter patrols would be maintained over the Fleet and various areas throughout early in the morning. Also several strike forces were flown off to engage land targets. Flying was halted around 0800 hours due to the unsuitable weather conditions.
At 0830A/14, HMS Inglefield rejoined. At 1338A/14, the destroyers HMS Westcott (Lt.Cdr. W.F.R. Segrave, RN) and HMS Volunteer (Lt.Cdr. N. Lanyon, RN) joined. At the same time HMS Inglefield and HMS Sikh were detached with orders to proceed to Scapa Flow while HMS Encounter was detached to Harstad. At 1350A/14, HMS Curlew rejoined but she left again at 2057A/14.
On the 14th, flying commenced only at 1100 hours when three Skua's were flown off for a fighter patrol over Bjerkvik. Fighted patrols were maintained throughout the day in various areas.
At 0615A/15, HMS Encounter rejoined. HMS Tartar parted company on the 15th, also to fuel at Harstad (no time given).
On 15 May, flying commenced shortly after 0400 hours, when two Skua's were flown off for a fighter patrol over Hartvig. Fighter patrols were maintained over several area's throughout the day. Also several stike forces of Swordfish aircraft were flown off during the day.
At 0703A/16, HMS Westcott parted company to proceed to Harstad to effect repairs there as she was suffering from engine trouble and her Asdic was out of action. At 1044A/16, HMS Tartar rejoined. At 1800A/16, HMS Volunteer was detached to fuel at Harstad.
On 16 May, flying commenced around 0300 hours, when a strike force of 9 Swordfish was flown off to attack enemy troops and stores on the Hemnes Peninsula in the Ranfjorden. Three Skua's were also flown off to give them fighter protection. They also were to sink the damaged troopship Chrobry (Polish, 11442 GRT, built 1939). One bomb hit the ship and she finally sank. Earlier attempts had failed to sink the derelict wreck. Fighter patrols made up of Skua's were flown off throughout the day to patrol in various areas. Also late in the afternoon a Swordfish was flown off for a photographic reconnaissance.
At 2100A/17, HMS Volunteer rejoined from Harstad.
On the 17th, fighter protection was provided for HMS Effingham (Capt. J.M. Howson, RN), HMS Cairo (Capt. P.V. McLaughlin, RN), HMS Coventry (Capt. R.F.J. Onslow, DSC, RN), HMS Matabele (Cdr. G.K. Whitmy-Smith, RN) and HMS Echo (Cdr. S.H.K. Spurgeon, DSO, RAN) which where en-route from Harstard to Bodo carrying troops. These fighter patrols continued until 0630A/18.
At 0200A/18, the destroyer HMS Brazen (Lt.Cdr. Sir M. Culme-Seymour, RN) joined. At 1445A/18, the destroyer HMS Antelope (Lt.Cdr. R.T. White, RN) joined. At 1800A/18, HMS Encounter was detached to oil. HMS Tartar was also detached on this day (no time given).
Late the 18th, two groups of three Skua's were flown off by HMS Ark Royal for figher cover in the Narvik area.
At 1612A/19, HMS Encounter rejoined. At 1900A/19, HMS Volunteer parted company to oil at Harstad.
On the 19th, No flying took place as conditions inshore were unsuitable.
At 1830A/20, HMS Volunteer rejoined and HMS Brazen was detached to oil at Harstad.
On the 20th, around 0330 hours, HMS Ark Royal flew off a strike force of 9 Swordfish that was to attack Hundalen and Sildvik. Around the same time 3 Skua's were flown off for a fighter patrol in the Narvik area. More Skua fighters patrols for the Narvik area were flown off at 0400 and 0600 hours. When these aircraft all returned later in the morning, visibility had deteriorated and flying was halted for the remainder of the day.
At 1928A/21, HMS Brazen rejoined.
On 21 June HMS Ark Royal flew of 6 Skua's around 0300 hours for a fighter patrol near Bardufoss airfield to cover the landing of Gladiator fighters there that were flown off from HMS Furious. Later Skua's were flown off to conduct a fighter patrol off Bardufoss.
Around 2345A/22, HMS Volunteer and HMS Encounter lost touch in thick fog. They only rejoined at 1523/23, after the fog had cleared. HMS Ark Royal now ended her operations off Norway and course was set to return to Scapa Flow.
At 0455A/24, HMS Antelope was detached followed by HMS Brazen at 1518A/24. HMS Ark Royal, HMS Volunteer and HMS Encounter arrived at Scapa Flow around 1915A/24.
11 May 1940
Around 1300A/11, the heavy cruiser HMS Devonshire (Capt. J.M. Mansfield, DSC, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.H.D. Cunningham, CB, MVO, RN) departed Tromso for Kirkenes.
She was escorted by the destroyer HMS Westcott (Lt.Cdr. W.F.R. Segrave, RN).
The destroyer HMS Volunteer (Lt.Cdr. N. Lanyon, RN) was unable to sail with them due to defects and was ordered to sail as soon as she was able to.
Later in the afternoon HMS Westcott reported a hole in her Asdic dome and that she was only able to use her Asdic at very slow speed.
HMS Devonshire arrived at Kirkenes around 1215A/12. HMS Westcott remained out in the Kors Fjord on A/S patrol.
Around 1630A/12, HMS Volunteer arrived and after disembarking a contingent of Royal Marines relieved HMS Westcott on patrol in the Kors Fjord.
Around 2030A/12, HMS Westcott sailed to take over the A/S patrol from HMS Volunteer which went alongside HMS Devonshire shortly after 2100A/11, to effect more repairs and also fuel from the cruiser.
Around 0300A/13, HMS Volunteer departed to take over the A/S patrol from HMS Westcott which then returned and oiled from HMS Devonshire and proceeded on patrol again around 0830A/13.
HMS Devonshire departed Kirkenes around 0900A/13 and was then joined by the destroyers in Kors Fjord.
Around 1300A/14, they made rendezvous, in position 70°53'N, 15°47'E, with the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) and her destroyer screen which at that time was made up of HMS Inglefield (Capt. P. Todd, RN), HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St J. Morgan, RN), HMS Sikh (Cdr. J.A. Giffard, RN) and HMS Tartar (Cdr. L.P. Skipwith, RN). HMS Westcott and HMS Volunteer then joined the carrier.
HMS Devonshire had been ordered to proceed to Tromso where she arrived around 0150A/15. She then commenced fuelling. The following day she had completed up to 75%. (32)
13 May 1940
French troops were landed at Bjervik, Norway today. This is just to the north of Narvik. The town was captured successfully.
Naval ships involved in landing the troops and to provide cover were; battleship HMS Resolution (Capt. O. Bevir, RN), light cruisers HMS Aurora (Capt. L.H.K. Hamilton, DSO, RN), HMS Effingham (Capt. J.M. Howson, RN) which both landed French troops, repair ship HMS Vindictive (Capt. A.R. Halfhide, RN), netlayer HMS Protector (Capt. W.Y la L. Beverley, RN) and the destroyers HMS Somali (Capt. R.S.G. Nicholson, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Havelock (Capt. E.B.K. Stevens, DSC, RN), HMS Fame (Cdr. P.N. Walter, RN), HMS Basilisk (Cdr. M. Richmond, OBE, RN) and HMS Wren (Cdr. H.T. Armstrong, RN). They had departed Harstad (Tjeldsund) the previous day.
Air cover for this operation was provided, from a distance, by aircraft from HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN).
Later this day these ships also bombarded Narvik with the assistance of aircraft from the Ark Royal.
25 May 1940
Around 1615A/25, the aircraft carriers HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) and HMS Furious (Capt. T.H. Troubridge, RN) departed Scapa Flow to replenish at Greenock. She was escorted by the destroyers HMS Antelope (Lt.Cdr. R.T. White, RN), HMS Amazon (Lt.Cdr. N.E.G. Roper, RN), HMS Campbell (Lt.Cdr. R.M. Aubrey, RN), HMS Volunteer (Lt.Cdr. N. Lanyon, RN) and HMS Viscount (Lt.Cdr. M.S. Townsend, OBE, RN) and
They arrived in the Clyde around 1700A/26. (33)
30 May 1940
Around 0545A/30, the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) departed Greenock for Scapa Flow. She was escorted by the destroyers HMS Acasta (Cdr. C.E. Glasfurd, RN), HMS Acheron (Lt.Cdr. R.W.F. Northcott, RN) and HMS Ardent (Lt.Cdr. J.F. Barker, RN).
They arrived at Scapa Flow around 0530A/31. (34)
31 May 1940
Around 0845A/31, the aircraft carriers HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) and HMS Glorious (Capt. G. D’Oyly-Hughes, DSO and Bar, DSC, RN) departed Scapa Flow for operations of northern Norway. They were escorted by the destroyers HMS Highlander (Cdr. W.A. Dallmeyer, RN), HMS Diana (Lt.Cdr. E.G. Le Geyt, RN), HMS Acasta (Cdr. C.E. Glasfurd, RN), HMS Acheron (Lt.Cdr. R.W.F. Northcott, RN) and HMS Ardent (Lt.Cdr. J.F. Barker, RN).
The aircraft carriers were to provide cover for the Allied withdrawal from Norway (HMS Ark Royal) and to evacuate RAF fighters (HMS Glorious, which carried therefore a reduced aircraft complement)
On 31 May, HMS Ark Royal kept up an A/S patrol throughout the day.
On 1 June, no flying operations were carried out due to the foggy weather conditions.
At 1741A/2, HMS Acasta and HMS Ardent were detached to fuel at Harstad.
On 2 June, A/S patrols were flown, in the morning by HMS Ark Royal and in the afternoon by HMS Glorious.
At 0723A/3, HMS Glorious and HMS Highlander were detached to operate independently to the north-west so as to conserve fuel until HMS Glorious was required to embark the RAF aircraft she was to evacuate.
At 1704A/3, HMS Acasta and HMS Ardent rejoined HMS Ark Royal. HMS Diana and HMS Acheron were then detached to fuel at Harstad.
On the 3rd, some Swordfish were flown off by HMS Ark Royal in the late afternoon / early evening for patrol. Also a Swordfish was flown off for a reconnaissance and weather reporting mission of the Narvik area.
Around 1200A/4, HMS Diana and HMS Acheron rejoined.
On 4th, HMS Ark Royal maintained A/S and fighter patrols throughout the day. A/S patrol was also provided for evacuation convoys.
At 1420A/5, HMS Glorious and HMS Highlander rejoined. HMS Highlander was then detached to Harstad to fuel shortly afterwards. The carriers then remained in close company, each screened by two of the destroyers, HMS Ark Royal was screened by HMS Acasta and HMS Ardent and HMS Glorious by HMS Diana and HMS Acheron.
On 5 June, only a Walrus landed on HMS Ark Royal coming from Harstad. It was flown off later again to return to Harstad. Other flying operations were cancelled due to fog. In the evening the weather cleared and flying operation were again possible. A/S and fighter patrols were flown off as was a reconnaissance Swordfish. Flying operation continued during the night of 5/6 June.
At 0940A/6, HMS Acasta and HMS Ardent were detached to fuel at Harstad.
At 1018A/6, HMS Glorious was detached escorted by the destroyer HMS Highlander which had just returned from fuelling.
On 6 June, flying operations were conducted during the entire day these included fighter patrols, A/S patrols, reconnaissance missions as well as attack missions on land targets.
At 0028A/7, HMS Acasta and HMS Ardent returned from fuelling and rejoined HMS Ark Royal. HMS Diana and HMS Acheron were then detached to fuel at Harstad.
At 1504A/7, HMS Glorious and HMS Highlander rejoined.
At 1612A/7, HMS Diana and HMS Acheron rejoinned from fuelling.
On the 7th, flying operations were conducted during the entire day these included fighter patrols, A/S patrols, reconnaissance missions as well as attack missions on land targets.
At 0103A/8, HMS Glorious acted independently to land on the RAF Gladiators and Hurricanes for transport back to the U.K. At 0253A/8, HMS Glorious parted company to return to the U.K. She took HMS Acasta and HMS Ardent with her as escorts.
8 Jun 1940
Evacuation of the 'Narvik / Harstad / Tromso area'.
2nd troop evacuation convoy from Harstad.
From 7 to 8 June 1940 the troopships Arandora Star (15501 GRT, built 1927), Duchess of York (20021 GRT, built 1929), Ormonde (14982 GRT, built 1917), Oronsay (20043 GRT, built 1925), Royal Ulsterman (3244 GRT, built 1936), Ulster Monarch (3791 GRT, built 1929) and Ulster Prince (3791 GRT, built 1930) embarked almost 10000 troops in the Andfiord, near Harstad, Norway. They did this one by one.
They then departed the Harstad area for the U.K. They were escorted by the light cruiser HMS Southampton (Capt. F.W.H. Jeans, CVO, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral M.L. Clarke, DSC, RN), AA cruiser HMS Coventry (Capt. R.F.J. Onslow, DSC, RN) and the destroyers HMS Beagle (Lt.Cdr. R.H. Wright, RN), HMS Delight (Cdr. M. Fogg-Elliott, RN), HMS Echo (Cdr. S.H.K. Spurgeon, DSO, RAN), HMS Fame (Cdr. P.N. Walter, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSC, RN) and HMS Havelock (Capt. E.B.K. Stevens, DSC, RN).
The aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) and her escort, the destroyers HMS Highlander (Cdr. W.A. Dallmeyer, RN), HMS Diana (Lt.Cdr. E.G. Le Geyt, RN) and HMS Acheron (Lt.Cdr. R.W.F. Northcott, RN) initially operated near the convoy but they acted independently to enable flying operations which continued throught the entire day. A/S and most of all fighter patrols were flown.
They were joined in the evening of the 9th by the battleship HMS Valiant (Capt. H.B. Rawlings, OBE, RN) and the destroyers HMS Tartar (Capt. C. Caslon, RN), HMS Mashona (Cdr. W.H. Selby, RN), HMS Bedouin (Cdr. J.A. McCoy, DSO, RN) and HMS Ashanti (Cdr. W.G. Davis, RN).
Around 0930/10, HMS Repulse (Capt. E.J. Spooner, DSO, RN) joined.
Around 2115/10, the destroyers HMS Maori (Cdr. H.T. Armstrong, RN) and HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN) joined.
On the 11th, HMS Valiant, HMS Repulse, HMS Tartar, HMS Bedouin, HMS Maori, HMS Forester, HMS Diana and HMS Acheron were detached to proceed to Scapa Flow.
The convoy arrived in the Clyde very late in the evening of the 12th.
9 Jun 1940
At 1245A/9, the battleship HMS Rodney (Capt. F.H.G. Dalrymple-Hamilton, RN, flying the flag of Admiral of the Fleet C.M. Forbes, KCB, DSO, RN), battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral W.J. Whitworth, CB, DSO, RN) escorted by the destroyers HMS Inglefield (Capt. P. Todd, RN), HMS Electra (Lt.Cdr. S.A. Buss, MVO, RN), HMS Escort (Lt.Cdr. J. Bostock, RN), HMS Zulu (Cdr. J.S. Crawford, RN) and HMS Kelvin (Lt.Cdr. J.L. Machin, RN) departed Scapa Flow to provide cover for convoys coming down from Norway and to search for the reported German capital ships. A sixth destroyer, HMS Amazon (Lt.Cdr. N.E.G. Roper, RN), which had been en-route from the Clyde to Scapa Flow, apparently joined at sea.
At 1345A/10, HMS Amazon was detached to fuel at Sullom Voe.
On June, 10th the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) was ordered to join this force which she did at 1525A/10. She had the destroyers HMS Ashanti (Cdr. W.G. Davis, RN), HMS Mashona (Cdr. W.H. Selby, RN) and HMS Highlander (Cdr. W.A. Dallmeyer, RN) with her. At 1140A/10, the destroyers HMS Diana (Lt.Cdr. E.G. Le Geyt, RN) and HMS Acheron (Lt.Cdr. R.W.F. Northcott, RN) had been exchanged for HMS Ashanti and HMS Mashona.
At 1925A/10, HMS Mashona was detached to join the destroyer HMS Campbell (Lt.Cdr. R.M. Aubrey, RN) and escort this destroyer, which had to proceed at the most economical speed due to fuel shortage, to Sullom Voe where they arrived at 0745A/12.
At 1020A/11, HMS Ashanti and HMS Highlander were detached to Scapa Flow. They were ordered to proceed through positions 64'N, 05'W and 61'N, 05'W.
The destroyers HMS Fearless (Cdr. K.L. Harkness, RN), HMS Escapade (Cdr. H.R. Graham, RN), HMS Antelope (Lt.Cdr. R.T. White, RN), and HMS Amazon departed Sullom Voe at 2230A/11th to join the Home Fleet at sea which they did at 0830A/12. [HMS Amazon did not join the Home Fleet so either she did not sail or returned.] At 2100A/12, the destroyer HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN) sailed from Scapa Flow to make rendez-vous with the Home Fleet in position 63'N, 04'W at 1300A/13. The destroyers HMS Mashona, HMS Campbell and HMS Veteran (Cdr. J.E. Broome, RN) departed Sullom Voe at 0400A/13 to do the same. They joined the Home Fleet at 1725A/14 with the exception of HMS Campbell which joined HMS Ark Royal's screen at 2230A/13.
Between 0007A/13and 0015A/13, HMS Ark Royal flew off fifteen Skuas to attack German warships at Trondheim. Seven of them returned around 0330A/13, eight had been lost.
Around 0430A13, HMS Electra collided with HMS Antelope in thick fog which the Fleet had just entered. HMS Inglefiel stood by HMS Antelope while HMS Zulu took HMS Electra in tow. All set course for Scapa Flow.
At 0600A/13, HMS Ark Royal was detached to proceed to Scapa Flow escorted by HMS Escort and HMS Kelvin. HMS Campbell joined them at 2230A/13. They arrived at Scapa Flow wit at 1545A/14.
At 1130A/13, the destroyers HMS Tartar (Capt. C. Caslon, RN), HMS Maori (Cdr. H.T. Armstrong, RN), HMS Bedouin (Cdr. J.A. McCoy, DSO, RN) and HMS Ashanti (Cdr. W.G. Davis, RN) departed Scapa Flow to make rendez-vous with the Home Fleet in position 65'N, 04'W. They joined at 0840A/14.
At 0950A/14, HMS Escapade was detached from the screen of the Home Fleet to join HMS Electra that was being towed by HMS Zulu..
At 0100A/15, HMS Forester and HMS Veteran were detatched from the Home Fleet to proceed to the Faroes for escort duty.
At 0330A/15, HMS Antelope, escorted by HMS Inglefield arrived at Scapa Flow.
At 1715A/15, HMS Rodney, HMS Renown, HMS Tartar, HMS Mashona, HMS Maori, HMS Bedouin, HMS Ashanti and HMS Fearless arrived at Scapa Flow.
At 1430A/16, HMS Electra, in tow of the tug HMS Brigand and escorted by HMS Zulu and HMS Escapade arrived at Scapa Flow. (30)
13 Jun 1940
While escorting HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) off Norway HMS Antelope (Lt.Cdr. R.T. White, DSO, RN) and HMS Electra (Lt.Cdr. S.A. Buss, RN) collide with each other in heavy fog. Both destroyers were damaged and repairs took until ca. mid-August.
14 Jun 1940
Around 1545A/14, HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Kelvin (Lt.Cdr. J.L. Machin, RN), HMS Escort (Lt.Cdr. J. Bostock, RN) and HMS Campbell (Lt.Cdr. R.M. Aubrey, RN) arrived at Scapa Flow. (35)
16 Jun 1940
Dakar, the French battleship Richelieu and the fall of France Timespan; 16 June to 7 July 1940.
The fall of France, 16 June 1940.
On 16 June 1940, less then six weeks after the invasion of France and the low countries had started on May 10th, all military resitance in France came to an end. The question of control of the French fleet had thus become, almost overnight, one of vital importance, for if it passed into the hands of the enemy the whole balance of sea power would be most seriously disturbed. It was therefore policy of H.M. Government to prevent, at all costs, the French warships based on British and French harbours overseas from falling into the hands of Germany.
The bulk of the French fleet was at this time based in the Mediterranean. There drastic steps were taken to implement this policy. Elsewhere the most important units were the two new battleships completing, the Jean Bart at St. Nazaire and more importantly as she was almost complete, the Richelieu, at Brest.
Events during the Franco-German negotiations 17-25 June 1940 and politics.
It was on the 17th of June 1940, when the newly-formed Pétain Cabinet asked the Germans to consider ‘honourable’ peace terms in order to stop the fighting in France. At 1516 (B.S.T.) hours that day the Admiralty issued orders that British ships were not to proceed to French ports. On receipt of these orders Vice-Admiral George D’Oyly Lyon, Commander-in-Chief South Atlantic, ordered the aircraft carrier HMS Hermes (Capt R.F.J. Onslow, DSC, MVO, RN) then on her way to Dakar after a patrol off the Canary Islands to proceed to Freetown instead at her best speed. At the same time he recalled the British SS Accra which had sailed from Freetown for Dakar at 1730 hours (zone +1) with 850 French troops on board. She returned to Freetown at 0800/18. The British transport City of Paris with 600 French troops on board from Cotonou was ordered to put into Takoradi. On the 18th the Commander-in-Chief was also informed by Commander Jermyn Rushbrooke, RN, the British Naval Liaison Officer at Dakar that the Commander-in-Chief of the French Navy, Admiral Darlan had ordered Admiral Plancon at Dakar to continue fighting and also that the shore batteries and AA personnel there had declared for the British. At 0245/18 Vice-Admiral Lyon passed this information to the Admiralty, cancelled his orders to HMS Hermes to proceed to Freetown and directed her with the armed merchant cruisers HMS Carnarvon Castle (Capt. M.J.C. de Meric, RN) and HMS Mooltan (Capt.(Retd.) G.E. Sutcliff, RN), which were on passage to Freetown from the Western Approaches, to proceed to Dakar at full speed in order to strengthen the French morale. That afternoon the Admiralty ordered HMS Delhi (Capt. A.S. Russell, RN) to leave Gibraltar and proceed to Dakar and join the South Atlantic Station. She left Gibraltar on the 19th with an arrival date of the 23rd. In the morning of the 18th the French troopship Banfora reached Freetown, from Port Bouet, Ivory Coast with 1000 troops on board, and sailed for Dakar without delay. The French armed merchant cruiser Charles Plumier, which had been on patrol south of the Cape Verde Islands reached Dakar at 1015/18.
Meanwhile the British Naval Liaison Officer, Dakar’s signal had been followed by a report from the Naval Control Service Officer at Duala that an overwhelming spirit existed amongst the military and civilian population of the French Cameroons to continue fighting on the British side, but that they required lead, as the Governer was not a forceful character; but that morning the Governor of Nigeria informed the Commander-in-Chief that he considered steps to be taken to prevent a hostile move from Fernando Po (off the entrance to the Cameroon River). Accordingly, at 1845/18, the armed merchant cruiser HMS Bulolo (A/Capt. C.H. Petrie, RN) sailed from Freetown at 14 knots to show herself off San Carlos on the morning of the 23rd, and thence to anchor of Manoka in the Cameroon River the next day (her draught prevented her from reaching Duala). A/Capt. Petrie was then to proceed to Duala and call a conference.
It was difficult to arrive at a clear appreciation of the situation in French West-Africa but on the morning of the 19th June the Commander-in-Chief informed the Admiralty that, as the evidence pointed to an established resolve on the part of the West-African Colonies to join Great Britain whatever happened, he intended to allow French troop movements to continue. This he anticipated would avoid French exasperation and mistrust. During the early afternoon he heard from the Governors of Nigeria and the Gold Coast that French officers and non-commissioned officers were planning to leave the Cameroons and to join the British forces in Nigeria. At 1900/19 the Commander-in-Chief held a conference with the Governor of Sierra Leone at which it was decided that the Governor should cable home urging immediate action to persuade the French colonial troops and authorities to remain in their territories and hold their colonies against all attacks. In the evening the Commander-in-Chief reported to the Admiralty that French Guinea was determined to keep fighting on the British side. Meanwhile the Governor-General of French Equatorial Africa at Brazzaville was wavering and suggested leading his troops to the nearest British Colony. Late that night, still on the 19th, the Commander-in-Chief informed him that it was essential that he should remain at his post and that it was the expressed intention of French West Africa to fight on to victory.
Next morning, on the 20th, the Admiralty informed the Commander-in-Chief that the new French battleship Richelieu (about 95% complete) had departed Brest for Dakar on the 18th. Her sister ship, Jean Bart (about 77% complete) had left St. Nazaire for Casablanca on the 19th. During the afternoon of the 20th the British Liaison Officer at Dakar reported that according to the French Admiral at Dakar the French Government had refused the German armistice terms and would continue the fight in France. This was entirely misleading. For nearly two days the Commander-in-Chief had no definite information till at noon on 22 June when a BB C broadcast announced the signing of a armistice between France and Germany, which was to followed by one between France and Italy. Still there was much uncertainty, and the rest of the day was apparently spent in waiting for news. Early next morning, the 23rd June, the Admiralty informed the Commander-in-Chief that the French Bordeaux Government had signed an armistice with Germany. As the terms were not fully known the attitude of the French Navy remained uncertain. Shortly after 0200/23 the Admiralty gave orders that HMS Hermes was to remain at Dakar, and gave the Commander-in-Chief the text of the British Government’s appeal to the French Empire and to Frenchmen overseas to continue the war on the British side. The final collapse of France naturally exercised an important influence on the dispositions and movements of the South Atlantic forces. Also on the 23rd the cruiser HMS Dorsetshire (Capt. B.C.S. Martin, RN) and the destroyer HMS Watchman (Lt.Cdr. E.C.L. Day, RN) departed Gibraltar for Dakar and Casablanca respectively, and the same morning HMS Bulolo arrived off Fernando Po and showed herself of San Carlos and Santa Isabel. At noon she anchored off Manoka, in the Cameroon River, in the hope of restoring morale at Duala. Meanwhile HMS Mooltan had arrived at Freetown from Dakar and the United Kingdom, and during the afternoon (1500/23) the armed merchant cruiser HMS Maloja (A/Capt. V. Hammersley-Heenan, RN) reached Dakar from the Northern Patrol to join the Freetown escort force. Half an hour later the Richelieu and escorting destroyer Fleuret arrived at Dakar.
For a time the attitude of the French Governor-General at Dakar, the French North African colonies and the French Mediterranean Fleet, and the battleship Richelieu remained in doubt. Then owning to the anticipated difficulty of maintaining French salaries and supplies if the French did not accept the British offer, the situation at Dakar rapidly deteriorated, and by the evening of the 23rd reached a critical state. Early on the 24th, therefore, the Admiralty ordered the Commander-in-Chief to proceed there as soon as possible. The Commander-in-Chief replied that he intended to proceed there in the ex-Australian seaplane carrier HMS Albatross (Cdr. W.G. Brittain, RN), which was the only available ship, and expected to reach Dakar around noon on the 25th. At 1015/24 he left Freetown and reached Dakar around 1600/25. Meanwhile the Richelieu had put to sea. From then on the naval operations centred mainly on the battleship.
The problem of the Richelieu, 25-26 June 1940.
The Richelieu which had been landing cadets at Dakar, had sailed with the Fleuret at 1315/25 for an unknown destination. She was shadowed by an aircraft from HMS Hermes until 1700 hours. She was reported to be steering 320° at 18 knots. At 1700 hours the Admiralty ordered HMS Dorsetshire to shadow her, and at 2200 hours HMS Dorsetshire reported herself as being in position 16°40’N, 18°35’W steering 225° at 25 knots, and that she expected to make contact with the Richelieu at midnight. At 2126 hours, the Admiralty ordered the Vice-Admiral aircraft carriers (Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) in HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN) to proceed with dispatch to the Canary Islands with HMS Hood (Capt. I.G. Glennie, RN) and five destroyers (actually only four sailed with them; HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Fearless (Cdr. K.L. Harkness, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. G.H. Peters, RN) and HMS Escapade (Cdr. H.R. Graham, RN)). They departed Gibraltar in the morning of the 26th.
Early on the 26th, the Admiralty informed the Commander-in-Chief, South Atlantic, and the Vice-Admiral, aircraft carriers, that His Majesty’s Government had decided that the Richelieu was to be captured and taken into a British port. They were to take every step to avoid bloodshed and to use no more force then was absolutely necessary. It was understood that the French battleship had H.A. ammunition on board but no main armament ammunition, that forenoon however, the British Liaison Officer Brest reported that she had embarked 15” ammunition before leaving there. HMS Hood was to perform this task if possible but that there were a risk that the Richelieu might get away before her arrival, or if she tried to enter a neutral port such as La Luz in the Canaries, HMS Dorsetshire was to take action. After the capture she was to be taken to Gibraltar. The battleship HMS Resolution (Capt. O. Bevir, RN), which was at Gibraltar, was detailed to intercept the Jean Bart in case she would depart Casablanca and deal with her in the same way.
Vice-Admiral Wells reported that HMS Ark Royal, HMS Hood and their escorting destroyers would pass through position 36°00’N, 06°35’W at 0300/26, steering 225° at 20 knots. HMS Dorsetshire, meanwhile, having seen nothing of the Richelieu by 0015/26, had proceeded to the northwestward, and then at 0230/26 turned to course 030°. At 0530/26 she catapulted her Walrus aircraft to search to the northward, and at 0730 hours it sighted the Richelieu in position 19°27’N, 18°52’W on course 010°, speed 18.5 knots. Eleven minutes later she altered course to 195°. The aircraft proceeded to shadow, but missed HMS Dorsetshire when it tried to return and in the end was forced to land on the sea at 0930 hours about 50 nautical miles to the southward of her. The Dorsetshire which had turned to 190° at 0905 hours was then in position 18°55’N, 17°52’W. She turned to search for her aircraft. Around noon she abandoned the search and steered 245° at 25 knots to intercept the Richelieu, which she correctly assumed to be continuing to the southward. She made contact soon after 1430 hours and at 1456 hours reported that she was shadowing the battleship from astern.
In the meantime the French Admiral at Dakar had informed Vice-Admiral Lyon that the ‘Admiral Afrique’ had ordered the Richelieu and the Fleuret to return to Dakar. At 1512 hours the Commander-in-Chief, South Atlantic asked the Admiralty whether, under these circumstances, HMS Dorsetshire was to attempt to capture the Richelieu. He was confident that any interference would antagonise all the local authorities and the French people in general. He also pointed out that His Majesty’s ships at Dakar would be placed in a most difficult position.
At 1630/26, HMS Dorsetshire, reported that she was in position 17°21’N, 18°22’W with the Richelieu within easy visual distance. Relations between the two ships remained cordial. The French ship had not trained her guns when she sighted the Dorsetshire, and she expressed regret that, having no aircraft embarked, she was unable to co-operate in the search for her missing Walrus aircraft but she signalled to Dakar for a French plane to assist. In view of her declared intention to return to Dakar, Capt. Martin took no steps to capture her and at 1700 hours he was ordered by the Admiralty to only shadow the Richelieu. At the same time HMS Hermes left Dakar to search for HMS Dorsetshire’s Walrus.
Shortly after 1900/26, the Admiralty ordered Ark Royal, HMS Hood and their four escorting destroyers to return to Gibraltar. At 2015 hours, the Admiralty ordered HMS Dorsetshire to cease shadowing the Richelieu and to search for her missing Walrus. On receipt of these orders she parted company with the Richelieu and Fleuret at 2300/26, being then some 70 nautical miles from Dakar. HMS Dorsetshire then proceeded to the north-north-eastward at 23 knots.
At first light on the 27th, HMS Hermes, then some 30 nautical miles to the southward, flew off seven aircraft to assist in the search. It was however HMS Dorsetshire herself which eventually found and recovered her aircraft at 1107/27. Meanwhile the Richelieu had arrived off Dakar at 0900/27 but did not enter the port. Shortly afterwards she made off the the north yet again. HMS Hermes then steered to the northward to be in a position to intercept if needed. Nothing was seen of the Richelieu until she was again located off Dakar at 0500/28. HMS Hermes, by that time about 400 nautical miles north of Dakar, was ordered to proceed southwards and return to Dakar.
The Commander-in-Chief, South Atlantic, at Dakar 26-29 June 1940.
While these movements were going on at sea, the position at Dakar was steadily deteriorating. At about 1830/26, the Commander-in-Chief had reported to the Admiralty that the French Admiral at Dakar had informed him, on Admiral Darlan’s instructions, that the presence of British warships at Dakar was in contrary to the terms of the Franco-German armistice. At 1700/26 (zone -1) however, the Admiralty had signalled to the Commander-in-Chief that, as the French codes were compromised, that French authorities could no longer be sure that orders came from Admiral Darlan but Admiral Plancon refused to question the authenticity of any signal he received. During the night the appointment of the British Liaison Officer at Dakar was terminated.
At 0500/27 the Richelieu was seen approaching Dakar, but 25 minutes later she turned to seaward again and the Commander-in-Chief ordered a Walrus aircraft from HMS Albatros to shadow her. That afternoon he informed the Admiralty that the Richelieu had put to sea to escort five French armed merchant cruisers [according to another source these were the armed merchant cruisers (four in number and not five) El D’Jezair, El Kantara, El Mansour, Ville d’Oran and the large destroyers Milan and Epervier which came from Brest] to Dakar. The Admiralty was clearly anxious that the Richelieu should not escape and at 0021/28, they ordered Vice-Admiral Wells with HMS Ark Royal, HMS Hood escorted by four destroyers (HMS Faulknor, HMS Fearless, HMS Foxhound and HMS Vidette (Cdr.(Retd.) D.R. Brocklebank, RN) to proceed to the Canaries to intercept her if she continued to steam to the northward. These ships (with HMS Escapade instead of HMS Vidette) had only returned to Gibraltar late the previous evening from their first sortie to intercept the Richelieu. Now they left again around 0600/28 but were quickly ordered to return to Gibraltar and were back in port around noon.
Around 0500/28 HMS Dorsetshire, proceeding back towards Dakar after having picked up her lost aircraft encountered the Richelieu about 10 nautical miles north of Dakar. Admiral Wells was then ordered by the Admiralty to return to Gibraltar. The rapid deterioration of the situation in West Africa is clearly shown in a series of signals which passed between the Commander-in-Chief South Atlantic and the Admiralty on 28 June. At 1100 hours, the Commander-in-Chief signalled that the French had refused HMS Dorsetshire permission to enter Dakar and that she was therefore proceeding to Freetown with all dispatch to fuel and return to the Dakar area as soon as possible. HMS Dorsetshire arrived at Freetown at 0545/29. At 1415/28 the Commander-in-Chief informed the Admiralty that the French Admiral at Dakar had issued orders to prevent H.M. ships from communicating with, or receiving stores, from the shore. In reply he had told the French Admiral that HMS Hermes would enter Dakar on the 29th to embark aircraft stores and fuel, and that he himself would sail from there in HMS Albatros after seeing the commanding officer of HMS Hermes. At 1515/28 the Commander-in-Chief informed the Admiralty of the steps he would take in case the Richelieu would proceed to sea again. The Admiralty then issued orders that Dakar was to be watched by an 8” cruiser within sight of the French port by dayand within three miles by night. HMS Hermes was to remain off Dakar until relieved by HMS Dorsetshire after this ship had returned from fueling at Freetown.
HMS Hermes arrived at Dakar at 0900/29. During the day she embarked Fleet Air Arm personnel and stores which had been landed there earlier. She then completed with fuel and sailed at 1800/29. She then patrolled off Dakar until she was relieved by HMS Dorsetshire at 1800/30. The Commander-in-Chief had sailed from Dakar in HMS Albatros at 1030/29. He arrived at Freetown at 1800/30 and transferred his flag to the accommodation ship Edinburgh Castle.
Deterioration of Franco-British relations, 1 – 3 July 1940.
The first few days of July saw a swift deterioration of Franco-British relations everywhere. The paramount importance of keeping the French fleet out of the hands of the enemy forced the British Government to take steps. According to the armistice terms the French fleet had to assemble at ports under German or Italian control and be demilitarized. To the Government it was clear that this would mean that the French ships would be brought into action against us. The Government therefore decided to offer the French naval commanders the following options; - to continue the fight against the Axis, to completely immobilization in certain ports or to demilitarize or sink their ships.
Already a powerful squadron, known as ‘Force H’ had been assembled at Gibraltar, in order to fill the strategic naval vacuum in the Western Mediterranean caused by the defection of the French fleet, and on 30 June Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville hoisted his flag in HMS Hood. His first task was to present the British alternatives to the Admiral commanding the French ships at Oran, failing the acceptance of one of them, he was to use force.
To return to West-Africa, HMS Hermes reached Freetown with the Fleet Air Arm passengers and stores from Dakar on 2 July. Early that afternoon the Commander-in-Chief asked the Consul General at Dakar to obtain, if possible, assurance from the French Admiral there that if British warships were not allowed to use Dakar, enemy men-of-war should also be forbidden to use it. At 1915/2, the ex-British Liaison Officer, who had not yet left Dakar, reported the arrival of a British merchant ship which had not been diverted. He also reported that the French ships Katiola and Potiers might be sailing for Casablanca, escorted by armed merchant cruisers and destroyers. The Admiralty however ordered HMS Dorsetshire, which was maintaining the watch on Dakar, to take no action. At 2310/2 the Commander-in-Chief asked the Consul-General whether there was any chance of the Polish and Belgian bullion which was in the armed merchant cruiser Victor Schoelcher being transferred to either the Katiola or Potiers. He received no reply, and the continued silence of the British Consul led him to believe that the Consul’s signals were either being held up or mutilated.
Next forenoon, 3 July, the Commander-in-Chief informed the Admiralty that he intended to divert all British shipping in the South Atlantic from all French ports. Early that morning Vice-Admiral Somerville’s Force H had arrived off Oran. For the next ten hours strenuous efforts were made to persuade the French Admiral to accept one of the British alternatives, but without success. At 1554 hours (zone -1) Force H sadly opened fire on the ships of their former ally at Mers-el-Kebir, inflicting heavy damage and grievous loss of life. None could predict the result of these measures on the Franco-British relations, but it was sure they would not be improved.
During the afternoon of July 3rd the Commander-in-Chief, South Atlantic, on Admiralty instructions, directed all British Naval Control Officers and Consular Shipping Advisers to order all Biritsh and Allied ships to leave French ports as soon as possible, if necessary disregarding French instructions. All British warships in French ports were to remain at short notice and to prepared for every eventuality. The only warship in a French port within the limits of the South Atlantic Station at the time was HMS Bulolo, which was at Manoka in the Cameroons. At 2048 hours (B.S.T.) the Admiralty ordered all British warships in French ports to proceed to sea and at 2223 hours the Commander-in-Chief, South Atlantic ordered HMS Bulolo to proceed to Lagos, where she was to remain with HMS Dragon (Capt. R.G. Bowes-Lyon, MVO, RN) until further orders.
HMS Dorsetshire off Dakar, 3-7 July 1940.
Meanwhile HMS Dorsetshire had continued her watch off Dakar. On 3 July 1940 there were sixteen French warships and seven auxiliaries in the harbour. This number included the battleship Richelieu, the large destroyers Fleuret, Milan, Epervier, the armed merchant cruisers El D’Jezair, El Kantara, El Mansour, Ville d’Oran, Ville d’Alger, Victor Schoelcher and Charles Plumier, the colonial sloop Bougainville, the submarines Le Heros and Le Glorieux. At 0917/3 the Admiralty asked the Commander-in-Chief for the Richelieu’s berth at Dakar. HMS Dorsetshire informed him that at 1125/3 she was in position 045°, Cape Manuel lighthouse, 2.6 nautical miles, ships head 230°. Captain Martin seems to have drawn his own conclusions from this question and at 1350 hours he signalled to the the Commander-in-Chief his opinion that the Richelieu’s propellers could be severely damaged by depth charges dropped from a fast motor dinghy, and he asked permission to carry out such an attack about 2300 hours that night. Vice-Admiral Lyon replied that he had no instructions from the Admiralty to take offensive action against the Richelieu. At 1625 hours, however, the Admiralty ordered HMS Dorsetshire to get ready, but to await approval before actually carrying out an attack. This was followed at 1745 hours by a signal that the proposed attack was not approved as it was feared to be ineffective and for the time being the idea was ‘shelved’. [More on this idea later on.]
At 1904/3, the Admiralty ordered HMS Hermes to leave Freetown with all despatch to join HMS Dorsetshire off Dakar at 0500/5. At 2112/3 the Admiralty ordered HMS Dorsetshire to shadow the Richelieu if she sailed and proceeded northwards. If the vessel however made for the French West Indies, the Dorsetshire was to make every effort to destroy her by torpedo attack, and, if that failed, by ramming [ !!! ]. Late that evening the French Government decreed that all British ships and aircraft were forbidden, under penalty of being fired upon without warning, to approach within 20 nautical miles of French territory at home or overseas. Just before midnight the Admiralty gave orders that HMAS Australia (Capt. R.R. Stewart, RN), after refueling at Freetown, was to join HMS Dorsetshire off Dakar. At 0926/4, the Commander-in-Chief, South Atlantic ordered HMS Hermes and HMAS Australia to rendez-vous with HMS Dorsetshire 21 nautical miles from Dakar instead of the 15 nautical miles previously arranged and at 1037 hours he informed all three ships that as the French Air Force and submarines had orders to attack British ships off Casablanca and Dakar. He therefore issued orders that French aircraft and submarines were to be attacked and destroyed on sight. During that afternoon the Prime Minister announced in the House of Commons that, as an alternative to the German demands, French warships might proceed to the West Indies. At 2041 hours the Commander-in-Chief, South Atlantic asked whether, in view of this, the Admiralty intended that the Richelieu should be attacked if she was to proceed to the West Indies. Before this message was received, a signal was sent at 2050 hours cancelling the orders for the Richelieu’s destruction and at about midnight the Admiralty directed that she should be shadowed only.
Early on the 5th the Consul-General at Dakar reported that the merchant vessel Argyll with Commander J. Rushbrooke, RN, the ex-British Naval Liaison Officer, Dakar and his staff onboard, had, in accordance with instructions from the French authorities left Dakar the previous day but that she was recalled on reaching the outer boom, an order which had led the Consul-General to make a protest. Soon after midnight 4/5 July orders were received from the Admiralty that the sloop HMS Milford (Capt. R.J. Shaw, MBE, RN) should be sent to join the patrol off Dakar to provide A/S protection. She left Freetown for Dakar at 1000/5.
At 0723/5, in view of the French order forbidding the approach of British vessels and aircraft within 20 nautical miles from French territory at home and overseas, the Commander-in-Chief ordered his ships off Dakar not to approach within 20 nautical miles of the shore and replied in the affirmative when HMS Dorsetshire asked whether this rule also applied by night. During the afternoon he informed his command that French warships was orders not to attack the British unless they were within these 20 nautical miles. He later added that also submarines had the same orders.
At 1853/5, the Commander-in-Chief ordered HMS Dorsetshire, HMAS Australia, HMS Hermes and HMS Milford not to attack French submarines outside the 20 mile zone unless they were obviously hostile. An Admiralty report then came in the the Richelieu was reported to have put to sea but HMS Dorsetshire quickly contradicted that report.
Dispositions off Dakar at 0300 on 7 July 1940.
At 0300/7, two of the British warships off Dakar which were under the command of Capt. Martin (being the senior officer) were patrolling of Dakar (HMS Dorsetshire and HMS Hermes). The third ship (HMAS Australia) was patrolling about 35 to 40 nautical miles further to the north. The fourth ship HMS Milford was approaching Dakar from the south. At 0307 hours a signal from the Admiralty was received which gave a completely different complexion to their operations.
More on this in the event for 7 July 1940, The attack on the Richelieu.. This event can be found on the pages of the ships involved; HMS Hermes, HMS Dorsetshire, HMAS Australia and HMS Milford. (36)
17 Jun 1940
HMS Diana (Lt.Cdr. E.G. Le Geyt, RN) and HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. G.H. Peters, RN) departed Scapa Flow at 0130A/17 for the Clyde. They were however recalled.
At 1545A/17 the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) departed Scapa Flow for the Clyde. She was escorted by the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Fearless (Cdr. K.L. Harkness, RN) and HMS Escapade (Cdr. H.R. Graham, RN). They were joined At 2115A/17 by HMS Foxhound. HMS Diana returned to Scapa Flow.
18 Jun 1940
Around 0400A/18, the battlecruiser HMS Hood (Capt. I.G. Glennie, RN) departed the Clyde for Gibraltar. She was escorted by the Canadian destroyers HMCS Fraser (Cdr. W.B. Creery, RCN), HMCS Restigouche (Lt.Cdr. H.N. Lay, RN), HMCS St. Laurent (Lt.Cdr. H.G. De Wolf, RCN), HMCS Skeena (Lt.Cdr. J.C. Hibbard, RCN) and the British destroyer HMS Wanderer (Cdr. J.H. Ruck-Keene, RN). HMS Wanderer was however replaced by the escort destroyer HMS Atherstone (Cdr. H.W.S. Browning, RN) shortly after sailing.
Around 1500A/18, rendez-vous was made with the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Fearless (Cdr. K.L. Harkness, RN) and HMS Escapade (Cdr. H.R. Graham, RN) which had departed Scapa Flow for the Clyde the previous day but while on passage through the Minches had been ordered to make rendezvous with HMS Hood to proceed direct to Gibraltar. The destroyer HMS Foxhound had also been with HMS Ark Royal but she had been detached at 0520A/18 to fuel at Milford Haven and then rejoin.
The destroyers that had been escorting HMS Hood were detached at 1625A/18.
In the late afternoon and evening of the 20th, HMS Fearless, HMS Faulknor and then HMS Escapade fuelled from HMS Hood.
At 1830A/21, HMS Foxhound finally was able to join.
23 Jun 1940
Around 0815A/23, HMS Hood (Capt. I.G. Glennie, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Fearless (Cdr. K.L. Harkness, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. G.H. Peters, RN) and HMS Escapade (Cdr. H.R. Graham, RN) arrived at Gibraltar.
25 Jun 1940
HMS Hood (Capt. I.G. Glennie, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Fearless (Cdr. K.L. Harkness, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. G.H. Peters, RN) and HMS Escapade (Cdr. H.R. Graham, RN) departed Gibraltar for operations.
[See the event ' Dakar, the French battleship Richelieu and the fall of France ' for 16 June 1940 for more information.]
27 Jun 1940
HMS Hood (Capt. I.G. Glennie, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Fearless (Cdr. K.L. Harkness, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. G.H. Peters, RN) and HMS Escapade (Cdr. H.R. Graham, RN) returned to Gibraltar.
28 Jun 1940
HMS Hood (Capt. I.G. Glennie, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Fearless (Cdr. K.L. Harkness, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. G.H. Peters, RN) and HMS Vidette (Lt. E.N. Walmsley, RN) departed Gibraltar for operations. They returned later the same day.
[See the event ' Dakar, the French battleship Richelieu and the fall of France ' for 16 June 1940 for more information.]
2 Jul 1940
Operations Catapult and Lever.
Operations agains the French Fleet at Mers-el-Kebir.
Timespan: 2 to 6 July 1940.
Polical situation June / July 1940.
The situation created by the collapse of French military resistance in June 1940 brought to the forefront the question of the disposal of the powerful modern French Fleet. With France eliminated from the contest, Great Britain would stand virtually alone, separated only by the English Channel from the triumphant German Army and threatened by the largest Air Force in the World. On her command of the sea depended her very existence. Suddenly to lose the co-operation of the French Fleet would be a severe blow, but it was a matter of life and death that it should not be added to those of her opponents and used against her.
In circumstances of increasing chaos the marsh of events was swift. On 11 June 1940 the French Prime Minister and the French Government retired to Tours, and three days later moved on to Bordeaux. On the same day the Germans entered Paris.
It was the French Prime Minister who had declared ‘We shall fight before Paris, we shall fight behind Paris. We shall shut ourselves up in one of our provinces and if they drive us out we shall go to north Africa and, if need be, to our American possessions. It was the French Prime Minister who asked the British Government on 16 June to release France from her treaty obligations. The Cabinet refused to do so asked for French warships to be despatched to British ports and offered an Act of Union. The offer fell on deaf ears. The French Prime Minister (Mr. M Reynaud) was no longer in power. He had been displaced in the night of 16/17 June by a defeatist group headed by Marshal Pétain, General Weygand, Admiral Darlan, Mr. Laval, Mr. Baudouin and other politicians.
Negotiations with Germany were opened on 17 June, when Marshal Pétain, in a letter to Hitler, asked if he was ready to sign with him, as between soldiers after the fight and in honour, terms that would put an end to the hostilities.
The British Government, receiving the news ‘with grief and amazement’ refused to release France from her treaty obligations, and announced its intention to continue the fight. Every effort was made to persuade the French Government to order the French Fleet to British ports, or to sink itself before armistice terms were discussed. But the situation was very confusing and no guarantees could be obtained. At the same time it was determined that, if all other courses failed, action should be taken to prevent any important French ships falling into the enemy’s hands. British offers of assistance to the French authorities in arranging for an evacuation from Marseilles to North African ports were declined.
The terms of the armistice signed by France were not made public until 25 June, the day on which the hostilities ended. The clauses effecting the French sea forces stated that the French Fleet was to be assembled in ports under German or Italian control and demilitarized.
It seemed clear to the British Government that in these clauses the enemy had merely provided themselves with a pretext for keeping the whole French Fleet in a state of readiness for action against us when an opportunity accurred. The British Government had evidence, too, that from 20 June the Germans were in possession of, and were using, French naval codes.
The first reactions to the armistice terms of the French naval, military and colonial authorities indicated a determination to fight on. This attitude, however, in face of instructions was however soon abandoned. The British Government consequently decided to offer the French Naval Commanders the following alternatives: to continue the fight; complete immobilisation in certain ports; to demilitarise or sink their ships. By no other means could the French Fleet be prevented from falling into the hands of the enemy.
Reports received from various sources indicated that, the senior French Naval Officers had elected to obey their central government, most junior Officers desired to continue the struggle. The men, divided in their loyalties and lacking firm leadership, were chiefly influenced by the fear of reprisals to their families.
The French Fleet at Oran, coast defences, etc.
The bulk of the French Fleet was distributed between Toulon and the French North African ports in the Western Mediterranean. A squadron of one battleship, four cruisers and a few destroyers was at Alexandria; operating with Admiral Sir Andrew Cunningham’s Mediterranean Fleet. The new battleships Richelieu and Jean Bart which had been completing at Brest had sailed a few days before respectively for Dakar and Casablanca. But by far the most important concentration of French warships was at Mers-el-Kebir, under Vice-Admiral Gensoul.
The shore defences of Mers-el-Kebir cosisted of a battery of two 7.5” guns on top of a hill to the west of the harbour. The harbour entrance was protected by an anti-torpedo boom and anti-submarine booms. A mine net stretched from Cape Falcon to a point one mile north of Cape Canastel. The breakwater (30 feet high) and Fort Mers-el-Kebir (100 feet high) afforded a certain amount of protection to the side armour of the ships inside the harbour from short range gunfire. Also in the vicinity of Oran there was a battery of two 9.2” guns at Cape Canastel.
Assembly of ‘Force H’ at Gibraltar.
In order to fill the Allied vacuum in the Western Mediterranean, caused by the defection of the French Fleet, the Admiralty decided to assemble a strong force, to be known as Force H, at Gibraltar. On 27 June Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville was ordered to hoist his flag in the light cruiser HMS Aretusa and to proceed there to take command of ‘Force H’. His immediate task was to secure the transfer, surrender or destruction of the French ships at Mers-el-Kebir and Oran, so as to ensure that they could not fall into German or Italian hands. It was hoped that the employment of force would be unnecessary, but every preparation to use it was to be made. This was explained to him in an interview with the First Lord and the First Sea Lord.
The Vice-Admiral sailed from Spithead in HMS Arethusa on 28 June. During his passage to Gibraltar he was in constant communication with the Admiralty. On the 29th he received Admiralty message 0435/29, stating certain alternatives which it was proposed to offer the French. (a) to steam their ships to a British port. (b) to sink their ships. (c) to have their ships sunk by gunfire. Later in the day the Admiralty directed the submarines HMS Pandora and HMS Proteus to patrol off Algiers and Oran respectively in order to report any French movements, but not to attack. On the 30th they ordered the Vice-Admiral, Aircraft carriers (Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells) to establish a destroyer patrol 30 nautical miles to the west of Oran and that should the French battlecruisers Dunkerque and Strasbourg proceed to the westward, they were to be captured and taken to the United Kingdom.
Vice-Admiral Somerville arrived at Gibraltar on 30 June where he transferred his flag to the battlecruiser HMS Hood. He lost no time with discussing the matter with the Vice-Admiral North Atlantic (Vice-Admiral Sir D.B.N. North) and later with Vice-Admiral Wells, his senior officers and with two officers who had recently been attached to the French as liaison officers. All were strongly opposed to the use of force, believing that this would alienate the French completely and turn them from a defeated ally into an active enemy. So impressed was Vice-Admiral Somerville by these views that he communicated them to the Admiralty at 1230 hours on 1 July together with certain alternative proposals. He received a reply that evening that it was the firm intention of His Majesty’s Government that if the French would not accept (any of) the alternatives then being sent to him, their ships must be destroyed.
Meanwhile a plan of operation had been drawn up, and the Admiralty was informed that the earliest date for it’s execution would be A.M. 3 July. The operation was named ‘Catapult’.
Admiralty instructions to Vice-Admiral Somerville.
At 0426, 2 July, Vice-Admiral Somerville received his final instructions from the Admiralty in dealing with the French Fleet at Mers-el-Keber. These may be summarised as follows: A) Four alternatives were to be offered to the French: (1) To sail their ships to a British port to continue the fight with us. (2) To sail their ships with reduced crews to a British port from which the crews would be repatriated whenever desired. (3) To sail their ships with reduced crews to a French port in the West Indies. After arrival there they would either be demilitarised to our satisfaction, if so desired or to be entrusted to U.S.A. jurisdiction for the remainder of the war. The crews would be repatriated. (4) To sink their ships.
In case of alternatives 1 or 2 being adopted the ships were to be restrored to France at the conclusion of the war, or full ompensation would be paid if they were damaged meanwhile. If the French Admiral accepted alternative 2 but asked that the ships would not be used during the war, we would accept this condition for so long Germany and Italy observed the armistice terms. We particularly did not want to raise this point ourselves.
B) If the French Admiral refused to observe all the above alternatives and suggested demilitarisation of his ships to our satisfaction at their present berths acceptance of this further alternative was authorised, provided that the Flag Officer, ‘Force H’ was satisfied that the measures for demilitarization could be carried out under his supervision within six hours, so as to prevent the ships being brought to service for at least one year, even at a fully equipped dockyard port.
C) If none of the alternatives were accepted by the French, the Flag Officer ‘Force H’ was to endeavour to destroy the ships in Mers-el-Kebir, particularly the Dunkerque and Strasbourg, using all means at his disposal. Ships at Oran should also be destroyed, if this did not entail any considerable loss of civilian life.
As it was undesirable to have to deal with the French Fleet at sea, the Flag Officer ‘Force H’ was instructed to arrive in the vicinity of Oran at his selected time, to send emissaries ashore, and to take such action as he considered fit in the period before the given time limit expired.
A further signal timed 0108 contained the terms in which these demands were to delivered to Admiral Gensoul.
Plan for ‘Operation Catapult’.
A meeting of Flag and Commanding Officers was held during the forenoon of 2nd July, at which the orders for ‘Operation Catapult’ were explained and discussed.
Capt. C.S. Holland, of the Ark Royal, who had recently been Naval Attaché at Paris, had been selected to act as emissary assisted by Lt.Cdr’s A.Y. Spearman and G.P.S. Davies, lately employed as liaison officers. The destroyer HMS Foxhound was detailed to embark these officers. Captain Holland was instructed, if necessity arose, to question the French concerning their plan for demilitarisation at two hours’ notice which had been mentioned to Vice-Admiral North at Gibraltar, and to enquire whether the proposed measures would render the ships ‘ineffective for service during 12 months, even with dockyard assistance.’
The intention of the Flag Officer ‘Force H’, if he was obliged to use force was: a) To destroy morale, damage AA equipment and induce the French crews to abandon their ships by means of long range gunfire with the main armaments of his capital ships, assisted by aircraft spotting. b) Bombing by the aircraft of HMS Ark Royal with the same object. c) Torpedo attack by aircraft from HMS Ark Royal in order to cripple those ships exposed to torpedo fire. d) Sinking of ships still afloat by demolition parties from destroyers. e) The cruisers were to engage light craft or shore batteries as ordered.
The orders drawn up did not propose the laying of magnetic mines by aircraft from HMS Ark Royal, which was held to interference with the first two alternatives offered to the French but if needed this measure could be resorted to.
Attempts to Communicate with Admiral Gensoul.
At 1500 hours, 2nd July, destroyers sailed to carry out an A/S sweep in Gibraltar Bay and approaches and ‘Force H’ cleared harbour at 1700A/2.
The composition of ‘Force H’ was as follows; battlecruiser HMS Hood (Capt. I.G. Glennie, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), battleships HMS Valiant (Capt. H.B. Rawlings, OBE, RN), HMS Resolution (Capt. O. Bevir, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN) [as Capt. Holland had been embarked on the destroyer HMS Foxhound, it was probably Cdr. R.M.T. Taylor, RN who was temporary in command], light cruisers HMS Arethusa (Capt. Q.D. Graham, RN), HMS Enterprise (Capt. J.C. Annesley, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Fearless (Cdr. K.L. Harkness, RN), HMS Foresight (Lt.Cdr. G.T. Lambert, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. G.H. Peters, RN), HMS Escort (Lt.Cdr. J. Bostock, RN), HMS Active (Lt.Cdr. E.C.L. Turner, RN), HMS Keppel (Lt.Cdr.(Emgy.) E.G. Heywood-Lonsdale, RN), HMS Wrestler (Lt.Cdr. E.N.V. Currey, RN), HMS Vortigern (Lt.Cdr. R.S. Howlett, RN) and HMS Vidette (Cdr.(Retd.) D.R. Brocklebank, RN).
The submarines HMS Pandora (Lt.Cdr. J.W. Linton, RN) and HMS Proteus (Lt.Cdr. R.T. Gordon-Duff, RN) were then nearing their patrol areas.
The operations orders referred to the possibility of interference but the only evidence of them being even remotely on the alert was that at 2247A/2 in position 36°12’N, 03°05’W HMS Vortigern reported a torpedo exploding ahead of her. This was indeed an attack by an Italian submarine, the Marconi. HMS Vortigern and HMS Vidette hunted the submarine for a little over an hour but without success.
At 0300A/3, HMS Foxhound was sent ahead and arrived of Cape Falcon at 0545A/3. Communication was established with the Port War Signal Station and at 0620 hours the following message was passed. ‘To Admiral Gensoul, The British Admiralty had sent Captain Holland to confer with you. The British Navy hopes that their proposals will enable you and the valiant and glorious French Navy to be by our side. In these circumstances your ships would remain yours and no one need to have anxiety for the future. A British fleet is at sea off Oran waiting to welcome you.’
Permission for HMS Foxhound to enter the port of Mers-el-Kebir was received at 0742 hours. She anchored at 0805A/3, outside the net defence, in a position 1.6 nautical miles, 115° from Mers-el-Kebir lighthouse. Five minutes later the French Flag Lieutenant came alongside and informed Capt. Holland that Admiral Gensoul was unable to see him, but would sent his Chief of Staff.
Admiral’s Gensoul refusal to confer with Capt. Holland was emphasized when at 0847 hours HMS Foxhound received a signal from him requisting her to sail immediately. She weighted accordingly, leaving Capt. Holland and Lt.Cdr’s Spearman and Davies behind in her motor boat. Meeting the French Flag Lieutenant off the entrance, Capt. Holland handed him the written British proposals to be given to Admiral Gensoul, saying that he would await a reply. It was around 0935 hours when they reached Admiral Gensoul. The French ships were reported by air reconnaissance to be raising steam. At 1000 hours the Flag Lieutenant returned and handed over a written reply from Admiral Gensoul. It stated the same that had earlier been said to Vice-Admiral North that the French Fleet would never be surrendered and that force would be met by force.
Then followed a further exchange of written statements and a discussion with the French Chief of Staff who came out at 1109 hours. As it was evident that Admiral Gensoul was resolved not to see Capt. Holland, the latter returned on board HMS Foxhound to communicate with Vice-Admiral Somerville.
Meanwhile ‘Force H’ had arrived off Mers-el-Kebir at 0910A/3 and by means of projectors transferred the following message (in French) ‘To Admiral Gensoul from Admiral Somerville. We hope most sincerely that the proposals will be acceptable and hat we shall ave you by our side.’
’Force H’ then proceeded to steam to and from across the bay while HMS Ark Royal, with a destroyer screen, was acting independently for flying off aircraft.
At 1140A/3 Lt.Cdr. Spearman was sent in with a message from the Flag Officer ‘Force H’ that the French ships would not be allowed to leave harbour unless the terms were accepted. It was at this time that Capt. Holland signalled to the French Admiral, from HMS Foxhound, information of the action taken by Admiral Godfroy at Alexandria to demilitarise his ships. HMS Foxhound then proceeded outside the outer boom to a position inside visual signalling range.
British delegate received and terms refused.
Admiral Gensoul’s reply reached HMS Hood at 1227A/3 and Vice-Admiral Somerville considering that it was unsatisfactory and indicated an intention to put to sea and fight, gave the order to mine the harbour entrance. Five mines were accordingly laid by aircraft inside the booms guarding the entrance to Mers-el-Kebir harbour.
It was Vice-Admiral Somerville’s first intention to open fire at 1330 hours but the time for a final answer was extended to 1500 hours on the strength of air reports that there was no immediate indication of the French ships proceeding to sea. In order to ensure the least possible delay, a signal was passed to Admiral Gensoul requisting him to hoist a large square flag at the masthead if he accepted the British terms.
These measures appeared to be effective, for at 1440 hours Admiral Gensoul signalled that he would receive a delegate for honourable discussion. This message forstalled, only by a few minutes, the despatch of a signal from Vice-Admiral Somerville notifying that he would proceed to destroy the French ships at 1530 hours. Despite Vice-Admiral Somerville’s suspicion that the French Admiral was temporizing, he authorised Capt. Holland to proceed, and the latter, in the motor boat from HMS Foxhound and accompanied by Lt.Cdr. Davies, reached the Dunkerque at 1615A/3.
Captain Holland’s reception on board the Dunkerque was coldly formal. Admiral Gensoul was extremely indignant and angry. A lengthy discussion ensued, in which he emphasised that the use of force would range the whole French Navy against the British, and that in effect he rejected all conditions proposed stating that he would only obey orders from his Government and Admiral Darlan. It was evident to Captain Holland that it was only during this discussion that Admiral Gensoul began to realise that force might actually be used.
Whilst the discussion was proceeding an Admiralty message was received at 1646 hours by HMS Hood instructing Vice-Admiral Somerville to settle matters quickly or he would have reinforcements to deal with. A signal accordingly passed by visual and wireless at 1715 hours to Admiral Gensoul informing him that if one of the alternatives was not accepted by 1730 hours his ships would be sunk. At the same time action stations was sounded in the ships of the British Fleet.
A summary of Admiral Gensoul’s final statement was passed by signal from Capt. Holland to Vice-Admiral Somerville. It read ‘Admiral Gensoul says crews being reduced and if threatened by enemy would go Martinique or U.S.A. but this is not quite our proposition. Can get no nearer.’
This signal was received on board HMS Hood at 1729 hours. As it did not comply with any of the alternatives laid down, the air striking force from HMS Ark Royal was ordered to fly off and the battleships stood in towards the coast.
Captain Holland left the Dunkerque at 1725 hours. As he left ‘Action stations’ was being sounded in the French ships, all of which were by that time in an advanced state of readiness for sea, with tugs standing by and control positions manned.
Meanwhile signs of movement of French ships in adjacent harbour of Oran having been reported by air reconnaissance, two mines were laid in it’s entrance, and the destroyer HMS Wrestler was ordered to relieve HMS Vortigern on patrol there.
Action against the French ships at Mers-el-Kebir.
At 1754A/3 fire was opened at 17500 yards. Aircraft were spotting. The line of fire was from the north-west, so that fire from the French ships was blanked to some extent by Mers-el-Kebir Fort, and risk of damage to civilian life and property reduced.
The four French capital ships and aviation transport were moored stern-on to the mole in the following order, from north-west to south-east; Dunkerque, Provence, Strasbourg, Bretagne and Commandant Teste while the remaining ships were moored on the west side of the harbour. The destroyers, according to an aircraft report, were underway inside the booms.
The effect of the opening salvoes was observed from the Foxhound’s motor boat. The first salvo fell short. The second hit the breakwater, sending large fragments of concrete flying through the air, which probably caused casualties amongst the crews of the ships. The third salvo fell amongst the ships and the battleship Bretagne blew up, a column of orange flame leaping into the sky, followed by an immense column of smoke several hundred feet high. Another smaller explosion indicated that a destroyer had blown up (Mogador). By this time the harbour was shrouded in smoke from explosions and fires. Direct spotting was almost impossible and air spotting most difficult. The French shore batteries and Dunkerque and Strasbourg opened fire about a minute after the first British salvo. The shore batteries were promptly engaged by HMS Arethusa, the older guns of HMS Enterprise being outranged. Heavy projectiles were soon falling near the British battleships as the French fire, at first very short, began to improve in accuracy. The observers in Foxhound’s motor boat recorded several direct hits on the French ships, another explosion with a sheet of orange flame from a battleship, and a direct hit on a large destroyer as she was leaving harbour.
None of the French projectiles hit, though a number of them fell close to – and in some cases straddled – the British ships. Some splinters caused some minor superficial damage in HMS Hood and injured one officer and a rating. After thirty-six salvoes of 15” the fire of the French ships died down, but hat of the forts became increasingly accurate. To avoid damage from the latter, course was altered 180° to port together and the ships were ordered to make smoke.
At 1803A/3 as the French ships were no longer firing, ‘cease fire’ was ordered. Vice-Admiral Somerville considered that this would give them an opportunity to abandon their vessels and as the entrance to the harbour had been mined they would make no attempts to put to sea. Repeated signals were being receive in HMS Hood from the shore visual and wireless stations requisting fire to be discontinued, to which the reply was made: ‘unless I see your ships sinking, I shall open fire again’. Vice-Admiral Somerville then proceeded to the westward to take up a position from which, if necessary, the bombardment could be renewed without causing casualties to men in boats or exposing the British ships to unduly fire from the forts. He also deemed it prudent to stand out to sea to avoid the possibility of a surprise attack by aircraft under cover of the clouds of smoke then laying between his ships and the shore.
When the pall of smoke over Mers-el-Kebir harbour cleared away, the scene viewed from HMS Foxhound’s boat showed the Dunkerque, which had slipped from the mole, lying stopped in the harbour. The Provence appeared to have been hit, fires were burning in the Commandant Teste, while nothing could be seen of the Bretagne. Clear of the harbour and gathering speed fast were the Strasbourg and two destroyers (thought to be Mogador-class), steering eastward close under the land.
Chase of, and F.A.A. attacks on, the Strasbourg.
Vice-Admiral Somerville received an air report at 1820A/3 that one of the Dunkerque-class battlecruisers had put to sea and was steering east. This report was confirmed 10 minutes later. An air striking force of six Swordfish aircraft of no. 818 Squadron armed with 250-lb. bombs and escorted by Skua’s was flow off by HMS Ark Royal at 1825 hours to attack the ships in Mers-el-Kebir but they were then diverted to attack the fleeing ship which was accompanied by eight destroyers. ‘Force H’ altered course to the eastward at 1838 hours and commenced a chase.
During this period, HMS Wrestler, which was patrolling of Oran, was heavily engaged by shore batteries. At least 100 shells fell near her before she withdrew in accordance with orders.
At 1843 hours the cruisers and destroyers with HMS Hood were ordered to proceed ahead. Both battleships following behind at their best speed without a destroyer screen. Every ships worked up to full speed.
The bombing attack on the Strasbourg was well pressed home, and, although it was met with heavy opposition, was believed to have obtained at least one hit. Two Swordfish aircraft failed to return, but the crews were picked up by HMS Wrestler.
At 1914A/3 HMS Wrestler picked up Capt. Holland and Lt.Cdr.’s Spearman, Davies and the crew from the motor boat of HMS Foxhound. The motor boat was then abandoned.
Between 1933 and 1945 hours a French destroyer, steering west close inshore, was engaged at ranges of 12000 and 18000 yards by the Arethusa and Enterprise. Later the Hood and Valiant fired a few 15” salvoes at her. At least three hits were observed before the destroyer turned back to Oran. The British ships were obliged to alter course to avoid torpedoes.
at 1950A/3 six Swordfish aircraft of no. 820 Squadron, armed with torpedoes were flown off from HMS Ark Royal, with orders to press home their attack, making use of the failing light. They attacked at 2055 hours, twenty minutes after sunset. Approaching from the land, with their target silhouetted against the afterglow, they were able to deliver the attack unseen, only the last two attacking aircraft encountered some machine gun fire from the screening destroyers. The observation of results was rendered difficult by darkness and funnel smoke, but an explosion was seen under the Strasbourg’s stern and there was some evidence of a hit amidships. All the aircraft returned safely, through one came under machine gun fire from a group of destroyers seven miles astern of the target.
Chase abandoned and return to Gibraltar.
Meanwhile Vice-Admiral Somerville had abandoned the chase about half-an-hour before the torpedo attack took place. At 2020A/3 the Strasbourg with her attendant destroyers, was some 25 nautical miles ahead of him. By that time the French Algiers force with several 8” and 6” cruisers was known to be at sea and was calculated to be able to join the Strasbourg shortly after 2100 hours.
Vice-Admiral Somerville considered that a night contact and engagement was not justified. His destroyers had not had recent experience of shadowing, and the French would be numerically superior. Besides that there were more reasons to disengage.
Accordingly at 2025A/3 course was altered to the westwards and the Admiralty was informed that ‘Force H’ would remain to the west of Oran during the night with the intention to carry out air attacks on the ships at Mers-el-Kebir at dawn.
Between 1930 and 2100 hours French reconnaissance and bomber aircraft were fired on. These dropped a few bombs which all fell wide except for four bombs which fell close to HMS Wrestler. The attacks were not pressed home.
At 2150A/3 the submarine HMS Proteus, which had been ordered to keep clear of ‘Force H’ to the northward during the day, was ordered to patrol north of 35°55’N off Cape de l’Aiguille or Abuja Point (15 nautical miles east of Oran). At the same time she and HMS Pandora (off Algiers) were ordered to sink any French ships encountered. The latter, which had reported six cruisers and four destroyers making to the westward at 1745A/3, was warned that the Strasbourg might arrive off Algiers at 2300A/3.
During the night of 3 / 4 July. ‘Force H’ steered to reach position 36°12’N, 01°48‘W (about 60 nautical miles west-north-west of Mers-el-Kebir) at 0430A/4. It was intended to then fly off 12 Swordfish and 9 Skua aircraft to finish off the ships remaining in the harbour. Shortly after 0400A/4, however dense fog was encountered. This rendered flying impossible. As Vice-Admiral Somerville had received a message from Admiral Gensoul the evening before (2250A/3) stating that his ships were ‘hors de combat’ (‘out of action’) and that he had ordered the crews to evacuate them, Vice-Admiral Somerville decided to return to Gibraltar where ‘Force H’ arrived at 1900A/4.
Review of the operation by Vice-Admiral Somerville.
Reviewing the operation, Vice-Admiral Somerville remarked that it was clear he committed an error of judgement in proceeding so far to the westward after ceasing fire, and gave his reasons for his decision.
He considered that the mines laid in the harbour entrance were sufficient to prevent any French ships from leaving and also he was under the impression that the French crews were abandoning their ships due to the signals to ‘cease shelling’ and the heavy explosions observed. The though uppermost in his mind was how to complete his task without causing further loss of life to the very gallant but ill-advised Frenchmen, and without exposing his fleet to damage by the shore batteries or to submarine attack. He was also under the impression that a torpedo flight, to complete the destruction of ships afloat, had either taken off or was about to do so. In fact, however, the repeated postponement of the attack by gunfire had, unknown to him, seriously upset the Ark Royal’s flying on and off programme.
Vice-Admiral Somerville went into question whether the use of force might have been avoided had Admiral Gensoul agreed at once to receive Capt. Holland. The French Admiral’s final offer differed, unfortunately, from the British proposals in the single proviso that the disablement of ships would only be carried into effect if there was a danger of the French ships falling into enemy hands. Admiral Gensoul maintained that this danger was not imminent, whereas we maintained that it was. Had more time been available Capt. Holland might possibly have converted Admiral Gensoul to the British point of view, but when he made his offer it was already too late, for the discussion could not be continued beyond 1720 hours as French reinforcements were approaching and the ordered of His Majesty’s Government were explicit that a decision had to be reached before dark.
’ I consider ‘ wrote Vice-Admiral Somerville, ‘ that Capt. Holland carried out his most difficult task with the greatest tact, courage and perseverance. That he failed in his mission was not his fault – that he nearly succeeded is greatly to his credit ‘.
Preparations to renew the attack on the Dunkerque.
After the arrival of ‘Force H’ at Gibraltar the ships were immediately completed with fuel and ammunition so to be able to carry out operations against the French battleship Richelieu at Dakar if required.
Vice-Admiral Somerville informed the Admiralty that it was not possible from aircraft observation positively to assess the damage done to the battlecruiser Dunkerque, but that she was aground. Consequently the Admiralty directed that unless Vice-Admiral Somerville was certain that the Dunkerque could not be refloated and repaired in less then a year, she was to be subjected to further destruction by bombardment. This was to precede any operation against the Richelieu.
To put this decision into effect, plans were drawn up for another operation (Operation Lever), and the Admiralty was informed that a further bombardment would be carried out at 0900A/6 by ‘Force H’.
At 2005A/4 a signal was received from the Admiralty. It contained instructions with regard to the attitude to be adopted towards French warships, which stated that ‘ships must be prepared for attack, but should not fire the first shot’. After confirmation at 2045A/5 that this applied to the submarines operating of Oran and Algiers, the instructions were passed on to HMS Pandora and HMS Proteus. It was however already too late.
Proceeding by British submarines 4-6 July 1940.
When ‘Force H’ returned to Gibraltar on 4 July, the submarines HMS Pandora and HMS Proteus remained on patrol off the North African coast.
At 1126A/4, HMS Pandora, off Algiers, sighted three destroyers 065° about 1 nautical mile from the shore, but she was unable to get within range. Three and a half hours later (1458A/4), however, she sighted a French cruiser thought at that time to be of the La Galissoniere class. In fact it was the sloop Rigault de Genouilly. HMS Pandora turned immediately to a firing course and at 1507A/4 HMS Pandora fired four torpedoes from about 3800 yards. Two certain and one probable hits were obtained. The French ship stopped at once and soon after she was observed to be on fire. Closing in HMS Pandora saw that there was no chance this ship could be saved. At 1632A/4 she was seen to sink by the stern and a few seconds later an extremely heavy explosion occurred, probably her magines blowing up.
For some time from 1718A/4 HMS Pandora was hunted by aircraft and a destroyer or patrol craft, explosions of bombs and or death charges were heard at intervals.
The Admiralty expressed deep regret to the French Ambassy for the tragic happening, which was ascribed to the fact that on completion of the operation at Mers-el-Kebir on 3 July, the instructions that French ships were no longer to be attacked did not reach one submarine.
The seaplane carrier Commandant Teste was more fortunate. She was sighted by HMS Proteus at 1447A/4. The weather was foggy and before an attack could be started the French ship altered course to the eastward and was soon lost out of sight.
At 2200A/5, in obedience to instructions, HMS Proteus proceeded to patrol off Cape Khamis, about 65 nautical miles east of Oran. At 0243A/6 a signal from the Flag Officer Commanding North Atlantic (F.O.C.N.A.) was received that French ships were not to be attacked unless they attacked first.
The Commandant Teste was again sighted at 1734A/6. This time she was accompanied by two destroyers. Shorty afterwards HMS Proteus was ordered to proceed to Gibraltar.
HMS Pandora remained on patrol until July 7th when she too was ordered to proceed to Gibraltar.
F.A.A. attack on the Dunkerque, 6 July 1940.
Meanwhile ‘Force H’ sailed from Gibraltar at 2000A/5. They first proceeded westwards but turned to the east at 2200 hours and proceeded at 22 knots towards Oran.
’Force H’ was now made up of the battlecruiser HMS Hood, battleship HMS Valiant, aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal, light cruisers HMS Aurora, HMS Enterprise and the destroyers HMS Fearless, HMS Forester, HMS Foxhound, HMS Escort, HMS Active, HMS Velox (Cdr.(Retd.) J.C. Colvill, RN), HMS Vidette, HMS Vortigern and HMS Wrestler.
At 0250A/6, Vice-Admiral Somerville received a signal from the Admiralty which instructed him to cancel the bombardment. He was ordered to attack the Dunkerque from the air until she was sufficiently damaged.
In position 36°19’N, 02°23’W (about 90 nautical miles from Oran) at 0515A/6, the first striking force was flown off. The attack on the Dunkerque was made in three waves. The aircraft taking part were armed with torpedoes, carrying Duplex pistols, set for depth 12 feet, speed 27 knots.
The first wave of six Swordfish of no. 820 Squadron took of from the Ark Royal at 0515 hours. It made landfall at Habibas Island (about 20 nautical miles west of Mers-el-Kebir) and then shaped course at 7000 feet to keep 15 miles from the coast in order to gain up-sun position from the target as the sun rose. The attack achieved complete surprise, only one aircraftbeing fired upon during the get-away. As the first rays of the sun, rising above thick haze, struck the Dunkerque, the flight commenced a shallow dive in line ahead down the path of the sun. Coming in low over the breakwater, the aircraft attacked in succession. The first torpedo hit the Dunkerque amidships, glanced off without exploding and continued it’s run. It had probably been released inside pistol safety range. The second was thought at the time to have hit and exploded under the bridge on the starboard side. The third torpedo to have missed and exploded ashore and the remaining three torpedoes to have hit and exploded near ‘B’ turret. In the light of later information, it seems that no torpedo in this or subsequent attacks actually hit and damaged her. The first (as noticed by the British) glanced off without exploding. The second exploded underneath the stern of a trawler, the Terre Neuve, which – apparently unnoticed by the aircraft – was about 30 yards to starboard of the battlecruiser and sank the trawler. Of the remainder three torpedoes may have hit without exploding or run into shallow water, and one missed. One torpedo exploded ashore against a jetty.
The second attack was made by three Swordfish of no. 810 Squadron with a fighter escort of six Skua’s. They took off at 0545 hours. This sub-flight manoeuvred to a position up-sun at 2000 feet. At 0647 hours they tuned to attack in line astern. They came under heavy AA fire and had to take avoiding action during their approach and they made their attack from over the breakwater. The torpedo of the first aircraft was not released. The second and third torpedoes are thought to have hit the starboard side of the Dunkerque. During the get-away a large explosion was observed, smoke and spray rising in a great column over 600 feet high which was thought to have possibly been a magazine explosion in the Dunkerque. Actually, one torpedo hit the wreck of the Terre Neuve, detonating about 24 to 28 depth charges with which she was loaded, and thereby causing considerable damage to the Dunkerque. The other torpedo missed astern and exploded ashore. No enemy aircraft were encountered, but the 6” and 4” batteries from the east of Oran to Mers-el-Kebir Point kept up continuous fire throughout the attack.
The third wave was also made up of three Swordfish from no. 810 Squadron. These too were escorted by six Skua’s. They wre flown off at 0620 hours. They made landfall at a height of 4000 feet at 0650 hours over Cape Falcon. In line astern the sub-flight made a shallow dive with avoiding action as the Provence and shore batteries opened fire. This sub-flight then came in low over the town of Mers-el-Kebir for its attack. The first torpedo is reported to have struck the Dunkerque amidships on her port side but it did not explode. The second, which would have hit the ship, exploded under a tug close to her which blew the tug into the air. The third torpedo was dropped too close and did therefore not explode, although it appeared to be going to hit. While making its get-away this sub-flight was engaged by French fighter aircraft. The Skua escorts had many dog fights with the French fighters which easily out-manoeuvred our aircraft but they did not press home their attacks. One Skua, damaged in combat, had to make a forced landing on the water on its return. The crew was rescued by a destroyer. There were no casualties although several aircraft were damaged by gunfire.
Vice-Admiral Somerville was satisfied with the results as it appeared that the Dunkerque for sure would be out of action for more then a year. ‘Force H’, having completed its task returned to Gibraltar at 1830A/6. After temporary repairs the Dunkerque arrived at Toulon only on 19 February 1942 having made the passage under her own power escorted by five destroyers. (37)
8 Jul 1940
The battlecruiser HMS Hood (Capt. I.G. Glennie, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), battleships HMS Valiant (Capt. H.B. Rawlings, OBE, RN), HMS Resolution (Capt. O. Bevir, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), light cruisers HMS Arethusa (Capt. Q.D. Graham, RN), HMS Enterprise (Capt. J.C. Annesley, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Fearless (Cdr. K.L. Harkness, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. G.H. Peters, RN), HMS Escort (Lt.Cdr. J. Bostock, RN), HMS Active (Lt.Cdr. E.C.L. Turner, RN), HMS Douglas (Cdr.(Retd.) J.G. Crossley, RN), HMS Velox (Cdr.(Retd.) J.C. Colvill, RN), HMS Vortigern (Lt.Cdr. R.S. Howlett, RN) and HMS Wrestler (Lt.Cdr. E.N.V. Currey, RN) departed Gibraltar as a diversion during operation in the central and eastern Mediterranean. They were also to conduct and air attack against Cagliary, Sardinia but this air attack was later cancelled.
In the late afternoon and early evening of the 9th Force H came under air attack by Italian aircraft. HMS Resolution and HMS Hood were near missed with bombs.
While on the way back to Gibraltar the destroyer HMS Escort was torpedoed by the Italian submarine Marconi around 0220A/11 in position 36°20'N, 03°46'W. She was heavily damaged and was taken in tow by HMS Forester while being screened by HMS Faulknor.
Force H meanwhile had arrived at Gibraltar around 0830A/11. The destroyers HMS Keppel (Lt.Cdr.(Emgy.) E.G. Heywood-Lonsdale, RN), HMS Foresight (Lt.Cdr. G.T. Lambert, RN) and HMS Foxhound were then sent out to escort the damaged HMS Escort but she later foundered while under tow.
23 Jul 1940
Around 2200A/23, the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), light cruiser HMS Enterprise (Capt. J.C. Annesley, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Foresight (Lt.Cdr. G.T. Lambert, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN) and HMS Escapade (Cdr. H.R. Graham, RN) departed Gibraltar to conduct and air attack on the harbour of Bordeaux.
During 24 July an A/S patrol was maintained by two Swordfish aircraft between 0550A/24 and 2100A/24.
At 2110A/24, HMS Forester was detached to return to Gibraltar.
At 0100A/25, Admiralty message 2355A/24 was received ordering the cancellation of the the attack on Bordeaux and that the force was to be in position 38°16'N, 12°28'W and then conduct an all round search to a depth of 120 miles looking for enemy merchant vessels. Course was altered accordingly. No merchant vessels were however located by this search. Course was then set to return to Gibraltar.
During the day, an A/S patrol of two Swordfish was kept up between 0545A/25 and 2100A/25.
At 0700A/26, nine Swordfish aircraft carried out an all round search to a depth of 120 miles from position 35°08'N, 11°30'W. No suspicious vessels were sighted.
A/S patrols were maintained throughout the day on the 26th from 0545A/26 onwards.
At 0800A/27, the destroyer HMS Vidette (either Cdr.(Retd.) D.R. Brocklebank, RN or Lt. E.N. Walmsley, RN) joined.
On the 27th A/S patrols were maintained from dawn onwards.
The force returned to Gibraltar around noon on the 27th. (38)
31 Jul 1940
Operation Hurry
Transfer of twelve Hurricane fighters and two Skua aircraft to Malta, air attack on Cagliari, minelaying in Cagliari Bay by Force H and diversion in the Eastern Mediterranean by the Mediterranean Fleet.
Operations of Force H.
Around 0800A/31, Force H, consisting of the battlecruiser HMS Hood (Capt. I.G. Glennie, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), battleships HMS Valiant (Capt. H.B. Rawlings, OBE, RN), HMS Resolution (Capt. O. Bevir, RN), aircraft carriers HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Argus (Capt. H.C. Bovell, RN), light cruisers HMS Arethusa (Capt. Q.D. Graham, RN), HMS Enterprise (Capt. J.C.A. Annesley, DSO, RN) and escorted by the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Foresight (Lt.Cdr. G.T. Lambert, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. G.H. Peters, RN), HMS Hotspur (Cdr. H.F.H Layman, DSO, RN), HMS Gallant (Lt.Cdr. C.P.F. Brown, RN), HMS Greyhound (Cdr. W.R. Marshall A'Deane, DSC, RN), HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St.J. Morgan, RN), HMS Escapade (Cdr. H.R. Graham, RN) and HMS Velox (Cdr.(Retd.) J.C. Colvill, RN) sailed from Gibraltar.
Passage eastward was uneventful until at 1749A/1 when eight Italian aircraft were seen coming in to attack in position 37°34'N, 04°10'E. The aircraft turned away before they reached a favourable attack position. A few minutes later a second wave of nine aircraft was seen coming in but this attack was also not pressed home with determination and no hits were obtained. Some 80 bombs in all were dropped and only a few near misses were obtained on HMS Ark Royal and HMS Forester.
At 2045A/1 the attack force for Cagliari was detached. This force was made up of HMS Hood, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Enterprise, HMS Faulknor, HMS Foresight, HMS Forester and HMS Foxhound. They proceeded at 20 knots towards position 38.30’N, 07.00’E where the striking force from HMS Ark Royal was to be flown off.
The remaining ships of Force H also proceeded eastwards to fly off the aircraft for Malta from HMS Argus at dawn. The position where the aircraft were to be launched depended on the latest weather reports coming in from Malta.
At 2130A/1, HMS Enterprise, was detached by the attack force to create a diversion and intercept a Vichy-French ship en-route from Algiers to Marseilles.
At 0200A/2, HMS Ark Royal and the destroyers proceeded ahead and aircraft were launched at 0230 hours. Twelve aircraft were launched, nine carried bombs and three carried mines. One of the aircraft crashed on taking off. Due to a misunderstanding the crew was not picked up and was lost.
In the air attacks direct hits were reported four hangars, two of which were reported to burn fiercely. At least four aircraft which were parked in the open were reported to have been destroyed in addition to those in the hangars. Many aerodrome buildings were destroyed or damaged. Three mines were laid inside Cagliari harbour. One Swordfish aircraft made a forced landing on an Italian airfield and the crew was made prisoner of war.
After flying of the air striking force the group of which HMS Ark Royal was part turned to the southward to rejoin the other ships of Force H which had in the meantime also proceeded eastwards and adjusted speed to be in position 37.40’N, 07.20’E at 0445A/2. Two flights of one Skua and six Hurricane’s each were launched from HMS Argus at 0515A/2 and 0600A/2. The two groups of ships from Force H sighted each other at 0520A/2 and then made rendez-vous which was affected at 0815A/2. All aircraft launched by HMS Argus reached Malta but one of the Hurricane’s crashed on lading.
At 0930A/3, HMS Arethusa, was detached to search for the Vichy French ship HMS Enterprise was also searching for. They both failed to intercept this ship. HMS Enterprise was to the north of Minorca and was in supporting distance from Force H and was therefore ordered to proceed to Gibraltar passing west of the Baleares. HMS Arethusa rejoined force H before dark on the 3rd.
HMS Ark Royal, escorted by HMS Hotspur, HMS Encounter and HMS Escapade, were detached as to arrive at Gibraltar before dark on the 3rd. The remainder of Force H arrived at Gibraltar around dawn on the 4th.
Diversions by the Mediterranean Fleet in the eastern Mediterranean. Operation MA 9.
Around 0600C/31, light cruisers HMS Orion (Capt. G.R.B. Back, RN, flying the flag of Vice Admiral J.C. Tovey, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Neptune (Capt. R.C. O'Conor, RN), HMAS Sydney (Capt. J.A. Collins, CB, RAN) and destroyers HMS Nubian (Cdr. R.W. Ravenhill, RN), HMS Juno (Cdr. W.E. Wilson, RN) and ORP Garland (Kpt. mar. (Lt.Cdr.) A. Doroszkowski) departed Alexandria for an anti-shipping raid / contraband control in the Gulf of Athens area. They were to pass through the Kaso Strait and arrived off the Doro Channel at dawn on 1 August. They then exercises contraband control during the day in the Gulf of Athens area retiring to the westward between Cape Malea and Agria Grabusa at dusk. After dark they returned to the Aegean to exercise contraband control on 2 August. They returned to Alexandria in the evening of 2 August 1940.
A cover force went to sea around 1420 hours, this force was made up of the battleships HMS Royal Sovereign (Capt. H.B. Jacomb, RN), HMS Malaya (Capt. A.F.E. Palliser, DSC, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral H.D. Pridham-Whippell, CB, CVO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Eagle (Capt. A.R.M. Bridge, RN). They were escorted by the destroyers HMS Jervis (Capt. P.J. Mack, DSO, RN), HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN), HMS Hero (Cdr. H.W. Biggs, DSO, RN), HMS Hereward (Lt.Cdr. C.W. Greening, RN), HMS Hostile (Lt.Cdr. A.F. Burnell-Nugent, DSC, RN), HMS Ilex (Lt.Cdr. P.L. Saumarez, DSC, RN) and HMS Imperial (Lt.Cdr. C.A.deW. Kitcat, RN) and HMAS Vendetta (Lt.Cdr. R. Rhoades, RAN). They carried out exercises and then proceeded westwards towards Gavdos Island to the south of Crete. Due to engine problems in HMS Malaya the cover force returned to Alexandria late on the the morning of August 1st. (39)
4 Aug 1940
The battlecruiser HMS Hood (Capt. I.G. Glennie, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), battleship HMS Valiant (Capt. H.B. Rawlings, OBE, RN), aircraft carriers HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Argus (Capt. H.C. Bovell, RN), light cruisers HMS Arethusa (Capt. Q.D. Graham, RN), HMS Enterprise (Capt. J.C.A. Annesley, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Fearless (Cdr. K.L. Harkness, RN), HMS Foresight (Lt.Cdr. G.T. Lambert, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. G.H. Peters, RN), HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St.J. Morgan, RN), HMS Escapade (Cdr. H.R. Graham, RN), HMS Gallant (Lt.Cdr. C.P.F. Brown, RN), HMS Greyhound (Cdr. W.R. Marshall A'Deane, DSC, RN) and HMS Hotspur (Cdr. H.F.H Layman, DSO, RN) departed Gibraltar as part of Force H had to proceed to the U.K.
HMS Ark Royal, HMS Enterprise, HMS Encounter, HMS Gallant, HMS Greyhound and HMS Hotspur parted company with Force H at 1040A/6 to return to Gibraltar where they arrived around 0900A/8.
At 0735A/9 the destroyers HMS Bedouin (Cdr. J.A. McCoy, DSO, RN), HMS Punjabi (Cdr. J.T. Lean, DSO, RN) and HMS Tartar (Cdr. L.P. Skipwith, RN) joined.
At 0745A/9 the battleship HMS Valiant, aircraft carrier HMS Argus and the destroyers HMS Faulknor, HMS Foresight and HMS Forester parted company to proceed to Liverpool where they arrived around 1530A/10.
HMS Hood, HMS Arethusa, HMS Escapade, HMS Foxhound, HMS Bedouin, HMS Punjabi and HMS Tartar arrived at Scapa Flow at 0600A/10.
13 Aug 1940
At 1630A/13, HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), departed Scapa Flow for Gibraltar. She was escorted until 1025A/14 by the destroyers HMS Bedouin (Cdr. J.A. McCoy, DSO, RN), HMS Mashona (Cdr. W.H. Selby, RN), HMS Punjabi (Cdr. J.T. Lean, DSO, RN) and HMS Tartar (Capt. C. Caslon, RN). On their return to Scapa Flow the destroyers were to conduct an A/S sweep. They arrived back at Scapa Flow at 0630A/15.
At 1059A/15 Vice Admiral Somerville received a signal from the Admiralty timed 1031A/15 ordering him to patrol off Iceland. It was thought German ships might be leaving Norway in that direction but this later proved to be incorrect and HMS Renown was ordered to continue her passage to Gibraltar at 0102A/16.
At 2235A/16, HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral L.V. Wells, CB, DSO, RN), HMS Enterprise (Capt. J.C. Annesley, DSO, RN), HMS Hotspur (Cdr. H.F.H. Layman, DSO, RN), HMS Greyhound (Cdr. W.R. Marshall A'Deane, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Gallant (Lt.Cdr. C.P.F. Brown, RN), HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St J. Morgan, RN) and HMS Wrestler (Lt.Cdr. E.N.V. Currey, RN) departed Gibraltar to make rendezvous with HMS Renown.
At 1615A/18, rendezvous was effected.
At 0215A/19, a shore broadcast was received stating that the merchant vessel Rowallan Castle (British, 7801 GRT, built 1939) was being shelled by a raider. The destroyer screen was ordered to return to Gibraltar whilst HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal proceeded to go the aid of the Rowallan Castle. HMS Enterprise proceeded independently.
The raidar report later proved to be false as it had been the armed merchant cruiser HMS Circassia (Capt.(Retd.) H.G.L. Oliphant, DSO, RN) who had been shelling Rowallan Castle thinking it was an enemy ship. HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal shaped course for Gibraltar at 1150A/19, earlier had not been possible as aircraft operating from Ark Royal first had to be recalled and landed on.
The destroyers meanwhile had arrived at Gibraltar to fuel and they departed from there again at 0215A/20 although it were not all the same destroyers that had been sent out earlier (see below), rejoining HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal around 1100A/20.
HMS Renown, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Hotspur, HMS Greyhound, HMS Griffin (Lt.Cdr. J. Lee-Barber, DSO, RN), HMS Gallant, HMS Encounter and HMS Velox (Cdr.(Retd.) J.C. Colvill, RN) arrived at Gibraltar at 2000A/20. HMS Enterprise had already arrived in the morning.
Upon return to Gibraltar Vice-Admiral Wells struck his flag in HMS Ark Royal. (40)
25 Aug 1940
At 0730A/25, HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN), HMS Enterprise (Capt. J.C. Annesley, DSO, RN), HMS Hotspur (Cdr. H.F.H. Layman, DSO, RN), HMS Griffin (Lt.Cdr. J. Lee-Barber, DSO, RN) and HMS Gallant (Lt.Cdr. C.P.F. Brown, RN) departed Gibraltar for exercises.
At 2030A/25, HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Greyhound (Cdr. W.R. Marshall A'Deane, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St J. Morgan, RN), HMS Velox (Cdr.(Retd.) J.C. Colvill, RN) and HMS Vidette (Lt. E.N. Walmsley, RN) departed Gibraltar to join the Ark Royal group at sea. Course was then set into the North Atlantic to make rendezvous with ships coming from the UK.
Rendezvous was effected around 0730A/27 with HMS Valiant (Capt. H.B. Rawlings, OBE, RN), HMS Illustrious (Capt. D.W. Boyd, DSC, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral A.L.St.G. Lyster, CVO, DSO, RN), HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN), HMS Calcutta (Capt. D.M. Lees, DSO, RN), HMS Coventry (Capt. D. Gilmour, RN), HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSC, RN), HMS Foresight (Lt.Cdr. G.T. Lambert, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Fortune (Cdr. E.A. Gibbs, DSO, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) and the transport Royal Scotsman (3244 GRT, built 1936).
HMS Enterprise, HMS Velox and HMS Vidette then parted company and escorted the Royal Scotsman to Gibraltar where they arrived around 0900A/28.
The remaining ships arrived at Gibraltar in the morning of the 29th. (40)
28 Aug 1940
Operation Menace, the attack on Dakar, 23-24 September 1940.
Part I, initial movements of the Allied naval forces
The actual attack on Dakar took place on 23 and 24 September 1940 but preparations off course started earlier.
28 August 1940.
The battleship HMS Barham (Capt G.C. Cooke, RN) departed Scapa Flow for Gibraltar. She was escorted by HMS Inglefield (Capt. P. Todd, DSO, RN), HMS Eclipse (Lt.Cdr. I.T. Clark, RN) and HMS Escapade (Cdr. H.R. Graham, DSO, RN). They were joined at sea by HMS Echo (Cdr. S.H.K. Spurgeon, DSO, RAN) which sailed later.
29 August 1940.
The transports Anadyr (British, 5321 GRT, built 1930), Casamance (French, 5817 GRT, built 1921), Fort Lamy (British, 5242 GRT, built 1919), Nevada (French, 5693 GRT, built 1918) and the tanker Ocean Coast (British, 1173 GRT, built 1935) split off in position 54’N, 18’W from convoy OB 204 (which had departed from the British east coast on 26/27 August) to proceed to Dakar. When they split off their escort towards Dakar were the Free French sloop Savorgnan de Brazza and the Free French A/S trawler President Houduce.
31 August 1940.
On this day three groups of ships departed from British ports.
From Scapa Flow the following ships sailed; troopships Ettrick (British, 11279 GRT, built 1938), Kenya (British, 9890 GRT, built 1938) and Sobieski (Polish, 11030 GRT, built 1939). These were escorted by the light cruiser HMS Fiji (Capt. W.G. Benn, RN) and the destroyers HMS Ambuscade (Lt.Cdr. R.A. Fell, RN), HMS Antelope (Lt.Cdr. R.T. White, DSO, RN), HMS Volunteer (Lt.Cdr. N. Lanyon, RN) and HMS Wanderer.
From Liverpool the following ships sailed; troopships Karanja (British, 9891 GRT, built 1931), Pennland (Dutch, 16082 GRT, built 1922) and Westernland (Dutch, 16313 GRT, built 1918) and the transport Belgravian (British, 3136 GRT, built 1937). These were escorted by the destroyers HMS Mackay (Cdr. G.H. Stokes, RN), HMS Vanoc (Lt.Cdr. J.G.W. Deneys, RN) and the corvette HMS Erica (Lt.Cdr. W.C. Riley, RNR).
From the Clyde the following warships sailed; HMS Devonshire (Capt. J.M. Mansfield, DSC, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.H.D. Cunningham, CB, MVO, RN, the Commander of the upcoming operation), the destroyer HMS Harvester (Lt.Cdr. M. Thornton, RN) and the French sloops (minesweepers) Commandant Dominé and Commandant Duboc.
All these ships were expected to arrive at Freetown on 13 September where they would be joined by ships coming from Gibraltar and ships that were based at Freetown.
1 September 1940.
The outward passage was initially uneventful and Vice-Admiral Cunningham’s group joined up with the group that came from Liverpool at 0600/1 (zone -1). But that evening misfortune occurred when HMS Fiji was torpedoed by the German submarine U-32 when about 40 nautical miles north-northeast of Rockall in position 58°10’N, 12°55’W. She then returned to the Clyde. Her convoy then continued on escorted by the four destroyers until they met Vice-Admiral Cunningham’s force at 0900/2. The convoy was now known as ‘Convoy MP’. The place of HMS Fiji in the operation was subsequently taken over by the Australian heavy cruiser HMAS Australia (Capt. R.R. Stewart, RN).
2 September 1940.
HMS Barham (Capt G.C. Cooke, RN), HMS Inglefield (Capt. P. Todd, DSO, RN), HMS Echo (Cdr. S.H.K. Spurgeon, DSO, RAN), HMS Eclipse (Lt.Cdr. I.T. Clark, RN) and HMS Escapade (Cdr. H.R. Graham, DSO, RN) arrived at Gibraltar from Scapa Flow.
The destroyer escort for the MP convoy parted company at 1400/2 and was ordered to join HMS Revenge (Capt. E.R. Archer, RN) which was escorting Canadian troop convoy TC 7 to the Clyde.
Passage of the MP convoy southwards was relatively uneventful except for some submarine alarms and also some engine defects during which speed had to be reduced a bit.
6 September 1940.
HMS Barham (Capt G.C. Cooke, RN), HMS Inglefield (Capt. P. Todd, DSO, RN), HMS Echo (Cdr. S.H.K. Spurgeon, DSO, RAN), HMS Eclipse (Lt.Cdr. I.T. Clark, RN) and HMS Escapade (Cdr. H.R. Graham, DSO, RN) departed Gibraltar for Freetown in the evening but now accompanied by ships from Force H; the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN), battleship HMS Resolution (Capt. O. Bevir, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Foresight (Lt.Cdr. G.T. Lambert, RN), HMS Fortune (Cdr. E.A. Gibbs, DSO, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) and HMS Greyhound (Cdr. W.R. Marshall A'Deane, DSO, DSC, RN).
After passing between Madeira and the Canary Islands on the 8th this force, which constituted the major part of the warships involved in the upcoming operation, turned south at 0900/9. By 0800/11 the force was in position 20°18’N, 19°54’W about 1000 nautical miles south of Casablanca.
Vice-Admiral Cunningham in HMS Devonshire was then in position 16°50’N, 22°00’W, about 240 nautical miles to the south-west ward of the main force. He had just sighted the MS convoy (the five transports), escorted by Savorgnan de Brazza, some 300 nautical miles north-west of Dakar. Vice-Admiral Cunningham ordered the convoy Commodore to take the convoy into Freetown.
A signal was then received that Vichy-French warships had passed the Straits of Gibraltar and had turned south. Three light cruisers and three large destroyers were reported to have made up this force. It was not known where they were bound for but possibly Casablanca. Their appearance seriously affected the whole operation.
The Vichy-French cruiser force.
At 1850 hours on 9 September 1940, H.M. Consul General, Tangier, had informed Admiral Sir Dudley North, Flag Officer commanding North Atlantic, and repeated to the Foreign Office, that a French Squadron in the Mediterranean might try to pass through the Strait of Gibraltar within the next 72 hours. This report received confirmation the next day when the French Admiralty requested the British Naval Attaché, Madrid, to advise the Naval authorities at Gibraltar of the departure from Toulon on the 9th of three light cruisers of the Georges Leygues class and three large destroyers of the Fantasque class. They would pass through the Straits of Gibraltar on the morning of the 11th, no mention was made of their destination. This information reached the Admiralty at 2350/10 and Admiral North at 0008/11.
The Government policy with regards to Vichy warships at that time had been defined in a signal sent to all Commanders-in-Chief and Flag Officers commanding shortly after the attack on the battleship Richelieu at Dakar in July. This message, after stressing the importance of terminating the state of tension then existing between the French navy and ourselves, stated that His Majesty’s Government had decided to take no further action in regard to French ships in French colonial and North African ports, and went on to say ‘ We shall, of course, however, reserve the right to take action in regard to French warships proceeding to enemy controlled ports.’ Recent intelligence had indicated that it was highly improbable that any warships would make for the German occupied Biscay ports, and a Admiral North had not been informed of the Dakar project, he saw no reason to take any steps to interfere with the movements of the French warships.
Early on September 11th, the destroyers HMS Hotspur (Cdr. H.F.H. Layman, DSO, RN), HMS Griffin (Lt.Cdr. J. Lee-Barber, DSO, RN) and HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St J. Morgan, RN), which were hunting a reported submarine to the eastward of the Strait of Gibraltar. At 0445 they sighted six French warships steaming fast to the westward and reported them. At 0617/11, Admiral North informed the Admiralty that the lights of six ships, probably warships, steering west at high speed, had been reported by HMS Hotspur at 0515 hours in position 36°03'N, 04°14'W (60 miles east of Gibraltar) and that he had ordered the destroyers to take no further action. At 0711 hours he added that he intended to keep in touch with this force by air and that he would report probable destination.
Meanwhile, Vice-Admiral Somerville, commanding Force H, on receiving the signal from HMS Hotspur had brought HMS Renown (Capt C.E.B. Simeon, RN) and the only destroyer available, HMS Vidette (Lt. E.N. Walmsley, RN), to one hour’s notice for full speed. He did not put to sea because he too, believed the Government’s policy was to avoid interference with French warships as stated in the signal of 12 July.
The French squadron passed Gibraltar to the westward shortly after 0830/11 having given it’s composition in reply to the demand as the light cruisers Georges Leygues, Gloire, Montcalm and the destroyers Le Malin, Le Fantasque and L’Audacieux. This information reached the Admiralty at 1043/11 in a signal sent by Admiral North at 0917/11.
No further action was taken during the forenoon and the situation at noon was that the French Squadron was in position 35°00'N, 06°40'W (about 75 nautical miles south-south-west of Gibraltar) steering 213° at 20 knots. They were being observed by reconnaissance aircraft from RAF 200 Sq. based at Gibraltar. The Admiralty and Air Ministery were being kept informed.
Here was a complication that might well effect the Dakar operation should Dakar be the destination of the French Squadron. It does not seem to have been viewed in this light at the Admiralty, until the 1st Sea Lord himself, who was attending a meeting in the Cabinet Offices that forenoon, telephoned orders for HMS Renown and all available destroyers to raise steam for full speed. A signal to this end was then sent to Admiral Somerville at 1239/11. This was over twelve hours after the original message from Madrid had reached the Admiralty.
Movements of Force H, 11 to 14 September 1940.
The noon position and their course indicated Casablanca as the most probable destination of the French Squadron and at 1347/11 the Admiralty ordered Admiral Somerville to sea to intercept them. Further instructions followed at 1429 hours. These was no objection with them going to Casablanca but they could not be allowed to proceed to Dakar. Shortly after 1600 hours aircraft reported that the French Squadron had entered Casablanca.
Admiral Somerville left Gibraltar at 1630 hours in the Renown escorted by the destroyers HMS Griffin, HMS Velox (Cdr.(Retd.) J.C. Colvill, RN) and HMS Vidette. At 2006 hours he was ordered by the Admiralty to establish a patrol to intercept the French Squadron if they sailed southwards from Casablanca. In the early morning hours of the 12th at 0235 hours, HMS Vidette, encountered a four-funneled French destroyer (this was Milan) in position 33°55'N, 08°31'W (west-north-west of Casablanca). She sighted a darkened ship some 6 miles on her port bow. She challenged but got no reply. A searchlight was turned on and revealed a four-funneled French destroyer. Vidette then fired two salvoes and the French destroyer, ignoring a signal to stop, then retired at high speed behind a smoke screen. Shortly afterwards Vidette was recalled from her patrol and ordered to rejoin Renown.
The French squadron was still at Casablanca at 0923/12 according to an aircraft report. At 0934 hours, Admiral Somerville turned north to meet three more destroyers coming from Gibraltar. These were; HMS Hotspur, HMS Encounter and HMS Wishart (Cdr. E.T. Cooper, RN). These were met at 1300 hours, in position 33°05'N, 09°40'W. They then turned to the south-west again. HMS Hotspur was stationed to patrol closer inshore.
At 0405/13, HMS Renown sighted three darkened ships in position 31°25'N, 11°30'W. These were thought to be the three Fantasque class destroyers. They were steaming north at 20 knots and were allowed to proceed. Admiral Somerville continued his patrol but fuel began to become an issue. The weather was to rough for the destroyers to fill up at sea and two of them will have to be detached that evening to refuel. This would much reduce the chance to intercept the French Squadron and Admiral Somerville informed the Admiralty of this. Adding tat he considered a patrol should be established off Dakar. His signal crossed one from the Admiralty stating that according to French sources the Squadron would remain only shortly at Casablanca before proceeding to Dakar.
This forecast proved correct. At 1530/13 aircraft reported that the light cruisers were no longer at Casablanca. Due to his fuel situation Admiral Somerville signalled that he would leave his patrol area for Gibraltar at 2000 hours that evening. But at 1916 hours the Admiralty ordered him to steer for Dakar at 18 knots. This was being done but Vidette and Velox were detached to Gibraltar to fuel.
At 2335/19 the Admiralty cancelled the order so at 0121/14, Renown and the four remaining destroyers set course to return to Gibraltar which they reached at 2000/14.
Patrol of Dakar by Vice-Admiral Cunningham’s forces.
To return to Vice-Admiral Cunningham. He knew that the French Squadron had left the Mediterranean at 1542/11 and that Vice-Admiral Somerville had been ordered to intercept them. Within a couple of hours he learnt that the French Squadron had entered Casablanca. The next forenoon (0947/12) he was informed that Vice-Admiral Somerville had been ordered to establish a patrol and to prevent them from proceeding to the south.
Vice-Admiral Cunningham’s forces were then approaching Freetown. At 1145/12, an aircraft from HMS Ark Royal approached HMS Devonshire to report that the Ark Royal would be in position 13°59'N, 20°08'W at 1300 hours and expected to arrive at Freetown with HMS Barham, HMS Resolution and ten destroyers at 0700/14. The next morning, 13 September, at 0820 hours an aircraft again closed HMS Devonshire. An order was then passed that four destroyers were to be detached to join HMS Devonshire and the convoy before dark. At 1008 hours HMS Devonshire left the convoy to close Ark Royal’s force, sighing it an hour later 20 nautical miles to the north-north-east. Devonshire remained in visual touch until 1700 hours when course was set to return to the convoy taking the destroyers HMS Faulknor, HMS Foresight, HMS Forester and HMS Fury with him.
Shortly after 1800/13, Vice-Admiral Cunningham was informed that the French cruisers had left Casablanca and that Vice-Admiral Somerville in the Renown had been ordered to proceed to the Dakar area.
Shortly after midnight 13th/14th, a signal came in from the Admiralty ordering Vice-Admiral Cunningham to establish a patrol immediately to prevent the French cruisers from reaching Dakar, employing every available ship. The same orders went to the Commander-in-Chief, South Atlantic. HMS Cumberland (Capt. G.H.E. Russell, RN), which had departed Freetown for the U.K. at 2000/13 was placed under Vice-Admiral Cunninham’s orders and HMS Cornwall (Capt. C.F. Hammill, RN), on her way from Simonstown to Freetown, was ordered to increase speed.
The original operation was now swallowed up in the task of intercepting the French ships. Time had become a factor of the utmost importance and without waiting for daylight, Vice-Admiral Cunningham and General Irwin, went over to see General de Gaulle on board the Westernland at 0120/14, who immediately roused Capitaine Thierry d’Argenlieu and armed him with a letter forbidding any French warship to proceed to Dakar. Within twenty minutes they were on their way back to the Dorsetshire with Capt. D’Argenlieu and the following measures were taken;
HMAS Australia which was coming from the Clyde to take the place of HMS Fiji was ordered to close HMS Devonshire, which would be steering for Dakar, then 400 nautical miles distant.
The Ark Royal was ordered to sent her six remaining destroyers; HMS Inglefield, HMS Greyhoud, HMS Fortune, HMS Echo, HMS Eclipse and HMS Escapade to Freetown to fuel and herself proceed with despatch to position 16’N, 17°40’W.
HMS Barham and HMS Resolution and the other four destroyers; HMS Faulknor, HMS Foresight, HMS Forester and HMS Fury, were to fuel at Freetown and leave for the Dakar area as soon as fuelling had been completed.
Convoy’s MP and MS were to proceed to Freetown with their French escorts.
HMS Devonshire meanwhile had altered course to the northward for Dakar at 0230/14, speed 18 knots. It was not possible to transfer General Irwin and his staff and the General thus found himself speeding northward with the orders for the landing while his troops went on to Freetown. HMAS Australia joined HMS Devonshire at 0300 hours and half an hour later the cruisers had worked up to 27 knots. HMS Cumberland and HMS Ark Royal were approaching from the south.
At 1000/14, HMS Devonshire and HMAS Australia were 200 nautical miles south of Dakar in position 11°23’N, 17°42’W, with HMS Cumberland and HMS Ark Royal respectively 45 and 100 miles astern of them. Aircraft from Ark Royal carried out reconnaissance ahead of Devonshire and Australia from this time onwards. Also flights over Dakar were carried out. That afternoon a large amount of shipping was reported in the harbour and also a submarine was sighted on the surface at 1533 in position 260°, Cape Manuel, 10 nautical miles, steering 260°. It could not be seen if the French cruisers had arrived at Dakar.
At 1900/14 the Devonshire and Australia, reduced to 17 knots on reaching the latitude of Dakar and then turned back to join Cumberland. She was met at 1940 hours and then the cruisers turned northward once more. They established a patrol line at 2320 hours, 4 miles apart, courses 270°-090°, between the meridians 17°30’W and 18°00W in latitude 16°00’N.
But they were too late. Just before midnight 14/15 September a message was received from the Admiralty that a Vichy report had announced that the cruisers had arrived safely at Dakar. The Vichy cruisers actually had arrived at Dakar at 1600/14.
Dawn air reconnaissance on the 15th failed to spot the cruisers at Dakar and by this time the three heavy cruisers were running low on fuel and at 1001 hours Vice-Admiral Cunningham sent a signal to the Admiralty to ask if he should withdraw to Freetown to refuel and prepare for operation ‘Menace’, leaving HMS Cumberland to patrol off Dakar, or to report the patrol about 0001/17 and accept indefinite delay of operation ‘Menace’. He recommended the first alternative.
At 1027 hours, however, the Ark Royal signalled that the cruisers had been located at Dakar. All ships then set course for Freetown to refuel except HMS Cumberland which was left to patrol off Dakar. The next day, the 16th, she met the Vichy French merchant vessel Poitiers (4185 GRT, built 1921) 100 miles south of Dakar and fired a salvo across her bows. Her crew then set her on fire and abandoned her. She was then sunk by gunfire from the cruiser.
Cancellation of Operation ‘Menace’.
By the evening of 15 September, Vice-Admiral Cunningham’s forces were all making once again for Freetown. A destroyer had been sent on ahead with the operation orders and two staff officers. The escape of the French cruisers, however, called for a drastic re-consideration of the original plan.
In London the War Cabinet met at 1000/16 to consider the new situation. The Prime Minister pointed out that in his view the operation had to be cancelled and at 1346/16, Vice-Admiral Cunningham received a signal that the landing of troops at Dakar in ‘Operation Menace’ was impracticable. It was proposed that General de Gaulle’s force should land at Duala with the object of consolidating his influence in the Cameroons, Equatorial Africa and the Chads. The British portion of the force was to remain at Freetown. Unless de Gaulle had any strong objection, this plan had to be put into operation forthwith.
Vice-Admiral Cunningham and General Irwin were reluctant to take this view. They replied at 1642 hours suggesting that if HMS Cornwall and HMS Cumberland would be added to their force they should be enough to deal with the French cruisers. The answer came at 2245 hours; they were left a liberty to consider the whole situation and discuss it with de Gaulle, whom they informed of the new proposal.
HMS Devonshire arrived at Freetown at 0630/17. The Vice-Admiral and the General proceeded to consult with General de Gaulle. The latter was much perturbed at the possible cancellation of the original plan and that very morning he sent a telegram to the Prime Minister desiring ‘to insist’ that the plan should be carried out and emphasising the vital importance to the Allies of gaining control of the basis in French Africa. He now urged on the Force Commanders that if the unopposed landing failed the Free French troops should attempt a landing at Rufisque. They decided to support this proposal and shortly after midnight they forwarded their recommendations to the Admiralty for consideration. The reply from H.M. Government came at 1159/18; ‘ We cannot judge relative advantages of alternative schemes from here. We give you full authority to go ahead and do what you think is best, in order to give effect to the original purpose of the expedition. Keep us informed.’
With a free hand such as is seldom enjoyed in these days of rapid communication by the leaders of an overseas expedition in unbroken touch with their Government, the Joint Commanders decided to proceed with ‘Menace’ on 22 September.
The French cruisers again, 19 to 26 September 1940.
The naval and military staffs were working hard at preparations for the landing when the next day, 19 September, French cruiser appeared again on the scene. HMAS Australia, which had left Freetown the day before to relieve HMS Cumberland on patrol, at 1019/19 in position 10°23’N, 16°54’W, north-west of Freetown, sighted the three La Galissonniere class cruisers 14 nautical miles off steering south-east. Once more the naval forces had to raise steam with all despatch. HMAS Australia and HMS Cumberland were already had on the trial. General de Gaulle again arranged for Captain Thierry d’Angenlieu to carry a message requisting the French cruisers to return to Casablanca.
General Irwin and his staff, with Admiral Cunningham’s Chief Staff Officer, Capt. P.N. Walter, were transferred to the troopship Karanja, and at 1400 hours HMS Devonshire left Freetown at 27 knots with the destroyers HMS Inglefield, HMS Greyhound and HMS Escapade. It was hoped to sight the French cruisers before dark. HMS Barham with HMS Fortune and HMS Fury made for a position to the south-east of the French. HMS Ark Royal, which had engine trouble to repair first, was to follow at 0500/20. A message came from the Admiralty that the French cruisers were not to return to Dakar.
The French cruisers turned back to the north-west and increased speed to 29 knots. Torrential rain was falling, hiding everything from view, but HMAS Australia and HMS Cumberland were able to keep in touch and at 1830/19 HMAS Australia managed to pass directions not to return to Dakar. She was then in position 09°02’N, 15°14’W, just keeping in touch while doing 31 knots. Then the French cruiser Gloire broke down and separated from the other two cruisers. The British then lost touch with these two cruisers. HMS Devonshire meanwhile was steaming to a position to cut off the way to Conakri in French Guinea. HMS Cumberland then regained touch with the two French cruisers (Georges Leygues (flag) and Montcalm) who were speeding north while HMAS Australia picked up the Gloire which was steering eastwards at reduced speed. Night had fallen when HMS Devonshire with HMS Inglefield still in company showed up. HMS Inglefield took Captain d’Argenlieu on board of the Gloire. The French captain refused to accede to his representations, but when Vice-Admiral Cunningham intervened he agreed to proceed to Casablanca. HMAS Australia escorted her until 21 September, leaving her then, on Admiralty instructions, to proceed unescorted.
HMS Cumberland meanwhile managed to keep in touch with the other two cruisers. Her attempts at parley failed, but the French signalled that ‘under no circumstances shall my cruisers pass under German control’. HMS Cumberland followed them all the way to Dakar but was unable to prevent them from entering, which they did at 0550/20.
Meanwhile, on 18 September, far away to the southward, a fourth French cruiser had been sighted escorting a naval tanker. This was the Primaguet escorting the Tarn. HMS Cornwall had departed Freetown on 16 September to meet HMS Delhi (Capt. A.S. Russell, RN) and HMS Dragon (Capt. R.J. Shaw, MBE, RN) off Cape Formosa (south Nigeria). They swept towards Fernando Po [now called Bioko] to intercept any French forces bound for the Cameroons with instructions to direct them back to Casablanca. On 17 September at 2000 hours information came that a French warship and an oiler had been in position 07°25’N, 14°40’W at 1500/15. The Cornwall proceeded to search and on the 18th her aircraft picked up the cruiser Primaguet and oiler Tarn 35 nautical miles ahead. The Commander-in-Chief, South Atlantic ordered her to be shadowed.
Her lights were sighted at 2142/18 but disappeared at 0425/19. When dawn broke the horizon was clear. She was picked up again at 1009/19. A boarding party from HMS Delhi went on board. The Captain, after making a formal protest, asked to be allowed to remain stopped until 1700/19 after which she proceeded, first westward, then northward, being shadowed by HMS Cornwall and HMS Delhi until 1830/21 when HMS Delhi had to proceed to Freetown to refuel. HMS Cornwall shadowed her alone untul the 23rd when she was rejoined by HMS Delhi. For two days they followed her close, still steaming north. On the 25th Primaguet fuelled from the Tarn. They were then off the Cape Verde Island. The next day the Admiralty approved the cruisers to return to Freetown. The Primaguet gave a promise that she would proceed to Casablanca with the Tarn where they indeed arrived in due course. The British cruisers then turned south. They had kept the Primaguet and Tarn in sight for five days. Thus two out of the four cruisers in the area had been diverted to Casablanca without the use of force. (36)
29 Aug 1940
Operation Hats.
Passage of reinforcements for the Mediterranean Fleet from Gibraltar to Alexandria, subsequent operations by the fleet as well as the passage of convoys MF 2 from Alexandria to Malta and AS 3 from Piraeus to Port Said.
29 August 1940.
At 2045C/29, convoy MF 2, made up of the transports Cornwall (10603 GRT, built 1920), Volo (1587 GRT, built 1938) and the Royal Fleet Auxiliary tanker Plumleaf (5916 GRT, built 1917) departed Alexandria for Malta. These ships were escorted by the destroyers (‘Force J’) HMS Jervis (Capt. P.J. Mack, DSO, RN), HMS Juno (Cdr. W.E. Wilson, RN), HMS Dainty (Cdr. M.S. Thomas, RN) and HMS Diamond (Lt.Cdr. P.A. Cartwright, RN).
30 August 1940.
At 0445C/30, the main battlefleet (‘Force I’) departed Alexandria and was made up of the battleships HMS Warspite (Capt. D.B. Fisher, CBE, RN, flying the flag of A/Admiral A.B. Cunningham, KCB, DSO and 2 Bars, RN), HMS Malaya (Capt. Sir A.F.E. Palliser, DSC, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral H.D. Pridham-Whippell, CB, CVO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Eagle (Capt. A.R.M. Bridge, RN), light cruisers HMS Orion (Capt. G.R.B. Back, RN) and HMAS Sydney (Capt. J.A. Collins, CB, RAN). Escort was provided by the destroyers HMAS Stuart (Capt. H.M.L. Waller, RAN), HMAS Voyager (Cdr. J.C. Morrow, RAN), HMAS Vampire (Lt.Cdr. J.A. Walsh, RAN), HMAS Vendetta (Lt.Cdr. R. Rhoades, RAN), HMS Decoy (Cdr. E.G. McGregor, RN), HMS Defender (Cdr. St.J.R.J. Tyrwhitt, RN), HMS Hereward (Lt.Cdr. C.W. Greening, RN), HMS Imperial (Lt.Cdr. C.A.deW. Kitcat, RN) and ORP Garland (Kpt. mar. (Lt.Cdr.) A. Doroszkowski).
Shortly afterwards the heavy cruiser HMS Kent (Capt. D. Young-Jamieson, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral E. de F. Renouf, CVO, RN), light cruisers HMS Liverpool (Capt. P.A. Read, RN), HMS Gloucester (Capt. H.A. Rowley, RN) and the destroyers Hyperion (Cdr. H.St.L. Nicolson, DSO and Bar, RN), HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN) and HMS Ilex (Lt.Cdr. P.L. Saumarez, DSC, RN) also departed Alexandria. These ships were also part of ‘Force I’.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
From Gibraltar the following forces went to sea, they departed around 0845A/30.
’Force B’ which was made up of the battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt C.E.B. Simeon, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN), light cruiser HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN). Escort was provided by the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN), HMS Fortune (Cdr. E.A. Gibbs, DSO, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSC, RN), HMS Foresight (Lt.Cdr. G.T. Lambert, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN) and HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St J. Morgan, RN).
At the same time ‘Force F’ departed, this force was the reinforcement for the Mediterranean Fleet and was made up of the battleship HMS Valiant (Capt. H.B. Rawlings, OBE, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Illustrious (Capt. D.W. Boyd, DSC, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral A.L.St.G. Lyster, CVO, DSO, RN), light (AA) cruisers HMS Coventry (Capt. D. Gilmour, RN), HMS Calcutta (Capt. D.M. Lees, DSO, RN). They were escorted by HMS Nubian (Cdr. R.W. Ravenhill, RN), HMS Mohawk (Cdr. J.W.M. Eaton, RN), HMS Janus (Cdr. J.A.W. Tothill, RN), HMS Hero (Cdr. H.W. Biggs, DSO, RN), HMS Gallant (Lt.Cdr. C.P.F. Brown, RN), HMS Greyhound (Cdr. W.R. Marshall A'Deane, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Griffin (Lt.Cdr. J. Lee-Barber, DSO, RN) and HMS Hotspur (Cdr. H.F.H Layman, DSO, RN).
A third ‘force’, called ‘Force W’ also departed at the same time, it was made up of the destroyers HMS Velox (Cdr.(Retd.) J.C. Colvill, RN) and HMS Wishart (Cdr. E.T. Cooper, RN). These destroyers were to split off from the other forces off the Baliaric Islands and proceed northwards and transmit false messages deceiving the Italians into thinking that ‘Force H’ from Gibraltar was proceeding towards the Genoa area.
31 August 1940.
During the day HMS Eagle flew off A/S and fighter patrols.
At 0845C/31, HMS Kent, HMS Liverpool, HMS Gloucester and their escort of HMS Hyperion, HMS Hasty and HMS Ilex were sighted by enemy aircraft. They made rendez-vous with the bulk of the Mediterranean Fleet later the same day which was then also sighted by enemy aircraft.
Shortly after noon convoy MF 2 was bombed by enemy aircraft in position 35°14’N, 23°11’E.
At 1420C/31, two Gladiators were flown off by HMS Eagle. When these returned at 1530C/31 they reported that they had shot down an Italian aircraft but another shadowing aircraft was heard to be making reports.
At 1554C/31, HMS Kent, HMS Liverpool and HMS Gloucester were detached to give AA protection to the convoy. They were ordered to rejoin the fleet at 2000C/31.
At 1635C/31 an aircraft reported that the transport Cornwall had been hit aft by a bomb and that she was on fire. It was also reported that the fire was under control and that Cornwall was still proceeding with the convoy.
At 1815C/31 HMS Decoy was detached to join the three cruisers.
Also at 1815C/31, an aircraft from HMS Eagle reported sighting an enemy force of two battleship, seven cruisers and eight destroyers in position 37°18’N, 18°52’E. Which was about 140 nautical miles from Warspite at that moment. This position was later corrected to 37°02’N, 19°04’E. It was therefore decided to remain close to the convoy during the night.
At 1930C/31, the three cruisers were sighted and between 1950C/31 and 2020C/31 all aircraft returned to HMS Eagle.
At 2057C/31, HMS Jervis reported that at 2015C/31 the convoy was in position 35°24’N, 21°50’E, course 260°, speed 9.5 knots. It was also reported that Cornwall her steering gear had been wrecked and that she was steering on her main engines.
Later that evening more sighting reports of enemy warships were received coming from two submarines.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
At 0815C/31, HMS Ark Royal launched six search aircraft. Fighter patrol was also maintained overhead
At 1240C/31, a section of Skua’s on fighter patrol were ordered to intercept an Italian shadower that had been detected by RD/F. They managed to intercept the enemy at 1248C/31 and shoot it down in flames.
At 1630C/31, another Italian shadower was shot down by the fighter patrol.
At 2150C/31, in position 39°30’N, 04°01’E, ‘Force W’ comprising HMS Velox and HMS Wishart, was detached for the W/T diversion. They were to proceed to the north-east and during the passage they were to transmit a series of messages by W/T in approximate position 41°00’N, 04°30’E. This part of the operation was called ‘Operation Squawk’.
1 September 1940.
At 0630C/1, HMS Eagle launched nine aircraft to conduct a search between 310° and 140° to a depth of 100 miles. These aircraft sighted nothing.
At 1035C/1, four more aircraft were flown off to search between 180° and 210° to a depth of 60 miles.
At noon ‘Force I’, the main battlefleet, was in position 34°48’N, 18°59’E.
At 1300C/1, HMS Eagle flew off four more aircraft to search between 235° and 315° to a depth of 60 miles. This search was maintained for the remainder of the day. Aircraft being flown off at 1545C/1 and 1745C/1. The last patrol returned at 2015C/1. No enemy forces had been sighted.
At 1330C/1 an, enemy reconnaissance aircraft was sighted over the fleet.
At 1400C/1, HMS Orion and HMAS Sydney were detached to make rendez-vous in position 34°42’N, 16°20’E with the destroyer HMS Wryneck (Lt.Cdr. R.H.D. Lane, RN) which had been refitting and rearming at Malta and had recently recommissioned for service. They were then to make rendezvous with ‘Force J’. The convoy was sighted at 1530C/1.
A flying boat operating from Malta reported enemy warships, a force made up of two battleships, ten cruisers and a large number of destroyers was sighted in position 38°52’N, 18°16’E at 1600C/1. They were steering towards Taranto. These forces were shadowed until 1857C/1 when it was absolutely clear that the enemy was returning to their bases.
During the night the fleet would remain near the convoy with the cruiser force to the north and the battleforce to the south of the convoy.
Plumleaf and Volo, escorted by HMS Dainty and HMS Diamond were ordered to proceed to Malta at maximum speed while HMS Jervis and HMS Juno remained behind with the damaged Cornwall.
From the main battleforce HMAS Stuart, HMAS Vendetta, HMAS Vampire and HMS Defender were detached to Malta at 2000C/1 where they were to refuel.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Meanwhile in the western Mediterranean at 0325C/1 a strike force was launched by HMS Ark Royal, 155 miles, 264° from Cagliari to raid Elmas aerodrome. After flying off the fleet altered course to the flying on position which was 120 miles, 226° from Cagliari.
The striking force consisted of nine Swordfish each armed with four 250lb G.P. bombs and 8 250lb incendiary bombs. Parachute flares were also carried by each plane. Weather conditions were good.
At 0600C/1, the aircraft attacked the aerodrome after establishing its position by dropping flares. Bombs were released from 3000 feet and hits were observed on the barracks, aerodrome buildings and aircraft dispersed round the aerodrome. Several fires were seen to start.
All aircraft returned safely, landing on around 0800C/1. On the way back they had attacked an enemy submarine with machine gun fire in position 38°20’N, 07°20’E. The submarine fired a yellow flare and then dived. HMS Greyhound and HMS Hotspur were then detached to hunt the submarine but they did not made contact with the enemy. The submarine involved was the Italian Diaspro. She was first machine gunned and reported the attacking aircraft as a Sunderland (sic). She then dived. Five explosions were then heard of which one was close enough to shake the submarine.
After landing on the striking force course was altered to the south-westward to give the Italians the impression that having bombed Cagliari the force had achieved its object and was withdrawing. But as there apparently there were no Italian aircraft shadowing the force at this moment this seems to have failed.
At 1030C/1, course was altered to 080°. From this time onwards fighter patrols, each of six aircraft, were maintained over the force throughout the day.
At 1630C/1, HMS Illustrious flew off seven aircraft to conduct a search to the eastward until maximum range.
At 1730C/1, RD/F reported an aircraft approaching the force from ahead. Intercepted Italian reports indicted that the force was being shadowed. Both carriers then vectored fighters. They did not sight enemy aircraft but a section of Fulmars from HMS Illustrious attacked a British Hudson in error.
At 2200C/1, when in position 38°06’N, 10°51’E, HMS Valiant, HMS Illustrious, HMS Coventry, HMS Calcutta, HMS Nubian, HMS Mohawk, HMS Janus, HMS Hero, HMS Gallant, HMS Griffin, HMS Greyhound and HMS Hotspur parted company and proceeded to the south-eastward.
The remainder of the ships proceeded to the northwards for 15 minutes and then altered course to the west and increased speed to 24 knots to reach a suitable spot for a second air strike on Cagliari.
2 September 1940.
At 0700C/2, A/S patrols were flown off by HMS Eagle and the mean line of advance was changed to 320° for the rendez-vous position with ‘Force F’. At 0800C/2 the fleet was in position 35°25’N, 13°48’E.
At 0900C/2, HMS Valiant and HMS Illustrious were sighted right ahead. With them were HMS Orion, HMAS Sydney, HMS Wryneck, HMS Gallant, HMS Greyhound, HMS Griffin and HMS Hotspur. HMS Coventry, HMS Calcutta, HMS Nubian, HMS Mohawk, HMS Janus and HMS Juno had been detached to Malta to refuel.
At 0930C/2, HMAS Vampire and HMAS Vendetta rejoined from Malta and HMS Hereward and HMS Ilex were now detached to refuel at Malta.
At 0940C/2, when the fleet was in position 35°40’N, 13°43’E, and steaming on a course of 140°, the fleet was formed as follows; HMS Warspite, HMS Illustrious, HMS Malaya, HMS Eagle, HMS Valiant. HMS Orion and HMAS Sydney were stationed 12 cables 20° on either bow. The destroyers were in Sreening Diagram No. 6A.
A standing patrol of four Fulmars from HMS Illustrious was maintained over the fleet at 12000 feet. A/S patrols were provided by Illustrious and Eagle if required.
At 1010C/2, HMS Valiant was detached to Malta with an escort of the destroyers HMS Hyperion, HMS Hasty, HMS Decoy and HMS Wryneck.
At 0930C/2 an enemy aircraft reported three cruisers and at 1030C/2, Rear-Admiral Cruiser Squadron 3 with HMS Kent, HMS Liverpool and HMS Gloucester, reported that they were being shadowed in position 35°29’N, 14°40’E. Three Fulmars for A/S protection were then flown off.
At 1050C/2, an enemy aircraft was heard to report a large naval force. An Italian reconnaissance aircraft was shot down shortly afterwards and nothing more was heard from this aircraft after this.
At 1130C/2, the Vice-Admiral Malta reported that the convoy had arrived there safely.
At noon the fleet was in position 35°29’N, 14°25’E steering 100°. The fleet remained about 35 nautical miles south of Malta during the afternoon.
At 1425C/2, HMS Janus was detached to Malta with correspondence and to refuel.
At 1504C/2, HMS Coventry, HMS Janus, HMS Juno, HMS Nubian and HMS Mohawk, joined the fleet.
At 1600C/2, the fleet was in position 35°14’N, 14°21’E. At this time a bombing attack took place. Eight bombs fell astern of HMS Eagle.
At 1645C/2, HMS Hereward and HMS Ilex rejoined the fleet.
At 1657C/2, HMS Malaya, HMS Eagle, HMS Coventry, HMS Janus, HMS Juno, HMS Dainty, HMS Diamond, HMAS Vampire, HMAS Vendetta (‘Force E’) and HMS Kent, HMS Liverpool, HMS Gloucester, HMS Nubian and HMS Mohawk (‘Force A’) were detached.
At 1730C/2, HMS Gallant and HMS Ilex reported a submarine contact and attacked with depth charges. The fleet made an emergency alteration of course.
At 1856C/2, HMAS Voyager was detached to Malta and at 1900C/2 HMS Calcutta, HMS Hasty, HMS Hero, HMS Decoy and HMS Wryneck rejoined.
Between 1900C/2 and 1910C/2, two bombing attacks were made on the fleet. During these attacks several Italian aircraft were shot down.
At 1945C/2, when in position 35°20’N, 14°07’E, the fleet altered course to 040° to close the Malta swept channel as HMS Valiant was expected to rejoin the fleet at this time. Valiant was , however, delayed until 2030C/2 owing to an air raid on Malta and course was altered to 140° at 15 knots at 2100C/2 in position 35°38’N, 14°26’E. In the meantime the last aircraft had returned at 2045C/2.
At 2200C/2, HMS Gallant, HMS Greyhound, HMS Griffin, HMS Hotspur and ORP Garland detached to Malta to refuel and then they were to proceed to Gibraltar.
At 2330C/2, HMS Valiant, screened by HMAS Stuart, HMS Hyperion, HMS Imperial and HMS Janus, was 10 nautical miles 270° from HMS Warspite. Course was altered to 090° and speed was increased to 18 knots at this time.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
At 0350C/2, HMS Ark Royal, launched a striking force of nine Swordfish aircraft armed with 4 250 lb. G.P. bombs and 20 lb. Cooper of 25 lb. incendiary bombs, in addition to parachute flares. Weather conditions were however not very good.
On reaching the vicinity of their objectives, the aerodrome and the power station, the aircraft encountered a layer of cloud at 5000 feet and another layer at 4000 feet. The valleys appeared to be filled with mist or fog and low clouds. Parachute flares were dropped at intervals for a period of about 45 minutes in the hope of identifying the targets, but without success.
Four aircraft then attacked searchlights, putting one of them out of action. Two attacked, what was thought to be, a flare path which turned out to be a field two miles to the north-west of the aerodrome, The three remaining aircraft jettisoned their bombs into the sea.
During the attack the aircraft encountered heavy AA barrage fire. This fire was continued until the aircraft were over 17 miles from the aerodrome. It was apparent that the AA defence had been increased since the last attack. Searchlights were few and ineffective and appeared to have no form of control.
By 0800C/2 all aircraft had returned and the fleet was in position 37°48’N, 06°11’E and the fleet proceeded at 26 knots to the westward to get out of range of the expected enemy air attack. These however did not develop as apparently the fleet was not shadowed by the enemy.
3 September 1940.
At 0130C/3, HMS Valiant took station astern of the line and HMAS Stuart, HMS Hyperion, HMS Imperial and HMS Janus joined the screen.
At 0640C/3, A/S patrols were flown off, two aircraft were searching up to a depth of 60 nautical miles.
At 0700C/3, HMS Defender rejoined. She had been delayed at Malta with a defective Asdic dome and had been docked there. Repairs however could not be made as there were no spare parts available at Malta.
At 0800C/3, the Commander-in-Chief, with ‘Force I’ was in position 35°27’N, 19°10’E, steering for the Kithera Channel and ‘Force A’ was in position 35°16’N, 20°58’E steering for the south of Crete. HMS Kent, HMS Liverpool, HMS Gloucester, HMS Nubian and HMS Mohawk had been detached at dawn and were proceeding direct to make rendez-vous with convoy AS 3 in position 37°10’N, 23°15’E (off the Gulf of Athens) at 1800/3.
Convoy AS 3 was made up of the following merchant vessels Cavallo (British, 2269 GRT , built 1922), Destro (British, 3553 GRT , built 1920), Ann Stathatos (Greek, 5685 GRT , built 1918) and Hydroussa (Greek, 2038 GRT , built 1922).
At 2200C/3, HMAS Stuart stopped with a burst steam pipe and was instructed to join convoy AS 3 after repairs.
At 2230C/3, HMS Ilex and HMS Decoy were detached for a dawn bombardment of Scarpanto.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Meanwhile in the western Mediterranean nothing of further interest occured with the fleet and ' Force H ' arrived at Gibraltar around 1100A/3.
At 1645C/3, HMS Gallant, HMS Griffin, HMS Greyhound, HMS Hotspur and ORP Garland departed Malta for Gibraltar. They first made an A/S sweep to the south and west of Malta before continuing on their passage.
4 September 1940.
At 0345C/4, in position 35°44’N, 25°56’E, eight Swordfish aircraft were flow off from HMS Illustrious to attack Calatos aerodrome (Rhodes). Twelve aircraft were initially intended to carry out this attack but due to a crash on deck the remainder could not be launched. Twelve aircraft were flown off by HMS Eagle to attack Maritsa aerodrome (also on Rhodes).
At 0400C/4, HMS Calcutta parted company to join convoy AS 3.
At 0505C/4, HMS Orion and HMAS Sydney were in position 35°09’N, 26°55’E. HMAS Sydney then proceeded to bombard Makryalo aerodrome and HMS Orion to bombard Pegadia Bay.
At 0625C/4, a Swordfish aircraft from HMS Illustrious crashed while taking off, two of the crew were rescued by HMS Imperial but the observer did not survive the crash.
Between 0730C/4 and 0740C/4 the striking forces returned to HMS Illustrious and HMS Eagle. The aircraft from Illustrious reported that at 0555C/4 two of them had attacked barracks and ammunition dumps at south-east of Callato. The other six Swordfish attacked Callato and a number of aircraft parked on the north edge of the field were probably destroyed. The aircraft from Eagle reported two main hangers hit at Maritsa as well as a petrol dump, barrack blocks and workshops set on fire. The aircraft from Eagle encountered fighters and our of them failed to return.
At 0800C/4, the Commander-in-Chief with his force was in position 35°00’N, 26°54’E, steering 150°. At 0820C/4, large volumes of smoke were seen over the horizon in the direction of Rhodes.
At 1055C/4, HMS Orion, HMAS Sydney, HMS Ilex and HMS Decoy rejoined. Orion reported that no military targets could be identified at Pegadia and what might have been the military barracks had a considerable village behind it. She had fired only a few rounds. Sydney reported that the eastern part of the landing ground at Makriyalo was plasetered. Only one small building was seen and it was destroyed. Two Motor Torpedo Boats which came out were engaged by Ilex and were reported sunk. Sydney’s aircraft reported that three more were present and that two retired and the third one was damaged.
Between 1110C/4 and 1158C/4, three bombing attacks were made on the fleet. Three aircraft dropped six bombs just astern of HMS Warspite. Another aircraft dropped a stick of six bombs near the destroyer screen. Another aircraft dropped a stick of bombs near HMS Ilex.
At 1145C/4, an A/S patrol aircraft dropped a bomb on a suspected submarine some two nautical miles from Warspite. HMS Imperial obtained a faint contact and attacked but without result.
At noon, the Commander-in-Chief, in HMS Warspite was with HMS Valiant, HMS Illustrious, HMS Hyperion, HMS Hero, HMS Hasty, HMS Hereward, HMS Imperial, HMS Janus and HMS Defender in position 34°42’N, 27°35’E. HMS Malaya, HMS Eagle, HMS Juno, HMS Dainty, HMS Diamond, HMAS Vampire, HMAS Vendetta and HMS Wryneck were 40 nautical miles to the southward proceeding independently to Alexandria where they arrived at 2100C/4 on this day.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Meanwhile in the western Mediterreanean, between 1225 and 1430C/4, HMS Gallant, HMS Griffin, HMS Greyhound, HMS Hotspur and ORP Garland were attacked by high level bombers without result.Garland had leaks in two boilers was towed from 1715C/4 to 1845C/4 by Griffin until she was able to proceed after repairs on one boiler.
5 September 1940.
At 0610C/5, HMS Hereward investigated a contact and the fleet made an emergency turn. Shortly afterwards, at 0700C/5, the swept channel was reached and the fleet entered Alexandria harbour without further incident.
HMS Kent, HMS Liverpool, HMS Gloucester were ordered to remain with convoy AS 3 until after dark and then to proceed to Alexandria where they arrived early the next day.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
HMS Gallant, HMS Griffin, HMS Greyhound, HMS Hotspur and ORP Garland arrived at Gibraltar at 2020A/5.
6 September 1940.
HMS Nubian and HMS Mohawk remained with convoy AS 3 until relieved at 0600C/6 by HMS Hereward and HMS Imperial. They arrived at Alexandria in the afternoon.
Already before noon HMS Coventry, HMS Calcutta and HMAS Stuart had arrived at Alexandria.
Convoy AS 3, now escorted by HMS Hereward and HMS Imperial arrived at Port Said in the afternoon as well. (41)
6 Sep 1940
The battleships HMS Barham (Capt G.C. Cooke, RN), HMS Resolution (Capt. O. Bevir, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN) and the destroyers HMS Inglefield (Capt. P. Todd, DSO, RN), HMS Greyhound (Cdr. W.R. Marshall A'Deane, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Foresight (Lt.Cdr. G.T. Lambert, RN), HMS Fortune (Cdr. E.A. Gibbs, DSO, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN), HMS Eclipse (Lt.Cdr. I.T. Clark, RN) and HMS Escapade (Cdr. H.R. Graham, DSO, RN) departed Gibraltar for Freetown / Operation Menace. The destroyer HMS Echo (Cdr. S.H.K. Spurgeon, DSO, RAN) was unable to sail with them but sailed later so as to overtake the force and join them at sea.
[For more info see the event ' Operation Menace, the attack on Dakar, 23-24 September 1940, Part I, initial movements of the Allied naval forces ' for 28 August 1940.]
23 Sep 1940
Operations Menace, the attack on Dakar, 23-24 September 1940.
Part II, the actual attack.
General intentions.
By 20 September the attack force was assembled at Freetown. It was made up of the following warships; battleships HMS Barham (Capt G.C. Cooke, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.H.D. Cunningham, CB, MVO, RN), HMS Resolution (Capt. O. Bevir, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN), heavy cruisers HMS Cumberland (Capt. G.H.E. Russell, RN), HMS Cornwall (Capt. C.F. Hammill, RN) (detached), HMAS Australia (Capt. R.R. Stewart, RN), HMS Devonshire (Capt. J.M. Mansfield, DSC, RN), light cruisers HMS Delhi (Capt. A.S. Russell, RN) (detached) and HMS Dragon (Capt. R.J. Shaw, MBE, RN), destroyers HMS Echo (Cdr. S.H.K. Spurgeon, DSO, RAN), HMS Eclipse (Lt.Cdr. I.T. Clark, RN) and HMS Escapade (Cdr. H.R. Graham, DSO, RN), HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Foresight (Lt.Cdr. G.T. Lambert, RN), HMS Fortune (Cdr. E.A. Gibbs, DSO, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) and HMS Greyhound (Cdr. W.R. Marshall A'Deane, DSO, DSC, RN) and HMS Inglefield (Capt. P. Todd, DSO, RN), sloops HMS Bridgewater (A/Cdr.(Retd.) H.F.G. Leftwich, RN), HMS Milford, Savorgnan de Brazza (Free French, Lt.Cdr. A. Roux), Commandant Dominé (Free French, Lt. J.P.Y. de la Porte des Vaux) and Commandant Duboc (Free French, Lt.Cdr. M.A.F. Bourgine) , auxiliary patrol vessel Président Houduce (Free French, Lt. L. Deschatres) and the net tender HMS Quannet (T/Lt. C.E. Richardson, RNR).
Vice-Admiral Cunningham then transferred his flag from HMS Devonshire to HMS Barham accompanied by General Irwin and his staff. All was ready for the passage to Dakar but at General de Gaulle request the opening day was deferred to 23 September.
The task force would arrive off Dakar at dawn on 23 September. It would patrol in groups while French airmen would take off in aircraft from HMS Ark Royal and land at Ouakam airfield to endeavour to win over the French air force. British aircraft meanwhile would drop proclamations and announcements of the arrival of de Gaulle on the town of Dakar and the forts.
An hour later, Captain d’Argenlieu would land in a motor boat with a communication from General de Gaulle to the Governor requiring a reply within two hours. The Free French sloops carrying de Gaulle’s troops would approach and, if necessary, force the anti-submarine boom. Meanwhile Vice-Admiral Cunningham’s Force with fighter and anti-submarine patrols would lie off the harbour as follows.
Group A) The two French troopships, Pennland and Westernland, ten miles to the south of Cape Manuel.
Group B) HMS Barham, HMS Resolution and the cruisers, two miles to the seaward of group A.
Group C) The four British troopships, two miles to the seaward of Group B.
Group D) The other transports, six miles to the seaward of Group C.
Group E) HMS Ark Royal further to the seaward.
If there appeared to be a good chance of a favourable reception the Free French sloops would land their troops at one of the wharves while the French troopships made for the harbour.
It was hoped that the forts would be reluctant to fire on French ships and as soon as de Gaulle was firmly established the British Force would withdraw. If the forts offered serious resistance General de Gaulle would call on Vice-Admiral Cunningham to quell it with a minimum of force. If it was clear that an organised and continuous resistance would be offered and local authorities refused to parley, the Free French ships would withdraw out of range while the British force broke down resistance and landed troops to capture the town and its defences.
The possible contingencies would be referred to as situation ‘Happy’, ‘Sticky’ or ‘Nasty’ according to events. ‘Happy’ would mean a favourable reception and unopposed landing. ‘Sticky’ would mean resistance of a formal or sporadic nature. ‘Nasty’ would mean serious resistance. HM ships then would move in to engage the forts, and British troops would prepare to land.
Commencement of operations.
The forces left Freetown in three groups;
Group I consisted of the five transports escorted by HMS Bridgewater, HMS Quannet and President Houduce. It had already left Freetown on the 19th of September.
Group II consisted of the French troopships Pennland and Westernland, the food ship Belgravian and the three Free French sloops and also of the British troopships Ettrick, Karanja, Kenya and Sobieski escorted by HMS Devonshire, HMS Faulknor, HMS Forester, HMS Fury and HMS Milford (Capt.(Retd.) S.K. Smyth, RN). This group departed Freetown at 0600/21.
Group III consisted of HMS Barham, HMS Resolution, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Inglefield, HMS Greyhound, HMS Foresight, HMS Fortune, HMS Echo and HMS Escapade. This group departed Freetown at 0900/21. Early the next day this group was joined by HMS Cumberland, HMAS Australia and HMS Dragon.
The weather was fine and the sea was calm. Passage north to Dakar was uneventful. Aircraft from the Ark Royal conducted photographic reconnaissance on the 22nd.
At Dakar there were the following French warships; the uncompleted battleship Richelieu, the light cruisers Georges Leygues and Montcalm, the destroyers Le Fantasque, Le Malin, L’Audacieux and Le Hardi, three submarines Ajax, Perseé and Bévéziers (this last one was in dock) and some smaller vessels.
Zero hour for the commencement of the attack was set at 0550/23 and all ships managed to get into their assigned positions at that time. Visibility was however very poor due to mist, and was no more then 3 to 5 nautical miles. The fog was expected to clear during the day but in fact the opposite happened and visibility decreased steadily during the day. The shore was rarely sighted.
During the forenoon, the warships and transports patrolled up and down. Punctually at daybreak (0505 hours), HMS Ark Royal, then some 25 nautical miles from Dakar, flew off five aircraft most of which were manned by Free French flying officers. Two of these aircraft landed safely at Ouakam airfield at 0554 hours. Within 10 minutes a signal was displayed indicating ‘success’. This however proved to be premature. At 0608 hours a third aircraft landed on the airfield. Disembarked her three passengers and then took off without much interference. Two minutes later the ‘success’ signal was removed and a fourth aircraft broke off her attempt to land. Nothing more was heard from the Free French officers that had been landed. Two fighters were then seen to take off and they chased away the three remaining aircraft together with AA fire from the Richelieu and from the battery on Gorée Island. The attempt to win over the airfield had failed.
HMS Barham had sighted the Westernland at 0600 hours and Vice-Admiral Cunningham had sent a message of goodwill to General de Gaulle. The Free French sloop Savorgnan de Brazza was of the boom at 0555 hours and her two motor boats, with Captain d’Argenlieu and the Generals other emissaries were on their way to the boom gate at 0605 hours. The gate was open and at 0640 hours they were entering the harbour.
Visibility was poor, and the Savorgnan de Brazza took station of the boom to keep the boats in sight. The emissaries landed and encountered a hot reception. They were fired on and wounded in resisting an attempt to arrest them, but managed to re-embark and withdraw under fire. A blank round was fired at the Savorgnan de Brazza at 0745 hours followed by three salvoes, which fell astern. Just then the motor boats were sighted and at 0750 hours Captain d’Argenlieu sent a signal that he had met serious resistance. This reached Vice-Admiral Cunningham at 0807 hours. The other French sloops were to be at the boom at 0905 hours to pass it (or force it if needed) and land their troops. If the reception had been favourable the French troopships were then to enter the harbour to disembark the main body of troops. The Commandant Dominé and Commandant Duboc were actually at the boom at 0805 hours, one hour early. They encountered no opposition until they approached the mole. They were taken under fire with heavy machine guns and were ordered to stop. The Richelieu fired a blank round and then opened fire with small guns. Both sloops then turned for the gate under the cover of a smoke screen. Also the guns from the Gorée Island battery were joining in. At 0820 hours the Commandant Dominé and Commandant Duboc were sighted by the Savorgnan de Brazza which was intended to lead them in at 0905 hours. The sloops had not expected such a hostile reception and retired on the British Fleet which was sighted a 0900 hours.
Meanwhile HMS Barham at 0706 hours had turned north-north-west towards the land, and at 0740 hours Cape Manuel was in sight some 5 nautical miles away. At 0827 hours, with the land still just visible from HMS Barham Vice-Admiral Cunningham asked General de Gaulle whether he wished the British ships to close the shore and show themselves at the risk of being fired on. Five minutes later came the signal ‘proposals rejected’. At 0840 hours General de Gaulle signalled that the Richelieu and Gorée Island guns had been firing and that he had ordered his own ships to make a determined effort; if they failed he suggested that the Vice-Admiral should show himself of Dakar. Just then, one minute later, came the signal from the Savorgnan de Brazza confirming the emissary’s proposals had been rejected.
Situation deteriorates.
It was clear by this time an unfavourable situation was rapidly developing. General de Gaulle’s proposals to the Governor had been rejected and two of his emissaries had been seriously wounded, his sloops had been fired upon and the Vichy French ships in the harbour were raising steam. In spite of these manifest tokens of hostility the General apparently still hoped for a peaceful solution. At 0905 hours, however, Vice-Admiral Cunningham warned his force that the situation was developing towards ‘Sticky’.
Valuable and comprehensive reports were coming in from the British aircraft reconnoitring Dakar. Although these aircraft were fired on by all the French ships in the harbour and by machine guns on the jetty, Vice-Admiral Cunningham gave orders that a French flying boat over the fleet should not be attaked, for there still seemed to be hopeful signs that the French air force might join de Gaulle. At 0948 hours a signal arrived from HMS Ark Royal to say that one of the Gloire class cruisers had slipped. The Vice-Admiral at once instructed HMS Foresight, the northern destroyer of the anti-submarine screen, to order any French cruiser sighted to return to harbour. At 1005 hours, however, the shore batteries opened fire on HMS Foresight and the Vice-Admiral ordered her to withdraw following this with a signal to HMS Ark Royal to stand by with six aircraft to bomb Gorée Island. He also warned the French Admiral that if the fire were continued he would regretfully be compelled to return it. The French Admiral replied that if Vice-Admiral Cunningham did not wish him to fire he should remove himself more then 20 nautical miles from Dakar. Meanwhile the force had turned westwards at 1016 hours. Two minutes later Vice-Admiral Cunningham detached HMAS Australia to examine a ship reported to the north. At 1025 hours, HMAS Australia, identified two Le Fantasque class destroyers steering westwards and ordered them to return to harbour, backing up this order with a warning shot. They at once turned back and the Australia then resumed her place in line after having been fired upon by shore guns.
At 1030 hours, two La Galissonnière class cruisers were reported leaving Dakar and Vice-Admiral Cunningham at once informed the French that if their ships left the harbour he would use force to compel their return. Two French submarines were also reported to be underway and at 1050 hours Vice-Admiral Cunningham warned the French Admiral that if they left Dakar harbour he would attack them. One minute later a report came in that the submarines were passing the entrance and when a torpedo missed HMS Foresight Vice-Admiral Cunningham cancelled the order for HMS Ark Royal to bomb Gorée Island but to bomb the submarines instead. At the same time he detached HMS Inglefield and HMS Foresight to attack them and he also turned the remained of the force to close Gorée Island to support them. Almost immediately HMS Foresight came under fire and at 1051 hours she was hit forward by a shell. Thus the actual first hit was made by the French.
By 1100 hours the whole force was under fire from the guns at Cape Manuel. HMS Inglefield reported also being missed by a torpedo. Two minutes later HMS Inglefield and HMS Foresight were were engaging one of the submarines (the Perseé) on the surface to the north-westward. Events followed rapidly. HMS Inglefield was hit by a shore battery. By 1104 hours the submarine was sighted on the Barham’s port bow. She was engaged by the 6” guns from HMS Barham, HMS Resolution and HMS Dragon. She was badly hit and soon abandoned by her crew, finally sinking at 1137 hours in position 065°, Cape Manuel lighthouse, 2740 yards. Simultaneously HMS Barham fired five 15” gun salvoes at the Cape Manuel battery but accordingly to a subsequent French broadcast they caused heavy civilian casualties ashore.
When the force turned back to the south-westwards at 1107 hours, HMS Inglefield was again hit aft by a shore battery. With HMS Foresight she engaged the second submarine (the Ajax) which at once made for the harbour entrance, and Vice-Admiral Cunningham, still hoping for a peaceful solution, and in accordance with the agreement to use no more force then necessary to overcome sporadic resistance, ordered the force to cease fire.
At 1119 hours however, HMS Dragon, ordered to attack the second submarine, came under fire from the guns at Cape Manuel. The whole force at once turned west but though the land was barely visible through the mist, HMS Foresight and HMS Cumberland, which were close to HMS Barham were hit almost immediately by the shore guns. The damage to HMS Cumberland was serious. She was struck by what was thought to be an 11.2” shell (actually it was a 9.4” shell) just above the armour belt on the port side. The engine rooms became temporary untendable and she was forced to withdraw to Bathurst, taking no further part in the operation. Nothing further was to be gained by remaining close inshore and at 1135 hours the force turned to the southward.
At 1154 hours a signal from the High Commissioner, French West Africa was received stating ‘We confirm that we will oppose all landings, you have taken the initiative in causing French blood to flow’. The situation at noon was thus far from hopeful but it was decided a final attempt to land the Free French troops at Rufisque would be undertaken (operation ‘Charles’).
Situation ‘Sticky’.
Operation ‘Charles’ was to be a final attempt for a peaceful landing of the Free French troops at Rufisque Bay before beginning a systematic reduction of the Dakar defences as a preliminary to a British landing.
It was considered essential in this plan to maintain the French character of the landing as far as possible; the Free French transports were to be accompanied as far as possible by their own warships, and by two British destroyers only, HMS Inglefield and HMS Forester, which would lead them in and, if necessary, provide flanking fire.
At 1158 hours, Vice-Admiral Cunningham signalled to de Gaulle, ‘what about operation ‘Charles’ now ?’. The General replied at 1212 hours that he desired to to ahead with operation ‘Charles’ but that he required the latest reports. He was then given the latest aircraft reports, which showed no surface ships outside the boom. A zero hour for ‘Charles’ was then set at 1530 hours if the Generals ships could reach Rufisque Bay in time. A signal was sent to the entire force that the situation was now ‘Sticky’.
General de Gaulle then asked Vice-Admiral Cunningham what opposition might be expected from shore batteries and the Vice-Admiral replied that the bad visibility would help the forces taking part in ‘Operation Charles’. At 1335 hours HMS Barham proceeded westwards to endeavour to locate the General’s flagship the Westernland but she could not be found. HMS Barham then spent three hours searching for her in the mist.
A baffling phase of uncertainty followed. In the thick weather which precluded visual signalling between Barham and Westernland radio telephony and wireless communication between Vice-Admiral Cunningham and General de Gaulle, though at first satisfactory, deteriorated progressively during the afternoon. This was due to jamming of radio telephony by a heavy traffic of military signals between the Westernland herself and the Free French sloops. At the root of the trouble was the fact that General de Gaulle was in a separate ship. Everything possible had been done to improvise additional lines of communication, but these proved inadequate to meet the situation. For some three hours that afternoon all contact was lost with General de Gaulle and the French transports.
At 1358 hours Vice-Admiral Cunningham informed the Admiralty that de Gaulle was attempting a landing but at 1445 hours a signal was received from de Gaulle to say that he was awaiting instructions to which the Vice-Admiral replied at 1504 hours ‘carry out Charles, report zero hour’.
But to carry out ‘Charles’, however, HMS Inglefield and HMS Forester had to get in touch with the French transports, and despite repeated calls for their positions no one knew where they were.
An ultimatum was made ready to be sent to the authorities and people of Dakar informing them that failing to accept General de Gaulle proposals, the British fleet would open fire on the fortifications of Dakar. This was misunderstood by General de Gaulle and he thought that the ultimatum had already been delivered so he suspended ‘Operation Charles’. Troops would not be landed by the transports but only a smaller number would be landed by the French sloops. Vice-Admiral Cunningham was only informed about this after two hours.
Meanwhile further complications had arisen. Aircraft reported a French destroyer off Gorée Island (this was the L’Audacieux), threatening the approach to Rufisque Bay. HMAS Australia, HMS Fury and HMS Greyhound were detached at 1608 hours to ward her off. The French destroyer was engaged and set on fire after she had fired two torpedoes at HMAS Australia.
Around 1630 hours HMS Devonshire finally sighted the French transports some 20 nautical miles from Rufisque Bay. This meant that ‘Charles’ could not be completed before dark. These was at least one enemy submarine (possibly two) in the area. In these weather conditions it was not though possible to give sufficient protection to the transports in Rufisque Bay. On these grounds Vice-Admiral Cunningham cancelled ‘Operation Charles’ at 1642 hours.
Two minutes later an air report reached him reporting two La Galissonniere class cruisers three nautical miles north-north-east of Gorée Island which were steering towards Rufisque Bay at 17 knots. Vice-Admiral Cunningham at once turned the battleships towards Rufisque to cover the Westernland and Pennland in case they were still making for it. He held this course until 1710 hours and then altered to the southward to regain contact with the British transports. A signal timed 1635 hours from General de Gaulle that he expected to arrive at 1650 hours, which would be zero hour, reached Vice-Admiral Cunningham at 1720 hours. Actually at that moment the Free French sloops, having parted from the French transports at 1648 hours reached Rufisque Bay. It is not clear how they were missed by the Vichy cruisers, which and air report placed, together with a large destroyer, two nautical miles were of Rufisque at 1740 hours. This was the last air report, for at 1745 hours weather conditions obliged HMS Ark Royal to withdraw all reconnaissance aircraft. It did not reach Vice-Admiral Cunningham until 1835 hours.
Meanwhile at 1805 hours, General de Gaulle’s signal timed 1620 hours had at last arrived and the Vice-Admiral knew that the Free French sloops would probably be attempting a landing. He immediately sent off HMS Inglefield and HMS Forester, which found the Westernland in position 155°, Rufisque Bay, 10 nautical miles at 1835 hours.
Free French sloops at Rufisque, 23 September 1940.
As mentioned previously the Free French sloops parted company with the Westernland and Pennland at 1648 hours some 7.5 nautical miles from Rufisque to carry out ‘their mission’. There seemed to be considerable doubt as to what this mission was. It certainly was not ‘Operation Charles’ as had been intended. The landing party in each sloop consisted of about 60 ‘fusilier marines’, making it about 180 in total. They arrived off Rusfisque at 1720 hours. The Savornan de Brazza, whose draught was greater then the other two, anchored about 500 yards from the shore. The Commandant Dominé and Commandant Duboc pushed in right towards the jetty, and all three lowered their boats. Fire was almost immediately opened on the Commandant Duboc by a 4” gun in a blockhouse at Cap de Biches. She was hit and one officer was killed and three men seriously wounded. Fire was opened by the sloops and the battery was knocked out. The Commandant Duboc then retired behind a smoke screen. Two of the Savorgnan de Brazza’s motor boats towing whalers were making for the beach to the right of the jetty. When within 300 yards from the shore they met with heavy machine gun fire and stopped, while the Commandant Dominé, covering them, opened fire on the shore emplacements, but could not locate them in the failing light and mist. But then at 1758 hours a signal was received from the Westernland cancelling ‘Operation Charles’. The landing parties were then re-embarked and at 1838 hours the three Free French sloops left for their patrol line.
Situation ‘Nasty’.
The day was drawing to a close. All hopes of a friendly reception had been scattered. The ships were lying in a fog off a hostile coast with submarines in the vicinity. Vice-Admiral Cunningham and General Irwin considered landing British forces at Rufisque, but decided against it.
At 1910/23, while the Free French sloops were closing the Westernland and Pennland, Vice-Admiral Cunningham with the ‘battlefleet’; HMS Barham, HMS Resolution and HMS Devonshire, turned west to cover the transports (which were still to the southward) for the night.
Ten minutes before, at 1900 hours, the Vichy French Governor General, M. Pierre Boisson, had in a broadcast stated emphatically that Dakar would not submit. There could be no further hope of a peaceful settlement and at 2052 hours General de Gaulle was asked whether he agreed that the situation was now ‘Nasty’ and to the issue of the ultimatum. The Admiralty had been kept fully informed of the situation and at 2105 hours a personal message from the Prime Minister arrived ‘Having begun we must go on to the end, stop at nothing’.
General de Gaulle reply arrived at 22235 hours, he agreed that the situation was now ‘Nasty’ and that the ultimatum should go out. It was broadcast at 2345 hours in French and English to the Admiral, Governor General and people of Dakar. They had prevented General de Gaulle from landing. Dakar might be seized by the Germans / Italians and the Allies were bound to prevent this. Their forces were approaching. The conditions offered must be accepted by 0600/24 or the guns of the Allies would open fire.
The Governor General’s answer reached Vice-Admiral Cunningham at 0400/24. It was an unqualified refusal; ‘I shall defend Dakar to the end’. There was nothing more to be said. At dawn the battlefleet was approaching the coast to take up their bombardment stations.
The attack on Dakar, the attack opens, 24 September 1940.
HMS Ark Royal had orders to carry out a reconnaissance as early as possible backed up by bombing attacks on the Richelieu, Forts Manual and Gorée, and the two light cruisers lying off Dakar.
Visibility had greatly improved since the previous day and was six nautical miles at 0625 hours when the first striking force of six Skua’s of No. 800 Squadron, loaded with 500 lb. S.A.P. bombs, took off from HMS Ark Royal to attack the cruisers and other suitable targets.
At 0703 hours aircraft reported a destroyer damaged off Rufisque, two cruisers in the roads and three destroyers coming slowly out. It was seven minutes later when the Skuas carried out a high level bombing attack on the Richelieu and one of the destroyers. By this time the battlefleet was on its bombardment course and the Barham’s spotting aircraft was in the air. They were followed by six Swordfish of No. 820 Squadron loaded with G.P. bombs for an attack on the town of Dakar, which was to synchronise with the ships bombardment.
It had been calculated that at 0725 hours the battlefleet would be within 16000 yards of the forts and fire could be opened, but unfortunately when the moment arrived nothing could be seen of them in the prevailing mist. A long range bombardment was clearly impractical, and the fleet turned away temporarily in order to re-dispose the cruisers and destroyers for a short range attack. At the same time HMS Fortune was detached to obtain a shore fix, but she came under accurate fire from the forts and her fix proved unreliable.
The Ark Royal’s first Swordfish striking force was diverted to bomb Cape Manuel. At 0800 hours she despatched another striking force of six Swordfish of No. 810 Squadron loaded with S.A.P. bombs to attack the Richelieu. It was hoped that by the time it attacked the Richelieu the opening of the naval bombardment would provide a diversion, but this did not occur; one Swordfish was shot down and two others failed to return.
A diversion was also provided on the enemy’s side. At 0805 hours HMS Fortune, which had rejoined the battlefleet, reported a submarine contact inside the screen and dropped three depth charges. At 0831 hours the Vichy French submarine Ajax surfaced. She was unable to dive or move and surrendered. Her whole crew was rescued before she sank. The Fortune’s boarding party found six ‘tube ready’ light burning, and it was evidently only the destroyers depth charges that saved the fleet from attack.
The incident still further delayed the bombardment and it was not till 0920 hours, forty minutes after the first Swordfish striking force had attacked the Richelieu with S.A.P. bombs, that Gorée Island was sighted. At 0935 hours the shore batteries opened fire and one minute later the Barham and Resolution replied with their 15” guns, firing on the Richelieu at ranges of 13600 to 15000 yards respectively, while the cruisers HMAS Australia and HMS Devonshire engaged a destroyer of the Le Fantasque class.
The first bombardment.
As soon as the British ships opened fire a French destroyer of the Le Fantasque class steamed south laying a smoke screen to the eastward of the anchorage and Gorée Island. The French cruisers inside the boom to the northward, sheltering amongst the many merchant vessels, also made a smoke screen, which drifted slowly south and, combining with the mist and heavy smoke from the vicinity of the Richelieu, eventually obscured all targets.
Shooting became extreme difficult, for range taking was nearly impossible. There were other serious handicaps. HMS Barham, which was newly commissioned after repairs, had never carried out any bombardment practice. Neither battleship had done any concentration firing, and neither had its customary observer in the air.
After engaging the Richelieu for nine minutes the Resolution’s director training gear failed and she shifted fire to the Cape Manuel battery, on which she probably obtained a hit. The Barham’s aircraft reported several straddles across the Richelieu, which was thought to have been hit. The smoke-laying cruiser was still active, and at 0942 hours the Barham’s 6” guns engaged her without success.
Meanwhile the Devonshire and Australia had engaged and damaged a large destroyer of Rufisque which was subsequently engaged by the Inglefield, Foresight and Forester, and left burning.
The fire encountered by the fleet consisted of occasional one- and two-gun salvoes (yellow splash) from the Richelieu’s 15” guns, salvoes of 9.4” from Cape Manuel (white splash), Gorée Island, and an unseen battery, and a number of smaller rounds from the Richelieu and various shore batteries. The French fire was slow but accurate. By 1010 hours the targets were wholly obscured by smoke, and shortly afterward the fleet withdrew to the southward, leaving the Ark Royal to report the result of the bombardment.
As the fleet made to the south, Vichy Glenn-Martin bombers made high level attacks on it without success, though three bombs fell close to HMAS Australia.
At 1141 hours the Ark Royal reported the results of the bombardment; several near misses with bombs on the Richelieu; one near miss with a bomb on a destroyers; one 15” hit on the Cape Manual battery, which had ceased fire; one 15” hit and repeated straddles on the Richelieu; straddles across the cruisers in Hahn Bay, one of which was set on fire aft. No hits had been obtained on the Gorée Island battery.
The second bombardment.
At 1146 hours relief spotting aircraft for the battleships were ordered and targets for a further bombardment at 1315 hours were allocated as follows; the Barham on Richelieu; the Resolution on Goréé Island; the Devonshire on Cape Manuel; the Australia on the cruisers inside the boom. The spotting aircraft took off from HMS Ark Royal at 1220 hours and as a report reached her about this time that Vichy cruisers and destroyers were proceeding towards Rufisque, a torpedo striking force was got ready to attack them immediately after the second bombardment.
French aircraft were still busy. At 1217 hours a French bomber dropped six bombs close to HMS Barham. It was driven off by Skuas. Shortly afterwards a shadowing cruiser was sighted while the fleet was approaching Gorée Island. She was engaged from 14500 yards by the main armament from HMS Barham and HMS Resolution. She then turned away under a smoke screen. Fire was then checked. At 1248 hours, Vice-Admiral Cunningham ordered the Devonshire and Australia to engage her, but cancelled this order five minutes later when his destroyers, which were coming under an accurate fire from shore batteries, were told to take station on his disengaged side. By an unfortunate mischance the first order – to engage the cruiser – never reached the Devonshire and she interpreted Vice-Admiral Cunningham’s second signal ‘cruisers negative engage’, which referred only to the hostile cruiser, as an order to take no further part in the bombardment. Accordingly at 1300 hours she turned away to the east with HMAS Australia and neither ship took part in the subsequent bombardment.
The bombardment was reopened in the afternoon, at 1300 hours HMS Barham obtained a shore fix and turned north-west on her bombardment course. Five minutes later she engaged the Richelieu bearing 330°, range 17000 yards. HMS Resolution opened fire on Gorée Island from 16000 yards. The batteries at Cape Manuel, which had been reported hit, Gorée Island and Dakar Point at once replied. The Richelieu also opened fire with her 15” guns firing two gun salvoes with fair accuracy. She continued firing until her fire was blanked by the mole.
The French gunfire concentrated on the Barham and was heaviest between 1312 and 1320 hours. At 1315 hours an 9.4” projectile hit the Barham. At 1320 hours she was hit again and two minutes later she was hit twice.
The smoke screen tactics of the forenoon were repeated as soon as the British ships were sighted, and by 1311 hours the targets again became obscured. Although spotting aircraft reported that the Barham was straddling the Richelieu, the salvos appeared to be out for line, and apparently the Vichy French battleship was not being hit. The Resolution did not succeed in silencing the main Gorée Island battery and it is doubtful whether she was being spotted on the correct target. She was straddled by several salvoes of 5.4” and 6” shells from the shore batteries. At 1323 hours the Richelieu ceased fire. A minute later HMS Barham and HMS Resolution broke off the attack and at at 1326 hours the shore batteries also ceased firing.
The results of the bombardment were not encouraging. Despite the expenditure of nearly 400 rounds of 15” ammunition, none of the larger shore batteries had been silenced. The Richelieu was still in action, and the position of several 5.4” batteries, whose fire had proven effective against the destroyers, and would be still more so against the transports, had not even been located.
In spite of the poor visibility the fire of the shore batteries had been remarkably accurate and indicated that their fire was directed by listening devices rather then from forward observation posts, from which the battlefleet would generally had been out of sight. French air action had increased considerably since the previous day and the French will to resist appeared unimpaired. A report from HMS Ark Royal stated that the hostile attitude of the French fighters had made it hazardous for her aircraft to operate in the Dakar harbour area.
The question of a landing in force still remained. In these circumstances Vice-Admiral Cunningham decided to consult General de Gaulle and at 1400 hours the Barham withdrew to the southward to meet the Westernland before dark.
Swordfish aircraft attack the French cruisers.
Then minutes later, at 1410 hours, HMS Ark Royal’s striking force of nine Swordfish aircraft of No. 820 and 810 Squadrons took off while a fighter escort of three Skuas to attack the Vichy-French cruisers proceeding towards Rufisque. At 1440 hours the leader was forced down with engine trouble, his crew being picked up by the destroyer HMS Escapade. At 1500 hours the eight remaining Swordfish Swordfish attacked the two La Galissonnière class cruisers and a destroyer in the bay. In the prevailing haze the attack, which was made from an east-south-easterly direction, took the French by surprise. When the first sub-flight came down just outside the anti-submarine nets the three vessels were barely moving, but they immediately put their helms hard over and turned to port at full speed. The Swordfish claimed hits on one of the cruisers and the destroyer but this seemed to be doubtful. One Swordfish was forced down by AA fire on her way back to the Ark Royal. The crew was rescued by the destroyer HMS Echo.
Conference with General de Gaulle.
HMS Barham stopped at 1615 hours. General de Gaulle then came on board to confer with Vice-Admiral Cunningham and General Irwin. General de Gaulle, though deeply distressed and surprised about the nature of the defences, was still confident that the situation in French West Africa would improve as the power of his movement grew stronger. He explained that in view of the determined opposition encountered, and the probable destructive effects of the bombardment, it was imperative, from the point of view from the French opinion, that he should not be closely connected with the destruction and loss of French life, which had presumably taken place, lest his further utility to the common cause should be hopelessly compromised.
Though he would prefer not to use his troops he was prepared, if really needed, to support a British landing regardless of consequences. He considered, however, that a British landing was no longer feasible, and emphasised that a reverse would be a most serious check to the Allied cause.
He blamed himself for undue optimism in underestimating the possibility of a resolute defence, and suggested that the bombardment should be suspended at his direct request and Dakar so informed; that his forces should go to Bathurst for exercises, with a view of a possible advance upon Dakar over land; that British naval action should be taken to cover his passage and prevent the reinforcement and revictualling of Dakar.
General de Gaulle returned to the Westernland at 1800 hours. The situation was considered by Vice-Admiral Cunningham and General Irwin in the light of these proposals. A Swordfish, which had crashed near the Barham at 1830 hours, reported that one cruiser was beached and burning east of Rufisque, one buring in Gorée Bay, and two detroyers were beached in Hann Bay (this information was subsequently found to be incorrect). It was essential to immobilise the Vichy French cruisers and neutralise the main armament of the French forts before attempting a landing. It was decided that the attack on the defences must be renewed the next day if weather conditions were favourable. General de Gaulle and the Admiralty were informed accordingly and dispositions were made for a landing of British troops at Rufisque, to follow up any success obtained by the bombardment.
Final bombardment. HMS Resolution torpedoed.
The next day, 25 September 1940, broke fine and clear with extreme visibility. The Ark Royal at 1531/24 had proposed bombing Ouakam and Gorée at dawn and at 2348/24 was ordered to do so, but owning to wireless congestion, this was not received until 0200/25 when Captain Holland considered it too late. The targets allocated to the battleships and cruisers were the same as for the second bombardment; spotting aircraft, with fighter protection, were to be in position at 0900/25. At 0530 hours three reconnaissance aircraft took off from the Ark Royal, but by 0700 hours, two had been driven back by French fighter patrols. At 0754 hours, HMS Devonshire sighted a submarine submerging some eight nautical miles to the east of the battlefleet, which was then some 25 nautical miles to the south of Dakar. HMS Forester was at once detached to hunt it, leaving only two destroyers to screen the battlefleet.
At 0803 hours they were ordered to withdraw to the disengaged flank as soon as the shore batteries opened fire. The battleships were then steaming towards Gorée Island ready to open fire, with the cruisers three miles away to the east. HMS Resolution had orders to take independent avoiding action if necessary during the bombardment. At 0857 hours a circular buoy was sighted which HMS Barham fired on, suspecting it to be a sound locating device. One minute later the Richelieu opened fire on HMS Barham from a range of 23000 yards.
At 0901 hours the signal to turn to the bombarding course (050°) was hauled down in HMS Barham. It was not only the British which acted on this signal. Captain Lancelot of the Vichy submarine Bévézièrs was watching the approaching battleships though the periscope. Experience with the Royal Navy before the fall of France had taught him our manoeuvring signals. On seeing ‘Blue 7’ hoised, he waited for it to be hauled down; then fired his torpedoes at the turning point. Thus it came about that as the Resolution was turning, five torpedoes were seen approaching her port beam. Already committed to the turn she could only apply full helm in the hope of turning short and combing the tracks. In this she almost succeeded, for three torpedoes passed ahead and another narrowly missed her astern. The fifth, however, struck her on the port side amidships causing serious flooding, but fortunately no loss of life. HMS Barham avoided the three torpedoes that had missed the Resolution ahead and they passed astern, exploding harmlessly on the bottom.
HMS Resolution, which had developed a list of 12° to port, was still able to steam. At 0905 hours HMS Barham opened fire on the Richelieu from 21000 yards and also the cruisers engaged their targets, HMS Devonshire firing on Cape Manuel and HMAS Australia on the French cruisers inside the boom. Fire from the Richelieu and shore batteries was deliberate and accurate; it was concentrated on HMS Barham and frequently straddled her. The British cruisers were also under heavy fire. HMS Barham was hit once and HMAS Australia twice. HMS Resolution was badly damaged and it was necessary for her to withdraw and at 0912 hours HMS Barham turned to cover her. About this time HMS Foresight reported that she had sunk the French submarine with depth charges (but this was not the case). She and HMS Inglefield were then ordered to cover HMS Resolution with a smoke screen. The two cruisers were recalled. About 0918 hours Vichy French fighters shot down the Australia’s Walrus aircraft. HMS Forester was ordered to try to rescue the crew but she came under heavy fire from shore batteries and had to retire.
At 0921 hours, HMS Barham ceased fire and took station close astern of HMS Resolution with HMS Devonshire and HMAS Australia on each quarter. The Ark Royal was ordered to provide maximum fighter protection, and the battlefleet withdrew to the southward.
HMS Resolution was steaming at 10 knots and between 0940 and 0950 hours two high level bombing attacks were made on her, both of them were unsuccessful. The whole force now steered south-west at the best possible speed and by 1134 hours the flagship, HMS Barham had the whole force in sight.
The Vice-Admiral now had to decide whether to continue the attack on Dakar or to withdraw his force. The chance of capturing Dakar was clearly remote and in the end it was decided to discontinue the attack and to withdraw his force to Freetown without further delay. A signal to this effect was made at 1152 hours.
Withdrawal to Freetown.
Before a signal could be passed to the Admiralty a signal was received from the Prime Minister who was aware of the damage to HMS Resolution. Vice-Admiral Cunningham was ordered to abandon the enterprise against Dakar.
By 2000/25, HMS Barham was about 100 nautical miles south of Dakar steering south at 7 knots. The next day the sea was smooth as the weather was fine. HMS Resolution was taken in tow by HMS Barham. On the 27th the tow parted but was quickly secured again and the battleships were able to continue southwards at 6 knots.
HMS Cumberland rejoined the force having effected temporary repairs at Bathurst. HMS Cornwall and HMS Delhi had also joined after having chased the French cruiser Primaguet and the tanker Tarn.
At 0550/29, HMS Barham passed the boom at Freetown followed by the rest of the force. So ended a difficult operation. No British warship had been sunk but several had been damaged. HMS Cumberland was out of action for 13 days and HMS Fiji for six months. HMS Resolution was temporarily patched up at Freetown but was not fully operational. She returned to England six months later but was then sent on to the U.S.A. for full repairs. It was a full year later before she was again ready for active service. Five more ships HMS Barham, HMAS Australia, HMS Dragon, HMS Inglefield and HMS Foresight were also damaged but their fighting efficiency was not seriously impaired. (36)
28 Sep 1940
Around 1345N/28, HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN) arrived at Freetown from operations off Dakar. (42)
29 Sep 1940
At 0700/29, HMS Renown (Capt C.E.B. Simeon, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), escorted by HMS Hotspur (Cdr. H.F.H. Layman, DSO, RN) , HMS Gallant (Lt.Cdr. C.P.F. Brown, RN) and HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St J. Morgan, RN) departed Gibraltar. In the Straits they were joined at 0730 by HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSC, RN) which had been on patrol. Course was set to the west.
The Admiralty was under the impression that the Vichy-French battleship Richelieu had departed Dakar en-route possibly to a Bay of Biscay port. And if that was correct the ship would fall in the hands of the Germans and this was to be avoided at all costs so HMS Renown was ordered to intercept.
On leaving harbour two Vichy-French destroyers were sighted proceeding westwards, these were the Epée and Frondeur. They increased speed to bout 28 knots on sighting HMS Renown. A signal was then sent to the Admiralty that HMS Renown had been seen proceeding westwards by the French ships.
At 1307/29, when in position 35°41'N, 07°14'W, a Vichy-French aircraft was sighted on Renown's port quarter. This aircraft shadowed HMS Renown until 1350/29 and then made off to the south-eastward. That Renown was shadowed was also reported to the Admiralty.
At 1333/29, a signal was received from the Admiral Commanding , North Atlantic Station, that owing to recent attacks on our aircraft by Vichy-French fighters, close observation of Casablanca was impracticable, and it wasintheded to maintain a patrol to the north-west of Casablanca in case Richelieu had gone there and was later to sail for a Bay of Biscay port. HMS Renown now set course towards Cape Finisterre.
At 2110/29 a signal was received from the Admiralty (sent 1910/29) which stated that air reconnaissance off Cape Finisterre was arranged for 29 September P.M. and that it was intended for HMS Renown to patrol to the westward of Gibraltar between 10°00'W and 15°00'W In view, however, of the report that two German merchant ships with troops on board had been reported in the south-east corner of the Bay of Biscay the Admiralty thought it possible that these vessels might be proceeding to capture the Azores, HMS Renown was ordered to proceed to the vicinity of these islands.
Vice-Admiral Somerville then requisted the RFA tanker Orangeleaf (5927 GRT, built 1917) to be sent out from Gibraltar to patrol on the parallel of 37°30'N between 27°00'W and 30°00'W. Later a signal was received that Orangeleaf was expected to arrive on the eastern edge of that patrol area at 1100/4.
At 0039/30, a signal was received from the Admiralty stating that if the Richelieu was encountered she was to be shadowed.
At 1240/30, when in position 36°23'N, 14°36'W, a merchant ship was sighted bearing 204°, range 14 miles. HMS Encounter was ordered to investigate and reported that it was a Greek ship and that she was allowed to proceed.
It was intended to oil the destroyers during 1 October but the first attempt (to oil HMS Hotspur) proved that this was not possible owing to the north-easterly swell.
At 1901/30, a signal had been received from the Admiralty giving possible landing places in the Azores, Vice Admiral Somerville decided to establish destroyer night patrols off the north and south approaches to Horta, Ponta Delgada and Angra. HMS Renown would remain in support of the destroyers to the south-west but unscreened.
At 1800/1 the destroyers were detached and were ordered to take up the following positions Encounter - Northern approaches to Horta. Hotspur - Southern approaches to Horta. Gallant - Off Angra. Firedrake - Off Ponta Delgada.
The destroyers were ordered to rejoin HMS Renown at 1300/2 in position 37°00'N, 28°10'W, for fuel, since they would have insufficient remaining by the time the Orangeleaf would arrive.
By noon on 2 October all destroyers were back with HMS Renown at the rendezvous and oiling commenced. There was still a south-easterly swell running, which made conditions difficult, but all destroyers were given 150 to 170 tons of fuel, together with fresh provisions, without incident. The last destroyer (order had been Encounter - Hotspur - Gallant - Firedrake) completed after dark at 2100 and all four destroyers were ordred to resume their patrols with HMS Renown proceeding to the westward.
The fuel given to the destroyers was sufficient to enable them to maintain their patrols until after daybreak on 4 October and then to proceed with HMS Renown to Gibraltar without refueling.
At 1912/2 Admiralty signal 1835/2 was received ordering HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN) to carry out air reconnaissance between the Azores and Cape Finisterre wth the object of identifying shipping approaching the Azores.
At 0010/4, Vice Admiral Somerville was ordered to leave patrol that morning and return to Gibraltar.
All destroyers had previously been instructed to rendezvous with HMS Renown in the forenoon and by noon the last one, HMS Firedrake had rejoined. She had intercepted and investigated two Portugese ships therefore she was a little late in rejoining.
At 1345/4, a ship was sighted well down to the westward and HMS Hotspur was sent to investigate. As anticipated this ship proved to be the Orangeleaf and she was instructed to return to Gibraltar.
At 1807/4, HMS Hotspur was detached again to investigate a merchant vessel which proved to be American and it was allowed to proceed.
At 0230/5, a darkened ship was sighted ahead crossing Renown's track from south to north. This proved to be the merchant vessel Highland Monarch (British, 14139 GRT, built 1928).
At 0810/5, a Greek vessel with Swiss markings was sighted. This ship had been reported to be in the area and was allowed to proceed.
During the forenoon of the 5th all ships carried out gunnery exercises.
At 1215/5, smoke and ships were sighted to the north-west and once again HMS Hotspur was sent to investigate. She was soon recalled as it appeared to be convoy SLS 49.
In the afternoon of the 5th all ships carried out AA gunnery exercises.
In the evening of the 5th dummy torpedo attacks were carried out by the destroyers on HMS Renown.
In the forenoon of the 6th a search and plotting exercise was carried out. Northing furter occured on the 6th.
HMS Renown, HMS Hotspur, HMS Gallant, HMS Firedrake and HMS Encounter arrived at Gibraltar at 0830/7. (43)
30 Sep 1940
Around 0630N/30, the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN), heavy cruiser HMAS Australia (Capt. R.R. Stewart, RN) and the destroyers HMS Greyhound (Cdr. W.R. Marshall A'Deane, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN) and HMS Fortune (Cdr. E.A. Gibbs, DSO, RN) departed Freetown for the Clyde.
Around 1900Z/3, the destroyers parted company to return to Freetown.
At 1525A/4, HMS Ark Royal flew off seven Swordfish aircraft for an air search on the line Azores - Cape Finisterre as reports had been received about a possible German invasion of the Azores. The aircraft returned about two hours later having seen nothing.
Around 2200A/4, HMAS Australia parted company to patrol off the Azores. HMS Ark Royal now proceeded on unescorted.
Around 0830A/6, HMS Ark Royal made rendezvous with the aircraft carrier HMS Argus (Capt. E.G.N. Rushbrooke, DSC, RN) and the destroyers HMS Havelock (Lt.Cdr. E.H. Thomas, RN and HMS Highlander (Cdr. W.A. Dallmeyer, RN). Shortly afterwards the destroyers HMS Hurricane (Lt.Cdr. H.C. Simms, RN) and a little later HMS Harvester (Lt.Cdr. C.M. Thornton, RN) also joined company.
Around 2200Z/6, HMS Harvester was detached to go to the aid of the torpedoed British tanker British General. She did however not sight the tanker and the ship was lost with the entire crew.
Around 0500A/8, HMS Argus parted company and proceeded up the Clyde to Greenock taking HMS Hurricane with her.
HMS Ark Royal arrived at Liverpool in the afternoon where she was then immediately docked in the Gladstone Dry Dock for a refit. She had flown off all her aircraft during the day.
HMS Havelock and HMS Highlander then went on to Plymouth where they arrived later on the 8th as did HMS Harvester. (44)
29 Oct 1940
HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN) is undocked and then departed Liverpool around 1100A/29 for the Clyde. En-route some aircraft were flown on.
She arrived in the Clyde around 0030A/30. (45)
31 Oct 1940
The aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN) landed on her aircraft while underway in the Clyde area. One Fulmar crashed into the sea, it's crew being rescued by the destroyer HMS Duncan (Cdr. A.D.B. James, RN).
Around 1300A/31, HMS Ark Royal, light cruiser HMS Glasgow (Capt. H. Hickling, RN), destroyers HMS Isis (Cdr. C.S.B. Swinley, DSC, RN), HMS Foxhound (Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN), HMS Duncan and the troop transport Pasteur (British, 29253 GRT, built 1938) departed the Clyde for Gibraltar.
Around 0815A/5, they were joined by the heavy cruiser HMS Berwick (Capt. G.L. Warren, RN).
Around 0900A/5, they were joined by the destroyers HMS Wishart (Cdr. E.T. Cooper, RN) and HMS Vidette (Lt. E.N. Walmsley, RN).
Around 0930A/5, HMS Ark Royal parted company to proceed ahead of the other ships to Gibraltar escorted by HMS Wishart and HMS Vidette. They arrived at Gibraltar around 1345A/6. Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN then hoisted his flag in HMS Ark Royal.
Around 1500A/6, HMS Berwick and HMS Glasgow arrived at Gibraltar.
Around 1700A/6, the Pasteur, HMS Isis, HMS Foxhound and HMS Duncan arrived at Gibraltar. (46)
4 Nov 1940
Several operations in the Mediterranean.
Operation MB 8, convoy operations in the Eastern Mediterranean.
Operation Coat, transfer of reinforcements from the Western Mediterranean to the Eastern Mediterranean.
Operation Crack, air attack on Cagliary, Sardinia.
Operation Judgment, air attack on Taranto.
4 November 1940.
Convoy AN 6 departed Port Said / Alexandria today for Greece. The convoy was made up of the following tankers; Adinda (Dutch, 3359 GRT, built 1939), British Sergeant (5868 GRT, built 1922), Pass of Balhama (758 GRT, built 1933) and the transports Hannah Moller (2931 GRT, built 1911), Odysseus (Greek, 4577 GRT, built 1913). Several more transports (probably Greek) were also part of this convoy.
The Pass of Balhama sailed from Alexandria, the others from Port Said.
The convoy was escorted by the A/S trawlers HMS Kingston Crystal (Lt.Cdr. G.H.P. James, RNR) and HMS Kingston Cyanite (Skr. F.A. Yeomans, RNR).
HMS Ajax (Capt. E.D. McCarthy, RN) and HMAS Sydney (Capt. J.A. Collins, CB, RAN) both proceeded from Alexandria to Port Said on this day. At Port Said the were to embark troops for Crete.
Owning to breakdowns in Kingston Crystal and Kingston Cyanite, HMS Dainty (Cdr. M.S. Thomas, DSO, RN), HMS Kingston Coral (Skr. W. Kirman, RNR) and HMS Sindonis (Ch.Skr. G. Rawding, RNR) departed Alexandria late on the 4th to rendez-vous with convoy AN 6.
5 November 1940.
Convoy MW 3 departed Alexandria for Malta. This convoy was made up of the transports Devis (6054 GRT, built 1938), Rodi (3220 GRT, built 1928, former Italian), Volo (1587 GRT, built 1938), Waiwera (12435 GRT, built 1934) and the Royal Fleet Auxiliary tanker Plumleaf (5916 GRT, built 1917).
Escort was provided by the AA cruisers HMS Coventry (Capt. D. Gilmour, RN), HMS Calcutta (Capt. D.M. Lees, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Diamond (Lt.Cdr. P.A. Cartwright, RN), HMAS Vampire (Capt. H.M.L. Waller, DSO, RAN), HMAS Voyager (Cdr. J.C. Morrow, DSO, RAN), HMAS Waterhen (Lt.Cdr. J.H. Swain, RN) and the minesweeper HMS Abingdon (Lt. G.A. Simmers, RNR).
Also sailing with this convoy were the transport Brisbane Star (12791 GRT, built 1937) and the Royal Fleet Auxiliary tanker (5917 GRT, built 1917), the the armed boarding vessels HMS Chakla (Cdr. L.C. Bach, RD, RNR) and HMS Fiona (Cdr. A.H.H. Griffiths, RD, RNR), net tender HMS Protector (Cdr. R.J. Gardner, RN). They were to sail with this convoy until off Crete when they were to be detached to proceed to Suda Bay.
HMS Ajax and HMAS Sydney departed Port Said for Suda Bay with Headquarters, 14th Infantery Brigade, one light and one heavy AA battery and administrative troops.
6 November 1940.
Vice-Admiral light forces, in HMS Orion (Capt. G.R.B. Back, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral H.D. Pridham-Whippell, CB, CVO, RN), left Alexandria for Piraeus to consult with the Greek authorities. Also some RAF personnel was embarked for passage.
At 0600B/6, convoy AN 6 was in position 34°40’N, 22°20’E.
The Commander-in-Chief departed Alexandria with the battleships HMS Warspite (Capt. D.B. Fisher, CBE, RN, flying the flag of Admiral Sir A.B. Cunningham, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Valiant (A/Capt. J.P.L. Reid, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Illustrious (Capt. D.W. Boyd, DSC, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral A.L.St.G. Lyster, CVO, DSO, RN). They were escorted by HMS Hyperion (Cdr. H.St.L. Nicolson, DSO and Bar, RN), HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN), ), HMS Havock (Cdr. R.E. Courage, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Hero (Cdr. H.W. Biggs, DSO, RN), HMS Hereward (Lt.Cdr. C.W. Greening, RN), HMS Ilex (Lt.Cdr. P.L. Saumarez, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Decoy (Cdr. E.G. McGregor, DSO, RN) and HMS Defender (Lt.Cdr. G.L. Farnfield, RN).
The Rear-Admiral 1st Battle Squadron sailed with HMS Malaya (Capt. A.F.E. Palliser, DSC, RN, flying the flag of A/Rear-Admiral H.B. Rawlings, OBE, RN), HMS Ramillies (Capt. A.D. Read, RN). They were escorted by HMS Jervis (Capt. P.J. Mack, DSO, RN), HMS Janus (Cdr. J.A.W. Tothill, RN), HMS Juno (Cdr. St.J.R.J. Thyrwhitt, RN), HMS Nubian (Cdr. R.W. Ravenhill, RN) and HMS Mohawk (Cdr. J.W.M. Eaton, RN). HMS Eagle had defects and was unable to proceed to sea with this group as had been originally intended. Three aircraft from Eagle were embarked on Illustrious.
The heavy cruiser HMS York (Capt. R.H. Portal, DSC, RN) and the light cruiser HMS Gloucester (Capt. H.A. Rowley, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral E. de F. Renouf, CVO, RN) also departed Alexandria for these operations.
The fleet was clear of the harbour by 1300B/6, and then proceded on a mean line of advance of 310° until 1800B/6 when it was changed to 270°. At 2000B/6, course was changed to 320°.
7 November 1940.
There were no incidents during the night.
At 0800 hours, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 34°15’N, 24°47’E.
Around 1000B/7, the Vice-Admiral light forces, arrived at Piraeus in HMS Orion.
At noon, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 34°26’N, 23°43’E. At this time the mean line of advance was changed to 320°.
At 1300B/7, aircraft were flown off to search a sector 300° to 360°. Nothing was however sighted by this search.
At 1700B/7, HMAS Sydney joined the Commander-in-Chief from Suda Bay. She reported that ships for Suda Bay had all arrived according to plan and that stores and troops had all ben landed by dark on 6 November.
At 1800B/7, the position of convoy MW 3 was 35°44’N, 22°41’E and shortly afterwards the convoy altered course to 290°.
At 2000B/7, the position of the convoy was 35°48’N. 21°45’E, course was now altered to 320°.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
At 1800A/7, ‘Force H’ departed Gibraltar for ‘Operation Coat’ and ‘Operation Crack’. ‘Force H’ was made up of the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), light cruiser HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSC, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Fortune (Cdr. E.A. Gibbs, DSO, RN), HMS Foxhound (Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN), HMS Duncan (Cdr. A.D.B. James, RN), HMS Isis (Cdr. C.S.B. Swinley, DSC, RN). Also part of this force were a group of warships that was to reinforce the Mediterranean Fleet. These were the battleship HMS Barham (Capt G.C. Cooke, RN), heavy cruiser HMS Berwick (Capt. G.L. Warren, RN), light cruiser HMS Glasgow (Capt. H. Hickling, RN) and the destroyers HMS Gallant (Lt.Cdr. C.P.F. Brown, RN), HMS Greyhound (Cdr. W.R. Marshall A'Deane, DSC, RN) and HMS Griffin (Lt.Cdr J. Lee-Barber, DSO, RN). These ships carried troops for Malta as well as three of the destroyers from ‘Force H’, HMS Faulknor, HMS Fortune, HMS Fury. A total of 2150 troops were embarked as follows; HMS Berwick 750, HMS Barham 700, HMS Glasgow 400, and the six destroyers had each 50 troops on board.
8 November 1940.
At 0001B/8, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 36°36’N, 21°08’E, the mean line of advance was 280°.
At 0400B/8, the mean line of advance was changed to 220°.
At 0645B/8, an air search was flown off to search a sector 310° to the Greek coast. It sighted nothing.
At 0900B/8, when the Commander-in-Chief was in position 36°40’N, 18°50’E course was changed to 180° to close the convoy.
At noon, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 35°57’N, 18°46’E. The convoy was at that time in position 35°46’N, 18°41’E. Also around noon he convoy was reported by an enemy aircraft and at 1230 hours one Cant. 501 was attacked by Gladiators but apparently managed to escape.
At 1400B/8, aircraft were flown off to search between 200° and 350°. Also one aircraft was flown off with messages for Malta. The air search again sighted nothing.
At 1520B/8, the fleet was reported by enemy aircraft.
At 1610B/8, three Fulmar fighters attacked a formation of seven Italian S. 79’s shooting down two of them. The remainder jettisoned their bombs and made off.
At 1700B/8, HMS Ajax joined the fleet coming from Suda Bay.
The fleet had remained in a covering position to the north of the convoy all day and at 1830B/8, when in position 35°’20’N, 17°25’E course was changed to 000°. At that time the convoy was only five nautical miles to the southward of the fleet.
At 2130B/8, the fleet altered course to 180°.
At 2230B/8, the fleet altered course to 210°.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
At dawn A/S air patrols were flown off by HMS Ark Royal. These were maintained throughout the day.
A fighter patrol was maintained throughout the afternoon but no enemy aircraft were encountered.
The weather was fine and visibility good it was considered very likely that the force would be sighted and attacked by enemy aircraft. So it was decided at 1530 hours that HMS Ark Royal, HMS Sheffield, HMS Glasgow and six destroyers would proceed ahead to carry out the planned attack (‘Operation Crack’) on the Cagliari aerodrome. [According to the plan these destroyers should be HMS Faulknor, HMS Foretune, HMS Fury, Gallant, HMS Greyhound and HMS Griffin. It is currently not known to us if it were indeed these destroyers that with this force when they split off from the other ships.]
That evening fighters from the Ark Royal shot down an enemy aircraft.
9 November 1940.
At 0001B/9, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 35°42’N, 17°09’E, the mean line of advance was 270°.
At 0800B/9, the convoy was closed in position 34°42’N, 15°00’E.
At 0920B/9, HMS Ramillies, HMS Hyperion, HMS Hero and HMS Ilex were detached to join the convoy and escort it to Malta. The weather was overcast and squally so no air search was flown off.
The main fleet remained to the south-west of the Medina-Bank during the day. The 3rd and 7th Cruiser Squadrons being detached to search to the north.
The main fleet was being shadowed by enemy aircraft and was reported four times between 1048B/9 and 1550B/9. One Cant 506B aircraft was shot down by a Fulmar at 1640B/9.
At noon, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 34°47’N, 16°35’E.
At 1219B/9, a Swordfish A/S patrol force landed near HMS Warspite shortly after taking off. The crew was picked up by HMS Jervis. The depth charge and A/S bombs exploded close to Warspite.
At 2100B/9, when the Commander-in-Chief was in position 34°45’N, 16°10’E, course was altered to 310° to make rendez-vous with ‘Force F’, the reinforcements for the Mediterranean Fleet coming from Gibraltar.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
At 0430B/9, HMS Ark Royal launched a strike force of nine Swordfish aircraft to bomb Cagliari aerodrome with direct and delay action bombs. On completion of flying off, course was altered to 160° for the flying on position.
At 0745B/9, a fighter section and a section of three Fulmars that were to be transferred to HMS Illustrious (via Malta) were flown off and the nine Swordfish of the strike force landed on. The fighter section for Illustrious landed at Malta at 1020 hours.
The raid on Cagliari appeared to have been quite successful. Five Swordfish attacked the aerodrome and hits were observed on two hangars an other buildings. Two fires were seen to break out and also a large explosion occurred. One Swordfish attacked a group of seaplanes moored off the jetty. Another Swordfish attacked some factories near the power station and obtained a direct hit with a 250-lb bomb and incendiaries. The remaining two aircraft were unable to locate the target and attacked AA batteries instead. Two fires were seen to start but the AA batteries continued firing.
On completion of flying on course was altered to rendez-vous with HMS Barham, HMS Berwick and the remaining five destroyers which were sighted at 0910 hours. The ships then formed up in formation and set off on an easterly course at 18 knots.
At 0930B/9 an enemy aircraft that was shadowing the fleet was picked up by RD/F at a distance of about thirty miles. After working round the fleet clockwise the aircraft was sighted by HMS Barham and then by the Fulmar fighter patrol. The aircraft, which was a large floatplane, was shot down at 1005B/9, twenty miles on the starboard beam of the fleet.
At 1048B/9, a large formation of enemy aircraft was located by RD/F about fifty miles ahead of the fleet and closing. Five minutes later a section of Skua’s was flown off.
A section of Fulmar’s intercepted the enemy as they were working their way round to the sun and forced them to turn away but ten minutes later the enemy again approached. The fleet was then bombed from a height of 13000 feet. No British ships were hit, although HMS Barham, HMS Ark Royal and HMS Duncan had been near missed. It was believed that one of the attackers was shot down.
Throughout the remainder of the day fighter patrols were kept up but no further enemy aircraft attacked the fleet.
At 1915B/9, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Sheffield, HMS Duncan, HMS Isis, HMS Firedrake, HMS Forester and HMS Foxhound turned to the west. HMS Barham, HMS Berwick, HMS Glasgow, HMS Faulknor, HMS Fortune, HMS Fury, HMS Gallant, HMS Greyhound and HMS Griffin continued to the east under the command of Capt. Warren of the Berwick, which was the senior Captain.
10 November 1940.
At 0001B/10, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 35°13’N, 15°25’E steering 300°. Shortly afterwards, at 0010 hours, two heavy explosions were felt. It appears that the fleet had been under attack at this time.
At 0700B/10, aircraft were flown off to search a sector 315° to 045°. Shortly after takeoff one Swordfish crashed into the sea. The crew was rescued by HMS Nubian.
At 0715B/10, the 3rd and 7th Cruiser Squadrons rejoined. Shortly afterwards, at 0730B/10, HMAS Vampire, HMAS Voyager, HMAS Waterhen, HMS Dainty, HMS Diamond, HMS Hyperion, HMS Havock and HMS Ilex joined the fleet. HMS Jervis, HMS Janus, HMS Juno, HMS Nubian, HMS Mohawk, HMS Decoy, HMS Defender and HMS Hasty were detached to fuel at Malta.
At 1015B/10, rendez-vous was made with ‘Force F’ which was made up of HMS Barham, HMS Berwick, HMS Glasgow, HMS Griffin, HMS Greyhound, HMS Gallant, HMS Fury, HMS Fortune and HMS Faulknor. HMS Fortune and HMS Fury joined the destroyer screen. The other ships were ordered to proceed to Malta to land troops and stores there. The course of he fleet was changed to 110° in position 36°08’N, 13°10’E around this time.
At noon, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 35°55’N, 13°30’E.
At 1330B/10, convoy ME 3 departed Malta. It consisted of the transports Memnon (7506 GRT, built 1931), Lanarkshire (11275 GRT, built 1940), Clan Macaulay (10492 GRT, built 1936) and Clan Ferguson (7347 GRT, built 1938). Escort was provided by the battleship HMS Ramillies, AA cruiser HMS Coventry and the destroyers HMS Decoy and HMS Defender.
Around 1400B/10 the monitor HMS Terror (Cdr. H.J. Haynes, DSC, RN) and the destroyer HMAS Vendetta (Lt.Cdr. R. Rhoades RAN) departed Malta for Suda Bay. Before departure HMAS Vendetta had first carried out an A/S patrol off Valetta harbour.
At 1435B/10, HMS Mohawk rejoined the fleet.
At 1450B/10, HMS Hero was detached to Malta with correspondence.
In the afternoon three Fulmars, which had been flown to Malta from HMS Ark Royal, landed on HMS Illustrious.
At 2100B/10, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 35°15’N, 14°16’E steering 090°. The 3rd and 7th Cruiser Squadrons were detached to search between 020° to 040°.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In the western Mediterranean all was quiet. Fighter patrols were maintained overhead during the day. Also A/S patrols were maintained all day.
11 November 1940.
At 0001B/11, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 35°18’N, 15°14’E. At 0100 hours the fleet altered course to 060°.
At 0135B/11, HMS Ramillies, which was with convoy ME 3, reported three explosions in position 34°35’N, 16°08’E. This might have been a submarine attack. [This was indeed the case as the Italian submarine Pier Capponi attacked a battleship around this time.]
At 0700B/11, an air search was launched to search between 315° and 045°. One aircraft was flown to Malta to collect photographs of Taranto harbour.
At 0800B/11, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 36°55’N, 17°36’E.
At noon, the Vice-Admiral light forces in HMS Orion coming from Piraeus, joined the fleet in position 36°10’N, 18°30’E. Correspondence was transferred to HMS Warspite via HMS Griffin.
At 1310B/11, the Vice-Admiral light forces, in HMS Orion and with HMS Ajax and HMAS Sydney, HMS Nubian and HMS Mohawk in company, parted company to carry out an anti-shipping raid into the Straits of Otranto.
At 1800B/11, HMS Illustrious, HMS York, HMS Gloucester, escorted by HMS Hyperion, HMS Hasty, HMS Havock and HMS Ilex were detached for ‘Operation Judgement’ the torpedo and dive-bombing attack on the Italian fleet in Taranto harbour.
For this operation this force proceeded to position 38°11’N, 19°30’E. Here aircraft were flown off in two waves, at 2000 and at 2100 hours.
At 2000B/11, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 37°54’N, 19°09’E. One hour later the fleet altered course to 000°.
At 2030B/11, the Vice-Admiral light forces with the cruisers passed through position 39°10’N, 19°30’E, course 340° doing 25 knots.
At 2140B/11, HMS Juno obtained an A/S contact and attacked it with depth charges.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In the western Mediterranean the fleet arrived back at Gibraltar around 0800A/11.
12 November 1940.
At 0700B/12, both detached groups rejoined the fleet. The attack on Taranto harbour was reported as a success. Eleven torpedoes had been dropped and hits were claimed on a Littorio-class and two Cavour-class battleships in the outer harbour. Sticks of bombs had been dropped amongst the warships in the inner harbour. Two aircraft failed to return to HMS Illustrious. [Damage was done to the battleships Littorio (three torpedo hits), Caio Duilio and Conte di Cavour (one torpedo hit each), in fact the Conti di Cavour never returned to service. Also damaged (by bombs) were the heavy cruiser Trento and the destroyer Libeccio.]
The raid into the Straits of Otranto had also been successful as an Italian convoy had been intercepted off Valona around 0115 and largely destroyed. The convoy had been made up of four merchant vessels which had all been sunk. There had been two escorts, thought to be destroyers or torpedo boats. These managed to escape. [The merchant vessels Antonio Locatelli (5691 GRT, built 1920), Capo Vado (4391 GRT, built 1906), Catalani (2429 GRT, built 1929) and Premuda (4427 GRT, built 1907) had been sunk. Their escorts had been the armed merchant cruiser Ramb III (3667 GRT, built 1938) and the torpedo boat Nicola Fabrizi. The convoy had been en-route from Vlore, Albania to Brindisi.]
At 0800B/12, the fleet was in position 37°20’N, 20°18’E.
At 0930B/12, HMS Warspite catapulted her Walrus aircraft to take massages to Suda Bay for forwarding to the Admiralty by transmission.
At noon, the fleet was in position 37°20’N, 20°08’E. Course at that time was 140°.
As it was intended to repeat ‘Operation Judgement’ tonight the fleet remained in the area. Course being altered to 340° at 1600 hours.
Fortunately the fleet was not reported at this time. Three enemy aircraft were shot down during the day but these were shot down before they had reported the fleet.
At 1800B/12, the decision was taken not to proceed with the repeat of ‘Operation Jugement’ due to the bad weather in the Gulf of Taranto. At that time the fleet was in position 37°06’N, 19°44’E. Course was set to 140° to return to Alexandria.
At 1830B/12, HMS Malaya, HMS Ajax, HMS Dainty, HMS Diamond, HMS Greyhound, HMS Griffin and HMS Gallant were detached to fuel at Suda Bay. HMS Berwick and HMS York were detached to proceed to Alexandria where they arrived in the evening of the 13th.
13 November 1940.
At 0001B/13, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 35°44’N, 20°53’E.
At 0630B/13, HMS Terror and HMAS Vendetta arrived at Suda Bay. Terror was to remain at Suda Bay as guardship.
At 1000B/13, the force with HMS Malaya arrived at Suda Bay. After fuelling the departed later the same day for Alexandria taking HMAS Vendetta with them.
Also around 1000B/13, convoy ME 3 arrived at Alexandria.
At noon, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 34°23’N, 23°43’E.
At about 1530B/13, Fulmar’s attacked an Italian shadowing aircraft which however managed to escape although damaged.
At 1600B/13, the fleet altered course to 050° when in position 33°23’N, 26°18’E. Course was altered back to 090° at 1800B/13. RD/F later detacted an enemy formation to the southward but the fleet was not sighted.
At 2000B/13, the fleet was in position 33°38’N, 27°34’E.
14 November 1940.
Around 0700B/14, the bulk of the fleet with the Commander-in-Chief arrived at Alexandria. (47)
7 Nov 1940
Around 1800A/7, ' Force H ' , made up of the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), light cruiser HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSC, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Fortune (Cdr. E.A. Gibbs, DSO, RN), HMS Foxhound (Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN), HMS Duncan (Cdr. A.D.B. James, RN), HMS Isis (Cdr. C.S.B. Swinley, DSC, RN) departed Gibraltar for operations. Also sailing with ' Force H ' were a group of warships that were to reinforce the Mediterranean Fleet. These were the battleship HMS Barham (Capt G.C. Cooke, RN), heavy cruiser HMS Berwick (Capt. G.L. Warren, RN), light cruiser HMS Glasgow (Capt. H. Hickling, RN) and the destroyers HMS Gallant (Lt.Cdr. C.P.F. Brown, RN), HMS Greyhound (Cdr. W.R. Marshall A'Deane, DSC, RN) and HMS Griffin (Lt.Cdr J. Lee-Barber, DSO, RN).
[For more info on the operations see the event ' Several operations in the Mediterranean ' for 4 November 1940 which includes info on Operation Coat, the transfer of reinforcements from the Western Mediterranean to the Eastern Mediterranean and Operation Crack, an air attack on Cagliary, Sardinia. (43)
11 Nov 1940
Shortly after 0800A/11, ' Force H ' , made up of the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), light cruiser HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSC, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Fortune (Cdr. E.A. Gibbs, DSO, RN), HMS Foxhound (Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN), HMS Duncan (Cdr. A.D.B. James, RN), HMS Isis (Cdr. C.S.B. Swinley, DSC, RN) arrived back at Gibraltar from operations. (43)
13 Nov 1940
Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN, transferred his flag from HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN) to HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN). (48)
15 Nov 1940
Operation White.
Transfer of aircraft to Malta.
At 0400A/15, ' Force H ', made up of the battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carriers HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN), HMS Argus (Capt. E.G.N. Rushbrooke, DSC, RN), light cruisers HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN), HMS Despatch (Commodore 2nd cl. C.E. Douglas-Pennant, DSC, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSC, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Fortune (Lt.Cdr. E.N. Sinclair, RN), HMS Foxhound (Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN), HMS Duncan (Cdr. A.D.B. James, RN), HMS Wishart (Cdr. E.T. Cooper, RN) departed Gibraltar in bright moonlight. Course was shaped at 16 knots to pass to the south of Alboran Island.
A/S patrols were flown off at dawn. The wind was westerly, force 4 throughout the day. For flying operations course had to be reversed. During the day some training exercises were carried out.
At 1130A/15, an aircraft, most probably a Spanish air liner from Tetuan to Melilla, passed down the starboard side of the Fleet on a westerly course, in position 35°50'N, 03°56'W at a range of about 12 miles. At 1315A/15, in position 35°35'N, 03°43'W a similar machine was seen passing the Fleet in the reverse direction. By this time however, the course of the Fleet was to the eastward. It is probable that these air lines report British units whenever sighted.
All aircraft were landed on by 1800A/15. At 1900A/15 course was altered to the north-eastward.
At 2101A/15 a signal was received from the Air Officer Commanding, Mediterranean that arrangements had been made for meeting the Hurricanes. These were that a Sunderland from Malta would be in the rendezvous position of Galita Island to meet the first range of Hurricanes flying off at 0615A/17, and a Glenn Martin from Malta to meet the second range flying off at 0710A/17.
After dawn on the 16th, course was altered to the south-eastward and shortly afterwards, fighter and A/S patrols were flown off. The westerly wind had increased to force 6 and remained at that strenght throughout the day.
By noon the sea had increased and the conditions for operating aircrft had become severe. As visibility from the air was low and as the RDF screen remained clear, Vice-Admiral Somerville decided to cancel flying operations and maintain a fighter section at readiness in the carrier.
As there appeared to be every chance of avoiding detection and since bad weather conditions appeared likely to persist, Vice-Admiral Somerville decided at 1430A/16 not to carry out the intended bombing attack on Alghero aerodrome.
Italian naval units were then reported to be at sea to the south of Naples and it was decided, in view of this, to launch the aircraft for Malta from as far west as the weather conditions would admit. HMS Argus reported that in te present weather the aircraft could be flown off from longitude 06°40'E.
At 1500A/16 the course of the fleet was therefore reversed for an hour to reduce the chances of detection before dark and in order to maintain a speed of not less then 16 knots during the night.
By 0200A/17 the strong westerly wind had backed sightly and dropped considerably. Visibility had improved and was maximum at dawn.
At 0545A/17 the force was split into two groups, HMS Argus, HMS Despatch and three of the destroyers were to fly off the Hurricanes for Malta. HMS Renown, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Sheffield and the remaining five destroyers were to fly off A/S patrols, a fighter section and a reconnaissance to the eastward.
At the time of flying off, the wind at 2000 feet in the flying off position was 220°, 20 knots, and the latest forecast received from Malta, which was timed 1130A/16, reported the wind in the Malta chennel as south-west. As no further report was received it was presumed there was no change.
Te first flight took off at 0615A/17 in position 37°29'N, 06°43'E and the second flight at 0715A/17 in position 37°24'N, 06°52'E.
Arrangements had been made for a Sunderland to meet the first flight five miles to the northward of Galita Island, and for a Glen Martin to meet the second flight in the same position. From signals intercepted, it was apparent that the Sunderlandhad effected a rendezvous but that the Glen Martin had failed to do so.
On completion of flying off, the two groups joined company and ' Force H ' withdrew to the westward at 18.5 knots.
Reconnaissance aircraft returned at 0945A/17 and reported nothing in sight within 100 miles to the east of ' Force H '. Two fighter sections were maintained in the air until 1400A/17 but no enemy aircraft appeared.
From signals it was learnt that only one Skua and four Hurricanes had arrived at Malta. It is suspected that easterly winds had been encountered resullting in the loss of many aircraft and their pilots.
At 1530A/17, the wind had increased to Force 6 so speed had to be reduced t 15 knots to avoid damage to the destroyers. A/S and fighter patrols were landed on and flying was cancelled for the day.
At 1550A/17, HMS Sheffield was sent on ahead in order that she might fuel and obtain a night in harbour befor proceeding to the westward to rendezvous with the transport ships of operation Collar. She arrived at Gibraltar around 1800A/18.
Speed had to be further reduced to 12 knots at 1635A/17, and to 10 knots at 1655A/17 to allow HMS Firedrake, which had dropped behind to effect some repairs, to regain station.
At 1800A/17, Admiralty's message 1727A/17 was received ordering ' Force H ' to return to Gibraltar at maximum speed. Vice-Admiral Somerville therefore reported position, course and speed (37°34'N, 03°31'E, 265°, 9 knots) and added that all ships were steaming into a full westerly gale.
Shortly afterwards Admiralty's message 1800A/17 was received stating that the German pocket battleship Admiral Scheer was thought to be in the vicinity of the Azores and ordering HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal and other units to proceed to Gibraltar at maximum speed, refuel and than proceed to the Azores. In reply Vice-Admiral Somerville stated that by proceeding without a destroyer screen HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal could proceed at a somewhat hight speed, provided that the situation justified additional submarine risks.
At 2006A/17, speed was increased to 12 knots and to 13 knots at 2035A/17. At 2100A/17, Admiralty's message timed 2025A/17 was received ordering Vice-Admiral Somerville to retain the destroyers.
A small fire was observed in HMS Argus at 2140A/17. At 2310A/17, HMS Fury reported that damage was being sustained and speed was reduced to 12 knots.
At 0417A/18, speed was increased to 13 knots and at 0454A/18 to 14 knots. At 0600A/18 the Admiralty was informed of the speed and position of ' Force H ' (37°24'N, 00°57'E). A further increase of speed to 18 knots was possible at 0837A/18.
At 1110A/18, speed was increased to 19 knots. HMS Argus, HMS Despatch, HMS Wishart, HMS Duncan and HMS Fury were then detached while HMS Renown, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Faulknor, HMS Firedrake, HMS Forester, HMS Fortune and HMS Foxhound proceeded ahead. They increased speed to 20 knots but at 1335A/18 speed had to be reduced to 18 knots and at 1435A/18 to 15 knots.
From this time onwards speed was varied between 15 and 20 knots in accordance with conditions prevailing. Arrangements were made with Admiral Commanding North Atlantic Station for HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal to oil in Gibraltar Bay, destroyers and A/S trawlers meanwhile carrying out an A/S patrol in the vicinity.
At 0230A/19, as the Renown group was about to enter Gibraltar Bay, Admiralty's message 0140A/19 was received cancelling the deployment of ships proceeding to the Azores. Renown and Ark Royal therefore proceeded into harbour. HMS Renown entered harbour at 0350A/19. HMS Argus and her group at 0850A/19. (43)
25 Nov 1940
Operation Collar and the resulting Battle of Cape Spartivento.
See also the event for 23 November 1940 called ‘Operation MB 9’ for the events in the Eastern Mediterranean.
Departure of the convoy from Gibraltar / passage through the Straits of Gibraltar and plan of the operation.
During the night of 24/25 November 1940 the three merchants / troop transports, Clan Forbes (7529 GRT, built 1938), Clan Fraser (7529 GRT, built 1939) and New Zealand Star (10740 GRT, built 1935), passed the Straits of Gibraltar. To the eastward of Gibraltar they were joined by the four corvettes (HMS Peony (Lt.Cdr. (rtd.) M.B. Sherwood, DSO, RN), (HMS Salvia (Lt.Cdr. J.I. Miller, DSO, RD, RNR), HMS Gloxinia (Lt.Cdr. A.J.C. Pomeroy, RNVR) and HMS Hyacinth (T/Lt. F.C. Hopkins, RNR) that were part of Force ‘F’, which was the close support force of the convoy. The other ships of Force ‘F’ were the light cruisers HMS Manchester (Capt. H.A. Packer, RN) and HMS Southampton (Capt. B.C.B. Brooke, RN) and the destroyer HMS Hotspur (Cdr. H.F.H Layman, DSO, RN), which was in a damaged state and was to proceed to Malta for full repairs. These last three ships sailed at 0800/25. The cruisers had each about 700 RAF and other military personnel onboard that were to be transported to Alexandria.
The cover force for this convoy, force ‘B’ also left Gibraltar at 0800/25. This force was made up of the battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN), the light cruisers HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN) and HMS Despatch (Commodore 2nd cl. C.E. Douglas-Pennant, DSC, RN). They were escorted by destroyers from the 8th and 13th Destroyer Flotillas; HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN, Capt. D.8), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSC, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN), HMS Duncan (Capt. A.D.B. James, RN, Capt. D.13), HMS Wishart (Cdr. E.T. Cooper, RN), HMS Vidette (Lt. E.N. Walmsley, RN), HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St.J. Morgan, RN), HMS Kelvin (Cdr. J.H. Allison, DSO, RN) and HMS Jaguar (Lt.Cdr. J.F.W. Hine, RN).
Force ‘F’ and the merchant ship New Zealand Star were to proceed to Alexandria except for HMS Hotspur which was to detach to Malta as mentioned earlier as well as the other two merchant ships. Force ‘B’ was to cover Force ‘F’ and the merchant ships during the passage of the Western Mediterranean. To the south of Sardinia these forces were to be joined around noon on 27 November 1940 by Force ‘D’ which came from the Eastern Mediterranean and was made up of the battleship HMS Ramillies (Capt. A.D. Reid, RN), the heavy cruiser HMS Berwick (Capt. G.L. Warren, RN), the light cruiser HMS Newcastle (Capt. E.A. Aylmer, DSC, RN) and the AA cruiser HMS Coventry (Capt. D. Gilmour, RN). They were escorted by the destroyers HMS Defender (Lt.Cdr. G.L. Farnfield, RN), HMS Diamond (Lt.Cdr. P.A. Cartwright, RN), HMS Gallant (Lt.Cdr. C.P.F. Brown, RN), HMS Greyhound (Cdr. W.R. Marshall A'Deane, DSC, RN) and HMS Hereward (Lt.Cdr. C.W. Greening, RN). [actually HMS Diamond however did not join Force 'D'] All forces were then to proceed towards the Sicilian narrows for a position between Sicily and Cape Bon which was to be reached at dusk. After dark Force ’F’, reinforced by HMS Coventry and the destroyers from Force ‘D’ were then to proceed through the narrows to the Eastern Mediterranean where they would be met the next day by ships of the Mediterranean Fleet. Force ‘B’ with HMS Ramillies, HMS Berwick and HMS Newcastle from Force ‘D’ were then to return to Gibraltar.
Disposition of British forces at 0800 hours, 27 November 1940.
At 0800/27, about half an hour before sunrise, the situation was as follows. Vice-Admiral Somerville in HMS Renown, with HMS Ark Royal, HMS Sheffield and four destroyers were in position 37°48’N, 07°24’E (about 95 nautical miles south-west of Cape Spartivento, Sardinia) steering 083° at 16 knots.
Some 25 nautical miles to the south-west of him, the Vice-Admiral 18th cruiser squadron in HMS Manchester, with HMS Southampton, HMS Despatch and five destroyers were in company with the convoy in position 37°37’N, 06°54’E. The four corvettes had been unable to keep up with the convoy and were about 10 nautical miles to the westward of it. The visibility was excellent, the wind south-easterly, force 3 to 4 and the sea was calm.
At this time HMS Ark Royal flew off a section of fighters, one A/S patrol, one meteorological machine and seven reconnaissance aircraft. Vice-Admiral Somerville continued on his easterly course to concentrate with Force ‘D’ which was approaching from the Skerki Bank. At 0900 hours he changed course to the south-west to join the convoy to provide additional AA defence for the convoy for expected air attacks from Sardinian aerodromes.
Reconnaissance aircraft report enemy forces at sea.
Shortly before the course change, at 0852/27 one of Ark Royal’s aicraft sighted a group of enemy warships about 25 nautical miles to the southward of Cape Spartivento and while closing to investigate at 0906 hours sent an alarm report of four cruisers and six destroyers, which, however was not received by any ship of the British forces. On sighting the convoy at 0920 hours, HMS Renown maneuvered to pass astern of it and take station to the southward and up sun, in the probable direction of any air attack. At 0956 hours, while still on the port quarter of the convoy, Vice-Admiral Somerville received from HMS Ark Royal an aircraft report timed 0920/27, of five cruisers and five destroyers some 65 nautical miles to the north-eastward of him.
Steam was at once ordered for full speed and screens of two destroyers each were arranged for both HMS Ark Royal and the merchant ships. Further reports from aircraft, confirmed by HMS Ark Royal, established by 1015/27 the presence of enemy battleships and cruisers and HMS Renown altered course to 075° to join HMS Ramillies increasing speed as rapidly as possible to 28 knots.
Measures to safeguard the convoy and to join Force ‘D’.
At 1035/27 the plot showed enemy forces to the north-east but their composition and relative position were still in doubt. In these circumstances Vice-Admiral Somerville decided that the convoy should continue to its destination steering a south-easterly course (120°) in order to keep clear of any action which might develop. It was given an escort of two cruisers, HMS Despatch and HMS Coventry and the destroyers HMS Duncan and HMS Wishart. The remaining two cruisers and three destroyers of Force ‘F’ were ordered to join Force ‘B’ which steered to make contact with Force ‘D’ which was approaching from the east and then to attack the enemy together. HMS Ark Royal was ordered to prepare and fly off a torpedo bomber striking force. She was to act independently escorted by HMS Kelvin and HMS Jaguar and under cover from the battlefleet.
At 1058/27 a Sunderland flying boat closed HMS Renown and reported Force ‘D’ bearing 070°, range 34 nautical miles. As the junction of the two forces seemed to be assured, the speed was reduced to 24 knots, in order to maintain a position between the convoy and the enemy force which estimated position was bearing 025°, range 50 nautical miles. The Sunderland flying boat was ordered to shadow and report its composition.
The cruisers HMS Manchester, HMS Southampton and HMS Sheffield had meanwhile concentrated with the destroyers in the van, bearing 5 nautical miles from HMS Renown in the direction of the enemy.
Reports from the reconnaissance aircraft of HMS Ark Royal contained a number of discrepancies which made it impossible to obtain a clear picture of the situation. Two groups of cruisers had been reported, as well as two battleships. It seemed certain that five or six cruisers were present, but the number of battleships remained in doubt. But whatever the composition of the enemy force in order to get the convoy through Vice-Admiral Somerville wanted to attack as soon as possible. At 1115/27 the enemy was reported to be changing course to the eastward.
All this time Force ‘D’ had been coming westwards and at 1128/27 they were sighted from HMS Renown bearing 073°, range about 24 nautical miles. The aircraft reports now indicated that the enemy force was made up of two battleships, six or more cruisers and a considerable number of destroyers. The action seemed likely to develop into a chase, and HMS Ramillies was therefore ordered to steer 045°, so as not to lose ground due to her slow speed. Vice-Admiral Holland was put in command of all the cruisers in the van and HMS Berwick and HMS Newcastle from Force ‘D’ were ordered to join him. It was shortly after this that HMS Ark Royal flew off her first torpedo bombers striking force.
The approach on the enemy.
At 1134 hours, Vice-Admiral Somerville increased to 28 knots and at 1140 hours altered course to 050° to close the enemy. The position of the British forces was now as follows. Fine on the port bow of HMS Renown were HMS Manchester, HMS Southampton and HMS Sheffield in single line ahead. HMS Berwick and HMS Newcastle was coming from the eastward to join them. Two miles astern HMS Faulknor (Capt. D 8) was gradually collecting the other ships of his Flotilla and HMS Encounter some of which had been screening the convoy. The four destroyers of Force ‘D’, HMS Defender, HMS Gallant, HMS Greyhound and HMS Hereward were proceeding westwards to join and were eventually stationed bearing 270°, 3 nautical miles from her.
Ten nautical miles fine on the starboard bow of HMS Renown, HMS Ramillies was altering to a parallel course. HMS Ark Royal had dropped some distance astern. She was carrying out flying operations between the main force and the convoy, which was now about 22 nautical miles west-south-west of HMS Renown.
At 1154 hours, the Sunderland aircraft returned and reported six cruisers and eight destroyers bearing 330°, range 30 nautical miles from HMS Renown. Her report unfortunately did not give course and speed of the enemy and she disappeared from sight before these could be obtained. It appeared now that one of the enemy forces was further to the west than previously thought and might be in a position to outflank the main force and attack HMS Ark Royal and the convoy. Course was therefore altered to the north in order to avoid getting to far to the eastward.
Vice-Admiral Somerville’s appreciation of the situation at noon, 27 November 1940.
The prospects of bringing the enemy into action seemed favourable. The composition of the enemy force was still not definitely established but there did not appear to be more than two battleships with them. The British had effected their concentration of which the enemy seemed to be unaware, since no shadowing aircraft had been sighted or detected by RD/F. The speed of the enemy was reported as being 14 to 18 knots. The sun was immediately behind the British forces, giving them the advantage of light and if the nearest reported position of the enemy was correct there seemed every possibility of bringing off a simultaneous surface and torpedo bombers attack, providing that the enemy did not retire immediately at high speed. Vice-Admiral Somerville’s intentions were; To drive off the enemy from any position from which he could attack the convoy and to except some risk to the convoy providing there was a reasonable prospect of sinking one or more of the enemy battleships. To achieve the second of them he considered that the speed of the enemy would have to be reduced to 20 knots or less by torpedo bombers attacks and that the enemy battleships could be attacked by HMS Renown and HMS Ramillies in concert.
Contact with the enemy.
At 1207/27, HMS Renown developed a hot bearing on one shaft which limited her speed to 27.5 knots. At the same time puffs of smoke were observed on the horizon bearing 006°, and the cruisers of the van sighted masts between 006° and 346°. At 1213 hours a signal came in from HMS Ark Royal reporting the composition of the enemy as two battleships, six cruisers accompanied by destroyers. The British cruisers in the van by this time had formed a line of bearing 075° to 255° in the sequence from west to east, HMS Sheffield, HMS Southampton, HMS Newcastle, HMS Manchester, HMS Berwick.
The nine destroyers were stationed five miles bearing 040° from HMS Renown in order to be placed favourably to counter-attack any destroyers attempting a torpedo attack on HMS Renown or HMS Ramillies.
The situation as seen by the cruisers immediately before the action commenced was as follows. Between the bearings of 340° to 350° three enemy cruisers and some destroyers were visible at a range of about 11 nautical miles. These were steering a northerly course. This force will be referred to as ‘the Western Group’. A second group of cruisers, also accompanied by destroyers, which will be referred to as the ‘Eastern Group’ bore between 003° and 013°. This group was further away and steering approximately 100°.
The action
At 1220/27 the enemy cruisers in the ‘Western Group’ opened fire, and the British advanced forces immediately replied. The enemy’s first salvo fell close to HMS Manchester. As soon as fire was opened by the British cruisers, the Italians made smoke and retired on courses varying between north-west and north-east. Behind their smoke screen they seemed to be making large and frequent alterations of course.
At 1224 hours HMS Renown opened fire at the right hand ship in the ‘Western Group’ which was identified as a Zara-class heavy cruiser. Range was 26500 yards. After six salvoes, the target was lost in smoke. HMS Ramillies also fired two salvoes at maximum elevation to test the range but both fell short. She then dropped astern in the wake of HMS Renown and tried to follow at her best speed, 20.7 knots, throughout the action.
Just before opening fire HMS Renown had sighted two ships which were not making smoke, bearing 020° at extreme visibility. These were thought at first to be the Italian battleships but later turned out to be cruisers of the ‘Eastern Group’. On losing her first target HMS Renown altered course to starboard to close these supposed battleships and to bring the cruisers of the ‘Western Group’ broader on the bow. She had hardly done so when the centre ship of the latter group appeared momentarily through the smoke and was given two salvoes. Again course was altered to open ‘A’ arcs on the left hand ship, at which eight salvoes were fired before she too disappeared in the smoke at 1245 hours. At this moment two large ships steering westward emerged from the smoke cloud but before fire was opened these ships were identified as French liners.
The enemy by this time was on the run and had passed outside the range of our capital ships although at 1311 hours, HMS Renown fired two ranging salvoes at two ships of the ‘Eastern Group’ but both fell short. Meanwhile the British cruisers had been hotly engaged at ranges varying between 23000 and 16000 yards. Many straddles were obtained, but smoke rendered spotting and observation very difficult.
HMS Manchester, HMS Sheffield and HMS Newcastle all opened fire on the right-hand ship of the ‘Western Group’. HMS Berwick engaged the left-hand ship of the same group and HMS Southampton engaged the left-hand ship of the ‘Eastern Group’. HMS Manchester and HMS Sheffield continued to fire at the same ship for about 20 minutes (until 1236 and 1240 hours respectively) but HMS Newcastle shifted target to the ship already engaged by HMS Berwick after 18 salvoes. HMS Southampton, after 5 salvoes shifted target to a destroyer which was seen to be hit. At least one other destroyer is believed to have been hit during this phase and two hits by a large caliber shell on a cruiser were observed by HMS Faulknor at 1227 and HMS Newcastle at 1233 hours.
The enemy’s fire was accurate during the initial stages but when fully engaged it deteriorated rapidly and the spread became ragged. Their rate of fire was described as extremely slow. The only casualties on the British side occurred in HMS Berwick when at 1222 hours she received a hit from an 8” shell which put ‘Y’ turret out of action. HMS Manchester was straddled several times but despite being under continuous fire from 1221 to 1300 hours escaped unscatched. Her passengers were quite excited about having been in a sea battle.
At 1245 hours the cruisers altered course to 090° to prevent the enemy from working round ahead to attack the convoy. This brought the relative beating of the ‘Eastern Group’ to Red 40° and HMS Manchester once more engaged the left-hand ship. Five minutes later a further alteration of course to the southward was made to counter what appeared to be an attempt by the enemy to ‘cross the T’ of the cruisers. The enemy however at once resumed their north-easterly course and Vice-Admiral Holland led back to 070° at 1256 hours and 030° at 1258 hours. The rear ship of the enemy line was heavily on fire aft and she appeared to loose speed. But at 1259 hours picked up again and drew away with her consorts.
At 1301 hours the masts of a fresh enemy unit steering to the south-west were seen at extreme visibility right ahead of HMS Manchester. It bore 045° and two minutes later two battleships were identified in it. Their presence was quickly corroborated by large splashes which commenced to fall near HMS Manchester and HMS Berwick and these ships were reported to Vice-Admiral Somerville. The end on approach resulted in the range decreasing very rapidly and at 1305 hours Vice-Admiral Holland turned to cruisers to 120° with the dual purpose of working round the flank of the battleships and closing the gap to HMS Renown. The enemy battleships were not prepared to close and altered course to the north-eastward, presumably to join their 8” cruisers. Vice-Admiral Holland therefore altered course to 090° at 1308 hours and shortly afterwards to 050°. The enemy were by now rapidly running out of range and ten minutes later the action came to an end.
First attack by the torpedo bombers from HMS Ark Royal
Meanwhile a torpedo bomber striking force consisting of 11 Swordfish of no. 810 Squadron had been flown off from HMS Ark Royal at 1130 hours with orders to attack the Italian battleships. At 1216 hours they sighted two battleships and altered course as to approach them from the direction of the sun. The ships were identified as one Littorio-class and one Cavour-class. They were screened by seven destroyers. Enemy course was easterly at a speed of 18 knots. The leading battleship (Littorio-class) was selected as the target and all torpedoes were dropped inside the destroyer screen at ranges of 700 to 800 yards. One hit was observed abaft the after funnel and another explosion was seen just astern of the target. Yet another explosion was seen ahead of the Cavour-class. No other hits were seen. All aircraft returned safely to HMS Ark Royal.
Vice-Admiral Somerville’s Appreciation at 1315/27.
At 1315/27 firing had practically ceased owning to the enemy drawing out of range. The heavy smoke made by the Italians during the chase had prevented accurate fire, and so far as was known, no serious damage was inflicted on them. The torpedo bomber striking force from HMS Ark Royal had attacked but no report had been received yet but it seemed evident that the speed of the enemy had not been materially reduced.
The British forces were meanwhile rapidly closing the enemy coast. The main object of the whole operation was the safe passage of the convoy. The main enemy units had been driven off far enough that they could no longer interfere with it. It was also important to provide additional AA protection to the convoy against enemy air attack at dusk and in order to reach the convoy in time to do this course had to be set for it before 1400 hours so it was decided to break off the chase.
The chase broken off and further attacks by aircraft from HMS Ark Royal.
Around 1345/27, a damaged enemy cruiser was reported, Vice-Admiral Somerville considered sending HMS Berwick and HMS Newcastle north to finish this ship off. As these two cruisers also needed a cover/support force this idea was quickly abandoned. HMS Ark Royal was ordered to attack this cruiser with aircraft. A second torpedo bomber squadron was about to take off and Skua dive bombers were also being armed. Capt. Holland of the Ark Royal intended to attack the battleships again with the torpedo bombers and sent out the dive bombers to attack the damaged cruiser.
The torpedo bomber force of 9 Swordfish was flown off at 1415 hours. The Squadron Leader was given the enemy battleships as his objective, but with the full liberty to change it to his discretion, as he alone would be in a position to judge the possibility or otherwise achieving a successful attack.
The aircraft sighted three cruisers escorted by four destroyers about 12 nautical miles off the south-east coast of Sardinia, steering to the eastward at high speed. Some 8 nautical miles ahead of these cruisers were the two battleships escorted by about ten destroyers. There was a total absence of cloud cover, and it was considered essential to attack from the direction of the sun, if any degree of surprise were to be achieved. As any attempt, however, to gain such a position with regard to the battleships would inevitably have led to the striking force being sighted by the cruisers it was decided to attack the latter.
The attack was carried out at 1520/27 and was not sighted by the enemy until very late, only two salvoes being fired against the aircraft before the first torpedo was dropped. As the first aircraft reached the dropping position, the cruisers turned together to starboard causing several of the following Swordfish who had already committed to their drop to miss their targets. One hit was claimed on the rear cruiser and a possible one on the leading cruiser. Two Swordfish were hit by shrapnel from enemy AA fire but air aircraft returned safely to HMS Ark Royal.
A striking force of 7 Skua’s had meanwhile been flown off at 1500 hours. They failed to locate the reported damaged cruiser but reported to have carried out an attack on three light cruisers steering north of the south-west corner of Sardinia. Two near misses may have caused some damage to the rear ship. On the way back to HMS Ark Royal they encountered and shot down an Italian RO 43 reconnaissance aircraft from the battleship Vittorio Venoto.
Enemy air attacks on British Forces.
While these British flying operations were taking place Vice-Admiral Somerville had been steering to the southward in accordance with his decision to close the convoy. HMS Ark Royal had lost sight of HMS Renown to the north-eastward about 1250 hours, but since the receipt of the signal ordering the retirement of the British forces, Captain Holland had been making good a course of 090°, so far as his flying operations permitted, in order to rejoin the Flag. The first RD/F indications of the presence of enemy aircraft were received in HMS Renown at 1407 hours. Shortly afterwards bomb splashes were seen on the horizon when the Italian aircraft were attacked by Fulmars from the Ark Royal and several machines jettisoned their bombs. Ten enemy aircraft were then seen to be coming in and they eventually dropped their bombs well clear of the heavy ships but close to the screening destroyers.
Two further attacks were made around 1645/27 when two groups of five aircraft each concentrated on HMS Ark Royal, which by that time was in company with the Fleet, but owning to flying operations, not actually in the line. Apart from a few bombs being jettisoned again as a result of the interception by the Fulmar fighters, the high level bombing performed from a height of 13000 feet was most accurate. Some 30 bombs fell near HMS Ark Royal, two at least within 10 yards, and she was completely obscured by splashes.
About 1,5 minutes after this attack a stick of bombs dropped by four Caproni bombers, which had not been seen during the previous attack, missed HMS Ark Royal by a very narrow margin. HMS Ark Royal fortunately suffered no damage.
The British ships sighted the convoy at 1700/27 and proceeded to join it for passage to the Sicilian narrows.
The Battle of Cape Spartivento from the Italian side
At noon on 26 November 1940 the Italian had received reports that British forces had left Gibraltar and Alexandria the day before. The Italians then went to sea from Naples and Messina in three forces;
From Naples.
Battleships Vittorio Veneto and Giulio Cesare, escorted by the 13th Destroyer Flotilla made up of the Granatiere, Fuciliere,
From Messina. Heavy cruisers from the 3rd Cruiser Division Trieste, Trento and Bolzano and the 12th Destroyer Flotilla made up of the Lanciere, Ascari, Carabiniere and Libeccio. This last destroyer had temporarily replaced the Carabinieri.
These forces were to intercept the British forces coming from Gibraltar.
From Trapani, Sicily, torpedo-boats from the 10th Torpedo-boat Flotilla, Vega, Sagittario, Alcione and Sirio, were ordered to patrol in the Sicily narrows to scout for possible British forces proceeding westwards from the Eastern Meditarranean. Sirio actually made an unobserved torpedo attack shortly after midnight (during the night of 26/27 November) on a group of seven enemy warships (Force ‘D’).
By 1015/27 the Italian forces were in the Sardinia-Sicily Channel. The only information available to the Italian Commander-in-Chief (Admiral Campioni in the Vittorio Veneto) up to that moment was that Force H had left Gibraltar westwards on the 25th and on the same day a force had also left Alexandria westwards. He assumed correctly that the force attacked by the torpedo-boat Sirio was en-route to rendez-vous with Force H.
Then at 1015 hours he received an aircraft report (from an aircraft catapulted by the heavy cruiser Bolzano) that at 0945/27 it had sighted a group of enemy warships comprising one battleship, two light cruisers and four destroyers 20 nautical miles north of Cape de Fer. Enemy course was 090°. These were also seven warships, the same number as reported by torpedo-boat Sirio the night before but these were too far to the West to be the same ships.
Then at 1144 hours he received another aircraft report (from an aircraft catapulted by the heavy cruiser Gorizia) that confirmed the position given at 1015 hours. It did not report the two cruisers however but by that time these had split from HMS Renown and had gone ahead.
Acting on the report of the aircraft of the Bolzano the Italian Admiral turned to course 135° at 1128/27. Both divisions of cruisers also turned round. He then thought to be making for an encounter with HMS Renown and two cruisers supported by a few destroyers. The 1144/27 report from the aircraft of the Gorizia confirmed him in this belief. The Italian admiral was unaware of the fact that by that time Force ‘D’ had already joined with the other British forces. He was also unaware that HMS Ark Royal was present although he was aware of the fact that she had left Gibraltar westwards with the other ships two days before.
The Italian admiral was very careful, after the attack on Taranto only two battleships were operational and he could not afford any further reduction in strength of the capital ships. He therefore decided that his forces were not to come in action but before he could sent out a signal regarding this his cruiser were already in action with the British. They were ordered to break off the action and retire at high speed.
The Italians were then attacked by aircraft from the Ark Royal but despite the claim by the British for hits none were actually obtained. The Italians claimed to have shot down two aircraft but this also was not the case.
At 1235/27, the destroyer Lanciere was hit by a 6” shell in the after engine room. This shell is thought to have been originated from HMS Southampton. She continued at 23 knots on her forward engines but at 1240 hours another shell struck her amidships on the port side, penetrating a petrol tank. Then a third shell struck her on the starboard side without exploding and without penetrating the hull. Around 1300 hours she came to a stop with no water in her boilers, and asked for a tow. Ater about one hour her boilers were relit (seawater being used to feed them) and her forward engines were restarted. At 1440 hours, the Ascari took her in tow and both made for Cagliari at 7 knots. The 3rd Cruiser Division was ordered to protect the retreat of these destroyers.
A force of 10 bombers and 5 fighters had taken off at 1330 hours. These were driven off but the Fulmars from HMS Ark Royal. Almost two hours later, at 1520 hours a second force of 20 bombers took off. It were these aircraft that attacked and almost hit HMS Ark Royal.
Convoy operations in the Eastern Mediterranean and the subsequent movements of the ‘Collar’ convoy.
Before and during operation Collar there were also convoy movements in the Eastern Mediterranean going on. [See also the event for 23 November 1940 called ‘Operation MB 9’ for the events in the Eastern Mediterranean.]
After passing through the Sicilian narrows the Clan Forbes and Clan Fraser went to Malta escorted by HMS Hotspur and HMS Decoy. Both destroyers were to repair and refit at Malta. The New Zealand Star proceeded to Suda Bay escorted by HMS Defender and HMS Hereward and covered part of the way by HMS Manchester and HMS Southampton. (49)
29 Nov 1940
Around 1430A/29, HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Berwick (Capt. G.L. Warren, RN), HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN), HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSC, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN) and HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) returned from Gibraltar from operation Collar. One hour later they were followed by HMS Ramillies (Capt. A.D. Read, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN), HMS Despatch (Commodore 2nd cl. C.E. Douglas-Pennant, DSC, RN), HMS Newcastle (Capt. E.A. Aylmer, DSC, RN), HMS Duncan (Capt. A.D.B. James, RN), HMS Wishart (Cdr. E.T. Cooper, RN), HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St.J. Morgan, RN), HMS Jaguar (Lt.Cdr. J.F.W. Hine, RN) and HMS Kelvin (Cdr. J.H. Allison, DSO, RN). (43)
8 Dec 1940
Around 0800A/8, the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN) departed Gibraltar for flying training in the Atlantic. During the battle of Spartivento it had become apparent that her Swordfish pilots lacked training in torpedo attacks on fast moving warships. During the flying training HMS Ark Royal was escorted by the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSC, RN) and HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN).
They returned to Gibraltar around 1330A/11. (50)
14 Dec 1940
At 0237/14 a signal was received from the Admiralty ordering ' Force H ' to sail as early as possible to the Azores.
At 1030/14, HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN), HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN), HMS Isis (Cdr. C.S.B. Swinley, DSC, RN), HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St.J. Morgan, RN) and HMS Duncan (A/Capt. A.D.B. James, RN) departed Gibraltar and proceeded westwards. Ark Royal flew off A/S patrol and also landed on aircraft from North Front.
At 1730/14, a signal from the Admiralty was received stating that the sailing of ' Force H 'was a precautionary move and that more information would follow later.
At 0730/15, a signal was received from the Admiralty timed 0216/15 stating that the RFA tanker Orangeleaf was to sail from Gibraltar to join ' Force H '.
At 0945/15, a signal was received from the Admiralty 0200/15 instructing Vice-Admiral Somerville to patrol of the Azores as a German invasion of the Azores was feared.
The dawn reconnassance report was blank. By this time a north-westerly swell had increased to such anextent that Vice-Admiral Somerville considered it advisable to cancel the afternoon reconnaissance owing to the risk of damage to aircraft.
At 1235/15 course was altered to 285° in order that the dawn reconnaissance the following day should cover the approach routes from the Bay of Biscay to the Azores.
At 1745/15, when in position 37°18'N, 15°20'E the A/S patrol sighted and reported a raft 15 miles on the starboard of HMS Renown. HMS Fury was detached to investigate and located the raft, which was found to belong to the Swedish merchant vessel Gwalia. There were no survivors.
At 2230/15, a darkened sailing ship was sighted in position 37°36'N, 17°00'E. Course was altered away and HMS Fury was detached to investigate. It proved to be a Portugese schooner which was allowed to proceed.
By dawn on 16 December the north-westerly swell had sussided slightly, and nine aircraft were flown off in position 38°15'N, 19°50'E, to carry out a reconnaissance between 200° and 335° to a depth of 140 miles. Nothing was sighted.
At 0900/16, a ship was sighted 18 miles on the starboard beam in position 38°16'N, 20°30'W. Again HMS Fury was sent to investigate and reported her to be the merchant vessel
Gunnery exercises were carried out in the afternoon.
At 1415/16, a second reconnaissance flight of nine aircraft was flown off in position 38°19'N, 21°57'W, co cover the area between 260° and 035° to a depth of 120 miles. Nothing as sighted.
At 0100/17, ' Force H ' was ordered to return to Gibraltar at best convenient speed so course was altered to 095° and speed was increased to 18 knots.
A dawn reconnaissance of nine aircraft was flown off at 0735/17 in position 38°13'N, 19°56'W, to cover the area between 000° and 160° to a depth of 130 miles. Only two British merchant vessels were sighted.
During the forenoon some exercises were carried out.
At 1400/17, the afternoon reconnaissance took off in position 38°18'N, 21°53'W, and covered the area between 035° and 170° to a depth of 150 miles. One one, Portugese, ship was sighted.
More exercises were carried out in the afternoon. Shortly after dark two destroyers were detached from the screen to carry out a night encounter exercise.
At dawn on the 18th, 12 aircraft were flown off to carry out an extensive search with the object of locating the German ship Baden which had been reported to have departed Tenerife on the night of 15/16 December.
More exercises were carried out during the day. The result of the reconnaissance was blank except that HMS Berwick was sighted proceeding to the Azores.
At 1400/18, HMS Renown, HMS Faulknor, HMS Forester and HMS Fury parted company with HMS Ark Royal, HMS Isis, HMS Encounter and HMS Duncan.
HMS Renown and her three escorting destroyers arrived at Gibraltar at 0830/19 followed by HMS Ark Royal and her three destroyers two hours later. (43)
15 Dec 1940
Operations MC 2, MC 3 and HIDE
Convoy operations in the Mediterranean (MC 2), raid by the Mediterranean fleet into the Straits of Otranto (MC 3) and the passage of two transports from Malta, HMS Malaya and five destroyers to Gibraltar (HIDE).
15 December 1940.
The Port Said section of convoy MW 5B departed today. It was made up of the transports Volo (1587 GRT, built 1938), Rodi (3220 GRT, built 1928, former Italian), tanker Pontfield (8290 GRT, built 1940) and transport Ulster Prince (3791 GRT, built 1930). They were escorted by the corvette HMS Peony (Lt.Cdr.(Retd.) M.B. Sherwood, RN).
Also on this day HMS Orion (Capt. G.R.B. Back, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral H.D. Pridham-Whippell, CB, CVO, RN) departed Alexandria for Suda Bay and Piraeus.
16 December 1940.
The Alexandria section of convoy MW 5B departed today. It was made up of the transport Devis (6054 GRT, built 1938) and the tanker Hoegh Hood (9351 GRT, built 1936, Norwegian). The submarine HMS Parthian (Lt.Cdr. M.G. Rimington, DSO, RN) also took passage in this convoy to Malta. Escort for this convoy was provided by HMS Havock (Cdr. R.E. Courage, DSO, DSC, RN). This convoy sailed before noon. The corvettes HMS Salvia (Lt.Cdr. J.I. Miller, DSO, RD, RNR) and HMS Hyacinth (T/Lt. F.C. Hopkins, RNR) joined the convoy at sea coming from Suda Bay.
Another convoy for Malta also departed today, MW 5A, this convoy was made up of the faster transports Waiwera (12435 GRT, built 1934), Lanarkshire (8167 GRT, built 1940). Close escort for this convoy was made up of the battleship HMS Malaya (Capt. A.F.E. Palliser, DSC, RN) and the destroyers HMS Defender (Lt.Cdr. G.L. Farnfield, RN) and HMS Diamond (Lt.Cdr. P.A. Cartwright, RN). This convoy sailed in the afternoon.
Cover for these convoys was provided by ships from the Mediterranean fleet which for this sortie was made up of the battleships HMS Waspite (Capt. D.B. Fisher, CBE, RN, flying the flag of Admiral Sir A.B. Cunningham, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Valiant (Capt. C.E. Morgan, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Illustrious (Capt. D.W. Boyd, DSC, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral A.L.St.G. Lyster, CVO, DSO, RN), heavy cruiser HMS York (Capt. R.H. Portal, DSC, RN), light cruiser HMS Gloucester (Capt. H.A. Rowley, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral E. de F. Renouf, CVO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Jervis (Capt. P.J. Mack, DSO, RN), HMS Janus (Cdr. J.A.W. Tothill, RN), HMS Juno (Cdr. St.J.R.J. Thyrwhitt, RN), HMS Mohawk (Cdr. J.W.M. Eaton, RN), HMS Greyhound (Cdr. W.R. Marshall-A’Deane, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Dainty (Cdr. M.S. Thomas, DSO, RN), HMS Hyperion (Cdr. H.St.L. Nicolson, DSO and Bar, RN), HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN), HMS Hero (Cdr. H.W. Biggs, DSO, RN), HMS Hereward (Lt.Cdr. C.W. Greening, RN) and HMS Ilex (Lt.Cdr. P.L. Saumarez, DSC and Bar, RN) . This cover force sailed from Alexandria around 0100 hours.
At 0745 hours, HMS York, HMS Gloucester, HMS Dainty and HMS Greyhound were detached to fuel at Suda Bay.
At noon the Commander-in-Chief in HMS Warspite was in position 33°36’N, 28°14’E. Course was set for the Kaso Strait which was reached at midnight.
Also on this day HMS Orion arrived at Piraeus. HMS Ajax (Capt. E.D. McCarthy, RN) and HMAS Sydney (Capt. J.A. Collins, CB, RAN) then departed that port for Suda Bay.
17 December 1940.
At 0400 hours, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 35°50’N, 25°56’E. Between 0345 and 0430 hours ten aircraft were flown off by HMS Illustrious to attack Stampalia and Rhodes. Results of these attacks were difficult to observe but several fires were seen to have been started at Stampalia. The weather over Rhodes was bad and only one aircraft was able to locate the target there.
At 0500 hours HMS York, HMS Gloucester, HMS Dainty and HMS Greyhound arrived at Suda Bay where they immediately started to fuel. They departed again at 0700 hours joined by the destroyer HMS Gallant (Lt.Cdr. C.P.F. Brown, DSC, RN). The 3rd Cruiser Squadron was to patrol off the Kithera Channel and the destroyers were to carry out an A/S patrol off the bay when the fleet was to fuel at Suda Bay.
At 0600 hours, HMS Orion arrived at Suda Bay from Piraeus. She sailed at 1130 hours to join HMS Ajax and HMAS Sydney which were patrolling to the west of Crete and had departed Suda Bay at 0300 hours today.
At 0800 hours, the Alexandria and Port Said sections of convoy MW 5B made rendez-vous in position 33°40’N, 27°10’E. Owning to the slow speed of the Hoegh Hood she was detached escorted by HMS Havock.
At 0830 hours, the fleet entered Suda Bay and the destroyers were fuelled.
At 1130 hours, the Rear-Admiral Aircraft Carriers proceeded independently with HMS Illustrious, HMS Valiant, HMS Jervis, HMS Janus, HMS Juno and HMS Mohawk. They were to make rendez-vous with the remainder of the fleet on the 18th but until then had to act independently.
At 1415 hours, the remainder of the fleet also departed. Course was set for the Anti-Kithera Channel which was passed at 1830 hours.
At 1600 hours, the destroyer HMS Griffin (Lt.Cdr. J. Lee-Barber, RN) departed Malta to join the Commander-in-Chief.
The 3rd Cruiser Squadron (York and Gloucester) and the 7th Cruiser Squadron (Orion, Ajax and Sydney) carried out a sweep to the north-west during the night.
At midnight the Commander-in-Chief was in position 34°42’N, 21°45’E.
18 December 1940.
At 0900 hours, the 3rd and 7th Cruiser Squadrons rejoined the Commander-in-Chief in position 36°45’N, 20°28’E. Also HMS Griffin joined from Malta.
At 0930 hours, the Rear-Admiral Aircraft Carriers, also joined.
During the afternoon the weather deteriorated, with high winds and bad visibility, and it appeared unlikely that the proposed bombardment of Valona could take place and that air operations were certainly out of the question.
It was however decided to proceed with the sweep into the Adriatic.
At 1600 hours therefore, a striking force made up of HMS Orion, HMS Ajax, HMAS Sydney, HMS Jervis, HMS Juno and HMS Mohawk was detached. They were ordered to cross latitude 40°25’N at 2330 hours.
At 1800 hours the air striking force, made up of HMS Illustrious, HMS York, HMS Gloucester, HMS Dainty, HMS Greyhound, HMS Gallant and HMS Griffin was also detached. They were to be in position 39°00’N, 20°00’E by 2200 hours.
At 2000 hours, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 39°19’N, 19°20’E.
19 December 1940.
At 0001 hours, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 40°15’N, 19°05’E and at that time the weather had undergone great improvement with good visibility.
It was therefore decided to go ahead with the bombardment. Course was altered to 120° at 0030 hours to close Valona. At 0110 hours, course was altered to a firing course of 140°. HMS Hasty and HMS Hereward swept ahead of HMS Warspite with T.S.D.S. (Two Speed Destroyer Sweep) but no mines were encountered.
At 0113 hours, fire was opened and ceased seven minutes later. About 100 round having been fired. The results of the firing could not be observed.
Between 0130 and 0200 hours, enemy starshell and searchlights were seen in the neighbourhood of Saseno but the bombardment appeared to be a complete surprise to the enemy.
Couse was altered to 210° at 0130 and to 170° and 0230 hours.
In the meantime the striking force had swept up to the line Bari – Durazzo but sighted nothing.
At 0800 hours, the Vice-Admiral light forces (in HMS Orion and his force rejoined the Commander-in-Chief in position 38°33’N, 19°32’E.
One hour later, the Rear-Admiral Aircraft Carriers (in HMS Illustrious and his force also rejoined the Commander-in-Chief. Course was then altered to 220°.
At noon, when in position 34°42’N, 18°44’E, the cuisers HMS Orion, HMS Ajax, HMAS Sydney, HMS Gloucester and HMS York as well as the destroyers HMS Dainty, HMS Gallant, HMS Greyhound, HMS Griffin and HMS Hasty were detached to cover the convoy’s.
At 1400 hours, one aircraft was flown off by HMS Illustrious to carry correspondence to Malta.
There were no further incidents during the day and course was altered to 180° at 1400 hours, to 240° at 2000 hours.
At midnight the Commander-in-Chief was in position 35°40’N, 16°37’E.
20 December 1940.
At 0300 hours, course was altered to 270°.
Early in the morning, convoy MW 5A and her escort of HMS Malaya, HMS Defender, HMS Diamond and now also HMS Nubian (Cdr. R.W. Ravenhill, RN) and HMS Wryneck (Lt.Cdr. R.H.D. Lane, RN) arrived at Malta. After fuelling the destroyers left Malta to join the Commander-in-Chief which they did around 0800 hours.
After these destroyers joined the Commander-in-Chief, HMS Hyperion, HMS Hero, HMS Hereward and HMS Ilex were then detached to fuel.
Meanwhile, at 0630 hours, the destroyers HMS Dainty, HMS Gallant, HMS Greyhound, HMS Griffin and HMS Hasty arrived at Malta to refuel. They had been detached by the Vice-Admiral light forces (in HMS Orion). After fuelling these five destroyers joined the Commander-in-Chief at 1000 hours.
At noon the Commander-in-Chief was in position 35°40’N, 14°10’E. HMS Warspite escorted by HMS Jervis, HMS Janus and HMS Juno then proceeded into Grand Harbour, Malta.
At 1205 hours, the first part of convoy MW 5B arrived at Malta, the other part arrived a little over an hour later except for the Hoegh Hood and her escort HMS Havock.
At 1250 hours, HMS Malaya, escorted by HMS Hyperion, HMS Hereward and HMS Ilex departed Malta to join HMS Illustrious and HMS Valiant and the remaining destroyers at sea.
At 1450 hours, convoy ME 5A sailed from Malta for the east. It was made up of the transports Clan Ferguson (7347 GRT, built 1938), Clan Macaulay (10492 GRT, built 1936), Memnon (7506 GRT, built 1931) and HMS Beconshire (9776 GRT, built 1939). They were escorted by the AA cruiser HMS Calcutta and the corvettes HMS Peony, HMS Salvia and HMS Hyacinth. The destroyer HMS Wryneck also joined.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Meanwhile in the western Mediterranean ‘Force H’ was to sail from Gibraltar today to provide cover for convoy MG 1 (see below) and HMS Malaya during their passage to Gibraltar.
At 0930 hours, five destroyers; HMS Duncan (A/Capt. A.D.B. James, RN), HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St.J. Morgan, RN), HMS Isis (Cdr. C.S.B. Swinley, DSC, RN), HMS Jaguar (Lt.Cdr. J.F.W. Hine, RN) and HMS Wishart (Cdr. E.T. Cooper, RN) departed Gibraltar eastward. This was done so they could sweep ahead of the fleet and that they could also economise fuel in a proportion of the destroyers so the be able to conduct another A/S sweep ahead of ‘Force H’ later in the Skerki Channel.
The remainder of ‘Force H’; battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN), light cruiser HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Fortune (Lt.Cdr. E.N. Sinclair, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN) and HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN), departed Gibraltar westwards at 18 knots at 1800 hours. It was then still daylight. At 1930 hours, when it was completely dark, they reversed course to pass Gibraltar eastwards and also increased speed to 23 knots.
21 December 1940.
At 0700 hours, Hoegh Hood and HMS Havock arrived at Malta.
At 0845 hours, the Vice-Admiral Light Forces which was escorting convoy ME 5, detached HMAS Sydney to Suda Bay where she was to pick up her damaged Walrus aircraft following which Sydney was to proceed to Malta for a short refit.
At 1000 hours, HMS Hyperion, HMS Hero, HMS Hereward and HMS Ilex put into Malta.
At noon, convoy MG 1 departed Malta for Gibraltar, it was made up of transports Clan Forbes (7529 GRT, built 1938) and Clan Fraser (7529 GRT, built 1939) escorted by HMS Hyperion, HMS Hasty, HMS Hero, HMS Hereward and HMS Ilex. At sea HMS Malaya also joined.
Also at noon, HMS Jervis, HMS Janus and HMS Juno departed Malta to proceed ahead of convoy MG 1 on an A/S sweep to the north-west of Pantelleria.
At 1300 hours, a reconnaissance aircraft from HMS Illustrious sighted an enemy convoy. This convoy was then attacked by nine Swordfish fitted with torpedoes. They managed to sink two Italian transports in position 34°39’N, 10°48’E. These were the Norge (6511 GRT, built 1907) and Peuceta (1926 GRT, built 1902).
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
As dawn broke the five destroyers that had sailed earlier were sighted by ‘Force H’ and then joined the fleet. Speed was reduced to 18 knots. A/S patrol aircraft were launched by Ark Royal and a section of fighters was kept at the ready but the RD/F (radar) screens remained clear.
At 1800 hours, four destroyers; HMS Duncan, HMS Encounter, HMS Isis and HMS Jaguar went ahead at 26 knots to make the A/S sweep referred to earlier. ‘Force H’ meanwhile increased speed to 20 knots and at 1930 hours to 22.5 knots.
22 December 1940.
At 0240 hours, HMS Malaya reported that HMS Hyperion had been mined in positon 37°04’N, 11°31’E. HMS Ilex was detached to pick up survivors which she did. She then proceeded to Malta to land them there.
HMS Dainty and HMS Greyhound were detached by the Rear-Admiral Aircraft Carriers to Malta to escort HMS Warspite which was due to return to rejoin the fleet at sea. She departed Malta at 0700 hours escorted by these two destroyers as well as HMS Havock. They rejoined the fleet shortly after 1100 hours in position 35°38’N, 14°06’E
Earlier that morning HMS Illustrious had launched a total of fifteen Swordfish aircraft, in two waves, at 0515 and 0615 hours, to attack Tripoli. Fires were seen to have been started and a warehouse was seen to blew up. All aircraft returned safely.
At 0900 hours, convoy MG 1 and her escort made rendez-vous with ‘Force H’ near Galita Island and continued on the west.
At noon, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 35°34’N, 14°15’E. Course was then set for the eastward.
At 1415 hours, an air search was flown off to search between the Sicilian coast and 070°. This search sighted nothing except a hospital ship.
At 1715 hours, HMS Dainty, HMS Greyhound and HMS Ilex departed Malta to joined the Commander-in-Chief around 0900 hours the next day.
The fleet proceeded to the eastward without incident. Course being altered to 070° at 1800 hours and to 100° at 2030 hours.
At midnight the Commander-in-Chief was in position 35°17’N, 17°56’E.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
The moon rose at 0135 hours and visibility was high. Therefore a torpedo bomber striking force was made ready on board HMS Ark Royal as of 0200 hours.
At 0400 hours, a signal was received from HMS Malaya, that one of the destroyers in her screen, HMS Hyperion, had been mined in position 37°04’N, 11°34’E.
At 0834 hours, a signal was received that HMS Hyperion had sunk and that HMS Ilex had the survivors on board and was proceeding to Malta leaving three destroyers with HMS Malaya.
Shortly before dawn eight aircraft were flown off by HMS Ark Royal but these sighted no enemy ships. Two enemy aircraft were sighted, one by a Swordfish aircraft and one by HMS Jaguar. HMS Duncan and HMS Isis rejoined with ‘Force H’. HMS Encounter and HMS Jaguar had been detached to join HMS Malaya which made rendez-vous with ‘Force H’ at 0940 hours. They then proceeded westwards at 15 knots.
Ark Royal launched a feighter patrol at 1020 hours and this was maintained throughout the day.
At 1245 hours another air search was flown off but again they sighted no enemy ships.
Shortly afterwards, when ‘Force H’ was in position 37°49’N, 08°33’E an aircraft was detected by RD/F and Ark Royal reported that her Skua patrol had driven off an Italian aircraft.
The remainder of the day was uneventful except for sighting a Vichy-French convoy which was not molested.
23 December 1940.
At 0745 hours, an air search was flown off to search a sector between 290° and 270°.
At 0800 hours, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 35°02’N, 20°35’E. Course was 095°.
At 1315 hours, HMS Dainty, HMS Greyhound and HMS Ilex joined the fleet. They had been delayed due to a defect to the steering gear of HMS Greyhound.
At 1400 hours, HMS Defender and HMS Griffin were detached for convoy escort duty with convoy AS 9. They arrived at Suda Bay later this day.
There were no further incidents during the day.
The Vice-Admiral Light Forces in HMS Orion arrived at Alexandia today with HMS Ajax and convoy ME 5. The third cruiser squadron (HMS Gloucester and HMS York) had been detached earlier for Piraeus where they arrived on this day. They had made a short stop at Suda Bay on 22 December.
HMAS Sydney arrived at Malta for a shot refit.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Meanwhile in the western Mediterranean all was quiet as well. Air patrol was kept up throughout the day but they saw no action. Some destroyers carried out exercises.
At 1700 hours, the force was split into two groups; HMS Renown, HMS Malaya and HMS Ark Royal went ahead with a screen on nine destroyers (HMS Faulknor, HMS Firedrake, HMS Forester, HMS Fortune, HMS Foxhound, HMS Fury, HMS Hasty, HMS Hero and HMS Hereward) and set course for Gibraltar at 18 knots. The merchant vessels proceeded at 13 knots escorted by HMS Sheffield and five destroyers (HMS Duncan, HMS Encounter, HMS Isis, HMS Jaguar and HMS Wishart).
24 December 1940.
At 0001 hours, the Commander-in-Chief was in position 33°34’N, 25°27’E steering 120°.
There were no incidents during the day and Alexandria was reached around 1500 hours.
’Force H’ and convoy MG 1 and it’s escort all arrived at Gibraltar today. At 0730 hours, HMS Renown and three destroyers (HMS Faulknor, HMS Forester and HMS Foxhound had increased speed to 24 knots to exercises with the defences of Gibraltar. All ships of the ‘fast group’ had entered Gibraltar by 1230 hours. The ‘slow group’ entered Gibraltar around 1500 hours. (47)
20 Dec 1940
At 0930A/20, five destroyers; HMS Duncan (A/Capt. A.D.B. James, RN), HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St.J. Morgan, RN), HMS Isis (Cdr. C.S.B. Swinley, DSC, RN), HMS Jaguar (Lt.Cdr. J.F.W. Hine, RN) and HMS Wishart (Cdr. E.T. Cooper, RN) departed Gibraltar eastward for an A/S sweep.
Around 1800A/20, the remainder of ' Force H ' made up of the battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN), light cruiser HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Fortune (Lt.Cdr. E.N. Sinclair, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN) and HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN), departed Gibraltar westwards for operations.
' Force H ' returned to Gibraltar, in several groups, on 24 December 1940.
[For more info on these operations see the event ' Operations MC 2, MC 3 and HIDE ' for 15 December 1940.] (43)
25 Dec 1940
Operations by 'Force H' following the attack by the German heavy cruiser Admiral Hipper on convoy WS 5A.
[For more info on convoy WS 5A on the first leg of her passage, it's composition, and the attack by the German cruiser Admiral Hipper see the event ' Convoy WS 5A and the attack by the German heavy cruiser Admiral Hipper ' for 18 December 1940 on for instance the page of HMS Berwick.]
25 December 1940.
At 1020/25 an enemy report of a pocket battleships (later corrected to an 8" cruiser), in position 43°59'N, 25°08'W, was received from HMS Berwick (Capt. G.L. Warren, RN). Vice-Admiral Somerville immediately ordered 'Force H' (less HMS Malaya) to come to one hour's notice for full speed. Twenty minutes later, instructions were received from the Admiralty for 'Force H' to raise steam with all despatch, and shortly afterwards for the force to proceed to sea.
Ships commenced to leave Gibraltar at 1315 hours and by 1430 hours; battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN), light cruiser HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Fortune (Lt.Cdr. E.N. Sinclair, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN), HMS Duncan (A/Capt. A.D.B. James, RN), HMS Hero (Cdr. H.W. Biggs, DSO, RN), HMS Hereward (Lt.Cdr. C.W. Greening, RN) and HMS Wishart (Cdr. E.T. Cooper, RN), were clear of the harbour and on a Westerly course.
Course was set to position 37°00'N, 16°00'W as this was considered to be the best position to either cover the convoy or assist in the hunt for the enemy. Vice-Admiral Somerville reported to the Admiralty that 'Force H' was proceeding to this position at high speed with eight destroyers, who would remain in company or follow, depending on the weather.
At 1500/25 a signal was received from the Admiralty ordering the convoy and escort to proceed to Gibraltar. At this time Vice-Admiral Somerville was not aware - nor apparently were the Admiralty - that the convoy had scattered. As there now appeared little chance to bringing the raider to action. Vice-Admiral Somerville decided to join the convoy and reported accordingly to the Admiralty. Weather conditions enabled the destroyers to remain in company at 27 knots.
An hour later a further signal was received from the Admiralty directing the convoy to pass through positions 41°00'N, 19°00'W and 37°00'N, 16°00'W. These instructions were only passed to HM Ships, all of whom, it was subsequently learnt, were out of touch with the scattered convoy.
In view of the low endurance of HMS Wishart, she was detached at 1845/25 with instructions to follow at economical speed and join the convoy during daylight on December, 27th in position 37°00'N, 16°00'W.
The first indication that the convoy had scattered was received at 2000/25 when HMS Dunedin (Capt. R.S. Lovatt, RN) reported that she had met the City of Canterbury who was proceeding to the convoy Commodore's Noon/26 rendez-vous.
Shortly after this reported a report was received from the corvette HMS Clematis confirming that the Commodore had ordered to convoy to scatter, it also stated that the troopship Empire Trooper was damaged, believed slightly.
At 2200/25, general instructions to all units were received from the Admiralty, still acting on the assumption that escort and convoy were in company. 'Force H' was directed to rendez-vous with HMS Berwick and escort the convoy until 'Force K' (aircraft carrier HMS Formidable (Capt. A.W.La T. Bisset, RN) and heavy cruiser HMS Norfolk (Capt. A.J.L. Phillips, RN) joined. 'Force K' was then to escort the main body of the convoy to Freetown, whilst 'Force H', with aircraft carrier HMS Argus (Capt. E.G.N. Rushbrooke, DSC, RN) and light cruisers HMS Bonaventure (Capt. H.G. Egerton, RN) and HMS Dunedin escorted the 'Operation Excess' section to Gibraltar. The damaged heavy cruiser HMS Berwick was to proceed to the U.K. if fit for passage. It also directed that if needed the upcoming 'Operation Excess' could be postponed for 24 hours.
26 December 1940.
At 0200/26 a signal was received from the Admiralty stating that the convoy had scattered and that the ships were most likely proceeding to one of the following positions; the Commodore's noon/26 rendezvous; position 41°00'N, 19°00'W; or direct to Gibraltar. Vice-Admiral Somerville was ordered to take charge.
As he was unaware of the position of 'Force K' he ordered the Senior Officer 'Force K' to report his position, course, speed and intention. Later the aircraft carrier HMS Furious (Capt. A.G. Talbot, DSO, RN) was also ordered to report similarly. All units were informed of the position, course and speed of 'Force H'.
No further news had been received regarding the damaged troopship Empire Trooper. At 0801/26, Vice-Admiral Somerville, ordered the armed merchant cruiser HMS Derbyshire (Capt.(Retd.) E.A.B. Stanley, DSO, MVO, RN) to proceed to her assistance.
At 1100/26, the situation was still obscure. No reply had been received from 'Force K' and HMS Furious. HMS Bonaventure had just reported that she was proceeding to the assistance of the corvette HMS Cyclamen (Lt. H.N. Lawson, RNR). Ships of the convoy were apparently scattered over a wide area, each making for one of three different positions. Visibility to the westward was apparently very low. Vice-Admiral Somerville therefore requested the Admiralty to broadcast instructions on commercial wave to ships of the convoy to proceed to position 37°00'N, 16°00'W. He also informed the Admiralty that it was his intention to have HMS Derbyshire to take over from HMS Bonaventure to enable Bonaventure to proceed to Gibraltar for 'Operation Excess'.
'Force K' and HMS Furious reported between 1200 and 1300/26. 'Force K' was intending to collect the convoy at the Commodor's noon/26 rendez-vous and escort them to 37°00'N, 16°00'W. HMS Furious reported that she was in company with HMS Argus so as to reach position 37°00'N, 16°00'W at 1300/27. Also it was reported that she needed to refuel at Gibraltar before she could proceed to Freetown.
A reconnaissance of nine aircraft was flow off by HMS Ark Royal at 1300 hours in position 38°23'N, 15°45'W but nothing was sighted by these aircraft.
A report from HMS Bonaventure was received at 1630/26. She had intercepted the German merchant ship Baden (8204 GRT, built 1922) in position 44°00'N, 25°07'W. The German ship could not be boarded in the foul weather and the Germans had also set it on fire. HMS Bonaventure sank the German ship with a torpedo. She also stated that she had not yet sighted the Empire Trooper.
The situation at 1700/26 was as follows; the approximate position of all H.M. Ships in the area was known (except for the corvettes). HMS Cyclamen, with her W/T out of action, was believed to be standing by the Empire Trooper, and it appeared probable that the three remaining corvettes (HMS Jonquil (Lt.Cdr. R.E.H. Partington, RNR), HMS Clematis (Cdr. Y.M. Cleeves, DSO, DSC, RD, RNR) and HMS Geranium (T/Lt. A. Foxall, RNR)) had proceeded to Ponta Delgada to fuel. Only one merchant ship had been located. The City of Canterbury, in company with HMS Dunedin. Whilst the situation of the Empire Trooper caused some anxiety priority was given to assist in rounding up and covering the remainder of the convoy which might be making for position 37°00'N, 16°00'W.
At 1720/26, all units were instructed to act as follows; 'Force H' was to maintain position between the northern and southern appoaches to position 37°00'N, 16°00'W. 'Force K' was to continue to search for ships passing through position 39°08'N, 21°38'W. HMS Furious was to arrive in position 37°00'N, 16°00'W at 1400/27, searching to the north and east for ships proceeding direct to Gibraltar. HMS Berwick was to search to the north and west of position 37°00'N, 16°00'W, during the forenoon of December, 27th. She was to make rendez-vous with 'Force H' at 1400/27. HMS Dunedin was also to make rendez-vous with 'Force H' at 1400/27. All ships were directed to report at 2200/26 and 1200/27 the number of merchant ships in company.
The 2200 reports received indicated that only three merchant ships had been located, two by 'Force K' and one by HMS Dunedin. Both HMS Norfolk and HMS Dunedin reported to be getting low on fuel. At the same time HMS Berwick reported to the Admiralty that she had to proceed to Gibraltar to make good underwater damage, to free 'X' turret and to fuel.
27 December 1940.
At 0145/27 the Admiralty informed Vice-Admiral Somerville that further steps were required to locate the Empire Trooper who had 2500 troops on board. In view of the existing fuel situation and the necessity for providing air reconnaissance to locate the damaged ship and as there were no further indications of the precense of the enemy cruiser Vice-Admiral Somerville decided to proceed with HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal to locate the Empire Trooper, whose last known position was some 600 nautical miles to the north-west. This nescessitated dropping the screening destroyers. Vice-Admiral Somerville therefore informed the Admiralty accordingly and directed 'Force K' to take charge of operations in connection to the convoy. At the same time Vice-Admiral Somerville instructed HMS Derbyshire to report her position, course and speed, and ordered HMS Clematis to report the position of the corvettes and to provide any further information regarding the condition of the Empire Trooper.
HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal proceeded at 22 knots, later increasing to 24 knots, to the north-westward, with the intention of locating the Empire Trooper by air after daylight the following morning.
At 0800/27, Vice-Admiral Somerville ordered HMS Cyclamen, if still in touch with the Empire Trooper, to report her position, course and speed and also requested the Admiralty to order the Empire Trooper herself to report her position.
Two hours later, HMS Clematis reported that she had sighted the Empire Trooper through the mist half an hour after the latter had been hit in No.1 hold. The transport was then steaming 13 knots and damage was not believed to be serious. Owning to low visibility the other corvettes had not been located. Shortly after this HMS Derbyshire reported her position, course and speed at 1000/27 and added that visibility was half a mile.
In view of the low visibility prevailing, which would preelude air reconnaissance, and of the encourageing report from HMS Clematis of Empire Trooper's condition, it appeared to Vice-Admiral Somerville doubtful wheter the presence of HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal would serve any useful purpose. Whilst so far to the northward they were unable to afford any protection to the remaining ships of the convoy, whose escorts in some cases were running short of fuel. Furtherm to remain in this position would inevitably result in delay in carrying out the upcoming 'Operation Excess'. Vice-Admiral Somerville there proposed to the Admiralty that HMS Derbyshire should remain in the vicinity of the Empire Trooper's last reported position and that HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal should return to Gibraltar, covering the convoy.
Pending the Admiralty reply to this signal, HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal proceeded to a suitable position to carry out a dawn reconnaissance with aircraft to locate the Empire Trooper should this be required whilst at the same time enabling Renown and Ark Royal to return to Gibraltar at high speed in time to carry out 'Operation Excess'.
Reports received from all units indicated that a total of four merchant ships had been located by 1200/27. The Senior Officer 'Force K', at this time ordered HMS Furious, HMS Argus, HMS Dunedin and the five transports which were to participate in 'Operation Excess', when collected, to proceed to Gibraltar with the nescessary destroyers. HMS Berwick, HMS Sheffield and the remaining destroyers to remain at the rendez-vous position until 'Force K' arrived there.
The Admiralty reply to Vice-Admiral Somerville's proposal was received at 1500/27 and directed the Vice-Admiral to remain in the area with HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal until the situation regarding the Empire Trooper had been cleared up or as long as endurance of the screen allowed.
As Vice-Admiral Somerville had previously reported that HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal had proceeded unscreened at 0200/27, he was uncerain how to interpret this signal. He assumed that it was intended that he should rejoin his destroyers in the vicinity of 37°00'N, 16°00'W and this was reported to the Admiralty accordingly.
At 1700/27 a report was intercepted from HMS Cyclamen that she was standing by the Empire Trooper who had been holed in No.1 and No.4 hatches and whose situation was serious. Her position at 0800/27 was given as 41°00'N, 22°09'W, course 138°, speed 4 knots. Shortly afterwards a report in Merchant Navy Code was intercepted from the Empire Trooper, in which she suggested that assistance should be sent to disembark the troops if necessary. The position given by the Empire Trooper differed considerably from that reported by HMS Cyclamen, whilst first class D/F bearing obtained at this time was also at variance with both positions. From all the evidence available it appeared that the Empire Trooper was in approximate position 40°40'N, 21°16'W at 1730/27.
in view of these less satisfactory reports, Vice-Admiral Somerville at once ordered HMS Bonaventure to proceed to the Empire Trooper estimated position. As it appeared possible that transfer of troops at sea might be necessary, the Vice-Admiral ordered HMS Sheffield to detach the two destroyers with the most fuel remaining to proceed at 16 knots towards the Empire Trooper. It was doubtful wheter these had enough endurance to return to Gibraltar, but in emergency they could proceed to the Azores if refuelling at sea was impracticable. In the meantime HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal proceeded westwards to reach the most favourable position for flying off a dawn reconnaissance should weather conditions enable this to be done.
At 2030/27, Admiralty instructions were received for Empire Trooper to steer for Ponta Delgada as soon as weather permitted. Twenty-five minutes later a signal from the Admiralty was received the the light cruiser HMS Kenya (Capt. M.M. Denny, CB, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral H.M. Burrough, CB, RN), who had previously had been ordered to join convoy SL 59, was ordered to join the Empire Trooper instead.
At 2300/27 Admiralty instructions to all concerned regarding the Empire Trooper were received. HMS Kenya, HMS Berwick, HMS Cyclamen, HMS Clematis, HMS Jonquil and HMS Geranium were ordered to join the Empire Trooper and escort her to Punta Delgada. If it was found that HMS Berwick could remain with the Empire Trooper, HMS Bonaventure was to be released for 'Operation Excess' as soon as HMS Berwick relieved her, otherwise HMS Bonaventure was to remain with the Empire Trooper.
HMS Berwick reported she expected to join the Empire Trooper by 1700/28. As Bonaventure's shortage of fuel would prelude her joining the Empire Trooper before the latter had been joined by HMS Berwick, Vice-Admiral Somerville ordered HMS Bonaventure to proceed to Gibraltar.
At midnight, Vice-Admiral Somerville received a signal from 'Force K' containing proposals for the future movements of the convoy and escort.
28 December 1940.
A report was received from HMS Cyclamen at 0330/28 giving the position of the Empire Trooper at 2000/27 as 40°12'N, 21°13'W, speed 6 knots. The damaged ship had thus made good some 250 nautical miles since being attacked. As it now appeared that sufficient ships would be available to stand by her and in view of the critical fuel situation in the two destroyer that had been ordered to join her (these were HMS Duncan and HMS Hero) they were ordered to proceed to Gibraltar.
The fore end of HMS Renown's starboard bulge, which had started to tear away some time previously, now became more serious, rendering it inadvisable for the ship to exceed 20 knots. As weather conditions still precluded flying, and as HMS Kenya, HMS Berwick, HMS Derbyshire and the four corvettes were all in the vicinity of or approaching the Empire Trooper, it dit not appear that any useful purpose would be served by HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal remaining unscreened in submarine infested waters and risking further damage to Renown's bulge.
The Admiralty was then informed that HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal were returning to Gibraltar. Also a signal was sent to prepare No.1 dock at Gibraltar for HMS Renown with all despatch.
As the docking of HMS Renown would involve some delay in 'Operation Excess', Vice-Admiral Somerville informed the Admiralty and the Commander-in-Chief Mediterranean, that the earliest possible D.1 for would be January, 1st, and that even this date was dependent on it being possible for Renown to be made seaworthy within 24 hours of docking.
By 1500/28 the weather had improved sufficiently for an A/S patrol to be flown off. This was maintained till dusk.
During the afternoon further damage was caused to the bulge. By this time about 30 feet of the top strake had been town away and a large number of rivets were leaking. Shores and cofferdams were placed.
In order to provide a screen for HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal, Vice-Admiral Somerville ordered HMS Duncan and HMS Hero, now on passage to Gibraltar, to rendez-vous with the capital ships at 1000/29, and also the Admiral Commanding, North Atlantic Station was asked to sail additional destroyers if pacticable. HMS Faulknor, HMS Firedrake, HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN) and HMS Jaguar (Lt.Cdr. J.F.W. Hine, RN) were sailed from Gibraltar to rendez-vous with the capital ships at 1100/29.
Air reconnaissance sighted nothing of interest during the day. At dusk couse was altered to pass north of convoy HG 49 which had left Gibraltar at 1800/28 and speed was reduced to 18 knots to increase the efficiency of the Asdic operating.
29 December 1940.
HMS Faulknor, HMS Firedrake, HMS Hasty and HMS Jaguar indeed joined 'Force H' at 1100/29.
30 December 1940.
HMS Renown, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Faulknor, HMS Firedrake, HMS Duncan, HMS Hasty, HMS Hero and HMS Jaguar arrived at Gibraltar at 0830 hours when HMS Renown immediately entered No.1 Dock. (43)
6 Jan 1941
Operations Excess and Operation MC 4.
Convoy operations in the Mediterranean.
Timespan; 6 January to 18 January 1941.
The principal object of this operation was the passage of a convoy of four ships (five were intended, see below) from Gibraltar to Malta and Piraeus (Operation Excess). One of these was to unload her stores at Malta, the other three had supplies on board for the Greek army.
Three subsidiary convoys (Operation M.C. 4) were to be run between Malta and Egypt. These consisted of two fast ships from Malta to Alexandria (convoy M.E. 5½), two fast ships from Alexandria to Malta (convoy M.W. 5½) and six slow ships from Malta to Port Said and Alexandria (convoy M.E. 6).
Composition of the convoys and their escort.
The ‘Excess convoy from Gibraltar’ was made up of one ship that was to proceed with stores to Malta. This was the Essex (11063 GRT, built 1936). The three other ships were to proceed with stores to Piraeus, these were the Clan Cumming (7264 GRT, built 1938), Clan Macdonald (9653 GRT, built 1939) and Empire Song (9228 GRT, built 1940). It had the light cruiser HMS Bonaventure (Capt. H.G. Egerton, RN) and the destroyers HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, RN), HMS Hero (Cdr. H.W. Biggs, DSO, RN), HMS Hereward (Cdr. C.W. Greening, RN) and HMS Duncan (A/Capt. A.D.B. James, RN) as close escort (‘Force F’). A fifth merchant ship was to have been part of this convoy and was to have proceeded to Malta with stores and troops. However this ship, the Northern Prince (10917 GRT, built 1929) grounded at Gibraltar and was not able to join the convoy. The about four-hundred troops now boarded HMS Bonaventure for passage to Malta.
The most dangerous part of the ‘Excess convoy’ would be the part between Sardinia and Malta. For a stretch of about 400 nautical miles ships were exposed to enemy air attack from bases in Sardinia and Sicily less then 150 nautical miles away from the convoy’s track. Also submarines and surface torpedo craft were a constant menace. An attack by large enemy surface forces was thought less likely although this was potentially more dangerous.
’Convoy M.W.5 ½ from Alexandria to Malta’ made the passage westwards at the same time as the Mediterranean fleet moved westwards (see below). This convoy was made up of HMS Breconshire (9776 GRT, built 1939) and Clan Macauley (10492 GRT, built 1936). These ships were escorted by HMS Calcutta (Capt. D.M. Lees, DSO, RN), HMS Defender (Lt.Cdr. G.L. Farnfield, RN) and HMS Diamond (Lt.Cdr. P.A. Cartwright, RN).
’Convoy’s M.E. 5½ and M.E. 6’ that sailed from Malta to Egypt will be dealth with later on.
Cover forces for these convoy’s
At Gibraltar there was ‘Force H’ which had the following ships available for the operation. Battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. C.E.B. Simeon, RN and flagship of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, RN, KCB, DSO, RN), battleship HMS Malaya (Capt. A.F.E. Palliser, DSC, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN), light cruiser HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Fortune (Lt.Cdr. E.N. Sinclair, RN), HMS Foxhound (Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) and HMS Jaguar (Lt.Cdr. J.F.W. Hine, RN).
’Force H’ was to provide cover for the ‘Excess convoy’ from Gibraltar to the Sicilian narrows.
South-south-west of Sardina ‘Force H’ was to be reinforced by ‘Force B’ which came from the eastern Mediterranean and was made up of the light cruisers HMS Gloucester (Capt. H.A. Rowley, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral E. de F. Renouf, CVO, RN), HMS Southampton (Capt. B.C.B. Brooke, RN) and the destroyer HMS Ilex (Capt. H.St.L. Nicholson, DSO and Bar, RN). The destroyer HMS Janus (Cdr. J.A.W. Tothill, RN) had also been part of 'Force B' during the passage from Alexandria to Malta but remained there for a quick docking. After this docking she departed Malta around noon on the 10th to join 'Force A'.
Further cover was to be provided by ‘Force A’, this was the Mediterranean fleet based at Alexandria. This force was made up of the following warships. Battleships HMS Warspite (Capt. D.B. Fisher, CBE, RN, flying the flag of Admiral Sir A.B. Cunningham, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Valiant (Capt. C.E. Morgan, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Illustrious (Capt. D.W. Boyd, CBE, DSC, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral A.L.St.G. Lyster, CB, CVO, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Jervis (Capt. P.J. Mack, DSO, RN), HMS Juno (Cdr. St.J.R.J. Thyrwhitt, RN), HMS Mohawk (Cdr. J.W.M. Eaton, RN), HMS Nubian (Cdr. R.W. Ravenhill, RN), HMS Greyhound (Cdr. W.R. Marshall-A’Deane, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Gallant (Lt.Cdr. C.P.F. Brown, DSC, RN), HMS Griffin (Lt.Cdr. J. Lee-Barber, RN) and HMS Dainty (Cdr. M.S. Thomas, DSO, RN).
During the passage of the ‘Excess convoy’ three submarines were stationed off Sardinia. HMS Pandora off the east coast and HMS Triumph and HMS Upholder were stationed to the south of Sardinia.
Chronology of events
The actual ‘Excess convoy’ and it’s escort (Force F) departed Gibraltar before dark in the evening of January 6th. Course was set to the west as if to proceed into the Atlantic. This was done to deceive enemy spies based in Spain. They turned back in the night after moonset and passes Europa Point well before daylight next morning. At dawn the next morning HMS Bonaventure parted company with the convoy to make rendez-vous with ‘Force H’ which departed Gibraltar around that time. All that day the ‘Excess convoy’ followed the Spanish coast so as if to make for a Spanish port. During the night of 7/8 January the convoy crossed over towards the coast of North-Africa and steered eastwards towards the Sicilian narrows while keeping about 30 nautical miles from the shore of North Africa. ‘Force H’ overtook the convoy during the night and was now stationed to the north-east of it to shield it from Italian air attack. If Italian naval units were reported the plan was that he would join the convoy.
In the morning of the 8th, HMS Bonaventure rejoined the actual ‘Excess convoy’. Late in the afternoon of the 8th HMS Malaya escorted by HMS Firedrake and HMS Jaguar parted company with ‘Force H’ and joined the ‘Excess convoy’ very early in the evening.
At dawn on the 9th ‘Force H’ was ahead of the convoy. At 0500/9, while in position 37°45’N, 07°15’E, HMS Ark Royal flew off five Swordfish aircraft for Malta which was still some 350 nautical miles away. All of which arrived safely. ‘Force H’ then turned back and joined the ‘Excess convoy’ at 0900/9 about 120 nautical miles south-west of Sardinia. HMS Ark Royal meanwhile had launched several aircraft, one of her reconnaissance aircraft reported at 0918 hours that it had sighted two enemy cruisers and two destroyers but this soon turned out to be Rear-Admiral Renouf’s ‘Force B’ which was to join the Excess convoy for the passage through the Sicilian narrows. They joined the convoy about one hour later.
’Force B’ had departed Alexandria in the morning of the 6th with troop for Malta on board. They had arrived at Malta in the morning of the 8th and after disembarking the troops (25 officers and 484 other ranks of the Army and RAF) sailed early in the afternoon. At 0900/9 ‘Force B’ was sighted by an Italian reconnaissance aircraft. This aircraft soon made off when being fired at. One hour later another Italian reconnaissance aircraft was however sighted. It was engaged by the fighter patrol from HMS Ark Royal but managed to escape. At 1320 hours, while in position 37°38’N, 08°31’E, Italian bombers arrived on the scene and made their attack on the convoy.
The convoy of the four merchant ships was steaming in two columns in line ahead, 1500 yards apart. HMS Gloucester and HMS Malaya were leading the columns while HMS Bonaventure and HMS Southampton were the sternmost ships. The seven destroyers were placed as a screen ahead of the convoy. ‘Force H’, with HMS Renown, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Sheffield and their five escorting destroyers were on the convoy’s port quarter, operating in close support. The mean line of advance was 088° and the ships were zigzagging at 14 knots.
The enemy consisted of ten Savoia bombers. HMS Sheffield detected them on her radar about 43 nautical miles off, this was the maximum range of her radar equipment. They were fine on the starboard bow and came into sight fourteen minutes later, flying down the starboard side of the convoy out of range of the AA guns at a eight of about 11000 feet. At 1346 hours, when they were broad on the bow, they started their attack. They came in from 145°, which was the bearing of the sun. All the ships opened up a very heavy fire and the enemy was diverted of their course. Eight of the aircraft were seen to drop bombs, some of which fell close to HMS Gloucester and HMS Malaya but no damage was caused. The other two bombers were seen to turn away during their approach. Both were shot down by a Fulmar fighter from HMS Ark Royal. Three men from their crews were picked up from the water. Another bombers is thought to have been shot down by HMS Bonaventure. The other seven are thought to have got away.
Nothing more happened during the afternoon of the 9th. Reconnaissance showed that the Italian fleet was not at sea so at dusk, while in position 37°42’N, 09°53’E, some 30 nautical miles west of the Sicilian narrows and north of Bizerta, Tunisia, ‘Force H’ parted company with the ‘Excess convoy’ and set course to return to Gibraltar. Rear-Admiral Renouf in HMS Gloucester meanwhile continued eastwards with the convoy with his three cruisers and five destroyers of forces ‘B’ and ‘F’.
They had a quiet night, passing Pantelleria after moonset. They remained in deep water to reduce the danger of mines. Next morning, at dawn on the 10th at 0720 hours, they encountered two Italian torpedo boats in position 36°30’N, 12°10’E. HMS Jaguar, the port wing destroyer in the screen, and HMS Bonaventure, stationed astern of the convoy columns, sighted the enemy at the same time. Initially thinking they might be destroyers from the Mediterranean Fleet, which the convoy was due to meet. British ships reported the contact by signal to Rear-Admiral Renouf. HMS Bonaventure challenged the ‘strangers’ and fired a star shell and then turned to engage the enemy working up to full speed. Rear-Admiral Renouf meanwhile turned away with the bulk of the convoy. HMS Southampton, HMS Jaguar and HMS Hereward hauled out from their stations on the engaged side of the convoy and made for the enemy. HMS Bonaventure meanwhile was engaging the right-hand ship of the pair. When the other three ships arrived on the scene Bonaventure shifted her fire to the other enemy ship which came towards her at full speed to attack. The enemy fired her torpedoes which HMS Bonaventure avoided. The four British ships now quickly stopped the enemy but she did not sink. In the end HMS Hereward torpedoed the damaged Italian torpedo boat some 40 minutes later. The other Italian torpedo-boat meanwhile had disappeared. [The Italian ships were the torpedo-boats Vega, which was sunk, and the Circe. HMS Boneventure had sustained some superficial damage from splinters during the action.
Enemy air attacks during 10 January.
At 0800/10, Admiral Cunningham arrived on the scene with ‘Force A’ before the fight was finished. ‘Force A’ turned to the south-east in the wake of the ‘Excess convoy around 0830 hours. While doing so, the destroyer HMS Gallant hit a mine and had her bow blown off. [This was a mine from the Italian minefield ‘7 AN’]. HMS Mohawk took the stricken destroyer in tow towards Malta escorted by HMS Bonaventure and HMS Griffin. They were later joined by HMS Gloucester and HMS Southampton. While HMS Mohawk was passing the towline two Italian torpedo planes attacked but they had to drop their torpedoes from long range and they missed. Between 1130 and 1800 hours, as the tow crept along at five or six knots, with their escort zig-zagging at 20 knots, they were attacked or threatened by aircraft ten times. Nearly all German high level bombers, which came in ones, twos or threes. The enemy dropped bombs in five out of the ten attempts but no hits were obtained. At 1300 hours German dive bombers arrived an obtained a near miss on HMS Southampton causing some minor damage.
At 0500/11, when about 15 nautical miles from Malta, all was going well and Rear-Admiral Renouf made off with for Suda Bay, Crete with HMS Gloucester, HMS Southampton and HMS Diamond. This last ship had joined the evening before. HMS Gallant, still being towed by HMS Mohawk and escorted by HMS Bonaventure and HMS Griffin arrived at Malta in the forenoon. At Malta, HMS Bonaventure disembarked the soldiers she had on board. [HMS Gallant was further damaged by bombs while at Malta and was eventually found to be beyond economical repair and was cannibalized for spares.]
Meanwhile, Admiral Cunningham in ‘Force A’ had a similar experience on a larger scale. He had sailed from Alexandria on the 7th and enemy aircraft spotted his force already on the same day. During the afternoon of the 10th heavy dive bombing attacks were pressed home by the enemy with skill and determination. The main target was HMS Illustrious. Had the enemy attacked the convoy itself the four transports would most likely all have been sunk, instead the Ilustrious was disabled and she would be out of action of many months.
At noon on the 10th the transports were steering south-eastward, zigzagging at 14 to 15 knots with an escort of three destroyers. At 1320 hours, HMS Calcutta joined them. HMS Warspite, HMS Illustrious and HMS Valiant were steaming in line ahead on the convoy’s starboard quarter, course 110° and zigzagging at 17 to 18 knots. These ships were screened by seven destroyers. The weather was clear, with high cloud.
The fleet was in position 35°59’N, 13°13’E some 55 nautical miles west of Malta when the battle began with an air attack by two Savoia torpedo planes which were detected six nautical miles away on the starboard beam at 1220 hours. They came in at a steady level, 150 feet above the water and dropped their torpedoes about 2500 yards from the battleships. They were sighted a minute before firing and the ships received them with a barrage from long- and short-range guns, altering course to avoid the torpedoes, which passed astern of the rearmost ship HMS Valiant. Five Fulmar fighters from the Illustrious had been patrolling above the fleet. One had returned before the attack being damaged while assisting to destroy a shadower some time before the attack. The other four aircraft chased the torpedo aircraft all the way to Linosa Island, which was about 20 miles to the westward. They claimed to have damaged both the enemy machines.
Directly after this attack, while the ships were reforming the line, a strong force of aircraft were reported at 1235 hours, coming from the northward some 30 miles away. The Fulmars, of course, were then a long way off, flying low and with little ammunition remaining. Actually two were even out of ammunition. They were ordered to return and the Illustrious sent up four fresh fighters as well as reliefs for the anti-submarine patrol. This meant a turn of 100° to starboard into the wind to fly off these aircraft. The enemy aircraft came into sight in the middle of this operation which lasted about four minutes. All the ships opened fire. The fleet had just got back to the proper course, 110°, and the Admiral had made the signal to assume loose formation, when the new attack began. The enemy had assembled astern of their target ‘in two very loose and flexible formations’ at a height of 12000 feet.
They were Junkers dive bombers, perhaps as many as 36, of which 18 to 24 attacked HMS Illustrious at 1240 hours, while a dozen attacked the battleships and the destroyer screen. They came down in flights of three on different bearings astern and on either beam, to release their bombs at heights from 1500 to 800 feet, ‘a very severe and brilliantly executed dive-bombing attack’ says Captain Boyd of the Illustrious. The ships altered course continually, and beginning with long-range controlled fire during the approach, shifted to barrage fire as the enemy dived for attack. The ships shot down at least three machines, while the eight Fulmar fighters that were up shot down five more, at the coast of one British machine. Even the two Fulmars that were out of ammo made dummy attacks and forced two Germans to turn away. But, as Captain Boyd pointed out ‘ at least twelve fighters in the air would have been required to make any impression on the enemy, and double that number to keep them off’.
HMS Illustrious was seriously damaged. She was hit six times, mostly with armour-piercing bombs of 1100 pounds. They wrecked the flight deck, destroyed nine aircraft on board and put half the 4.5” guns out of action, and did other damage, besides setting the ship on fire fore and aft and killing and wounding many of the ship’s company (13 officers and 113 ratings killed and 7 officers and 84 ratings injured) . The Warspite too, narrowly escaped serious injury, but got away with a split hawsepipe and a damaged anchor.
As HMS Illustrious was now useless as a carrier and likely to become a drag on the fleet Captain Boyd decided to make for Malta. The Commander-in-Chief gave her two destroyers as escort, one from his own screen and one from the convoy’s (these were HMS Hasty and HMS Jaguar) and she parted company accordingly. She had continual trouble with her steering gear, which at last broke down altogether, so that she had to steer with the engines, making only 17 to 18 knots. Her aircraft that were in the air also proceeded to Malta.
A third attack came at 1330 hours. By this time HMS Illustrious was 10 nautical miles north-eastward of the battleships which, due to the manoeuvres during the previous attack, were nearly as far away from the transports. The enemy came in again with high level bombers. Seven machines attacked the Illustrious and seven more the battleships. They were received with heavy AA fire. All the bombs they dropped fell wide. HMS Calcutta claimed to have destroyed one of the attackers.
More serious in it’s results was a second dive-bombing attack upon HMS Illustrious at 1610 hours. There were 15 JU-87’s Stuka’s escorted by 5 fighters. Actually 9 of the Stuka’s dropped their bombs, the other 6 were kept at bay due to heavy AA fire from the Illustrious, Hasty and Jaguar. One bomb hit and two near misses on the Illustrious were obtained by the enemy for the loss of one of their aircraft which was shot down by the Illustrious and the Jaguar. A few minutes later the 6 Stuka’s that had been driven off attacked the battleships but they again retired after fire was opened on them.
At 1715 hours, 17 more Stuka’s attacked the battleships. Again they were received with heavy AA fire. The enemy dropped their bombs from a greater height and non of them hit although splinters from a near miss killed a rating on board HMS Valiant and a bombs fell very near HMS Janus but it did not explode. The ships may have destroyed one aircraft with their AA fire. Three of the Fulmars from the Illustrious came from Malta and destroyed three of the attackers.
This turned out to be the end of the ordeal for the ‘Excess Convoy’ and its supporting ships of war, but not for HMS Illustrious which had one more encounter with the enemy before she reached Malta. At about 1920 hours, a little more then an hour after sunset and in moonlight, some aircraft approached from seaward when she was only five nautical miles from the entrance to Grand Harbour, Malta. She had received warning from Malta that enemy aircraft were about and she sighted two – probably torpedo planes. Illustrious, Hasty and Jaguar fired a blind barrage on which the enemy disappeared. Directly afterwards HMS Hasty obtained an Asdic contact and attacked it with depth charges, but whether it was a submarine remains uncertain. HMS Illustrious finally entered harbour at 2100 hours accompanied by HMS Jaguar which had passengers to land.
Movements of the actual ‘Excess Convoy’.
In the meantime, after the mild attack at 1340/10, the convoy went on its way unhindered. Its movements then became involved in those of the Malta to Egypt convoys, which were to sail under cover of the main operation with the special support of Vice-Admiral Pridham-Whippell’s ‘Force D’ which was made up of the cruisers HMS Orion (Capt. G.R.B. Back, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral H.D. Pridham-Whippell, CB, CVO, RN), HMS Ajax (Capt. E.D.B. McCarthy, RN), HMAS Perth (Capt. P.W. Bowyer-Smith, RN) and HMS York (Capt. R.H. Portal, DSC, RN). The first of these convoys, the two ships of M.W. 5½ (see above), had left Alexandria for Malta on 7 January, some hours after Admiral Cunningham sailed westwards with ‘Force A’ to meet the ‘Excess Convoy’. To reinforce ' Force D ' the light cruiser HMAS Sydney (Capt. J.A. Collins, CB, RAN) and destroyer HMAS Stuart (Capt. H.M.L. Waller, DSO, RAN) departed Malta on 8 January 1941. They joined ' Force D ' on the 9th. Both transports of this convoy reached Malta without adventure in the morning of the 10th escorted by HMS Calcutta, HMS Diamond and HMS Defender. On arrival HMS Calcutta joined the six slow ships which made up convoy M.E. 6 which was bound for Port Said and Alexandria. The ships in this convoy were the; Devis (6054 GRT, built 1938), Hoegh Hood (tanker, Norwegian, 9351 GRT, built 1936), Pontfield (tanker, 8290 GRT, built 1940), Rodi (3220 GRT, built 1928, former Italian), Trocas (tanker, 7406 GRT, built 1927) and Volo (1587 GRT, built 1938). They were escorted by four corvettes; HMS Peony (Lt.Cdr.(Retd.) M.B. Sherwood, DSO, RN), HMS Salvia (Lt.Cdr. J.I. Miller, DSO, RN, RNR), HMS Hyacinth (T/Lt. F.C. Hopkins, RNR), HMS Gloxinia (Lt.Cdr. A.J.C. Pomeroy, RNVR). At the end of the searched channel this convoy was joined by ‘Force D’. HMS Calcutta was then ordered to join the ‘Excess Convoy’ and arrived in time to defend it from the Italian bombers as already described.
The last convoy, M.E. 5½, two fast ships (the Lanarkshire (8167 GRT, built 1940) and Waiwera (12435 GRT, built 1934)) bound for Alexandria, also left Malta in the morning of the 10th under escort of HMS Diamond. They were to join the ‘Excess Convoy’ until they were to turn to the south to clear Crete and then proceed to Alexandria. The ‘Excess Convoy’ would then proceed to Piraeus, Greece. The two convoys met that afternoon. The transport Essex then left and proceeded to Malta escorted by HMS Hero. After the Essex was safely inside Grand Harbour, HMS Hero joined the fleet.
Vice-Admiral Pridham-Whippell stayed with convoy M.E. 6 until dark on the 10th. As ‘Force A’ was somewhat behind due to the air attacks and Admiral Cunningham ordered Vice Admiral Pridham-Whippell to position HMS Orion and HMAS Perth to the north of the convoy to be in a good position in case of an attack by Italian surface forces. ‘Force A’ made good ground during the night and was some 25 nautical miles north of the convoy by daylight on the 11th at which time Orion and Perth joined ‘Force A’. Their forces stayed within a few miles of the convoy until the afternoon when they turned back to help HMS Gloucester, HMS Southampton which had come under air attack (see below). In the evening the ships destined for Alexandria left the convoy, while HMS Calcutta went ahead to Suda Bay to fuel there. The three ships and their destroyer escort continued on to Piraeus where they arrived safely next morning, at 1000 on the 12th.
HMS Ajax and HMS York had been ordered to join convoy M.E. 6. HMS Ajax however was ordered to proceed to Suda Bay soon after she had joined the convoy. In the morning of the 11th therefore, Rear-Admiral Renouf in HMS Gloucester and with HMS Southampton and HMS Diamond in company, was ordered to overtake the convoy and support it. They were at that moment steering for Suda Bay having left the disabled Gallant off Malta some hours before. Rear-Admiral Renouf altered course accordingly and made 24 knots against the convoys 9 to 10 knots. He also send up a Walrus aircraft to find the convoy.
The sinking of HMS Southampton.
At 1522 hours, when his ships were some 30 nautical miles astern of the convoy, and in position 34°56’N, 18°19’E, they were suddenly attacked by a dozen German Ju-87 ‘Stuka’ dive-bombers. Fortune was against them. The attack came as an entire surprise and according to Captain Rowley of the Gloucester the ‘aircraft were not sighted until the whistle of the first bomb was heard’. Six machines attacked each cruiser, diving steeply from the direction of the sun, releasing a 550-lb bomb each, at heights of around 1500 to 800 feet. The ships opened fire with 4” AA guns and smaller AA guns. They also increased speed and altered course to avoid the attack but two bombs, perhaps three hit HMS Southampton causing disastrous damage. Another hit and some near misses did some damage to HMS Gloucester, most important damage was to her DCT (director control tower). Half-an-hour later seven high-level bombers attacked but they were detected in time and taken under fire as a result of which all bombs fell wide. During the attack the Walrus from HMS Gloucester returned and ditched alongside HMS Diamond which took off the crew and then scuttled the aircraft.
Rear-Admiral Renouf immediately reported the damage to his cruisers to Admiral Cunningham who went to their aid. He send Vice-Admiral Pridham-Whippell ahead with the Orion, Perth, Jervis and Janus. From Malta HMS Griffin and HMS Mohawk were sent. Before they arrived however, Rear-Admiral Renouf reported that the Southampton must be abandoned and that he would sink her. HMS Gloucester took on board 33 officers and 678 ratings of which 4 officers and 58 ratings were wounded while HMS Diamond took on board 16 wounded ratings. Upon this signal the battleships turned east again. HMS Southampton had cought fire badly upon being hit. For a time the ships company fought the fire successfully and kept the ship in action and under control but in the end the fire got out of control. Also it was found that some magazines could not be flooded. In the end the crew had to give it up and was taken off. A torpedo was fired into her by HMS Gloucester but it did not sink her. Soon afterwards Vice-Admiral Pridham-Whippell arrived on the scene and his flagship, HMS Orion then scuttled her with three more torpedoes (four were fired).
Further proceedings of the convoys and the fleet.
Next morning, the 12th, HMS Orion, HMS Perth, HMS Gloucester, HMS Jervis and HMS Janus joined Admiral Cunningham’s Force off the west end of Crete meeting there also A/Rear-Admiral Rawlings (‘Force X’) in HMS Barham (Capt. G.C. Cooke, RN, flying the flag of A/Rear-Admiral H.B. Rawlings, OBE, RN) and with HMS Eagle (Capt. A.R.M. Bridge, CBE, RN), HMS Ajax and their destroyer screen made up of HMAS Stuart, HMAS Vampire (Cdr. J.A. Walsh, RAN), HMAS Vendetta (Lt.Cdr. R. Rhodes, RAN), HMAS Voyager (Cdr. J.C. Morrow, DSO, RAN) and HMS Wryneck (Lt.Cdr. R.H.D. Lane, RN) which had departed Alexandria on 11 January. These ships were to have begun a series of attacks on the Italian shipping routes but the disabling of HMS Illustrious put an end to that part of the plan so Admiral Cunningham took HMS Warspite, HMS Valiant, HMS Gloucester and the destroyers HMS Jervis, HMS Janus, HMS Greyhound, HMS Diamond, HMS Defender, HMS Hero and HMAS Voyager straight to Alexandria where they arrived in the early morning hours of the 13th.
HMS Barham, HMS Eagle, HMS York, HMS Orion, HMS Ajax, HMAS Perth, HMAS Stuart, HMAS Vampire, HMAS Vendetta, HMS Wryneck, HMS Griffin and HMS Mohawk then proceeded to Suda Bay to fuel where they arrived around 1900/12.
After fuelling at Suda Bay, Vice-Admiral Pridham-Whippell took HMS Orion, HMAS Perth to Piraeus where they arrived at 0230/13. There they took some troops from the ‘Excess Convoy’ on board and departed for Malta at 0600/13, a task the Southampton was to have done. They arrived at Malta around 0830/14. After unloading HMS Orion departed for Alexandria later the same day together with HMS Bonaventure and HMS Jaguar. They arrived at Alexandria in the morning of the 16th. HMAS Perth remained at Malta due to defects.
Meanwhile the six ships of convoy M.E. 6 arrived safely at their destinations on 13 January.
HMS Barham, HMS Eagle, HMS Ajax, HMAS Stuart, HMS Juno, HMS Hereward, HMS Hasty and HMS Dainty departed Suda Bay for operations south-west of Crete early in the morning of the 13th. The destroyers HMS Ilex, HMS Wryneck, HMAS Vampire and HMAS Vendetta also departed Suda Bay to conduct a sweep in the Kythera Channel. They joined ‘Force X’ around noon but Vampire and Vendetta were soon detached to investigate explosions which turned out to be underwater volcano activity. Meanwhile Ilex and Wryneck were also detached for a sweep towards Stampalia. These four destroyers fuelled at Suda Bay on the 14th and then departed for Piraeus where they arrived in the evening of the 14th. An A/S sweep had been carried out en-route.
’Force X’ returned to Suda Bay in the afternoon of the 15th and departed from there on the 16th for Alexandria where they arrived on the 18th, although some of the destroyers remained behind at Suda Bay.Leave van given to their crews at Piraeus and the destroyers departed Piraeus early on the 16th. HMS Ilex proceeded independently while HMAS Vampire, HMAS Vendetta and HMS Wryneck peroceeded to Suda Bay joining ' Force X ' on its departure.
Not a single of the 14 merchant ships in the convoys was lost but the fleet paid a heavy price for this loosing a light cruiser and a valuable aircraft carrier out of action for many months. As there were now German aircraft based in Italy future operations for the supply of Malta would be extremely difficult and dangerous.
The return of ' Force H' to Gibraltar.
That now leaves us with the return of ' Force H ' to Gibraltar which parted company with the eastbound convoy and its escort at 1920/9 in position 37°42'N, 09°53'E. ' Force H ' turned away to port. At 1935/9, ' Force H ' alter course to 300° and increased speed to 20 knots. Further alterations to course were made at 2200/9 to 260° and at mindnight durng the night of 9/10 January to 290°.
At 0100/10 course was altered for a quarter of an hour to clear three merchant vessels which had been sighted to the northward in position 38°03'N, 07°58'N, steering 180°. At 0900/10, course was altered to 246° and speed reduced to 18 knots.
A reconnaissance flight of seven aircraft was flown off to carry out an all round search to a depth of 50 miles from position 38°44'N, 05°18'E. On their return at 1030/10, they had nothing to report. Visibility was variable - from 5 to 15 miles. There was a slight sea and wind, force 3 from south-south-west. Speed was increased to 19 knots at 1110/10 since there appeared vibration in HMS Malaya when proceeding at 18 knots.
During the afternoon, three attack exercises were carried out on ' Force H ' by a total of nine Swordfish. Flying was completed by 1800/10. Moonlight exercises were cancelled due to a deterioration of weather and visibility. During the night the wind veered to the southwest and increased to force 6.
At 2345/10, Captain (D), 8th Destroyer Flottila, reported that the destroyers could maintain 19 knots provided that their A/S domes were housed, but would have to reduce to 16 knots if they were to remain lowered. Destroyers were accordingly orderd to house their domes.
The sea increased considerably, and by 0020/11 it was necessary to reduce speed to 14 knots in order to prevent damage to the destroyers. Course was altered for a short time at 0135/11 to avoid a merchant ship sighted in position 36°37'N, 00°06'W, steering to the north. Speed was further reduced to 11 knots by 0310/11, but gradual improvement in sea conditions permitted a corresponding increase of speed, so that by 0700/11, ' Force H ' was proceeding at 17 knots. Later in the day HMS Fury reported tat her forward gun shield had been distorted and that the gun could not be trained.
Six Swordfish were flown off by HMS Ark Royal at 0715/11 in order to carry out a light torpedo attack on ' Force H '. They were landed at 0815/11. At 0930/11, course was altered to 270° and speed increased to 19 knots. Weather conditions continued unfavourable, and not only had air training to be abandoned, but also the projected reconnaissance flight to Oran and Mers-el-Kebir to obtain photographs requisted by the Admiralty.
A London flying boat sent out from Gibraltar as A/S patrol ahead of ' Force H ' was sighted at 1015/11. By 1220/11, the sea had moderated sufficiently for the destroyers to increase speed and HMS Renown, HMS Sheffield, HMS Faulknor and HMS Foxhound proceeded ahead at 24 knots, increasing at 1730/11 to 26 knots. They arrived in harbour at 1920/11. The remainder of ' Force H ' arrived in harbour at 2020/11. (51)
28 Jan 1941
At 1530/28, HMS Renown (Capt R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN) and their destroyer escort made up of HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St.J. Morgan, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN) and HMS Jersey (Lt.Cdr. A.F. Burnell-Nugent, DSC, RN) departed Gibraltar for exercises in the Alboran Sea.
Shorty afterwards the destroyer HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN) also sailed. She had been unable to sail with the remainder of the force as she was repairing defects which were not fully completed at the time of the sailing.
Early in the evening another destroyer joined the force, this was HMS Jupiter (Lt.Cdr. N.V.J.P. Thew, RN). She too had been repairing defects at the time of the sailing of the force and had been unable to sail with them at the intended time. (52)
29 Jan 1941
HMS Renown (Capt R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN), HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St.J. Morgan, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN), HMS Jersey (Lt.Cdr. A.F. Burnell-Nugent, DSC, RN) and HMS Jupiter (Lt.Cdr. N.V.J.P. Thew, RN) all returned to Gibraltar in the afternoon upon completion of their exercises. (52)
31 Jan 1941
Operations Picket and Result.
Operations against the Lake Omodeo Dam in central Sardinia (Picket) and the bombardment of Genoa (Result).
31 January 1941.
'Force H' departed Gibraltar for these operations. It was diverted into four groups, these were;
Group 1 was made up of the battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), battleship HMS Malaya (Capt. A.F.E. Palliser, DSC, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN) and the light cruiser HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN).
Group 2 was made up of the destroyers HMS Fearless (Cdr. A.F. Pugsley, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) and HMS Jersey (Lt.Cdr. A.F. Burnell-Nugent, DSC, RN).
Group 3 was made up of the destroyers HMS Duncan (A/Capt. A.D.B. James, RN), HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St.J. Morgan, RN), HMS Isis (Cdr. C.S.B. Swinley, DSC, RN) and HMS Jupiter (Lt.Cdr. N.V.J.P. Thew, RN).
And finally Group 4 was made up of the RFA tanker Orangeleaf (5927 GRT, built 1917) escorted by the auxiliary A/S trawlers HMS Arctic Ranger (Cdr.(Retd.) J.H. Young, RN) and HMS Haarlem (T/Lt. L.B. Merrick, RNR).
On leaving harbour HMS Ark Royal flew off one aircraft for A/S patrol. This patrol was maintained throughout the day.
At 1930/31, group 2 (six destroyers) were detached in position 36°25'N, 03°24'W and were ordered to proceed at economical speed to a position to the north of the Balearics where they were to rendez-vous with the remainder of the force (minus the tanker group) during the forenoon of 2 February.
1 February 1941.
At 0845/1, when in position 37°05'N, 00°32'E, groups 1 and 3 altered course to the north-east.
From 1130/1 onwards a section of fighters from HMS Ark Royal was maintained overhead until dusk.
At 1500/1 course was altered to 084°.
By 1810/1 all aircraft had returned to HMS Ark Royal.
At 1900/1, HMS Malaya escorted by HMS Encounter and HMS Jupiter were detached and ordered to rendez-vous with the remainder of 'Force H' at 0900/2 in position 40°55'N, 06°30'E. This was to economize fuel in HMS Malaya to enable to her to retreat after the bombardment of Genoa at a higher speed.
At 1910/1, HMS Renown, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Sheffield, HMS Duncan and HMS Isis, altered course to 062° and increased speed to 24 knots to arrive in the flying off position for Operation Picket.
2 February 1941.
At 0555/2, eight Swordfish were flown off from HMS Ark Royal in position 40°07'N, 06°54'E. They were armed with torpedoes to attack the dam.
At 0730/2, two more Swordfish were flown off to locate HMS Malaya and her two escorting destroyers and direct her to a rendez-vous position of 40°34'N, 06°38'E at 1000/2.
The first of seven Swordfish that returned from the raid on the dam landed on at 0830/2. The last aircraft landed on at 0848/2. One Swordfish failed to return.
The two Swordfish that had located HMS Malaya returned at 0900/2.
The striking force had encountered rain and hail showers over the land and severe icing conditions in a cloud level of 5000 feet. Ground defences were unduly alart and after the first five miles over the land, fire was encountered from Bofors and light automatic guns apparently posted along the roads leading to Tirso. throughout the final approach fire was heavy, becoming intense in the vicinity of the dam.
One aircraft becoming lost in the cloud, never located the target and finally returned to HMS Ark Royal with his torpedo. The remaining seven aircraft made individual approaches and all except one came under heavy fire. As a result of intense opposition and icing conditions in the clouds, two aircraft jettisoned their torpedoes. Of the remaining five, one was shot down, one made a high drop, nose down, two dropped approximately correctly, and one was able to take good, steady aim. No explosions were observed. The last pilot, after his attack, flew over the dam at a height of 60 feet, machine gunning the defences. He observed no damage on the south face of the dam. It is thought that if the torpedoes failed to reach the dam their run may have been stopped by a bank of silt. Information was later received from an Italian broadcast that the crew of the Swordfish that had been shot down had been taken prisoner.
The wind was by now force 6, with a rising sea, and HMS Duncan reported damage to the gun shield of 'A' gun. Visibility was moderate but improving.
At 1005/2 course was altered to 290° and eight minutes later HMS Malaya and her two escorting destroyers were sighted.
By 1115/2 HMS Malaya, HMS Encounter and HMS Jupiter had rejoined. At noon HMS Ark Royal reported that flying conditions were becoming hazardous so the A/S patrol was abandoned. Only a section of Fulmar fighters were maintained in the air as conditions were unsuitable for Skua's. At times HMS Ark Royal was dipping her flight deck into the sea. Speed had also to be reduced to 15 knots as this was the maximum speed the destroyers could proceed without sustaining damage.
At 1530/2 HMS Malaya requisted permission to turn down wind to make repairs as her cable lockers were flooding beyond the capacity of the pumps. Course was altered and speed was reduced to 10 knots at 1540/2. The original course and 15 knots speed were resumed at 1635/2.
Four Swordfish aircraft, which had been flown off to locate the six detached destroyers reported them as bearing 285°, distance 40 nautical miles at 1615/2. Course was altered to 000° at 1730/2 to ensure contact was made before dark and one hour later the destroyers joined the screen.
The northwesterly gale which had persisted all day had prevented 'Force H' from making the nesecssary ground to the west and north. Throughout the day various destroyers had reported damage at a speed of 15 knots and by the time the rendezvous with the six detached destroyers had been effected, Vice-Admiral Somerville was left with the choice of abanadoning operastion Result or making good a speed of 20 knots thoughout the night. This latter would have been impossible with the destroyers in company and problematical without them. Consideration was given to only attack Genoa with aircraft from HMS Ark Royal but in the end it was decided to abandon the operation.
3 February 1941.
At 0400/3 course was altered to 210°. The wind was still force 6, with a short sea. HMS Fearless reported at 0530/3 tht she was beginning to bump badly and speed was reduced to 13 knots.
HMS Ark Royal flew off three Swordfish at 0745/3 to seach for shipping between Cape Tortosa and Alicante up to fifty miles from the coast. A similar search was carried out in the afternoon between Cape San Antonio and Cape Palos. It was the intention to detach destroyers to close and investigate all ships reported by the aircraft but the only ship located was already in the approaches to Valencia and therefore could not be intercepted in time before it reached that port.
During the forenoon exercises were carried out during which HMS Jersey was serving as 'target'.
Course was altered to south at 1335/3 and speed was increased to 18 knots. The wind had veered to north-north-west and was still force 6. The wind eased a little towards the end of the afternoon but then increased to force 8 by 1700/3.
At 1715/3, dive bombing exercises were carried out on the fleet by four Skua's. After the first attack one aircraft force-landed in the sea on the starboard beam of the Fleet close to the destroyer screen. The crew was picked up by HMS Jupiter. The aircraft then sank.
All flying was completed by 1815/3. After dark course was reversed for twenty minutes in preparation for a night encounter exercises with HMS Jersey and HMS Jupiter which had been detached from the screen at dusk. These two destroyers, attacking from leeward, were sighted at long range. Evasion, counter-attack, star-shell and searchlights were exercised and the practice was completed by 2038/3.
4 February 1941.
A speed of 17 knots was maintained during the night and at 0100/4 course was altered to the westward. The wind remained a steady force 6 from the north-north-west.
At 0630/4, HMS Ark Royal screened by three of the destroyers hauled out of the line and they proceeded independently for flying off Swordfish aircraft for a dawn light torpedo attack on the Fleet. This attack was well delivered.
At 0800/4 speed was increased to 18 knots and HMS Sheffield took station eleven miles on the starboard beam to act as a target for gunnery exercises by HMS Renown and HMS Malaya. On completion HMS Sheffield then carried out an exercise with the leading destroyer of the screen. Finally HMS Fearless and HMS Foresight then carried out an exercise on HMS Sheffield.
By noon the sea had moderated and the wind had dropped to force 5. During the afternoon destroyers of the screen carried out exercises.
The ships of 'Force H' entered harbour at Gibraltar between 1715 and 2000 hours. (52)
6 Feb 1941
Operation Grog.
Bombardment of Genoa.
6 February 1941.
'Force H' departed Gibraltar for this operation. It was diverted into three groups, these were;
Group 1 was made up of the battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), battleship HMS Malaya (Capt. A.F.E. Palliser, DSC, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN) and the light cruiser HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN).
Group 2 was made up of the destroyers HMS Fearless (Cdr. A.F. Pugsley, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN), HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St.J. Morgan, RN) and HMS Jersey (Lt.Cdr. A.F. Burnell-Nugent, DSC, RN).
Group 3 was made up of the destroyers HMS Duncan (A/Capt. A.D.B. James, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Isis (Cdr. C.S.B. Swinley, DSC, RN) and HMS Jupiter (Lt.Cdr. N.V.J.P. Thew, RN).
Group 2 departed Gibraltar between 1200 and 1400 hours in pairs of two. They proceeded eastwards as to be on patrol or exerising. When out of sight from land they continued on to the eastwards at economical speed to rendez-vous with groups 1 and 3 later on.
Groups 1 and 3 were clear of the harbour by 1700 hours. They then proceeded westwards as to cover convoy HG 53 which was forming up in the Strait of Gibraltar at this time.
The force was cut up into small sections and one by one they passed the Strait of Gibraltar to the eastward.
7 February 1941.
At 0300/7 all ships of groups 1 and 3 had joined company again and continued their passage eastwards.
An A/S patrol was flown off by HMS Ark Royal at 0730/7 and maintained throughout the day. Visibility was good with wind force 3 from the west. Six Skua's were flown off at 0835/7 to carry out dummy dive bombing attacks on the Fleet. Opportunity was taken to exercises all forms of AA armament.
By 1100/7 the wind had dropped to light westerly airs and there was a slight haze over the horizon which limited visibility to 10/15 miles throughout the day.
At 1155/7, in position 36°37'N, 01°21'W, HMS Firedrake investigated a contact and fired two depth charges. This contact was most likely non-sub.
All flying was completed by 1815/7. No radar contacts had been obtained all day and it seems probable that the fleet was not detected.
At 1930/7 course was altered to 035° in order to pass between Ibiza and Majorca during the dark hours.
8 February 1941.
Course was altered to 340° at 0100/8 and to 035° at 0500/8 for the passage west of the Balearics. An A/S air patrol was flown off at 0730/8 and a fighter patrol at 0930/8. These were maintained throughout the day. The six destroyers of group 2 joined at 0830/8.
During the day six aircraft were sighted but none are thought to have been enemy, almost all could be identified as being French.
During the day, a Skua and a Fulmar crashed on the deck of HMS Ark Royal when landing but no one was injured. All flying was completed by 1800 hours and ten minutes later course was altered to 090° and speed to 18 knots. At 1900/8 speed was increased to 21 knots.
At 2330/8 course was altered to the final approach course towards Genoa.
9 February 1941.
At 0400/9 HMS Ark Royal parted company escorted by HMS Duncan, HMS Encounter and HMS Isis so as the carrier could act independently to carry out air attacks on Leghorn and La Spezia.
At 0505/9, when in position 43°19'N, 08°41'E, HMS Ark Royal flew off a striking force of 14 Swordfish, followed by four Swordfish carrying magnetic mines and later by three standby spotting aircraft with an escorting section of fighters.
At 0719/9 a section of Fulmars was flown off to patrol over HMS Ark Royal.
Meanwhile the bombardment force continued on towards Genoa. At 0635/9 some unidentifiable mountain tops were just visible above the haze, silhouetted against the sky to the north-east of Rapallo, but it was not until 0649 hours that the headland of Porto Fino could be identified. It was soon seen that the Fleet was almost exactly in the position they wanted to be in.
Between 0630 and 0707 hours, HMS Sheffield and HMS Malaya catapulted their aircraft for spotting duties. HMS Renown also launched her spotting aircraft [time is not noted in the report.]
Course was altered to 290° at 0655/9 and speed was reduced to 18 knots. 13 minutes later course was altered to 270° and at 0713 back to 290°.
At 0711/9 Renown's spotting aircraft reported that no battleships were present. By 0714 hours, when fire was opened, nothing could be seen of Genoa from the ships, so the firing was carried out under direction of the spotting aircraft.
The observers in the spotting aircraft were able to indentify their targets with the greatest ease as they had been trained by using a model that had been constructed by a Commissioned Gunner of HMS Renown.
The opening salvoes from HMS Renown fell as anicipated south of Malo Principe and were quickly spotted onto the Ansaldo Works, marshalling Yards and factories on both banks of the Torrente Polcevera. Numerous explosions and considerable fires were obsevered in this area. Target was then shifted to the vicinity of the commercial basin where a big fire was caused and a merchant ship was hit. A salvo in the vicinity of the power station caused a perticularly violent explosion and an oil tank was observed to be on fire. The smoke from this and various warehouses prevented the spotting of several salvoes but a little later rounds were observed to fall in the area west of Ponte Daglio Asscreto and Ponte Caracciolo. The last salvoes fired in this area fell on the latter causing an explosion followed by a considerable fire. Target was again shifted, and the electrical works appeared to recieve a direct hit. Fire was moved up the left bank of the Torrente Polcevera and having crossed it salvoes were spotted directly on to Ansaldo Works, but smoke by then rendered observation difficult. The secondary armament engaged the area along the water front.
HMS Malaya engaged the dry docks a d targets in their vicinity throughout. Big explosions were observed in the docks and among warehouses. Several salvoes could not be spotted owing to smoke, but the last four were seen to fall among houses just north-east of the docks.
Sheffield's opening salvoes were placed short in the sea and were readily spotted. Having found range, rapid salvoes were ordered and fire was directed at the industrial installations on the left bank at the mouth of the Torrente Polcevera. Many fires and two big explosions were caused in this area. Later, as smoke was obscuring the area, fire was shifted to a tanker under way off the port and although three salvoes straddled no actual hits were observed.
The only opposition encountered by the bombarding ships was from a shore battery mounting about two 6" guns, and by the spotting aircraft from long and close range AA weapons. In both cases the fire was quite inefficient. During the bombardment two of the destroyers were ordered to make smoke to hamper gun fire from the shore battery.
The following ammunition was expended; HMS Renown 125 rounds of 15" HE and 400 rounds of 4.5" HE, HMS Malaya 148 rounds of 15" CPC and HMS Sheffield 782 rounds of 6" HE.
Whilst the main force was approaching Genoa, HMS Ark Royal's striking force of fourteen Swordfish each armed with four 250lbs. G.P. bombs and sixteen incendiaries had proceeded to attack the Azienda Oil Refinery at Leghorn. Eleven aircraft dropped their bombs on the refinery but no clear estimate could be formed of the amount of damage inflicted except that one definite explosion was observed. Surprise was evidently achieved as only one or two HA guns opened fire when the attack started. About six minutes later however, the HA fire became severe.
Two of the striking force, having mistaken their landfall, attacked alternative targets, one attacks Pisa aerodrome and the other Pisa railway junction.
One of the aircraft that attacked the refinery failed to return.
Three of the minelaying Swordfishmade a gliding approach over the town of Spezzia, two laying in the western entrance of the harbour and one in the eastern entrance. The fourth aircraft approached from the opposite direction and laid in the western entrance. There was only a partial black out of the town. Short range AA weapons of the Bofors type engaged the aircraft during their final approach and these was also some AA fire from guns round the town, but these appeared to be firing blind into the air.
Balloon barrages were noticed at Leghorn over the town and west of the Azienda Refinery along the coast and also at Genoa by the Torrente Polcevera.
By 0848 all spotting, minelaying and striking force aircraft had landed on (with the exception of the one reported missing) and HMS Ark Royal proceeded to rendez-vous with the rest of 'Force H' in position 43°48'N, 08°50'E at 0900/9. By 0919/9 the whole force was steering 180° at 22 knots.
It was evident that both the ship and air bombardment had effected complete surprise, and that no precautions had been taken by the enemy to guard against an invasion into the Gulf by 'Force H'.
Throughout the day six fighters were kept patrolling over the Fleet. At 0934/9 two aircraft were detected by RD/F bearing 060° waiting at 27 miles. Ten minutes later a Cant. flying boat was sighted low down to the north-north-east. The aircraft withdrew before the fighters could get in touch. The other aircraft also withdrew on a bearing 070°. The visibility at this time was six miles at 3000 feet and 15 miles at 15000 feet. After this the RD/F sreen remained clear until 1047 hours when a raid was detected at 40 miles closing from 070°. This turned out to be a shadower, a Cant. 506B, which was located and shot down by fighters to the north of the fleet. Course was altered to 200° at 0955/9 and to 244° at 1035/9.
At 1120/9 a raid was detected at 30 miles closing on a bearing of 350°. This raid consisted of two aircraft which appeared to be Fiat BR.20 bombers. Four bombs were dropped well astern of HMS Ark Royal and the aircraft then retired to the northward. Fighters were unable to make contact with the enemy who were at about 12000 feet.
A convoy of seven merchant vessels was encountered at noon in position 43°07'N, 08°08'E, steering 090° and HMS Foresight was detached to investigate. The convoy consisted of six French and one Turkish merchant vessels outward bound and was allowed to proceed.
A formation of aircraft was detected at 1210/9 on a bearing of 160° but it dit not close and eventually faded.
At 1300/9 the weather became very favourable to a succesful withdrawal, the visibility having decreased and the sky overcast with low cloud. A shadower was detected at 1325/9 astern of the fleet. it was located by the fighters and proved to be a Cant. Z.1007B, it was shot down at 1355/9.
Several formations were detected by RD/F to the eastward at 1412/9 but they did not close to less than about 30 miles and finally faded. At 1500/9 the fighters chased a shadower but lost him in the clouds.
Between 1615 and 1700 hours several raids were again detected to the eastward but none materialised. Thereafter the RD/F screen remained clear until 'Force H' arrived at Gibraltar.
Two aircraft were launched at 1651/9 to search for the destroyers HMS Firedrake and HMS Jupiter which had been detached to carry out a W/T diversion east of Minorca at 2345/8 to cover the approach of the force to Genoa.
Course 232°, speed 17 knots was maintained during the night.
10 February 1941.
At 0740/10 HMS Ark Royal flew off two A/S patrols and five Swordfish to carry out a search for shipping in the area between lines joining Cape San Sebastian to Minorca and Cape San Antonio to Ibiza. Five French ships and the Spanish ships were reported.
Only one ship was within range and the Spanish ship Maria (347 GRT, built 1907) was boarded (by HMS Foresight). She was bound from Barcelona to Cartagena with a general cargo and was therefore allowed to proceed.
HMS Firedrake and HMS Jupiter rejoined at 0915/10. At 1300/10 course was altered to 184°. In the afternoon four aircraft searched an area 50 miles from territorial waters between Valencia and Cartagena but only a French merchant vessel was sighted steering northwards very close to the Spanish territorial waters.
Course was altered to 222° at 1804/10 and a few minutes later HMS Ark Royal was detached with three destroyers to act independently for the remainder of the passage to Gibraltar in order to facilitate training flights. HMS Fearless and HMS Fury were detached at dusk in order to shadow the Fleet from the port quarter and to deliver a dummy attack at dawn.
11 February 1941.
Course was altered to the westward at 0230/11. At 0735/11 HMS Fearless and HMS Fury carried out an attack from the port bow, ships in the line and on the screen were using searchlights.
It had been intended to exercise dive bombing on the fleet and smoke burst target practice for destroyers but low cloud prevented this. At 1100/11 six Swordfish aircraft carried out light torpedo attacks and nine Swordfish runner attacks on the fleet. HMS Fearless and HMS Fury were again detached but now to pick up torpedoes.
On approaching the Rock a range and inclination exercise was carried out for the benefit of the shore defences, destroyers were screening the heavy ships with smoke.
'Force H' entered the harbour between 1430 and 1615 hours. (52)
6 Feb 1941
Convoy HG 53.
This convoy departed Gibraltar on 6 February 1941.
It was made up of the following merchant vessels, though some of them joined later at sea coming from Spain or Portugal; Brandenburg (British, 1473 GRT, built 1910), Britannic (British, 2490 GRT, built 1918), Courland (British, 1325 GRT, built 1932), Coxwold (British, 1124 GRT, built 1938), Dagmar I (British, 2471 GRT, built 1903), Dago (British, 1757 GRT, built 1902), Disa (Swedish, 2002 GRT, built 1918), Egyptian Prince (British, 3490 GRT, built 1922), Empire Lough (British, 2824 GRT, built 1940), Empire Tern (British, 2479 GRT, built 1919), Empire Warrior (British, 1306 GRT, built 1921), Estrellano (British, 1982 GRT, built 1920), Iceland (British, 1236 GRT, built 1914), Jura (British, 1759 GRT, built 1929), Marklyn (British, 3090 GRT, built 1918), Ousel (British, 1533 GRT, built 1922), Sally Maersk (British, 3252 GRT, built 1923), Tejo (Norwegian, 967 GRT, built 1916), Toward (British (rescue ship), 1571 GRT, built 1923), Vanellus (British, 1886 GRT, built 1921), Varna (British, 1514 GRT, built 1924) and Wrotham (British, 1884 GRT, built 1927).
On departure from Gibraltar the convoy was escorted by the destroyer HMS Velox (Lt.Cdr. E.G. Roper, DSC, RN) and the sloop HMS Deptford (Lt.Cdr. G.A. Thring, DSO, RN).
The convoy was spotted at 0729B/8 by the German submarine U-37.
At 2145B/8, the German submarine attacked the convoy with three torpedoes but no hits were obtained.
At 0430B/9, U-37 again attacked the convoy with two torpedoes. Now the merchant vessels Courland and Estrellano were hit and sunk in position 35°53'N, 13°13'W.
At 0545B/9, U-37 attack with one torpedo but no hit was obtained.
During 9 February U-37 sent out homing signals and the convoy was then attacked in the afternoon by 5 FW 200 aircraft from 2/KG.40. These managed to sink the following ships; Britannic, Dagmar I, Jura, Tejo and Varna in position 35°42'N, 14°38'W.
At 2227B/9, U-37 attacked again with one torpedo but it missed it's intended target.
At 0427B/10, U-37 attacked yet again, this time with two torpedoes. Again no hits were obtained.
At 0632B/10, U-37 again fired two torpedoes. This time the merchant vessel Brandenburg was hit and sunk in position 36°10'N, 16°38'W. Following this attack U-37 was depth charges by HMS Deptford but she was not damaged.
On 11 February 1941, a straggler from the convoy was sunk in position 37°03'N, 19°50'W by the German heavy cruiser Admiral Hipper.
On 11 February 1941, HMS Velox parted company with the convoy to return to Gibraltar.
On 12 February, when it had become apparent that the German heavy cruiser Admiral Hipper had been operating in the Atlantic, ' Force H ' departed Gibraltar at 1830A/12 to provide cover for convoys of which HG 53 was one. ' Force H ' was made up of the battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN), light cruiser HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN) and the destroyers HMS Wishart (Cdr. E.T. Cooper, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) and HMS Jersey (Lt.Cdr. A.F. Burnell-Nugent, DSC, RN).
On 18 February 1941, the convoy was joined by the sloop HMS Londonderry (Cdr. J.S. Dalison, RN).
On 22 February 1941, the convoy was joined by the destroyers HMS Leamington (Lt.Cdr. H.G. Bowerman, RN), HMS Sabre (Lt. P.W. Gretton, DSC, RN) and the corvette HMS Anemone (Lt.Cdr. H.G. Boys-Smith, DSO, RNR).
The convoy arrived in U.K. waters on 24 February 1941.
9 Feb 1941
Convoy WS 6A.
This convoy departed U.K. waters on 9 February 1941 and arrived at Freetown on 1 March 1941.
The convoy was formed at in position from three sections of troopships / transports coming from Avonmouth, Liverpool and the Clyde.
The convoy was made up of the following troopships / transports; Almanzora (British, 15551 GRT, built 1914), Ascanius (British, 10048 GRT, built 1910), Bellerophon (British, 9019 GRT, built 1906), Bergensfjord (Norwegian, 11015 GRT, built 1913), Burdwan (British, 6069 GRT, built 1928), Cape Horn (British, 5643 GRT, built 1929), City of Athens (British, 6558 GRT, built 1923), City of Corinth (British, 5318 GRT, built 1918), City of Hankow (British, 7360 GRT, built 1915), City of Pittsburg (British, 7377 GRT, built 1922), Consuelo (British, 4847 GRT, built 1937), Dalesman (British, 6343 GRT, built 1940), Highland Brigade (British, 14134 GRT, built 1929), Kina II (British, 9823 GRT, built 1939), Leopoldville (Belgian, 11509 GRT, built 1929), Llandaff Castle (British, 10799 GRT, built 1926), Llangibby Castle (British, 11951 GRT, built 1929), Logician (British, 5993 GRT, built 1928), Masheer (British, 7911 GRT, built 1925), Manchester Citizen (British, 5343 GRT, built 1925), Mataroa (British, 12390 GRT, built 1922), Nova Scotia (British, 6796 GRT, built 1926), Opawa (British, 10354 GRT, built 1931), Port Alma (British, 8400 GRT, built 1928), Rangitata (British, 16737 GRT, built 1929), Ruahine (British, 10832 GRT, built 1909), Salween (British, 7063 GRT, built 1937), Scythia (British, 19761 GRT, built 1920) and Thysville (Belgian, 8351 GRT, built 1922).
Escort was initially provided by the light cruisers HMS Birmingham (Capt. A.C.G. Madden, RN), HMS Phoebe (Capt. G. Grantham, RN), armed merchant cruiser HMS Cathay (A/Capt.(Retd.) C.M. Merewether, RN), destroyers HMAS Napier (Capt. S.H.T. Arliss, RN), HMAS Nizam (Lt.Cdr. M.J. Clark, RAN), HMCS Ottawa (Cdr. E.R. Mainguy, RCN), HMCS Restigouche (Cdr. H.N. Lay, OBE, RN), HMCS St. Laurent (Lt. H.S. Rayner, RCN), HMCS Skeena (Lt.Cdr. J.C. Hibbard, RCN), HMS Legion (Cdr. R.F. Jessel, RN), Piorun (Cdr. E.J.S. Plawski), ORP Garland (Lt.Cdr. K.F. Namiesniowski, ORP), HMS Keppel (?), HMS Broadwater (Lt.Cdr. C.L.de H. Bell, RD, RNR) and the escort destroyers HMS Atherstone (Lt.Cdr. R.F. Jenks, RN) and HMS Cottesmore (Lt.Cdr. J.C.A. Ingram, RN).
Information on this convoy is difficult to find but it appears that most of the A/S escort parted company with the convoy in the early evening of 12 February (according to the logbook of HMS Birmingham) and then proceeded as follows; HMAS Napier and HMAS Nizam to Scapa Flow passing north of Rockall, HMS Keppel, HMS Atherstone and HMS Cottesmore to Londonderry, HMCS Ottawa, HMCS Restigouche, HMCS St. Laurent and HMCS Skeena through area 52°N to 53°N, 23°W to 20°W and then to Greenock through position 55°N, 15°W, HMS Legion, HMS Broadwater, ORP Piorun and ORP Garland through position 57°N, 19°W and then to Greenock while passing north of Rockall. All groups were to conduct A/S sweeps on their way back.
Shortly before noon on the 15th the battleship HMS Rodney (Capt. F.H.G. Dalrymple-Hamilton, RN) was sighted which was to join the convoy.
Shortly after Rodney joined HMS Phoebe parted company with the convoy to fuel at Gibraltar.
HMS Rodney remained with the convoy until 1700/16. She then set course to join convoy HX 108.
The battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN) and aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN) joined the convoy at 1000/17. They remained with the convoy until 1030/21 when they were relieved by HMS Malaya (Capt. A.F.E. Palliser, DSC, RN).
HMS Phoebe rejoined the convoy shortly before noon on 23 February 1941.
Shortly after noon on 25 February 1941 the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN) and HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN) joined the convoy.
At 2030/25 the armed yacht HMS Surprise (Capt.(Retd.) E.C. Stubbs, RN) also joined.
Around 0900/27 the sloop HMS Milford (Cdr.(Retd.) the Hon. V.M. Wyndham-Quin, RN) and the destroyers HMS Vidette (Lt. E.N. Walmsley, RN) and HMS Wishart (Cdr. E.T. Cooper, RN) joined the escort of the convoy.
On February 28th, HMS Malaya parted company with the convoy to proceed to Freetown taking the destroyers HMS Faulknor and HMS Forester with her. Also on this day the destroyers HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St J. Morgan, RN) and HMS Isis (Cdr. C.S.B. Swinley, DSC, RN) joined the escort of the convoy.
At 1226A/1, a Walrus aircraft from HMS Birmingham force landed on the water 95° from position 09°25'N, 16°39'W. Birmingham searched for the aircraft rejoining the convoy for the night not having found the aircraft. A new search was not possible without first fuelling at Freetown.
Shortly before arrival at Freetown on 2 March 1941 the corvettes HMS Calendula (Lt.Cdr. A.D. Bruford, RNVR) and HMS Clematis (Cdr. Y.M. Cleeves, DSC, RD, RNR) joined. (53)
12 Feb 1941
Due to a report of an enemy raider 'Force H' departed Gibraltar to proceed into the Atlantic to provide cover for convoy HG 53.
'Force H' departed Gibraltar at 1830/12 and was made up of the battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN), light cruiser HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN) and the destroyers HMS Wishart (Cdr. E.T. Cooper, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Foxhound (Lt.Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) and HMS Jersey (Lt.Cdr. A.F. Burnell-Nugent, DSC, RN).
Later that evening Vice-Admiral Somerville was informed that her was to take over the escort of troop convoy WS 6 and to make the rendez-vous he decided that he had to let go of his destroyer sceen which would be unable to keep up due to the weather conditions. The destroyers were ordered to return to Gibraltar arriving there at 0830/13. [For more info on convoy WS 6, see the event ' Convoy WS 6 ' for 9 February 1941.]
At 1130/13, HMS Sheffield parted company with HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal to proceed to cover convoy SLS 64 and HG 53.
[For more info on convoy SLS 64, see the event ' Convoy SLS 64 ' for 30 January 1941.]
[For more info on convoy HG 53, see the event ' Convoy HG 53 ' for 6 February 1941.] (52)
25 Feb 1941
HMS Renown (Capt R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN) and aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN) returned to Gibratar at 0945/25. They had been joined at sea at 0935/24 by the destroyers HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Fortune (Lt.Cdr. E.N. Sinclair, RN) and HMS Foxhound (Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN) which escorted them in. (54)
1 Mar 1941
Convoy SL 67.
This convoy departed Freetown on 1 March 1941 and arrived at Liverpool on 26 March 1941.
This convoy was made up of the following merchant vessels; Alphard (Dutch, 5483 GRT, built 1937), Anadyr (British, 5321 GRT, built 1930), Ashworth (British, 5227 GRT, built 1920), Banffshire (British, 6479 GRT, built 1912), Baron Belhaven (British, 6591 GRT, built 1925), Baron Cawdor (British, 3638 GRT, built 1935), Beaconstreet (Detached to Gibraltar on 11 March) (British, 7467 GRT, built 1927), Bolton Castle (British, 5203 GRT, built 1939), British Captain (British (tanker), 6968 GRT, built 1923), British Diligence (British (tanker), 8408 GRT, built 1937), British Hope (Detached to Gibraltar on 11 March) (British (tanker), 6951 GRT, built 1928), British Integrity (British (tanker), 8412 GRT, built 1927), British Security (British (tanker), 8470 GRT, built 1937), Celtic Monarch (British, 5824 GRT, built 1929), City of Cairo (British, 8034 GRT, built 1915), City of Dunkirk (British, 5861 GRT, built 1912), City of Kimberley (British, 6169 GRT, built 1925), City of Nagpur (British, 10146 GRT, built 1922), City of Rangoon (British, 6635 GRT, built 1914), Clan Macbean (British, 5000 GRT, built 1918), Copeland (British (rescue vessel), 1526 GRT, built 1923), Deebank (British, 5060 GRT, built 1929), Defender (British, 8258 GRT, built 1915), Dunkwa (British, 4752 GRT, built 1927), Friesland (Dutch, 2662 GRT, built 1930), Godfrey B. Holt (British, 3585 GRT, built 1929), Guido (British, 3921 GRT, built 1920), Harmodius (British, 5229 GRT, built 1919), Harpefjell (Norwegian, 1333 GRT, built 1939), Helder (Dutch, 3629 GRT, built 1920), Henrik Ibsen (Norwegian, 4671 GRT, built 1906), Hindpool (British, 4897 GRT, built 1928), Inneroy (Norwegian (tanker), 8260 GRT, built 1936), King Edwin (British, 4536 GRT, built 1927), Lahore (British, 5304 GRT, built 1920), Llangollen (British, 5056 GRT, built 1928), Martaban (British, 4161 GRT, built 1934), Mendoza (British, 8233 GRT, built 1919), Nagina (British, 6551 GRT, built 1921), Nardana (British, 7974 GRT, built 1919), Nebraska (British, 8261 GRT, built 1920), Ogmore Castle (British, 2481 GRT, built 1919), Peisander (British, 6225 GRT, built 1925), Queen Anne (British, 4937 GRT, built 1937), Recorder (British, 2276 GRT, built 1902), Roxane (British (tanker), 7813 GRT, built 1929), Sansu (British, 5446 GRT, built 1939), Sire (British, 5664 GRT, built 1938), Solfonn (Norwegian (tanker), 9925 GRT, built 1939), Taxiarchis (Greek, 4221 GRT, built 1913), Tielbank (British, 5084 GRT, built 1937), Tunisia (British, 4337 GRT, built 1927), Turkistan (British, 6935 GRT, built 1939), Umberleigh (British, 4950 GRT, built 1927), Urbino (British, 5198 GRT, built 1918), Winsum (Dutch, 3224 GRT, built 1921) and Zamalek (British (rescue vessel), 1567 GRT, built 1921).
[It is possible some of these ships did not sail from Freetown but joined the convoy at sea.]
On departure from Freetown the convoy was escorted by the armed merchant cruiser HMS Cilicia (Capt.(Retd.) V.B. Cardwell, OBE, RN), corvette HMS Asphodel (Lt.Cdr.(Retd.) K.W. Stewart, RN) and the auxiliary A/S trawlers HMS Kelt (T/Lt. W.T. Hodson, RNVR), HMS Spaniard (Lt.Cdr. F.J. Webster, RNR) and HMS Turcoman (Skr. A.G. Day, RNR).
At 1700/3 the battleship HMS Malaya (Capt. A.F.E. Palliser, DSC, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN) and HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN) joined the escort of the convoy.
At 1800/4 the three A/S trawlers parted company with the convoy.
In the early morning hours of 8 March 1941 the convoy was attacked by the German submarines U-105 and U-124. Five ships of the convoy were sunk, these were the Harmodius, Hindpool, Lahore, Tielbank and Nardana.
At 1330/8 HMS Forester, which was well to the west of the convoy, briefly sighted the German battlecruisers Scharnhorst and Gneisenau steaming towards the convoy. The German ships were also sighted around the same time by HMS Malaya's Swordfish aircraft. Following the report of the sighting HMS Malaya and HMS Faulknor left the convoy to join HMS Forester to put themselves between the convoy and the enemy.
At 1645/8 hours HMS Malaya and the Scharnhorst sighted each other and the German battlecruisers turned away being chased briefly by HMS Malaya and the destroyers. As Malaya's speed was much lower contact was soon lost and the battleship and the destroyers then returned to the convoy. At 1900 hours they rejoined the convoy
In the afteroon of March, 10th, the battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN) and aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN) joined the escort of the convoy. HMS Malaya then parted company with the convoy and set course for Gibraltar.
At 1730/11, HMS Asphodel parted company with the convoy with the tankers Beaconstreet and British Hope which she then escorted to Gibraltar.
At 1000/13, HMS Faulknor and HMS Foresight parted company with the convoy and set course for Gibraltar.
At 1000/19, HMS Kenya (Capt. M.M. Denny, CB, RN) joined the convoy to take over the escort. At 1600/19, HMS Renown, HMS Ark Royal and HMS Cilicia parted company with the convoy.
On 21 March the escort of the convoy was reinforced with the destroyers HMS Havelock (Cdr. E.H. Thomas, DSC, RN), HMS Hesperus (Lt.Cdr. A.A. Tait, RN), HMS Hurricane (Lt.Cdr. H.C. Simms, RN), HMS Veteran (Cdr. W.T. Couchman, OBE, RN), HMS Verity (Cdr. R.H. Mills, RN), HMS Wolsey (Lt.Cdr. C.H. Campbell, DSC, RN), HMS Salisbury (Lt.Cdr. H.M.R. Crichton, RN), HNoMS Mansfield (Cdr. F. Ulstrup, RNorN), the corvettes HMS Arbutus (T/Lt. A.L.W. Warren, RNR), HMS Camellia (Lt.Cdr. A.E. Willmott, RNR) and the catapult ship HMS Pegasus (Capt.(Retd.) P.G. Wodehouse, RN). HMS Kenya parted company with the convoy in the afternoon and proceeded to join convoy HG 56.
HMS Havelock and HMS Verity parted company with the convoy on 24 March as did HMS Veteran on the 25th.
3 Mar 1941
Around 1400A/3, the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN) departed Gibraltar for flying exercises in the Alboran Sea. She was escorted by the destroyers HMS Fortune (Lt.Cdr. E.N. Sinclair, RN) and HMS Duncan (Lt.Cdr. A.N. Rowell, RN).
They returned to Gibraltar around 1640A/4. (55)
8 Mar 1941
At 2145/8, HMS Renown (Capt. R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. C.S. Holland, RN), HMS Arethusa (Capt. A.C. Chapman, RN), HMS Velox (Lt.Cdr. E.G. Roper, DSC, RN) and HMS Wrestler (Lt. E.L. Jones, DSC, RN) departed Gibraltar for the Canary Islands area. Speed was set to 27 knots. The German battlecruisers Scharnhorst and Gneisenau had been reported in that area by HMS Malaya (Capt. A.F.E. Palliser, DSC, RN) trying to attack convoy convoy SL 67.
At 0015/9, the destroyers were detached being unable to keep up with the larger ships in the current weather conditions.
A reconnaissance of six aircraft was flow off by HMS Ark Royal at 1500/9 to search from 180° through west to 360° to a depth of 130 miles. The visibility was 30 miles. Two ships were sighted, one Ocean Boarding Vessel and a British tanker.
At 1030/9, Vice-Admiral Somerville received instructions from the Admiralty that HMS Arethusa was to return to Gibraltar and that HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal were to take over the escort of convoy SL 67 from HMS Malaya p.m. 10th March after which HMS Malaya was to return to Freetown. HMS Arethusa was then detached in position 32°42'N, 13°08'W.
Course was altered to 230° at 1900/9.
At 0830/10, course was altered to 220° to rendezvous with HMS Malaya and an A/S and security patrol were flown off in low visibility. A reconnaissance of six aircraft was flown off at 0950/10 to search from 180° through west to 360° to a relative depth of 70 miles but nothing was sighted. The visibility was 15 miles.
A further reconnaissance was of six aircraft was flown off at 1330/10 to search from 090° through south to 270° to a depth of 80 miles. The convoy having been located by the air search, course was altered to 160° and at 1720/10 HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal joined the convoy which was being escorted by HMS Malaya, HMS Cilicia (Capt.(Retd.) V.B. Cardwell, OBE, RN), HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN) and HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), in position 26°12'N, 19°38'W. At 1730/10, HMS Malaya was detached to return to Freetown. [For more info on this convoy see the event ' Convoy SL 67 ' for 1 March 1941.]
A dusk reconnaissance to a depth of 45 miles sighed nothing in a visibility of 8 to 15 miles.
A reconnaissance was flown off at a.m. and p.m. on the 11th but nothing was sighted. Two aircraft armed with depth charges and one without broke their undercarriages while landing on. There was a moderate swell and wind force 6. A/S bombs were therefore carried till conditions improved.
At 0700/12, A/S and security patrols were flown off followed an hour later by a reconnaissance of nine aircraft to carry out an all round search to a depth of 90 miles. Visibility was 10 - 15 miles. The only ships sighted were the ones that had been detached from the convoy earlier.
The p.m. reconnaissance carried out an all round search to a depth of 90 miles sighted nothing.
At 0700/13 the A/S patrol was flown off. Later a reconnaissance was flown off which conducted an all round search for a depth of 120 miles. Visibility was 10 miles but was deteriorating.
At 1000/13, HMS Faulknor and HMS Forester were detached for Gibraltar.
During the forenoon HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal conducted exercises with aircraft from Ark Royal which then also conducted practice attacks on ships in the convoy.
The evening reconnaissance on the 13th from position 32°12'N, 21°07'W, searched to a depth of 120 miles but sighted nothing except HMS Faulknor and HMS Forester returning to Gibraltar.
At 0650/14, an A/S patrol was flown off and an all round reconnaissance an hour later. They searched to a depth of 100 miles from position 33°27'N, 21°27'W but they sighted nothing of interest. During the forenoon some flying exercises were carried out.
The afternoon reconnaissance was flown off and searched for a depth of 1000 miles again sighted nothing of interest.
At 2200/14, a signal was received with instructions that HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal were to leave the convoy at dusk on 19 March.
At 0250/15, when in position 35°24'N, 22°18'W, a darkened ship was sighted crossing ahead of the convoy. HMS Cilicia was ordered to investigate and it turned out to be the merchant vessel St.Clair II (British, 3753 GRT, built 1929) bound for Freetown.
At 0650/15, the A/S patrol was flown off. Ten minutes later the merchant vessel New Westminster City (British, 4747 GRT, built 1929) was sighted in position 35°46'N, 22°09'W. On sighting HMS Renown she made a raider report but cancelled it 22 minutes later.
In the forenoon more flying exercises were carried out and HMS Cilicia was ordered to proceed to the tanker Roxane (British, 7813 GRT, built 1929) which had straggled from the convoy. The forenoon reconnaissance to a depth of 110 miles sighted noting.
The afternoon reconnaissance searched to a depth of 120 miles from position 36°50'N, 22°25'W. They sighted a Spanish tanker but nothing further of interest. One Swordfish aircraft failed to return and was considered lost with its crew.
Around dawn on the 16th the usual A/S patrol and reconnaissance aircraft were flown off. They searched to a depth of 100 miles but nothing was sighted.
The afternoon reconnaissance also searched to a depth of 100 miles (from position 39°30'N, 23°05'W) sighted five merchant vessels but nothing further.
At 2200/16, a signal was received from the Admiralty in which Vice-Admiral Somerville was informed of the fact that the German heavy cruiser Admiral Hipper had departed Brest.
A darkened ship was sighted at 0140/17 which was found on investigatation by HMS Cilicia to be merchant vessel River Lugar (British, 5423 GRT, built 1937) bound for Freetown.
The A/S and security patrol flew off at dawn and at 0950/17 they reported they sighted the armed merchant cruiser HMS Bulolo (Capt.(Retd.) R.L. Hamer, RN) which was en-route to Freetown.
A full reconnaissance was carried out at 1100/17 to a depth of 130 miles with average visibility of 20 miles. The only ship sighted was the ocean boarding vessel HMS Hilary (Cdr. T.L. Owen, RD, RNR) in position 43°08'N, 24°38'W. She passed the convoy at 1800/17.
At 1700/17, a reconnaissance was flown off to the north and east to a depth of 100 miles but nothing was sighted.
At 0700/18, the A/S and security patrols were flown off. At 0800/18 the forenoon reconnaissance was flown off from position 43°25'N, 23°48'W to search to a depth of 140 miles. Only one merchant vessel was sighted.
The afternoon reconnaissance sighted nothing in a search to a depth of 140 miles between 325° and 045° and 135° and 225° from position 44°40'N, 23°40'W.
At 0700/19 an A/S patrol was flown off followed at 0745/19 by a reconnaissance to a depth of 160 miles from position 45°40'N, 23°40'W. This reconnaissance informed HMS Kenya (Capt. M.M. Denny, CB, RN) of the position, course and speed of the convoy, which she joined at 1000/19. Also a merchant vessel was sighted which appeared somewhat suspicious and HMS Cilicia was ordered to investigate and then return to Freetown.
Meanwhile information had been received that the German tanker Antarktis (10711 GRT, built 1939) had sailed from Vigo during the night 17/18 March and it was Vice-Admiral Somervilles intention to search for this ship to the north-east and south-east of the Azores before returning to Gibraltar.
HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal parted company with the convoy at 1600/19. Also a reconnaissance was flown off to locate the suspicious merchant vessel. At 1906/19 a report was received that it had been sighted in position 45°15'N, 23°48'W at 1800/19 steering 280° at slow speed. This information was passed on to HMS Cilicia. Shortly afterwards a second merchant vessel was sighted which also fitted the discription of the suspicious merchent vessel (close observation was not possible, the aircraft had been ordered to remain out of sight). This too was passed on to HMS Cilicia.
The evening reconnaissance reported the Norwegian tanker Bianca (5688 GRT, built 1926) in position 45°22'N, 23°35'W at 1740/19, steering 090°, 12 knots, half laden. An Admiralty signal had been intercepted at 1800/15 containing the names of 14 outward bound tankers estimated to be within 150 miles from where raider signals had been received on that day. As Bianca was one of these ships mentioned, and as she was evidently in ballast and steering for Bordeaux, Vice-Admiral Somerville concluded that she must have a German price crew on board. He therefore decided to intercept in the morning before starting the search for the Antarktis.
At 0655/20 an A/S patrol was flown off followed at 0740/20 by a reconnaissance to a depth of 120 miles from south through west to north. At 0857/20, the Bianca was reported to be in postion bearing 180°, 68 miles from HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal. HMS Renown then set course to intercept parting company with HMS Ark Royal which continued her flying operations.
At 1147/20 an aircraft dropped a message on board HMS Renown that the British tanker San Casimiro (8046 GRT, built 1936) had been sighted in position 44°50'N, 22°15'W, steering 076° at 11 knots. An hour later another aircraft reported having sighted the Norwegian tanker Polykarp (6405 GRT, built 1931) at 0920/20 in position 45°40'N, 23°26'W, steering east at 7 knots and that she had altered course to 010° on being sighted. Both these tankers were included in the Admiralty's signal referred to earlier so it was thought these tankers were also under German control. Vice-Admiral Somerville decided to try to intercept the Bianca and sSan Casimiro today and the Polykarp with the help of an air search the following morning.
The Bianca was sighted at 1210/20 in position 44°16'N, 19°21'W. HMS Renown closed and sent a boarding party. The weather was perfect for boarding . When Renown was still 6 miles from Bianca she was seen to be abandoning ship, and as the boats pulled clear scuttling charges exploded and fire broke out in the engine room aft and also on the bridge. The boarding party proceeded on board and the launch rounded up the Bianca's boats and ordered them to return to their ship. The fires were extinguished but the ship was low in the water with a considerable list to port and down by the stern. It soon became apparent that the ship could not be saved.
By 1500/20 Bianca's ship's company, the German prize crew and the boarding party had returned on board HMS Renown and a course of 340° was shaped at 24 knots to intercept the San Casimiro.
Vice-Admiral Somerville gave orders to HMS Ark Royal that when HMS Renown appeared in sight of the San Casimiro the shadowing aircraft was to close and deter the prise crew from scuttling the ship.
The San Casimiro was sighted at 1715/20 in position 45°12'N, 19°42'W. Immediately afterwards she abandoned ship and scuttling charges were fired. The bridge of the ship was soon engulfed in flames. By the time HMS Renown was near her she was low in the water and was listing to port.
The tankers boats were closing HMS Renown and the boarding party were in the act of transferring some of San Casimiro's officers from the boats to the launch in order to return to their ship and see if anything could be done to save the ship when an enemy report was received by V/S from a Fulmar at 1815/20 that two enemy battlecruisers had been sighted at 1730/20 in position 45°56'N, 21°36'W, steering north at 20 knots. This position was 110 miles north-west of HMS Renown. At this time HMS Ark Royal was in sight from Renown bearing 215°.
Boats were immediately recalled and clearedso at 1850/20 HMS Renown proceeded to close HMS Ark Royal. As it was obvious nothing could be done to save the San Casimiro a few rounds of 4.5" were fired into her when HMS Renown passed.
The W/T installation of the Fulmar had malfunctioned therefore she had to close HMS Renown to pass the enemy report. HMS Ark Royal was informed by the Fulmar at 1825/20. The distance of the enemy ships to HMS Ark Royal at this moment was estimated to be 147 miles. At 1844/20 HMS Ark Royal reported that she had shadowers ready on deck but they would be unable to make contact before dark.
At 1830/20, an enemy report was sent to the Admiralty together with the position, course and speed of HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal. By 1915/20, HMS Renown had closed HMS Ark Royal and a course of 340° was shaped at 25 knots to overhaul the enemy. A Fulmar to search for the enemy was flown off at 1930/20.
This Fulmar reported at 2040/20, 'thick weather, nothing sighted', having searched to a depth of 168 miles and having encountered thick cloud down to the sea level between bearing 320° and 070° with further cloud patches to the westward, and eventually returned soon after 2100/20 and made a perfect arrival without any aid. This was a most creditable piece of work on behalf of the pilot and his observer.
Although it seemed unlikely, owing to the poor visibility to the northward, that the enemy could have ben kept under observation Vice-Admiral Somerville consider that HMS Ark Royal should have flown off a fighter to shadow as soon as possible after the receipt of the enemy report.
At 2110/20, Vice-Admiral Somerville informed the Admiralty that night shadowing and to attack was impracticable due to low visibility and that he intended a dawn search in the direction of convoy SL 67 and to the westward of that convoy. If nothing was sighted he told the Admiralty it was his intention to return to Gibraltar.
His choices to search this sector were based on the following. 1) Shore based air and surface reconnaissance from the UK could cover to some extent the area to the eastward but not to the westward. 2) It was considered possible but unlikely that the enemy would make for Brest, France in view of its proximity to the UK. 3) A more probable course of action by the enemy appeared to be an attack on convoy SL 67 or, after starting off to the westward, a run to the south to be followed by an attack on the trade routes at prestent being used by convoys in this area.
Course was altered at 2200/20 to 003° to reach the best possible position for the dawn reconnaissance.
At 0345/21, Vice-Admiral Somerville was informed that HMS Malaya, escorting convoy SL 68 had been torpedoed.
At 0645/21, a reconnaissance of nine Swordfish flew off from position 49°25'N, 19°50'W, to search between 250° through north to 040°. The depth of the search was limited to appoximately 50 miles by a heavy fog bank extending to a height of 3000 feet and nothing was sighted.
All reconnaissance aircraft landed on at 1100/21 and course was then altered to 150° and speed reduced to 19 knots.
At 1630/21, A Swordfish armed with depth charges, cashed over the bows of HMS Ark Royal when being accelerated for an A/S patrol. The aircraft appeared to break in half across the rear cockpit and fell straight into the sea immediately ahead of the ship. The depth charges fired under 35 station and some damage was caused. The crew of the aircraft was killed.
The afternoon reconnaissance flew off from position 50°05'N, 18°50'W an searched from 110° through south to 230° to a depth of 160 miles without sighting anything.
At 0630/22, an A/S patrol was flown off followed at 0700/22 by a reconnaissance from position 45°52'N, 17°39'W. This covered the area between 280° and 050° to a depth of 70 miles and from 050° to 100° to a depth of 135 miles. Nothing was sighted.
The p.m. reconnaissance searched to a depth of 150 miles from position 44°10'N, 16°50'W from 100° through south to 280°. Nothing was sighted. Course was then set as to arrive at Gibraltar early on the 24th.
On 23 March the usual A/S patrol was maintained during the day. Instructions were received from the Admiralty that on return to Gibraltar, HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal were to fuel as soon as possible to return to the Atlantic and continue operations against the enemy battlecruisers.
At 1335/23, the destroyers HMS Fearless (Cdr. A.F. Pugsley, RN), HMS Forester, HMS Velox and HMS Wrestler made rendezvous.
HMS Renown arrived at Gibraltar around 0700/24. HMS Ark Royal escorted by HMS Fearless, HMS Forester, HMS Velox and HMS Wrestler entered the harbour around 0945/24 first having replacement aircraft being flown on from North Front. (56)
24 Mar 1941
At 2230/24, HMS Renown (Capt. R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN) and HMS Fortune (Lt.Cdr. E.N. Sinclair, RN) departed Gibraltar for a patrol off the Bay of Biscay. The whereabouts of the German battlecruisers Scharnhorst and Gneisenau were still not known although it was suspected that had arrived in Brest.
A course of 285° was maintained until 1930/25 when an alteration was made to the north-west. A/S patrol was maintained throughout the day. In the afternoon some flying exercises were carried out. At 2120/25 HMS Foresight and HMS Fortune parted company. In the evening flying exercises with dropping flares were carried out.
Durnig the night of 25/26 March a signal from the Admiralty was received. This stated that it was not considered shore-based air reconnaissance could be relied upon to detect the departure of the enemy in time. Submarine patrols were being established and it was hoped that this information would be received from that source. It was therefore considered desirble that ' Force H ' should operate generally in the vicinity of the convoy routes between the latitudes of Ushant and Lisbon, outside the area of enemy shore-based air reconnaissance.
Around 1000/26, HMS Forester was detached to Gibraltar after first having collected mail from HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal. Course was to the west to close the convoy routes as soon as possible.
During the forenoon of the 26th an all round reconnaissance to a depth of 60 miles from position 38°58'N, 15°18'W sighted nothing.
Some exercises were carried out during the forenoon. Fog was encountered at noon but it cleared later. A reconnaissance was flown off at 1640/26 from position 39°35'N, 17°12'W to search to a depth of 100 miles from south through north. Nothing was sighted.
In the late afternoon / early evening (dog watches) fighter training was carried out followed by shadowing and night flying exercises. The last aircraft landed on around 2100/26. At midnight course was altered to the north.
On 27 March flying was not possible throughout the day due to the weather conditions. ' Force H ' operated in the vicinity of 42°00'N, 19°40'W. At 2000/27 course was set to 170° for the night. This was to run parallel to convoy OG 36.
Information was receinved during the day that a reliable source had stated that the enemy battlecruisers had entered Brest.
At 0200/28 an enemy unit was reported by D/F about 350 miles to the northward of Renown and Ark Royal but in view of the improbability of being able to operate aircraft Vice-Admiral Somerville decided to remain to the southward in the vicinity of the convoys.
Daylight on the 28th brought moderate but deteriorating visibility, and an A/S patrol only was flown off. The visibility soon became very bad with rain and squalls and by noon the A/S patrol was withdrawn.
Instructions were received that ' Force ' was going to be relieved p.m. on 30th March.
At 1800/28 course was altered to 090° to keep clear of the convoy route, and at 2000/28 again altered to 010° to reach at dawn a more favourable position for the interception of the enemy battlecruisers should a report of their departure be received from the submarines patrolling the Bay of Biscay. Information was received at 2130/28 that the Scharnhorst and Gneisenau had been located by air reconnaissance to be in Brest.
At 0700/29, course was altered to 050° towards Brest so as to reach a suitable position should any further information be received concerning the enemy battlecruisers. The A/S patrol was flown off, but low visibility precluded long distance reconnaissance.
Bu 1000/29, no news regarding the enemy had been received. Course was altered to 300° with a view to standing to the westward till dusk. The visibility improved but wind and sea conditions prevented flying off a reconnaissance. The A/S patrol also had to be abandoned.
During the day QQQQ (raider) signals were intercepted from three merchant vessels but these were all cancelled. These signals wre made from the vicinity of 44°N, 30°W, where our Ocean Boarding Vessels were known to be patrolling.
By 1500/29 speed was reduced to 12 knots on account of the sea conditions, but by nightfall conditions had improved and when course was altered to 085° at 2230/29 speed was increased to 18 knots.
At 0800/30 course was altered to 160° and speed was increased to 19.5 knots to make for the rendezvous with the destroyer screen in position 37°35'N, 14°28'W.
The usual A/S patrol was maintained and an a.m. and p.m. reconnaissance both sighted nothing. Also some flying exercises were carried out.
At 1345/30 information was received that the enemy battlecruisers were still at Brest.
At 0845/31, the destroyers HMAS Napier (Capt. S.H.T. Arliss, RN), HMAS Nizam (Lt.Cdr. M.J. Clark, RAN) and HMS Fortune joined in position 37°34'N, 14°28'W. Course was then shaped for Gibraltar at 24 knots.
The usual A/S patrol was maintained and during the day some flying exercises were carried out.
HMS Renown, HMS Ark Royal, HMAS Napier, HMAS Nizam and HMS Fortune arrived at Gibraltar at 0630/1. (52)
2 Apr 1941
Operation Winch.
Around 0300/2, the battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN (Capt. D.8)), HMS Fearless (Cdr. A.F. Pugsley, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Fortune (Lt.Cdr. E.N. Sinclair, RN) and HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) departed Gibraltar and proceeded eastwards. HMS Ark Royal had on board 12 Hurricane fighters for Malta.
Light cruiser HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN) was delayed in leaving the harbour and joined at sea at dawn.
The weather was very favouravle for the evasion of merchant vessels. Visibility was moderate at daylight but deteriorated steadily until at 1630/2 it was as low as 4000 yards. The wind, which had been light from the west, increased to force 4 by this this time. In order to avoid delays caused by turning back into the wind, with some risk to the Hurricanes parked on deck, no flying was carried out by HMS Ark Royal. No aircraft were sighted during the day.
A course of 060° was steered from 1220/2, to simulate a move to the north-eastward in the event of ' Force H ' being sighted and reported. At 2000/2 course was altered to 093° for the flying off position, and half-an-hour later ' Force H ' emerged from the area of low visibility and the wind dropped to light westerly airs.
At 0050/3 and 0430/3, Vice-Admiral Somerville received satisfactory weather reports from Malta. At 0450/3 a fix on the Bourgaronie light showed that ' Force H ' was further to the south then intended and course was altered to 060°.
At 0600/3, course was altered to 250° into a light breeze, and twelve Hurricanes and two Skua's were flown off for Malta from position 37°42'N, 06°52'E. The Hurricanes took off easily and in most cases were air-borne between the island and the bow of HMS Ark Royal. ' Force H ' then withdrew to the westward at 24 knots.
The weather at this time was fair with good visibility, and with wat little wind there was favourable to the aircraft on passage to Malta.
Speed was soon increased to 27 knots on a course of 285° and an A/S patrol was flown off at 0745/3.
At 0815/3, a Cant floatplane was sighted low down seven miles away on bearing 030°, steering east. This aircrft had not been detected by RDF until after it was spotted. Three Fulmars were flown off by HMS Ark Royal to intercept it.
At 0840/3, a second Cant floatplane was sighted at a range of about 10 miles, bearing 060° and very low. Position was 37°50'N, 05°37'E. Fire was opened by HMS Ark Royal to indicate this aircraft to the fighters. Also a second section of fighters was flown off.
This shadower, a Cant 506, was sighted and chased by the fighters. It was eventually caught just before entering a cloud bank 40 miles to the eastward of ' Force H ' and shot down by two Fulmars.
As the fighters were returning they sighted the first Cant. 506 and attacked and hit it before it finally managed to escape into the clouds.
During the forenoon the A/S patrol was dispensed with in order to reduce the delays caused by having to turn into the wind, and to leave HMS Ark Royal free to develop the maximum fighter effort should it be required. One Fulmar crashed into the safety barrier on landing. There were no casualties.
At 1050/3 an aircraft, which appeared to be a Heinkel was sighted by HMS Renown bearing 250°, distant 8 miles. Fire was opened on it to indicate it to the fighters. The latter, however, failed to locate the aircraft before it retired to the south-east in low cloud in position 37°40'N, 04°21'E. Later it was heard that a German reconnaissance plane had reported warships at this time in position 38°00'N, 05°00'E. This report cleary referred to ' Force H ' but the course given in the report was 180° in error.
By 1100/3, the sky was completely overcast and there was reduced visibility ahead. Information was received from Malta at 1106/3 that all aircraft had arrived safely.
By 1130/3, ' Force H ' had run into very poor visibility with heavy overcast sky and intermittent rain. At noon speed was reduced to 24 knots, all fighters landed on and an A/S patrol was established.
At 1400/3, a tanker, evidently in ballast, was sighted to the south-west. Immediately on sighting ' Force H ' she turned inshore and proceeded towards Algiers, distant some 30 miles.
Information was received that H.M.Government might decide to prevent the Vichy-French battlecruiser Dunkerque leaving Mers-El-Kebir the follwimg day by torpedoing her without warning, and that two submarines were being sailed to take up an intercepting position.
The weather cleared about 1600/3 and in view of a report received from the Captain on the Staff, Alexandria, at 1530/3, that at 1005 GMT a German aircraft had been ordered to make weather reports for the area between 01°30'E and 05°30'E in latitude 38°30'N, fighter patrols were resumed till dark.
At 1630/3, information was received from the Vice-Admiral Commanding North Atlantic Station, that the submarines referred to earlier had sailed from Gibraltar at 1400/3. HMS Olympus (Lt.Cdr. H.G. Dymott, RN) routed through 36°15'N, 03°00'W to patrol in position 37°00'N, 00°40'W and HMS Otus (Lt.Cdr. E.C.F. Nicolay, RN) routed through 35°45'N, 03°00'W to patrol in position 35°55'N, 00°40'W. Their speed of advance was 12 knots.
The course of ' Force H ' was adjusted, by altering to 250° at 1730/3, to give these submarines as wide a berth as possible and at 0330/4 they were approximately 20 miles north and south of ' Force H ' respectively when course was altered to 270° to pass north of Alboran Island.
At 0300/4, Admiralty message 0204/4 was received informing Vice-Admiral Somerville that operation Principal (attack on the Dunkerque was to be carried out. At this time, an subsequently, Vice-Admiral Somerville was not aware whether any specific warning had been issued to the Vichy-French Government that the departure of Dunkerque from Mers-el-Kebir would be opposed. If no warning had been given, it seemed probable that departure would not take place until after dark. On the other hand, if the Vichy-French had reason to believe that departure would be opposed, it was probable that the ship would sail as soon after news was received of the arrival of ' Force H ' at Gibraltar.
It appeared that in any case, if Dunkerque was torpedoed, the Vichy-French would assime at once that this had been done by a British submarine since their can be little doubt but that they would have advised the Italians of the intended movement.
If Dunkerque was torpedoed, an immediate and heavy air attack on Gibraltar must be expected, and having regard to the relatively low standard of AA defence at this base, it was imperative that the harbour should be cleared of as many ships as possible. Vice-Admiral Somerville informed the Admiralty to this effect in his message 0503/4. Speed was increased to 24 knots to arrive at Gibraltar as soon as possible.
At 0700/4, HMS Ark Royal with HMS Faulknor and HMS Fortune went ahead at full speed to Gibraltar. They arrived at Gibraltar around 1115/4. The other ships arrived half-an-hour later. (52) 4 Apr 1941 Swapping of aircraft between HMS Ark Royal and HMS Furious.
At 1915A/4, HMS Renown (Capt. R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN), HMS Furious (Capt. A.G. Talbot, DSO, RN), HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN), HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN (Capt. D.8)), HMS Fearless (Cdr. A.F. Pugsley, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Fortune (Lt.Cdr. E.N. Sinclair, RN) departed Gibraltar and proceeded to the eastward at 18 knots until 2200A/4 when course was reversed and speed increased to 20 knots.
During the night information was received that operation 'Principal' (attack on the Vichy-French battlecruiser Dunkerque) was cancelled until further orders.
An A/S patrol was flown off at 0700A/5. HMS Ark Royal and HMS Furious each screened by two destroyers, operated independently from 0830a/4 and carried out operation 'Tender'. Four Swordfish (fitted with ASV) and ten Fulmars were transferred from HMS Furious to HMS Ark Royal while four Swordfish and nine Skuas were transferred from HMS Ark Royal to HMS Furious. Another Skua was unable to take off from HMS Ark Royal due to defects. One of the Fulmars broke its back on lading on HMS Ark Royal.
Operation 'Tender' was completed at 1045A/5, at which time HMS Furious escorted by HMS Faulknor and HMS Fortune were detached to join the Repulse group which had departed Gibraltar earlier in the day.
' Force H ' then set course to return to Gibraltar at 24 knots in order to enter harbour late in the evening. HMS Ark Royal carried out deck landing training for the remainder of the forenoon.
' Force H ' entered harbour at 2230A/5. As HMS Renown was securing, a massage from the Admiralty was received ordering ' Force H ' and HMS Fiji to raise steam. HMS Ark Royal was at this time entering harbour. Pending further instructions, ships were ordered to complete with fuel with all despatch. (52) 6 Apr 1941 Shortly after midnight Vice-Admiral Somerville was informed that there were indications that the German battlecruisers Scharnhorst and Gneisenau might leave Brest on the night of 6/7 April. He was instructed to leave Gibraltar with ' Force H ' as soon as possible and proceed westwards. ' Force H ' was placed under the orders of the Commander-in-Chief, Home Fleet.
At 0300 'Force H', made up of the following ships; battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN), light cruisers HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN), HMS Fiji (Capt. P.B.R.W. William-Powlett, RN), destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN (Capt. D.8)), HMS Fearless (Cdr. A.F. Pugsley, RN) and HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), departed Gibraltar. They were ordered to patrol off the Bay of Biscay.
At 0650/6, an A/S patrol was flown off and at 0730/6 three Fulmars and five Swordfish were landed on coming from North Front (the airbase at Gibraltar). An additional A/S patrol was glown off in view of information received from th Vice-Admiral Commanding North Atlantic Station, that five Italian submarines might be passing through the Straits into the Atlantic. Speed was increased to 23 knots at 1000/6 to reach a position from which a reconnaissance from HMS Ark Royal on the evening of the 7th might locate the enemy should he leave Brest on the previous night and steer south-west.
In the late afternoon / early evening an exercise was carried out during which ranges and bearings were obtained by the new radar set in HMS Fiji and were passed on to HMS Renown. HMS Sheffield served as the 'target' during this exercise. This was to investigate the possibility of HMS Renown engaging the enemy at night or in low visibility. Results were promising, but not entirely satisfactory, largely owing to lack of experience in HMS Fiji in operating this new radar set.
At 2000/6, when in position 37°46'N, 11°04'W, course was altered to 328° and speed increased to 24 knots. Further instructions for all units taking part in the operation were received.
Shortly after midnight Vice-Admiral Somerville leant that reconnaissance at 1830/6 had located both enemy battlecruisers at Brest. He therefore decided to maintain the course and speed of ' Force H ' till 1000/7 asnd then if no report had been received if the enemy having left Brest during the night of 6/7 April to reduce speed and alter course to the westward. As it was anticipated that activity by Focke Wulf aircraft would probably accompany the departure of the battlecruisers from Brest, a section of fighters was ranged on deck of HMS Ark Royal after the usual A/S patrol had flown off at 0655/7.
During the forenoon the employment of HMS Fiji's radar set by HMS Renown was again exercises on HMS Sheffield. During the afternoon each destroyer proceeded alongside HMS Renown and received 105 tons of oil. The time taken averaged 1 hour 14 minutes. During this period HMS Renown maintained a steady course of 290° at 10 knots. HMS Ark Royal acted independently. Weather conditions for fuelling were moderate.
At 1420/7 the A/S patrol aircraft, which was then seven miles to the northward of HMS Renown, reported having sighted three miles to the north-west of his position what appreared to be a four-engine monoplane flying 090° at 1000 feet. Renown's position was then 43°05'N, 15°47'W, and the visibility from 1000 feet, 7 miles. The aircraft was at first presumed to be a Focke Wulf, and it was doubtful whether or not ' Force H ' had been sighted. Nothing however was picked up on HMS Fiji's radar and later the crew of the Swordfish reported it was possible that they had seen a section of Fulmars which was flying in formation at that time and mistaken it for the single large aircraft reported.
No report having been received y 1500/7 regarding the presence or otherwise of the enemy battlecruisers at Brest, Vice-Admiral Somerville decided to send off a reconnaissance from HMS Ark Royal to search their furthest-on position assuming theyy had let Brest at nightfall on 6 April and passed between our submarine patrols and Cape Finisterre. Accordingly at 1625/7, nine aircraft were flown off from position 43°15'N, 16°15'W to search between 000° and 110°. Just after they had taken off a report was received that at 1145/6 the enemy was still in Brest harbour. The reconnaissance landed at 2010/7, having searched to a depth of 130 miles without sighting anything. Earlier receipt of the Brest report would have obviated the necessity for this reconnaissance.
Course was altered to the southward at 2130/7 amd to the eastward at 0200/8 to remain in the most favourable position for covering the south-west corner of the Bay of Biscay should the enemy leave Brest during the night.
At 0510/8 the result of the photographic reconnaissance of Brest on the afternoon of the 7th came in. This showed one battlecruiser had moved into dry dock. The other was in the harbour.
The A/S patrol was flown off at 0655/8 and at 0800/8 course was altered to 065° to reach a good position for an evening reconnaissance in the event of no information having been received that the enemy were still in Brest, and to enable a surface reconnaissance to be established the south-west of Cape Finisterre during the night if definite information wre received of the enemy's departure.
During the forenoon RDF trials were again carried out between HMS Fiji and HMS Renown, HMS Sheffield again acting as the 'target'. At the end of the exercise two rounds of 15" were fired with the object of HMS Fiji could range on the splashes but nothing was detacted on the screen. The exercises continued to show promise. A search and plotting exercise was also carried out during the forenoon.
The visibility was variable throughout the day and by 1120/8 the A/S patrol had to be abandoned. It was possible to restart it an hour later when one aircraft was flown off and instructed to investigate some flashes that had been reported by HMS Faulknor just above the horizon, on a bearing 130°. This observation could not be confirmed and nothing was seen by the aircraft.
Between 1600/8 and 1845/8 ' Force H' entered fog and at times the visibility was only a few hundred yards. The A/S patrol was fitted with ASV and by mean of this succeeded in landing on HMS Ark Royal down wind sustained some damage in the safety net. As any form of reconnaissance was clearly out of the question in this area, course was altered to the westward at 1700/8 and later the the southward in ordered to cover by air reconnaissance next moring, a possible enemy break out between our submarine patrols and Cape Finisterre.
At 2100/8 Vice-Admiral Somerville received instructions that the Commander-in-Chief, Home Fleet in HMS King George V was to return to Scapa Flow and that HMS Repulse was to proceed to Gibraltar and the command of the remaining forces in the Bay of Biscay area was now transferred to Vice-Admiral Somerville.
The position allocated to HMS Queen Elizabeth and to a less extent that allocated to HMS Hood appeared to Vice-Admiral Somerville to be too far to the westward to provide a reasonable prospect of making contact with the enemy before shadowing by shore base aircraft ceased owing to darkness or distance from their base. Vice-Admiral Somerville, however, cosidered that it was justigiable to break W/T silence at this stage.
At 0645/9, an A/S patrol was flown off, followed at 0800/9 by a reconnaissance of nine aircraft from position 42°03'N, 15°41'W. An all round search was flown with the object of locating the enemy battlecruisers should they had left Brest during the night of 7/8 April and passed south of our submarine patrol in the Bay of Biscay. The reconnaissance was limited by poor visibility and some aircraft had to return early. Nothing was sighted.
Soon after 1000/9 an immediate plain language signal was interepted from 19 Group, Headquartes, instructing RAF aircraft SQ8M to 'patrol to maximum prudent limit of endurance. Battlecruisers may have left 0830'. The time of origin of this signal was 1009/9. Vice-Admiral Somerville was surprised that a signal of this nature should have been made in plain language.
Course was altered to 320° at 0915/9 for oiling the destroyers and each of the three took 107 tons in an average of 67 minutes. On completion of oiling this course was maintained in order to close HMS Repulse, who was returning to Gibraltar in accordance with Admiralty signal 1859/8, as Vice-Admiral Somerville wanted to pass a cypher to her for transmission on the first occasion of breaking W/T silence.
At 1140/9, a signal was intercepted from the Commander-in-Chief, Plymouth, informing HMS Dunedin, who was on passage to Gibraltar, that a large vessel, possibly a warship, escorted by three destroyers, was leaving Brest. This vessel eventually proved to be a merchant vessel. News of the enemy leaving Brest was eagerly awaited in HMS Renown as this was the anniversary of Renown's previous encounter with the battlecruisers of Norway.
A reconnaissance of eight aircraft flew off at 1600/9 from position 42°11'N, 16°04'W, to search between 220° and 000° with the object of locating HMS Repulse. She was sighted fine on the starboard bow, and passed at a distance of seven miles at 2000/9 in position 43°00'N, 16°53'W. The reconnaissance aircraft dropped onboard HMS Repulse a message to be transmitted to the Admiralty as soon as the breaking W/T silence was considered justified. This message requisted the Admiralty to move HMS Hood and HMS Queen Elizabeth further in towards Brest and to give earlier information concerning the results of air reconnaissance.
HMS Ark Royal's reconnaissance also sighted at 1635/9 a Bermuda rigged cutter in position 42°11'N, 16°52'W steering 240° and wearing no flag. This report was not received till shortly before dark and as the position was then some 45 miles on Renown's port quarted Vice-Admiral Somerville did not detach a destroyer to investigate. This cutter, which was probably a Portugese fruit boat, was heading for the Azores.
Course was altered to 215° at 2000/9 and continued throughout the night so as to be in position at 0800/10 to cover the enemy;s furthest on position had they left Brest on the night of 8/9 April and steered south-west. No news of the enemy was received all day.
At 0230/10 a signal was received stating that photographs taken at 1830/9 showed both battlecruisers still at Brest. An A/S patrol was flown off at 0700/10 and at 0740/10 speed was reduced to 14 knots on account of the sea and rising wind from north-east. Course was altered to 340° to bring the sea on the beam and thus improve conditions for the destroyers.
During the forenoon HMS Sheffield was stationed 12 miles on the port beam for an exercise. At 1300/10 course was altered to 120° to avoid getting too far to the north-west and to keep as much to windward as possible without punishing the destroyers.
At 2000/10 course was altered to 330° for the night. This took ' Force H ' about 60 miles north of its area by 0800/10 but it was considered desirable for A/S reasons to get clear of the area in which we have been operating fo the last 48 hours. There were no indications of early departure of the enemy and the weather reports suggested that the area to the north-west would in all probability be the least favourable for air reconnaissance.
At 2100/10, HMS Fiji was detached in position 41°56'N, 14°36'W, to return to Gibraltar to fuel and sail for Freetown in accordance with Admiralty's 1829/8. The wind and sea had risen considerably and a speed of 12 knots could not be exceeded without the destroyers bumping excessively.
At 0200/11, Vice-Admiral Somerville received the Commander-in-Chief. Home Fleet's intended dispositions for the patrol. These coincided very closely with his own but necessitated ships moving further eastward then Vice-Admiral Somerville had suggester in his signal sent 1330/9.
The usual A/S patrol flew off at 0720/11, and by 0830/11 the sea had moderated sufficiently to allow a speed of 16 knots. A reconnassance of 12 aircraft was flown off at 0904/11 in position 43°48'N, 16°10'W, for an all round search for the enemy battlecruisers in case they might be in the vicinity, no news having been received of them later than that spplied by photographs at 1830/9.
At 1000/11, signals were received which showed both battlecruisers at Brest at 1620/10. These signals from the Admiralty were in Naval Code with no indication of priority. They were originated at 2324/10 and 0234/11 but were not received in HMS Renown until 0845/11 and there was then a futher delay in decoding due to this lack of any indication of priority. As a result 12 aircraft had been flown off on a needless reconnaissance in conditions where there was considerable chance of damage on landing and ' Force H ' was committed to a definite course and speed till all aircraft returned.
Speed had to be reduced to 15 knots at 1130/11 as the destroyers had again started to bump.
The reconnaissance landed on at 1300/11 having sighted nothing. Course was then altered to the westward for two hours with the object of avoiding steaming through the same water when making ground to the north-west.
Course was altered to 330° at 1530/11. The decisiom to move north-west was based on several factors. HMS Queen Elizabeth was proceeding from her patrol position in the vicinity of 45°00'N, 23°00'W, to fuel at Gibraltar, and would therefore temporarily cover the sector previously patrolled by ' Force H ', whilst the latter Force would be moving towards Queen Elizabeth's former position. The centre sector of the Bay of Biscay was being uncovered by the removal of our submarines to the UK and Gibraltar. Weather reports indicated better prospects for efficient reconnaissance to the north-west and it was clearly advantageous from an A/S point of view to shift the area of operations.
At 1700/11, information was received that both enemy battlecruisers were still in Brest at 1400/11. This early receipt of the results of reconnaissance was of great value.
HMS Fearless investigated an A/S contact at 2130/11 in position 44°24'N, 17°02'W, and HMS Faulknor assisted, but the echo was not good and was considered to be non-sub. After dropping a pattern of depth charges the destroyers rejoined.
Having made enough ground tp the north-ward course was altered to 270° at 0100/12 to avoid approaching the position where HMS Fearless had obtained a contact. HMS Sheffield was detached at 0500/12 on receipt of instructions that she was to return to Gibraltar.
Course was altered to the eastward at 0650/12 to aoid moving too far from Brest, and as weather conditions were then favourable for oiling destroyers, course was altered to 140° at 1030/12 and speed reduced to 10 knots for this purpose. Each destroyers received approximately 77 tons.
A short search and plotting exercise was carried out during the forenoon and HMS Ark Royal exercised fighters. Further fighter training and a dummy torpedo bombing attack was carried out p.m.
At 1800/12, in position 44°08'N, 16°50'W, a life saving raft marked Bianca was sighted. This position was 110 miles 274° from where the Bianca had been scuttled on March 20th when intercepted by HMS Renown. During the morning watch an empty lifeboat had been investigated and it is probable this also belonged to either the Bianca or San Casimiro, who had been scuttled some 60 miles north-west of the Bianca on the same day.
On completion of oiling, course was altered to 090° to make ground to windward and towards Brest in case any report should be received of the enemy leaving harbour. At 1700/12 information was received that up to 1300/12 reconnaissance of Brest had been unsuccessful. No reconnaissance was flown as he position of ' Force H ' and visibility did not suggest that any useful results would be otained. Course was maintained to the eastward.
At 0019/13, a signal was received stating that the ASV patrol off Brest was not being flown and since there had been no reconnaissance of the port the previous day it was decided to turn to, the north-eastward to take up the best position for an air reconnaissance from HMS Ark Royal in the evening to cover the possible position of the enemy if they had left during the night of 12/13 April. Course was accordingly altered to 060° at 0400/13.
HMS Faulknor dropped depth charge on a contact in position 44°48'N, 14°06'W at 1400/13 but resumed station at once as the contact was considered doubtful and a large fish was seen to break surface near the depth charge explosions.
At 1530/13, course was altered to 150°. information was received at 1625/13 (Admiralty message 1456/13) that up to 1300/13 no reconnaissance of Brest had been possible. Twelve aircraft were flown off at 1630/13 from position 44°43'N, 13°33'W, to cover the enemy's possible position had he sailed during the first half of last night and steered between 220° and 255° between 20 and 24 knots. These aircraft landed on at 2000/13 having sight nothing except a 3-masted brigantine 120 miles north of HMS Renown heading to the westward. No steps were taken to investigate this craft as it would have been dark before a destroyer could reach the position.
Course was altered to 210° for the night to enable a morning reconnaissance to cover the enemy's possible position if he had avoided detection by, or passed to the south-east of the area covered by, the days search. News was received at 2125/13 that no reconnaissance of Brest had been carried out up to 1800/13 and that a report hat stated that Gneisenau had been seriously hit aft by two bombs.
An A/S and security patrol was flown off at 0650/14. At 0800/14 course was altered to 320° to maintain the same distance from Brest, and a reconnaissance of eight aircraft was flown off from position 41°30'N, 14°50'W, to carry out a search to the north-eastward to a depth of 120 miles. Nothing was sighted. Course was altered to 065° at noon so that the evening reconnaissance from HMS Ark Royal could cover the enemy's furthest on position should the reconnaissance of Brest indicate that the battlecruisers had sailed.
During the day HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal carried out 4.5" gunnery exercises at a target towed by one of the destroyers. Dummy dive bombing practices were carried out on the destroyers by Fulmars.
Information was received at 1245/14 that one battlecruiser had been seen at Brest at 0730/14 but owing to low visibility the dry dock had not been seen.
At 1630/14, a signal (C-in-C, Home Fleet, 1435/14) was received directing the Commander-in-Chief, Home Fleet, to assume command of all the units operating in the Bay of Biscay area from 1600/14.
Failing further news of the enemy Vice-Admiral Somerville did not consider it desirable to carry out an evening reconnaissance, as to reach his possible position it would have been nesccessary for the aircraft to fly off very late and to carry out a very deep search. As nothing more was heard by 1800/14 course was altered to the westward for two hours and then to 150° to return to Gibraltar. It was etimated that HMS Repulse, northbound to start her patrol, would cross the latitude of ' Force H ', southbound, a.m. on the 15th.
At dawn on the 15th the usual A/S patrols were flown off. Speed was increased to 19 knots at 1000/19. During the forenoon fighters carried out dummy dive bombing attacks on HMS Renown for the training of the close range AA personnel.
Information was received at 1300/15 that both the enemy battlecruisers had been seen at Brest at 0845/15.
At 1345/15, when in position 39°05'N, 11°24'W, a signal was received that a German Focke Wulf aircraft had been operating near 38°00'N, 12°00'W at 1135/15. In the afternoon two sections of fighters were therefore flown off to maintain a high and low patrol. These patrols landed at 1610/15, nothing had been sighted.
There were signs of considerable U-boat activity in the Gibraltar area. Three definite reports of sightings were made in the past twenty-four hours, one 53 miles east of Gibraltar, one 100 miles were of Tarifa, and one 28 miles of Lisbon. Course was accordingly altered to 180° at 2000/15 in case ' Force H ' had been sighted and reported by U-boat or aircraft.
At 2255/15, a raider signal was received from an unknown ship in position 37°09'N, 18°43'W, some 400 miles due west of ' Force H '. With the fuel remaining only one search over a relatively small area was possible and the destroyers could not accompany the force. In view of the reported presence of U-boats in the vicinity and the very small prospects of effecting contact coupled with the necessity for ships and destroyers of ' Force H ' to make good defects in preparation for forthcoming operations, Vice-Admiral Somerville decided that it was undisirable to investigate this report. The ocean boarding vessel HMS Camito was known to be in the vicinity of the position or the raider report.
Course was altered to the eastward at 2330/15 and speed was increased to 24 knots at midnight.
A double A/S patrol was flown off at 0625/16 and later five aircraft were flown off to land at North Front landing ground to be available for various training exercises while the ships would be in harbour.
' Force H ' entered harbour at 1245/16. (52) 24 Apr 1941 Transfer of fighter aircraft to Malta and reinforcements for the Mediterranean Fleet.
Timespan: 24 to 28 April 1941.
24 April 1941.
At 2200/25, ‘Force S’, made up of the light cruiser HMS Dido (Capt. H.W.U. McCall, RN, Senior Officer), fast minelayer HMS Abdiel (Capt. Hon. E. Pleydell-Bouverie, MVO, RN), destroyers HMS Kelly (Capt. L.F.A.V.N. Mountbatten, GCVO, DSO, RN), HMS Kashmir (Cdr. H.A. King, RN), HMS Kelvin (Cdr. J.H. Allison, DSO, RN), HMS Kipling (Cdr. A. St. Clair-Ford, RN), HMS Jackal (Lt.Cdr. R.McC.P. Jonas, DSC, RN) and HMS Jersey (Lt.Cdr. A.F. Burnell-Nugent, DSC, RN) departed Gibraltar westwards but they soon turned eastwards again to pass Gibraltar eastwards after dark. The ships also had on board stores for Malta. Most of these on HMS Dido and HMS Abdiel.
They were followed one hour later, at 2300/25, by ‘Force H’. They departed Gibraltar and immediately turned eastwards. ‘Force H’ for this occasion was made up of the battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN), light cruiser HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Fearless (Cdr. A.F. Pugsley, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Fortune (Lt.Cdr. E.N. Sinclair, RN) and HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN).
25 April 1941.
On 26 April 1941 both forces proceeded to the east independently. At 2050 hours ‘Force H’ altered course and increased speed to reach the flying off position for the Hurricanes for Malta. They were to reach approximate position 37°40’N, 06°10’E at dawn the next day.
At 2120 hours a signal was received from Malta reporting that the weather was unsuitable and that the flying off had to be postponed for 24 hours. Speed was then reduced and at 2300 hours ‘Force H’ altered course to the westwards for an area to the south-west of Ibiza.
26 April 1941.
In the morning weather reports came in from Malta which were favourable. ‘Force H’ then altered course to 220° and at 1100 hours course was altered to the north-east. The object was to remain unsighted throughout the day. This was successful due to the poor visibility. Two more favourable weather reports came from Malta throughout the day.
In the evening a signal was received from HMS Dido stating that ‘Force S’ had also postponed their passage to Malta by 24 hours.
At 2100 hours ‘Force H’ was in position 38°35’N, 02°14’E. They then altered course to 106° and increased speed to 24 knots to again reach the flying off position for the Hurricanes at dawn.
27 April 1941.
Two more favourable weather reports were received during the early hours of the night. Weather in ‘Force H’ position was however not so good and at 0445 hours, in position 37°40’N, 05°55’E the destroyers had to be detached as they had difficulty keeping up with the other ships in the rising sea.
Flying off started at 0515 hours and was completed at 0613 hours. A total of 23 Hurricanes were flown off in two batches of eight and one of seven. These were all led by a Fulmar. On completion of flying off the Hurricanes an A/S patrol was launched as well as some Fulmars for fighter protection while the ships retired to the northwest on course 300° at 27 knots.
Though visibility was poor, a lone Heinkel appeared from the clouds over HMS Renown at 0850 hours and fire was opened on it. The enemy aircraft then made off the north-east with some of the Fulmars chasing it. The enemy was able to get back in the clouds before the Fulmars could overtake it. This aircraft reported the position, course and speed of the formation.
At 1000 hours a new section of Fulmars was flown off to relieve the others and at 1036 hours a signal was received from Malta that all the Hurricanes and their escorting Fulmars had landed safely.
At noon the destroyers rejoined and formed an A/S screen. Speed was reduced to 18 knots. ‘Force H’ remained in a position to support ‘Force S’ if needed. Aircraft for A/S and fighter protection were flown off during the day.
By 2000 hours all aircraft had returned to HMS Ark Royal and course was set to return to Gibraltar.
28 April 1941.
At dawn nine Swordfish were flown off for a practice attack on ‘Force H’. However one of the Swordfish hit the bridge of HMS Ark Royal and crashed into the sea. HMS Sheffield was able to pick up two of the three crew members. There was now sign of the air gunner and he was missing, presumed killed in the crash.
More air exercises were carried out during the day.
At 1130 hours, HMS Sheffield was detached to proceed to Gibraltar for a docking.
All ships of ‘Force H’ arrived at Gibraltar later on the day.
The ships of ‘Force S’ arrived safely at Malta on the 28th. (52) 1 May 1941 5 May 1941 Timespan: 5 to 12 May 1941.
5 May 1941.
Western Mediterranean.
Part of Convoy WS 8A was approaching Gibraltar from the west. This part of convoy WS 8A was to proceed to Malta during operation ‘Tiger’.
It was made up of five transports; Clan Campbell (7255 GRT, built 1937), Clan Chattan (7262 GRT, built 1937), Clan Lamont (7250 GRT, built 1939), Empire Song (9228 GRT, built 1940) and New Zealand Star (10740 GRT, built 1935). During the passage from the U.K. it had been escorted by the battlecruiser HMS Repulse (Capt. W.G. Tennant, CB, MVO, RN), light cruiser HMS Naiad (Capt. M.H.A. Kelsey, DSC, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral E.L.S. King, CB, MVO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Harvester (Lt.Cdr. M. Thornton, DSC, RN), HMS Havelock (Cdr. E.H. Thomas, DSC, RN) and HMS Hesperus (Lt.Cdr. A.A. Tait, RN) (with the additional local escorts when still close to the U.K.)
Around 0700A/5, HMS Repulse, HMS Harvester, HMS Havelock and HMS Hesperus were relieved from the escort by the battleship HMS Queen Elizabeth (Capt. C.B. Barry, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Fearless (Cdr. A.F. Pugsley, RN) , HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN) , HMS Fortune (Lt.Cdr. E.N. Sinclair, RN) and HMS Velox (Lt.Cdr. E.G. Roper, DSC, RN). The Repulse and the three H-class destroyers then proceeded to Gibraltar to refuel where they arrived shortly before 1800 hours. It had originally been intended to include Repulse in the upcoming operation but she was left at Gibraltar due to her inadequate anti-aircraft armament.
HMS Naiad had already arrived at Gibraltar around 0900/4, having been relieved shortly after noon on the 2nd of May by HMS Mauritius (Capt. W.D. Stephens, RN). Around the same time HMS Naiad arrived at Gibraltar the cruiser HMS Fiji (Capt. P.B.R.W. William-Powlett, RN) arrived, she had been part of the escort of convoy SL 72.
Around 0930A/5, the battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN), light cruisers HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN), HMS Fiji and the destroyers HMS Kashmir (Cdr. H.A. King, RN), HMS Kipling (Cdr. A. St. Clair-Ford, RN) and HMS Wrestler (Lt. E.L. Jones, DSC, RN). Kashmir and Kipling had departed a little earlier and carried out an A/S sweep in Gibraltar Bay first.
For the upcoming operation two groups were formed; The cover force which was formed on Renown was group I, the close escort, which was to remain with the transports was group II. When they arrived near the convoy at 1800A/5, group I was formed and was made up of Renown, Queen Elizabeth, Ark Royal, Sheffield, Fiji, Kashmir and Kipling. Group II remained with the convoy and was (for the moment) made up of Fearless, Foresight, Fortune, Velox and Wrestler. Group II and the convoy proceeded towards the Straits of Gibraltar at 13 knots while Group I proceeded to the south until 2130 hours when course was changed to 074°. At 1930 hours, Group I, had been joined by HMS Naiad. This cruiser had sailed from Gibraltar at 1300 hours.
Eastern Mediterranean.
Convoy MW 7B departed Alexandria for Malta this day. It was made up of the Norwegian tankers Hoegh Hood (9351 GRT, built 1936) and Svenor (7616 GRT, built 1931). These tankers were able to proceed at 10 knots. Escort was provided by the AA-cruisers HMS Carlisle (Capt. T.C. Hampton, RN), HMS Coventry (Capt. D. Gilmour, RN), destroyers HMS Defender (Lt.Cdr. G.L. Farnfield, RN), HMS HMS Greyhound (Cdr. W.A. Marshall-A’Deane, DSO, DSC, RN) and HMS Hasty (Lt.Cdr. L.R.K. Tyrwhitt, DSC, RN). Also part of the escort of this convoy was the corvette HMS Gloxinia (Lt.Cdr. A.J.C. Pomeroy, RNVR) which was to serve as minesweeper at Malta and the whaler HMS Swona which was to be outfitted as minesweeper (LL-sweep) at the Malta Dockyard.
6 May 1941.
Western Mediterranean.
The convoy with Group II passed through the Straits of Gibraltar between 0130 and 0330 hours followed by Group I between 0300 and 0430 hours. Although the moon did not set until 0314 hours the sky was completely overcast and visibility was low.
At 0330 hours, HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN), HMS Harvester, HMS Havelock and HMS Hesperus departed Gibraltar followed at 0420 hours by HMS Gloucester (Capt. H.A. Rowley, RN) which had completed her repairs and undocking shortly before.
By 0550 hours, Group I was about 32 miles to the east of Gibraltar with the convoy and Group II 10 miles to the north. At this time Faulknor, Forester and Fury joined Group I. At 0615 hours Queen Elizabeth with Kashmir and Kelvin was detached to join Group II, followed thirty minutes later by Naiad.
At 0625 hours, Gloucester joined Group I and speed was then increased to 24 knots to draw well ahead of the convoy. During the day Group I steered 060°. Group II was steering parallel to the Spanish coast at 13 knots. Velox and Wrestler were detached from Group II to arrive at Gibraltar after dark to avoid being sighted returning from the East.
At 1740 hours Renown, in position 37°05’N, 00°21’W sighted a French merchant ship most likely en-route to Oran. On sighting the British ships she immediately steered clear to the westward. Shorty afterwards Group I reduced speed to 17 knots as to not get too far ahead of Group II and the convoy.
By midnight Group I was about 150 nautical miles east-north-east of Group II.
Eastern Mediterranean.
The Mediterranean Fleet departed Alexandria in the forenoon, it was made up of the battleships HMS Warspite (Capt. D.B. Fisher, CBE, RN, flying the flag of Admiral Sir A.B. Cunningham, GCB, DSO and 2 Bars, RN), HMS Barham (Capt. G.C. Cooke, RN), HMS Valiant (Capt. C.E. Morgan, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Formidable (Capt. A.W.la T. Bisset, RN), light cruisers HMS Orion (Capt. G.R.B. Back, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral H.D. Pridham-Whippell, CB, CVO, RN), HMS Ajax (Capt. E.D.B. McCarthy, RN), HMAS Perth (Capt. P.W. Bowyer-Smith, RN), destroyers (D.14) HMS Jervis (Capt. P.J. Mack, DSO, RN), HMS Jaguar (Lt.Cdr. J.F.W. Hine, RN), HMS Juno (Cdr. St. J.R.J. Tyrwhitt, RN), HMS Kandahar (Cdr. W.G.A. Robson, DSO, RN), HMS Kimberley (Lt.Cdr. J.S.M. Richardson, DSO, RN), HMS Kingston (Lt.Cdr. P. Somerville, DSO, DSC, RN), (D.7) HMAS Napier (Capt. S.H.T. Arliss, RN), HMAS Nizam (Lt.Cdr. M.J. Clark, RAN), HMS Imperial (Lt.Cdr. C.A.de W. Kitcat, RN), HMS Havock (Lt. G.R.G. Watkins, RN), HMS Hotspur (Lt.Cdr. C.P.F. Brown, DSC, RN) and HMS Griffin (Lt.Cdr. J. Lee-Barber, DSO, RN). The fast minesweeper HMS Abdiel (Capt. E. Pleydell-Bouverie, MVO, RN) and the naval transport HMS Breconshire (9776 GRT, built 1939) also sailed with the Fleet. HMS Abdiel was to lay a minefield off Lampedusa. HMS Breconshire had on board oil and petrol for Malta as well as oil to supply this to destroyers at sea. Abdiel took station in the destroyer screen while Breconshire took station in the battleship line. After sailing the fleet proceeded to the northwest. No aircraft were flown off by HMS Formidable due to a dust storm and very limited visibility.
After the Fleet sailed, convoy MW 7A departed Alexandria. It was made up of four transport vessels; Amerika (10218 GRT, built 1930), Settler (6202 GRT, built 1939), Talabot (6798 GRT, built 1936) and Thermopylae (6655 GRT, built 1930). These were able to proceed at 14 knots. Escort was provided by the light cruisers HMS Dido (Capt. H.W.U. McCall, RN), HMS Phoebe (Capt. G. Grantham, RN), AA-cruiser HMS Calcutta (Capt. D.M. Lees, DSO, RN) and the destroyers (D.2) HMS Ilex (Capt. H.St.L. Nicholson, DSO and Bar, RN), HMS Isis (Cdr. C.S.B. Swinley, DSC, RN), HMS Hereward (Lt. W.J. Munn, RN) and HMS Hero (Cdr. H.W. Biggs, DSO, RN).
One of the destroyers from the escort of convoy MW 7B, HMS Defender, that had sailed on the 5th had to return to Alexandria due to condenser problems.
7 May 1941.
Western Mediterranean.
At 0400 hours, Group II, which was approximately 30 nautical miles east of Cape Palos, altered course to the south for about two hours before turning eastwards for the run to Malta.
Group I meanwhile had altered course to the northward at 0130 hours to pass between Ibiza and Majorca in order to carry out a diversion to the north of the Baleares during the day should this appear desirable.
By 0715 hours there was no indication that Group I had been sighted, and as visibility varied from poor to moderate, course was altered to pass again between Ibiza and Majorca to reach a position well ahead of Group II so as to divert any attention of any enemy aircraft from Group II and the convoy.
At 1000 hours, when 33 nautical miles south-west of Malta, Group I encountered a small Spanish fishing vessel which was seen to proceed towards Palma de Majorca.
At noon, Group I altered course to 140°. At 1630 hours course was altered to 100° to keep about 40 nautical miles to the eastward of Group II. Group I streamed paravanes at 1800 hours.
At 1945 hours, two Sunderland flying boats flying east passed north of the force and did not identify themselves till challenged. At the same time smoke was sighted astern and shortly afterwards a fighter aircraft reported that it was the convoy at a distance of 26 nautical miles.
At 2100 hours, Group I altered course to the north-east until dark in order to mislead any hostile aircraft. The sky had been overcast all day but towards the evening the visibility improved considerably and the convoy was clearly visible to the southwestward making a great deal of smoke.
At 2225 hours, RD/F in Fiji detected a group of aircraft bearing 170°, range 30 miles. The bearing changed to 154° and the range opened to 40 miles until the echo faded at 2230 hours. Group I altered course to 080° at 2300 hours.
Eastern Mediterranean.
All forces continued on their way during the day without incident. Destroyers were being fuelled from Breconshire one at a time.
The submarine HMS Triumph reported three transports proceeding towards Benghazi. Accordingly HMS Ajax, HMS Havock, HMS Hotspur and HMS Imperial were detached to attack Benghazi during the night of 7/8 May.
The Vice-Admiral Malta reported that the harbour had been mined and that the destroyers based at Malta were therefore unable to leave the harbour and participate in the convoy operations.
8 May 1941.
Western Mediterranean.
Soon after midnight Group I had to alter course to avoid being sighted by a lighted merchant ship steering a course of 110°.
At 0535 hours, HMS Ark Royal launched three reconnaissance A.S.V. aircraft in position 38°06’N, 06°26’E to search to the eastward south of Sardinia. At 0700 hours a fourth aircraft was flown off to search to the west of Sardinia. These aircraft returned at 0800 hours and had nothing to report. They had covered 140 miles to the eastward and 50 miles to the westward. Group I then proceeded to join the convoy. The first fighter patrol was flown off by Ark Royal at 0830 hours.
By 1000 hours, Group I had joined the convoy, which was proceeding on a course of 085° at 14 knots. This was the Clan Campbell’s best speed. Renown and Ark Royal took station on the starboard side of the convoy in order to facilitate flying operations and at the same time provide AA protection for the convoy. Queen Elizabeth took station astern of Ark Royal to provide AA protection for this vulnerable ship. Gloucester and Fiji formed on the transport ships.
At 1115 hours an enemy signal was intercepted that our forces had been sighted at 0800 hours. Naiad detected an enemy aircraft approaching at 1133 hours and three minutes later a large float-plane emerged from the clouds ahead of the convoy. Naiad opened fire and the aircraft retreated into the clouds. Fighters were sent in pursuit but failed to intercept. At noon a full and accurate report was made by this float-plane on the composition of our forces.
The sky cleared to some extent at noon, it had been overcast all morning. Visibility continued to improve all day although considerable cloud prevailed until the evening.
At 1345 hours, eight aircraft were seen approaching very low, fine on the starboard bow. These were engaged as they approached, but the AA fire appeared to be not very well directed. Torpedoes were dropped from outside the destroyer screen, which was roughly 3000 yards ahead of the convoy and extended to starboard to cover Renown, Ark Royal and Queen Elizabeth. The four Fulmar fighters on patrol at this time were engaging CR. 42 fighters that had accompanied these torpedo aircraft.
Torpedoes were evidently aimed at Renown and Ark Royal but by very skilful handling by the Commanding Officers of these two ships all tracks were combed or avoided. Two torpedoes passed close to Renown. A third which was being successfully combed made a sudden alteration of 60° towards Renown and a hit forward seemed inevitable when the torpedo reached the end of it’s run and sank. Two torpedoes passed to port and two to starboard of Ark Royal.
Of the eight aircraft which attacked one was brought down during the approach, probably by AA fire from the destroyers. Two others were seen to fall from the sky during their retirement. The destroyers were disappointingly slow in opening fire on the approaching torpedo-bombers and a full barrage never developed. During the action between the Fulmar’s and the CR. 42’s one Fulmar was brought down and the crew of two was lost.
At 1400 hours a few bomb splashes were observed on the horizon to the northwestward.
At 1525 hours, two sections of Fulmar’s attacked and shot down in flames an S.79 shadower. On returning from this attack one Fulmar had to make a forced landing on the water about 9 nautical miles from the fleet. HMS Foresight closed the position and was able to pick up the crew of two. At this time the fleet was about 28 nautical miles north of Galita Island.
At 1600 hours, as the wind had backed from south of east to north of east. The starboard column; Renown, Ark Royal and Queen Elizabeth, was moved over to the port quarter of the convoy and the destroyer screen was readjusted accordingly. This allowed freedom of manoeuvre for flying operations and enabled the column to increase speed and snake the line whenever a bombing attack developed, in order to hamper the bombers and at the same time remain in a position to afford full AA support of the convoy.
The first high level bombing attack of the day developed at 1622 hours when three S.79’s approached from astern at about 5000 feet, i.e. just under the cloud level. One, diverted by AA fire, jettisoned his bombs and subsequently crashed astern of the Fleet. The other two dropped twelve bombs close ahead of Ark Royal and escaped into the clouds. It is probable that both of these were hit by the concentrated AA fire with which they were met. About 10 minutes later a single aircraft approached from astern and encountering heavy AA fire turned across the stern of the Fleet, dropping its bombs well clear.
At 1710 hours, another S.79 shadower was shot down in flames on the port quarter of the Fleet by a Fulmar fighter. Twenty minutes later five S.79’s attacked the fleet from south to north. Two broke formation under gunfire and the remainder delivered a poor attack, bombs falling near the destroyer screen. A similar attack by three S.79’s took place at 1800 hours, when bombs were again dropped near the destroyer screen.
The provision a adequate fighter protection for the Fleet was a difficult problem with the small numbers of fighters available. Aircraft returned to the carrier at various times with damage and failure of undercarriage, and every opportunity was taken, whenever the RD/F screen cleared to land on, refuel and rearm the Fulmars, sometimes singly and sometimes two or three at a time. There were occasions when no more then two fighters were in the air, but whenever an attack appeared to be impending every fighter that could be made serviceable was sent up.
At 1910 hours enemy aircraft were detected at a range of 70 miles approaching from Sicily. At this time only seven Fulmars remained serviceable of which only three were in the air. The other four were immediately flown off. The total number of hostile aircraft is uncertain, but the Fulmars sighted three separate formations of sixteen Ju.87’s, twelve Ju.87’s and six Me.110’s. One formation was seen from Renown for a short time at 1933 hours in a patch of clear sky. RD/F indicated several formations circling to the northwest of the Fleet for nearly one hour and several bomb splashes were seen well away to the northward and northwestward. During this period Fulmars intercepted the enemy and, although greatly outnumbered, fought several vigorous and gallant actions, resulting in the certain destruction of one Ju.87 and damage to several others, including at least one Me.110. These attacks disorganised the enemy and forced them to the northward with the result that they probably missed sighting the Fleet. They then entered thick cloud and it is possible that the groups became separated and all cohesion in the attack disappeared. Whatever the reason RD/F showed these groups retiring to the northward and no attack on the Fleet developed.
The Fleet reached the entrance to the Skerki Channel at 2015 hours. ‘Force B’ then turned westwards. It was made up of Renown, Ark Royal, Sheffield, Harvester, Havelock and Hesperus. Queen Elizabeth was ordered to join ‘Force F’.
The turn to the west was just being completed when ‘Force B’ was attacked at 2030 hours by three torpedo-bombers which came from right ahead. The destroyers were still manoeuvering to take up their screening positions and did not sight the enemy aircraft in time to put up a barrage of AA fire. This attack was pressed home by the enemy with great determination. All three aircraft were heavily engaged and two were seen to be hit. Renown combed the torpedo tracks, two passing close down the port side and one down the starboard side.
During this attack No. P (port) 3, 4.5” gun turret in Renown malfunctioned and fired two round into the back of No. P 2 gun turret. This resulted in five ratings killed, five seriously wounded of which one later died and one officer and twenty-five ratings wounded.
Speed was increased to 24 knots at 2038 hours and a westerly course was maintained throughout the night.
As a result of the day’s air attacks, seven enemy aircraft were destroyed, two probably destroyed and at least three, probably more, damaged. Of the seven destroyed AA fire accounted for four and feighters for three. No hits, either by bomb or torpedo were obtained on our ships, nor were there any casualties besides than caused by the accident in Renown. Two Fulmars were lost, the crew of one of them was saved.
Meanwhile the convoy continued eastwards escorted now by HMS Queen Elizabeth, HMS Naiad, HMS Gloucester, HMS Fiji, HMS Faulknor, HMS Fearless, HMS Foresight, HMS Forester, HMS Fortune, HMS Fury, HMS Kashmir and HMS Kipling.
Eastern Mediterranean.
Visibility was still poor with patches of heavy rain. This helped the Fleet and convoy from being detected by the enemy and attacked by aircraft. On the other hand it resulted in the loss of two Albacore aircraft. One Fulmar was lost in combat with enemy aircraft.
HMS Ajax, HMS Havock, HMS Hotspur and HMS Imperial rejoined the Fleet at 1700 hours. Their attack on Benghazi had been successful although there was little shipping in the harbour two transports were intercepted after the bombardment. The largest blew up, and the other was ran aground and was left on fire after several explosions. These were the Italian Tenace (1142 GRT, built 1881) and Capitano A. Cecchi (2321 GRT, built 1933).
The Fleet remained with convoy MW 7A during the day and at dark moved to the southward. HMS Dido, HMS Phoebe, HMS Calcutta, HMS Carlisle and HMS Coventry were detached from their convoy’s to join the Tiger convoy coming from Gibraltar.
Both MW convoy’s made direct for Malta escorted by HMS Hotspur, HMS Havock and HMS Imperial. All other destroyers had been oiled from Breconshire during the past two days.
9 May 1941.
Western Mediterranean.
Further torpedo-bomber attacks were expected and a screen made up of Sheffield and the three destroyers was stationed ahead, astern and on either beam of Renown and Ark Royal at 5000 yards. The night was however uneventful and at 0800 hours speed was reduced to 20 knots and screening diagram no.4 was resumed by the escorts.
A shadower was detected, bearing 115°, range 12 nautical miles at 1027 hours. Two fighters were flown off but failed to intercept the enemy. An enemy sighting report was intercepted in Renown.
At 1100 hours a merchant vessel was sighted in position 37°54’N, 03°30’E about 8 nautical miles to the northward. At the same time Ark Royal reported that a periscope had been sighted about 4000 yards away. No further action was taken as detaching a single destroyer to search for the submarine was thought to be of little use and it was not thought wise to detach more then one destroyer as there were only three present.
At 1300 hours course was altered to 145° and speed reduced to 16 knots to conserve fuel in the destroyers.
At 1700 hours five search aircraft were flown off from position 37°27’N, 01°29’E to search between bearings 045° and 340° from Oran and south of parallel 38°45’N. Nothingwas sighted except for a merchant vessel. A Fulmar was also flown off to carry out a reconnaissance of Oran. This aircraft took photographs and reported the battlecruiser Dunkerque in her usual position at Mers-el-Kebir surrounded by nets, with lighters alongside and a pontoon gangway to the shore. One large and two small destroyers were sighted inside Oran harbour and probably six or seven submarines.
The six destroyers from the 8th Destroyer Flotilla which had taken part in getting the ‘Tiger’ convoy to as far as Malta sailed from there at 2000B/9 for their return passage to Gibraltar. HMS Foresight however had to return to Malta with an engine problem.
At 2200 hours ‘Force B’ altered course to the eastward as to be in a position to support the destroyers during their passage west at daylight the next day when they were passing south of Sardinia.
The Tiger convoy and it’s escort.
Shortly after midnight the transport Empire Song was mined and damaged. Initially she was able to remain with the convoy but around 0140 hours she was slowly sinking having also been on fire. The destroyers HMS Foresight and HMS Fortune were detached to stand by her. In the end Empire Song blew up during which Foresight was damaged.
The transport New Zealand Star was also damaged but she was able to remain with the convoy as her speed was not affected.
The convoy was attacked by torpedo-bombers early in the night but no damage was done by them. One torpedo passed very close to HMS Queen Elizabeth.
Around 0700 hours the Tiger convoy was joined by HMS Dido and HMS Phoebe. An hour later HMS Calcutta, HMS Carlisle and HMS Coventry also joined.
At 1515 hours the Tiger convoy made rendez-vous with the Mediterreanean Fleet about 50 nautical miles south of Malta.
Eastern Mediterranean.
Convoy’s MW 7A and MW 7B both arrived safely at Malta. Both were swept in by HMS Gloxinia who succeeded in exploding a number of mines. The 5th Destroyer Flotilla was then also able to leave the harbour and they joined the Mediterranean Fleet; these were HMS Kelly (Capt. L.F.A.V.N. Mountbatten, GCVO, DSO, RN), HMS Kelvin (Cdr. J.H. Allison, DSO, RN) , HMS Jackal (Lt.Cdr. R.McC.P. Jonas, DSC, RN) and HMS Janus (Cdr. J.A.W. Tothill, RN)
Also Breconshire arrived at Malta where she fuelled HMS Hotspur, HMS Havock and HMS Imperial.
As said above, at 1515 hours the Tiger convoy made rendez-vous with the Mediterreanean Fleet about 50 nautical miles south of Malta. HMS Queen Elizabeth then joined the battleship column. The Fleet then turned eastward but remained near the convoy for the remainder of the day. During the night he Fleet covered the convoy from a position to the north-eastward of it.
10 May 1941.
Western Mediterranean.
At 0700 hours, when in position 37°35’N, 03°02’E, course was altered to the westward at 15 knots. This being the most comfortable speed for the destroyers in the rising westerly gale.
At 1000 hours, the Capt. (D) 8th Destroyer Flotilla, reported he was in position 37°18’N, 08°45’E steering 275° at 28 knots. He also reported hat his ships were being shadowed by enemy aircraft. The enemy aircraft report was intercepted at 1025 hours. Course was then altered by ‘Force B’ to the eastward to reduce the distance between the two forces.
At 1100 hours, the Capt. (D) 8th Destroyer Flotilla, reported he was in position 37°22’N, 07°54’E, still steering 275° at 28 knots. The destroyers were still being shadowed.
At noon ‘Force B’ altered course to the westward. The wind was by then force 8 with a rising sea. Ten minutes later the enemy aircraft was again heard to report the position of the 8th Destroyer Flotilla and it’s course and speed.
At 1300 hours, the Capt. (D) 8th Destroyer Flotilla, reported he was in position 37°25’N, 07°01’E, steering 270° at 28 knots and that his ships were still being shadowed. At this time ‘Force B’ was 134 nautical miles to the westward and they could only maintain 13 knots in the sea without suffering damage. In view of the weather conditions and the fact that HMS Ark Royal had now only four serviceable fighters available it was not possible to afford the 8th Destroyer Flotilla any fighter protection without hazarding Ark Royal unduly. It was hoped that if an attack would develop the destroyers were able to avoid damage by high speed manoeuvring.
At 1430 hours a signal was received that the 8th Destroyer Flotilla was being bombed in position 37°25’N, 06°18’E and that HMS Fortune had been hit and her speed had been reduced to 8 knots. ‘Force B’ immediately altered course to the eastward and ran before the sea at 24 knots the maximum safe speed for the destroyers in the prevailing weather conditions.
An unidentified aircraft that had been detected by RD/F overtook the force at 1530 hours and was fired at by HMS Sheffield. The aircraft retired to the northward before resuming it’s easterly course. A reconnaissance of three aircraft was flown off at 1600 hours to cover the area to the northward and eastward of the 8th Destroyer Flotilla to maximum depth, in case enemy surface units were out in pursuit. These aircraft reported having sighted nothing on their return.
At 1750 hours a signal was received that the 8th Destroyer Flotilla had been subjected to another bombing attack but that no damage had been done. ‘Force B’ continued eastwards to provide close support in case of more air attacks.
At 1820 hours rendes-vous was made with the 8th Destroyer Flotilla and all ships proceeded westwards steering 280° at 12 knots. This was the best course and speed HMS Fortune could maintain. By this time this destroyer was down by the stern with seas breaking continually over her quarterdeck.
Five search aircraft were flown off by Ark Royal to search to maximum depth between 025° and 090°. Nothing was sighted except for one enemy aircraft. By 2030 hours all aircraft had returned.
As a speed of 12 knots subjected Fortune’s bulkhead to undue strain, HMS Fury was ordered to escort Fortune and proceed at 8 knots for the night. The remainder of the force zig-zagged, clear of these two destroyers, at higher speed.
It became also clear that Fortune had not received a direct hit but that five near misses had bent one shaft and caused flooding in several compartments aft, and minor flooding in the engine room.
Eastern Mediterranean.
The Battlefleet remained near the convoy for the entire day. Visibility improved throughout the day although conditions were still difficult for the enemy to attack from the air. One Ju.88 aircraft was shot down and another one was damaged. One Fulmar was lost when taking off from Formidable.
No enemy air attacks developed until dark when a number of aircraft, probably torpedo bombers, endeavoured to attack the convoy and battlefleet. A very heavy blind barrage of AA fire however kept them off and no torpedoes were seen.
At 1700 hours, Capt. D.5 in HMS Kelly was detached with the ships of the 5th Destroyer Flotilla (besides Kelly these were Kashmir, Kelvin, Kipling and Jackal) to bombard Benghazi before returning to Malta. The bombardment was carried out successfully. Following the bombardment they were dive bombed by German aircraft and all but Kipling were near missed. The Flotilla reached Malta p.m. on the 11th.
11 May 1941.
Western Mediterranean.
At 0532 hours, Vice-Admiral Somerville sent a signal to the Vice-Admiral commanding the North Atlantic station at Gibraltar reporting the position, course and speed of his forces. He also requested a tug to be sent for the assistance of HMS Fortune.
The wind eased considerably during the morning and at daylight Fortune and Fury were sighted about 4 nautical miles in advance of the Fleet and making good about 10 knots.
A reconnaissance of six aircraft were flown off at 0700 hours. These searched for a depth of about 140 miles between 030° and 085°. Visibility was reported as being 10 to 20 miles. Also a search was conducted for a depth of about 100 miles between 085° and 110° with a visibility of 3 to 5 miles. Only a few French merchant vessels were sighted.
Nothing happened during the day.
At 1700 hours a reconnaissance was flown of from position 36°54’N, 01°11’E to a depth of 180 nautical miles between north and east and to a depth of 90 nautical miles between north and 290°. The visibility was reported as being 10 to 15 nautical miles. Nothing was sighted.
The Fleet turned to the eastward for an hour before dark to take up a position well astern of Fortune and Fury during the night.
Eastern Mediterranean.
The Tiger convoy and the Fleet continued eastwards. Enemy aircraft were in the vicinity all day but no attacks developed. One Ju.88 was shot down and another one was damaged, one Fulmar was lost. At dark the cruisers were detached to proceed to Alexandria and the Fleet went on ahead of the convoy.
12 May 1941.
Western Mediterranean.
Just before daylight contact was made by the Fleet with Fortune and Fury. At dawn the tug HMS St. Day and four ML’s arrived from Gibraltar.
HMS Sheffield, HMS Harvester, HMS Hesperus and the four ML’s then remained with HMS Fortune and HMS Fury. Fortune was now able to make 12 knots.
HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal, screened by HMS Faulknor, HMS Fearless, HMS Forester, HMS Foresight and HMS Havelock, then proceeded ahead to conduct flying exercises east of Gibraltar before entering harbour.
A reconnaissance was flown off at 0800 hours to search to the east but nothing was sighted. On their return these aircraft made a practice attack on Renown and Ark Royal. More exercises were carried out during the day.
The Fleet arrived at Gibraltar at 1800 hours. Renown berthed in no.1 dock to enable her damaged 4.5” gun turret to be hoised out.
HMS Sheffield entered harbour at 2030 hours followed shortly afterwards by the damaged Fortune and her escorts.
Eastern Mediterranean.
The bulk of the Fleet arrived at Alexandria around 1000 hours. The convoy arrived later, around 1300 hours. Some ships had been detached from the fleet to arrive early, fuel and then depart again for escort duties.
(58) 16 May 1941 They returned to Gibraltar between 1930A/17 and 2045A/17. (52) 18 May 1941 Part I.
Departure of the Bismarck from the Baltic.
At 2130B/18 the German battleship Bismarck and the German heavy cruiser Prinz Eugen departed Gotenhafen for an anti-shipping raid in the North Atlantic. The following morning they were joined off Cape Arkona by the German destroyers Z 16 / Friedrich Eckhold and Z 23. They then proceeded through the Great Belt. The four ships were joined by a third destroyer, Z 10 / Hans Lody shortly before midnight on 19 May.
First reports of Bismarck and British dispositions 20-21 May 1941.
On 20 May 1941 two large warships with a strong escort were seen at 1500 hours northward out of the Kattegat. This information originated from the Swedish cruiser Gotland which had passed the Germans off the Swedish coast in the morning. The Naval Attaché at Stockholm received the news at 2100/20 and forwarded it to the Admiralty. At 0900/21 the Bismarck and her consorts entered Kors Fjord, near Bergen, Norway and anchored in nearby fiords. A reconnaissance aircraft flying over Bergen at 1330/21 reported having seen two Hipper class heavy cruisers there. One of these ships was later identified on a photograph as being the Bismarck. This intelligence went out at once to the Home Fleet.
The ships of the Home Fleet were at this time widely dispersed on convoy duties, patrols, etc. Some of the units were ranging as far as Gibraltar and Freetown. The Commander-in-Chief, A/Admiral Sir John Tovey, was at Scapa Flow in his flagship, HMS King George V (Capt. W.R. Patterson, CVO, RN). With him were her newly commissioned sister ship HMS Prince of Wales (Capt. J.C. Leach, MVO, RN), the battlecruiser HMS Hood (Capt. R. Kerr, CBE, RN, with Vice-Admiral L.E. Holland, CB, RN, onboard), the aircraft carrier HMS Victorious (Capt. H.C. Bovell, RN), the light cruisers HMS Galatea (Capt. E.W.B. Sim, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral K.T.B. Curteis, CB, RN), HMS Aurora (Capt. W.G. Agnew, RN), HMS Kenya (Capt. M.M. Denny, CB, RN), HMS Neptune (Capt. R.C. O'Conor, RN) and the destroyers HMS Achates (Lt.Cdr. Viscount Jocelyn, RN), HMS Active (Lt.Cdr. M.W. Tomkinson, RN), HMS Antelope (Lt.Cdr. R.B.N. Hicks, DSO, RN), HMS Anthony (Lt.Cdr. J.M. Hodges, RN), HMS Echo (Lt.Cdr. C.H.deB. Newby, RN), HMS Electra (Cdr. C.W. May, RN), HMS Icarus (Lt.Cdr. C.D. Maud, DSO, RN), HMS Punjabi (Cdr. S.A. Buss, MVO, RN) and HMAS Nestor (Cdr. A.S. Rosenthal, RAN). HMS Victorious was under orders to escort troop convoy WS 8B from the Clyde to the Middle East. HMS Neptune was working up for service with the Mediterranean Fleet and was to escort convoy WS 8X from the Clyde to the Middle East on completion. She did not sail to operate against the Bismarck having only just began her post-refit work-up programme.
Rear-Admiral W.F. Wake-Walker (commanding the first Cruiser Squadron), with the heavy cruisers HMS Norfolk (Capt. A.J.L. Phillips, RN) (flag) and HMS Suffolk (Capt. R.M. Ellis, RN) was on patrol in the Denmark Straight. The light cruisers HMS Manchester (Capt. H.A. Packer, RN) and HMS Birmingham (Capt. A.C.G. Madden, RN) were patrolling between Iceland and the Faeroes. The battlecruiser HMS Repulse (Capt. W.G. Tennant, CB, MVO, RN) was at the Clyde to escort troop convoy WS 8B.
Action taken by the Commander-in-Chief, Home Fleet
Admiral Tovey took the following action when he received the news the Bismarck had been spotted at Bergen. Vice-Admiral Holland with the Hood, Prince of Wales, Achates, Antelope, Anthony, Echo, Electra and Icarus was ordered to cover Rear Admiral Wake-Walker's cruisers in the Denmark Straight. His force departed Scapa Flow around 0100/22.
HMS Arethusa (Capt. A.C. Chapman, RN), which was taking the Vice-Admiral, Orkneys and Shetlands, to Reykjavik on a visit of inspection, was ordered to remain at Hvalfiord and placed at Rear-Admiral Wake-Walkers disposal. HMS Manchester and HMS Birmingham were ordered to top off with fuel at Skaalefiord and them to resume their patrol. The other ships that remained at Scapa Flow were brought to short notice for steam.
The Free French submarine FFS Minerve (Lt. P.M. Sonneville), which was on patrol off south-west Norway was ordered to proceed to position 61°53'N, 03°15'E and HMS P 31 (Lt. J.B.de B. Kershaw, RN) was ordered to proceed to position 62°08'N, 05°08'E which is to the west of Stadtlandet.
The sailing of HMS Repulse and HMS Victorious with troop convoy WS 8B was cancelled and the ships were placed at the disposal of Admiral Tovey.
A reconnaissance aircraft flying over Bergen reported that the German ships were gone. This information reached Admiral Tovey at 2000/22. HMS Suffolk which had been fuelling at Hvalfiord was ordered to rejoin HMS Norfolk in the Denmark Strait. HMS Arethusa was ordered to join HMS Manchester and HMS Birmingham to form a patrol line between Iceland and the Faeroes. Vice-Admiral Holland, on his way to Iceland was told to cover the patrols in Denmark Strait north of 62°N. Admiral Tovey would cover the patrols south of 62°N.
Commander-in-Chief leaves Scapa Flow on 22 May 1941
The King George V, with Admiral Tovey on board, departed Scapa Flow at 2245/22. With the King George V sailed, HMS Victorious, HMS Galatea, HMS Aurora, HMS Kenya, HMS Hermione (Capt. G.N. Oliver, RN), HMS Windsor (Lt.Cdr. J.M.G. Waldegrave, DSC, RN), HMS Active, HMS Inglefield (Capt. P. Todd, DSO, RN), HMS Intrepid (Cdr. R.C. Gordon, DSO, RN), HMS Punjabi, HMS Lance (Lt.Cdr. R.W.F. Northcott, RN) and HMAS Nestor. HMS Lance however had to return to Scapa Flow due to defects.
At A.M. 23 May they were joined off the Butt of Lewis by HMS Repulse escorted by HMS Legion (Cdr. R.F. Jessel, RN), HMCS Assiniboine (A/Lt.Cdr. J.H. Stubbs, RCN) and HMCS Saguenay (Lt. P.E. Haddon, RCN) coming from the Clyde area which they departed on 22 May.
The Commander-in-Chief was 230 miles north-west of the Butt of Lewis in approximate position 60°20'N, 12°30'W when at 2032/23 a signal came in from HMS Norfolk that she had sighted the Bismarck in the Denmark Strait.
HMS Suffolk and HMS Norfolk made contact with the Bismarck in the Denmark Strait on 23 May 1941.
At 1922/23 HMS Suffolk sighted the Bismarck and Prinz Eugen in position 67°06'N, 24°50'W. They were proceeding to the south-west skirting the edge of the ice in Denmark Strait. HMS Suffolk immediately sent out an enemy report and made for the mist to the south-east. HMS Norfolk then commenced closing and sighted the enemy at 2030 hours. They were only some six nautical miles off and the Bismarck opened fire. HMS Norfolk immediately turned away, was not hit and also sent out an enemy report.
Although HMS Suffolk had sighted the enemy first and also sent the first contact report this was not received by the Commander-in-Chief. The enemy was 600 miles away to the north-westward.
Vice-Admiral Holland had picked up the signal from the Suffolk. He was at that moment about 300 nautical miles away. Course was changed to intercept and speed was increased by his force to 27 knots.
Dispositions, 23 May 1941.
At the Admiralty, when the Norfolk's signal came in, one of the first considerations was to safeguard the convoys at sea. At this time there were eleven crossing the North-Atlantic, six homeward and five outward bound. The most important convoy was troop convoy WS 8B of five ships which had left the Clyde the previous day for the Middle East. She was at this moment escorted by the heavy cruiser HMS Exeter (Capt. O.L. Gordon, MVO, RN), light cruiser (AA cruiser) HMS Cairo (A/Capt. I.R.H. Black, RN) and the destroyers HMS Cossack (Capt. P.L. Vian, DSO, RN), HMS Maori (Cdr. G.H. Stokes, DSC, RN), HMS Zulu (Cdr. H.R. Graham, DSO, RN), ORP Piorun (Kmdr.por. (Cdr.) E.J.S. Plawski), HMCS Ottawa (Cdr. E.R. Mainguy, RCN), HMCS Restigouche (Cdr. H.N. Lay, RCN) and the escort destroyer HMS Eridge (Lt.Cdr. W.F.N. Gregory-Smith, RN). HMS Repulse was also intended to have sailed with this convoy but she had joined the Commander-in-Chief instead.
Force H was sailed around 0200/24 from Gibraltar to protect this important convoy on the passage southwards. Force H was made up of the battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt Sir R.R. McGrigor, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN), light cruiser HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Foxhound (Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) and HMS Hesperus (Lt.Cdr. A.A. Tait, RN).
HMS Norfolk and HMS Suffolk shadowing Bismarck 23 / 24 May 1941.
During the night of 23 / 24 May 1941 HMS Norfolk and HMS Suffolk hung on to the enemy, The Norfolk on their port quarter, Suffolk on their starboard quarter. All through the night they sent signals with updates on the position, course and speed of the enemy. At 0516 hours HMS Norfolk sighted smoke on her port bow and soon HMS Hood and HMS Prince of Wales came in sight.
HMS Hood and HMS Prince of Wales 23 / 24 May 1941.
At 2054/23 the four remaining escorting destroyers were ordered to follow at best speed in the heavy seas if they were unable to keep up with the capital ships which were proceeding at 27 knots. Two destroyers, HMS Antelope and HMS Anthony had been ordered to proceed to Iceland to refuel at 1400/23. The destroyers all managed to keep up for now and at 2318 hours they were ordered to form a screen ahead of both capital ships. At 0008/24 speed was reduced to 25 knots and course was altered to due north at 0017 hours. It was expected that contact with the enemy would be made at any time after 0140/24. It was just now that the cruisers lost contact with the enemy in a snowstorm and for some time no reports were coming in. At 0031 hours the Vice-Admiral signalled to the Prince of Wales that if the enemy was not in sight by 0210 hours he would probably alter course to 180° until the cruisers regained touch. He also signalled that he intended to engage the Bismarck with both capital ships and leave the Prinz Eugen to Norfolk and Suffolk.
The Prince of Wales' Walrus aircraft was ready for catapulting and it was intended to fly it off, but visibility deteriorated and in the end it was defuelled and stowed away at 0140 hours. A signal was then passed to the destroyers that when the capital ships would turn to the south they were to continue northwards searching for the enemy. Course was altered to 200° at 0203/24. As there was now little chance of engaging the enemy before daylight the crews were allowed to rest.
At 0247/24 HMS Suffolk regained touch with the enemy and by 0300 hours reports were coming in again. At 0353 hours HMS Hood increased speed to 28 knots and at 0400/24 the enemy was estimated to be 20 nautical miles to the north-west. By 0430 hours visibility had increased to 12 nautical miles. At 0440 hours orders were given to refuel the Walrus of HMS Prince of Wales but due to delays due to water in the fuel it was not ready when the action began and it was damaged by splinters and eventuelly jettisoned into the sea.
At 0535/24 hours a vessel was seen looming on the horizon to the north-west, it was the Bismarck. She was some 17 nautical miles away bearing 330°. Prinz Eugen was ahead of her but this was not immediately realised and as the silhoutte of the German ships was almost similar the leading ship was most likely thought to be the Bismarck on board HMS Hood.
Battle of the Denmark Strait, action with the Bismarck and Prinz Eugen. Loss of HMS Hood.
At 0537/24 HMS Hood and HMS Prince of Wales were turned together 40° to starboard towards the enemy. At 0549 hours course was altered to 300° and the left hand ship was designated as the target. This was a mistake as this was the Prinz Eugen and not the Bismarck. This was changed to the Bismarck just before fire was opened at 0552 hours. At 0554 hours the Bismarck and Prinz Eugen also opened fire. In the meantime Prince of Wales had also opened fire at 0053 hours. Her first salvo was over. The sixth salvo was a straddle. The Norfolk and Suffolk were too far astern of the enemy to take part in the action.
At 0555 hours Hood and Prince of Wales turned two points to port. This opened up Prince of Wales' A arcs as her ninth salvo was fired.
Shortly before 0605 hours Hood signalled that another turn of two points to port had to be executed. Bismarck had just fired her fifth salvo when the Hood was rent in two by a huge explosion rising apparently between the after funnel and the mainmast. The fore part began to sink seperately, bows up, whilst the after part remained shrouded in a pall of smoke. Three or four minutes later, the Hood had vanished between the waves leaving a vast cloud of smoke drifting away to the leeward. She sank in position 63°20'N, 31°50'W (the wreck was found in 2001 in approximate position 63°22'N, 32°17'W, the exact position has not been released to the public.)
The Prince of Wales altered course to starboard to avoid the wreckage of the Hood. The Bismarck now shifted fire from her main and secondary armament to her. Range was now 18000 yards. Within a very short time she was hit by four 15" and three 6" shells. At 0602 hours a large projectile wrecked the bridge, killing or wounding most of the personnel and about the same time the ship was holed underwater aft. It was decided temporarily to discontinue the action and at 0613 hours HMS Prince of Wales turned away behind a smoke screen. The after turret continued to fire but it soon malfunctioned and was out of action until 0825 hours. When the Prince of Wales ceased firing the range was 14500 yards. She had fired 18 salvos from the main armament and five from the secondary. The Bismarck made no attempt to follow or continue the action. She had also not escaped unscatched and had sustained two severe hits.
Such was the end of the brief engagement. The loss by an unlucky hit of HMS Hood with Vice-Admiral Holland, Captain Kerr and almost her entire ships company was a grievous blow, but a great concentration of forces was gathering behind the Commander-in-Chief, and Admiral Somerville with Force H was speeding towards him from the south.
The chase
When the Hood blew up, HMS Norfolk was 15 nautical miles to the northward coming up at 28 knots. By 0630/24 she was approaching HMS Prince of Wales and Rear-Admiral Wake-Walker, signalling his intention to keep in touch, told her to follow at best speed. The destroyers that had been with HMS Hood and HMS Prince of Wales were still to the northward. They were ordered to search for survivors but only HMS Electra found three. The Prince of Wales reported that she could do 27 knots and she was told to open out to 10 nautical miles on a bearing of 110° so that HMS Norfolk could fall back on her if she was attacked. Far off the Prinz Eugen could be seen working out to starboard of the Bismarck while the chase continued to the southward.
At 0757 hours, HMS Suffolk reported that the Bismarck had reduced speed and that she appeared to be damaged. Shortly afterwards a Sunderland that had taken off from Iceland reported that the Bismarck was leaving behind a broad track of oil. The Commander-in-Chief with HMS King George V was still a long way off, about 360 nautical miles to the eastward, and Rear-Admiral Wake-Walker on the bridge of HMS Norfolk had to make an important decision, was he to renew the action with the help of the Prince of Wales or was he to make it his business to ensure that the enemy could be intercepted and brought to action by the Commander-in-Chief. A dominant consideration in the matter was the state of the Prince of Wales. Her bridge had been wrecked, she had 400 tons of water in her stern compartments and two of her guns were unserverable and she could go no more then 27 knots. She had only been commissioned recently and barely a week had passed since Captain Leach had reported her ready for service. Her turrets were of a new and an untried model, liable for 'teething' problems and evidently suffering from them, for at the end of the morning her salvoes were falling short and wide. It was doubted if she was a match for the Bismarck in her current state and it was on these grounds that Rear-Admiral Wake-Walker decided that he would confine himself to shadowing and that he would not attempt to force on an action. Soon after 1100/24 visibility decreased and the Bismarck was lost out of sight in mist and rain.
Measures taken by the Admiralty, 24 May 1941.
After the loss of HMS Hood the following measures were taken by the Admiralty. To watch for an attempt by the enemy to return to Germany, HMS Manchester, HMS Birmingham and HMS Arethusa had been ordered at 0120/24 to patrol off the north-east point of Iceland. They were told to proceed to this location with all despatch.
HMS Rodney (Capt. F.H.G. Dalrymple-Hamilton, RN), which with four destroyers was escorting the troopship Britannic (26943 GRT, built 1930) westward, was ordered at 1022/24 to steer west on a closing course and if the Britannic could not keep up she was to leave her with one of the destroyers. Rodney was about 550 nautical miles south-east of the Bismarck. At 1200/24 she left the Britannic in position 55°15'N, 22°25'W and left HMS Eskimo (Lt.Cdr. E.G. Le Geyt, RN) with her. HMS Rodney then proceeded with HMS Somali (Capt. C. Caslon, RN), HMS Tartar (Cdr. L.P. Skipwith, RN) and HMS Mashona (Cdr. W.H. Selby, RN) westwards on a closing course.
Two other capital ships were in the Atlantic; HMS Ramillies (Capt. A.D. Read, RN) and HMS Revenge (Capt. E.R. Archer, RN). The Ramillies was escorting convoy HX 127 from Halifax and was some 900 nautical miles south of the Bismarck. She was ordered at 1144/24 to place herself to the westward of the enemy and leaving her convoy at 1212/24 in position 46°25'N, 35°24'W, she set course to the north. HMS Revenge was ordered to leave Halifax and close the enemy.
Light cruiser HMS Edinburgh (Capt. C.M. Blackman, DSO, RN) was patrolling in the Atlantic between 44°N and 46°N for German merchant shipping and was ordered at 1250/24 to close the enemy and take on relief shadower. At 1430/24 she reported her position as 44°17'N, 23°56'W and she was proceeding on course 320° at 25 knots.
Rear-Admiral Wake-Walker was ordered to continue shadowing even if he ran short of fuel so to bring the Commander-in-Chief into action.
The Bismack turns due south at 1320 hours on 24 May 1941.
In the low state of visibility, HMS Norfolk and HMS Suffolk had to be constantly on the alert against the enemy falling back and attacking them. At 1320/24 the Bismarck and Prinz Eugen altered course to the south and reduced speed. HMS Norfolk sighted them through the rain at a range of only 8 nautical miles. Norfolk had to quickly turn away under the cover of a smoke screen.
It was at 1530/24 when HMS Norfolk received a signal made by the Commander-in-Chief at 0800/24 from which it was estimated that the Commander-in-Chief would be near the enemy at 0100/25. This was later changed to 0900/25.
At 1545/24, Rear-Admiral Wake-Walker was asked by the Admiralty to answer four questions;
1) State the remaining percentage of the Bismarck's fighting efficiency.
2) What amout of ammunition had the Bismarck expended.
3) What are the reasons for the frequent alterations of course by the Bismarck.
4) What are your intentions as regards to the Prince of Wales' re-engaging the Bismarck.
The answers by Rear-Admiral Wake-Walker were as follows.
1) Uncertain but high.
2) About 100 rounds.
3) Unaccountable except as an effort to shake off HMS Norfolk and HMS Suffolk.
4) Consider it wisely for HMS Prince of Wales to not re-engage the Bismarck until other capital ships are in contact, unless interception failed. Doubtful if she has the speed to force an action.
The afternoon drew on towards evening. Still the Bismarck and Prinz Eugen held on to the south while the Norfolk, Suffolk and Prince of Wales were still keeping her in sight.
At 1711/24 in order to delay the enemy if possible, by attacking him from astern, the Prince of Wales was stationed ahead of the Norfolk. The enemy was not in sight from the Norfolk at that time, but the Suffolk was still in contact.
At 1841/24 the Bismarck opened fire on the Suffolk. Her salvoes fell short, but one or two shorts came near enough to cause some minor damage to her hull plating aft. HMS Suffolk replied with nine broadsides before turning away behind a smoke screen.
On seeing the Suffolk being attacked, HMS Norfolk turned towards and she and HMS Prince of Wales opened fire, the latter firing 12 salvoes. By 1856 hours the action was over. Two of the guns on the Prince of Wales malfuntioned again. After the action the cruisers started to zig-zag due to fear for German submarines.
British dispositions at 1800 hours on 24 May 1941.
From the Admiralty at 2025/24, there went out a signal summarising the situation at 1800/24. The position, course and speed of the Bismarck was given as 59°10'N, 36°00'W, 180°, 24 knots with HMS Norfolk, HMS Suffolk and HMS Prince of Wales still in touch. The Commander-in-Chiefs estimated position at 1800/24 was 58°N, 30°W, with HMS King George V and HMS Repulse. HMS Victorious was with the 2nd Cruiser Squadron (HMS Galatea, HMS Aurora, HMS Kenya). They had parted company with the Commander-in-Chief at 1509/24. Heavy cruiser HMS London (Capt. R.M. Servaes, CBE, RN) was in position 42°45'N, 20°10'W and had been ordered to leave her convoy and close the enemy. HMS Ramillies was in estimated position 45°45'N, 35°40'W. She had been ordered to place herself to the west of the enemy. HMS Manchester, HMS Birmingham and HMS Arethusa were returning from their position off the north-east of Iceland to refuel. HMS Revenge had left Halifax and was closing convoy HX 128. HMS Edinburgh was in approximate position 45°15'N, 25°10'W. She had been ordered to close and take over stand by shadower.
Evening of 24 May 1941.
At 2031/24 HMS Norfolk received a signal sent by the Commander-in-Chief at 1455/24 stating that aircraft from HMS Victorious might make an attack at 2200/24 and Rear-Admiral Wake-Walker now waited for an air attack which he expected at 2300 hours. By that time Bismarck had been lost from sight but at 2330/24 HMS Norfolk briefly sighted her at a distance of 13 nautical miles. At 2343/24 aircraft from HMS Victorious were seen approaching. They circled round HMS Prince of Wales and HMS Norfolk and the latter was able to direct them to the enemy. At 0009/25 heavy anti-aircraft gunfire was seen and the Bismarck was just visible as the aircraft attacked.
HMS Victorious and the 2nd Cruiser Squadron detached by the Commander-in-Chief.
At 1440/24 the Commander-in-Chief ordered the 2nd Cruiser Squadron (HMS Galatea, HMS Aurora, HMS Kenya, HMS Hermione) and HMS Victorious to a position within 100 nautical miles from Bismarck and to launch a torpedo bombing attack and maintain contact as long as possible. The object of the torpedo bombing attack was to slow the enemy down. On board the Victorious were only 12 Swordfish torpedo bombers and 6 Fulmar fighters. Victorious was only recently commissioned and her crew was still rather green. She had on board a large consignment of crated Hurricane fighters for Malta which were to be delivered to Gibraltar.
At 2208/24 HMS Victorious commenced launching 9 Swordfish in position 58°58'N, 33°17'E. Two minutes later al were on their way to find the Bismarck. The Squadron was led by Lt.Cdr.(A) E. Esmonde, RN.
HMS Victorious aircraft attack the Bismarck.
When the Swordfish took off from HMS Victorious the Bismarck was estimated to be in position 57°09'N, 36°44'W and was steering 180°, speed 24 knots. At 2330/24 they sighted the Bismarck but contact was lost in the bad weater. Shortly afterwards the Swordfish sighted HMS Prince of Wales, HMS Norfolk and HMS Suffolk. HMS Norfolk guided them to the enemy which was 14 nautical miles on her starboard bow. At 2350 hours a vessel was detected ahead and the squadron broke cloud to deliver an attack. To their surprise they found themselves over a United States Coastguard cutter. The Bismarck was 6 nautical miles to the southward and on sighting the aircraft opened up a heavy barrage fire. Lt.Cdr. Esmonde pressed home his attack, 8 of the Swordfish were able to attack, the other had lost contact in the clouds.
The 8 planes attacked with 18" torpedoes, fitted with Duplex pistols set for 31 feet. At midnight three Swordfish attacked simultaneously on the port beam. Three others made a longer approach low down attacking on the port bow a minute later. One took a longer course, attacking on the port quarter. One went round and attacked on the starboard bow a couple of minutes after midnight. At least one hit was claimed on the starboard side abreast the bridge. The Germans however state that no hit was scored but that the violent maneuvering of the ship to avoid the attack, together with the heavy firing by the Bismarck caused the leak in no.2 boiler room to open up. No.2 boiler room was already partially flooded and now had to be abandoned.
All Swordfish from the striking had returned to HMS Victorious by 0201/25. Two Fulmars launched at 2300/24 for shadowing failed to find their ship in the darkness due to the failure of Victorious' homing beacon. Their crews were in the end picked up from the chilly water.
HMS Norfolk and HMS Suffolk loose contact at 0306/25.
While the aircraft from HMS Victorious were making their attack, HMS Norfolk sighted a ship to the south-west and gave the order to open fire. HMS Prince of Wales was able to identify it in time as an American coast guard cutter, but in the movements prepartory to opening fire HMS Norfolk lost touch with the enemy for a time and it was not until 0116/25 that she suddenly sighted the Bismarck only 8 nautical miles away. There followed a brief exchange of fire. HMS Norfolk and HMS Prince of Wales turned to port to bring their guns to bear and the latter was ordered to engage. It was then 0130/25. The Prince of Wales fired two salvoes at 20000 yards by radar. The Bismarck answered with two salvoes which fell a long way short. The light was failing and the enemy was again lost to sight. HMS Suffolk, which had to most reliable RDF set was told to act independently so as to keep in touch.
Around 0306/25 the Suffolk lost touch with the Bismarck. At 0552/25 Rear-Admiral Wake-Walker asked if HMS Victorious could launch aircraft for a search at dawn.
Search measures, 25 May 1941.
With the disappearance of the Bismarck at 0306/25 the first phase of the pursuit ended. The Commander-in-Chief, in HMS King George V with HMS Repulse in company was then about 115 nautical miles to the south-east. At 0616/25, Rear-Admiral Wake-Walker signalled that it was most probable that Bismarck and Prinz Eugen made a 90° turn to the west or turned back and 'cut away' to the eastward astern of the cruisers. Suffolk was already searching to the south-west and Norfolk was waiting for daylight to do the same. Prince of Wales was ordered to join the King George V and Repulse.
Force H was still on a course to intercept the Bismarck while steaming on at 24 knots. The Rear-Admiral commanding the 2nd Cruiser Squadron in HMS Galatea had altered course at 0558/25 to 180° for the position where the enemy was last seen and the Victorious was getting 8 aircraft ready to fly off at 0730/25 for a search to the eastward. This plan however was altered on orders being recieved from the Commander-in-Chief to take the cruisers and Victorious and carry out a search to the north-west of the Bismarck's last reported position. Five Fulmars had already been up during the night, two of them had not returned to the ship. The search therefore had to be undertaken by Swordfish, the only aircraft available. At 0810/25, seven Swordfish were flown off from position 56°18'N, 36°28'W to search between 280° and 040° up to 100 nautical miles. The search was supplemented by Victorious herself as well as the cruisers from the 2nd Cruiser Squadron (Galatea, Aurora, Kenya and Hermione) which were spread some miles apart.
DF position of the Bismarck of 0852/25.
HMS King George V was still proceeding to the south-west when at 1030/25 the Commander-in-Chief recieved a signal from the Admiralty that the Bismarck's position had been obtained by DF (direction finding) and that it indicated that the Bismarck was on a course for the North Sea by the Faeroes-Iceland passage. To counter this move by the enemy the Commander-in-Chief turned round at 1047/25 and made for the Faeroes-Iceland passage at 27 knots. HMS Repulse was no longer in company with HMS King George V, she had been detached at 0906/25 for Newfoundland to refuel. Suffolk also turned to the eastward to search, her search to the south-west had been fruitless. The search by HMS Victorious, her aircraft and the 2nd Cruiser Squadron to the north-west also had no result. Six Swordfish were landed on by 1107/25, one failed to return. HMS Galatea, HMS Aurora and HMS Kenya now turned towards the DF position of the Bismarck to search in that direction. HMS Hermione had to be detached to Hvalfiord, Iceland to refuel as she was by now down to 40%. The other cruisers slowed down to 20 knots to economise their remaining fuel supply wich was also getting low. At this moment HMS King George V had about 60% remaining.
Events during 25 May 1941.
At 1100/25, HMS King George V, HMS Suffolk and HMS Prince of Wales were proceeding to the north-east in the direction of the enemy's DF signal. HMS Rodney was in position 52°34'N, 29°23'W some 280 nautical miles to the south-eastward on the route towards the Bay of Biscay. On receiving the Commander-in-Chiefs signal of 1047/25 she too proceeded to the north-east.
Meanwhile to Admiralty had come to the conclusion that the Bismarck most likely was making for Brest, France. This was signalled to the Commander-in-Chief at 1023/25 to proceed together with Force H and the 1st Cruiser Squadron on that assumption.
In the absence however of definite reports it was difficult to be certain of the position of the enemy. The DF bearings in the morning had not been very definite. At 1100/25, HMS Renown (Force H), was in position 41°30'N, 17°10'W was ordered to act on the assumption the enemy was making for Brest, France. She shaped course accordingly and prepared a comprehensive sheme of air search. At 1108/25, HMS Rodney, was told to act on the assumption that the enemy was making for the Bay of Biscay. At 1244/25 the Flag Officer Submarines ordered six submarines to take up intercepting positions about 120 nautical miles west of Brest. The submarines involved were HMS Sealion (Cdr. B. Bryant, DSC, RN), HMS Seawolf (Lt. P.L. Field, RN), HMS Sturgeon (Lt.Cdr. D. St. Clair-Ford, RN) from the 5th Submarine Flottilla at Portsmouth, HMS Pandora (Lt.Cdr. J.W. Linton, DSC, RN), which was on passage to the U.K. from the Mediterranean to refit, HMS Tigris (Lt.Cdr. H.F. Bone, DSO, DSC, RN), from the 3rd Submarine Flottilla at Holy Loch and HMS H 44 (Lt. W.N.R. Knox, DSC, RN), a training boat from the 7th Submarine Flotilla at Rothesay which happened to be at Holyhead. Seawolf, Sturgeon and Tigris were already on patrol in the Bay of Biscay, Sealion departed Portsmouth on the 25th as did H 44 but she sailed from Holyhead. Pandora was on passage to the U.K. to refit and was diverted.
At 1320/25 a good DF fix located an enemy unit within a 50 mile radius from position 55°15'N, 32°00'W. This was sent by the Admiralty to the Commander-in-Chief at 1419/25 and it was received at 1530/25. It was only in the evening that it was finally clear to all involved that Bismarck was indeed making for a French port. Air searches had failed to find her during the day. (59) 18 May 1941 Part II.
26 May 1941.
By now the question of fuel was becoming acute. For four days ships had been steaming at high speeds and the Commander-in-Chief was faced with the reality of fuel limits. HMS Repulse had already left for Newfoundland, HMS Prince of Wales had by now been sent to Iceland to refuel. HMS Victorious and HMS Suffolk had been forced to reduce speed to economise their fuel.
Coastal Command started air searches along the route towards the Bay of Biscay by long range Catalina flying boats. Lack of fuel was effecting the destroyer screens of the capital ships. There was no screen available for HMS Victorious. The 4th Destroyer Flotilla, escorting troop convoy WS 8B, was ordered at 0159/26 to join the Commander-in-Chief in HMS King George V and HMS Rodney as was HMS Jupiter (Lt.Cdr. N.V.J.P. Thew, RN) which sailed from Londonderry. Leaving the convoy the 4th D.F. proceeded to the north-east. Force H in the meantime was also approaching the immediate area of operations. These forces were to play an important part in the final stages of the chase of the Bismarck.
Force H, 26 May 1941.
HMS Renown, HMS Ark Royal and HMS Sheffield were having a rough passage north in heavy seas, high wind, rain and mist. Their escorting destroyers had already turned back towards Gibraltar at 0900/25. At dawn on the 26th there was half a gale blowing from the north-west. At 0716/26 HMS Ark Royal launched a security patrol in position 48°26'N, 19°13'W to search to the north and to the west just in case the Scharnhorst and Gneisenau had departed Brest to come to the aid of the Bismarck. At 0835/26 there followed an A/S patrol of ten Swordfish. All planes had returned by 0930. None had seen anything.
Bismarck sighted at 1030/26.
It was at 1030/26 that one of the long range Catalina's of the Coastal Command sighted the Bismarck in position 49°30'N, 21°55'W. It was received in HMS King George V at 1043 hours and in HMS Renown in 1038 hours. It placed the enemy well to the westward of the Renown. It was confirmed within the hour when two Swordfish from the Ark Royal which reported the Bismarck in position 49°19'N, 20°52'W some 25 miles east of the position given by the Catalina. The Commander-in-Chief was at that moment about 130 miles to the north of the Bismarck but it was soon clear that the Bismarck had too great a lead to permit her being overtaken unless her speed could be reduced. Nor was the question one merely of distance and speed. The Bismarck was approaching a friendly coast and could run her fuel tanks nearly dry and was sure of air protection, while the British ships would have a long journey back to base in the face of air and submarine attack. HMS Renown was ahead of the Bismarck but it was important that she did not engage the Bismarck unless the latter was already heavily engaged by the better armoured HMS King George V and HMS Rodney.
When the Catalina found the Bismarck at 1030 hours, the 4th Destroyer Flotilla was steering east to join the Commander-in-Chief. They seem to have crossed astern of the enemy's track about 0800/26. The Catalina's report reached Capt. Vian in HMS Cossack at 1054/26 and 'knowing that the Commander-in-Chief would order him to intercept the enemy' Capt. Vian altered course to the south-east.
First attack by aircraft from the Ark Royal.
At 1315/26 HMS Sheffield was detached to the southward with orders to close and shadow the enemy, who was estimated to be 40 nautical miles south-west of the Renown. The visual signal ordering this movement was not repeated to HMS Ark Royal, an omission which had serious consequenses for the aircraft that were to take off did not know that HMS Sheffield had parted company.
At 1450/26 HMS Ark Royal launched a striking force of 14 Swordfish aircraft with the orders to proceed to the south and attack the Bismarck with torpedoes. Weather and cloud conditions were bad and a radar contact was obtained on a ship some 20 nautical miles from the estimated position of the enemy that had been given to the leader shortly before takeoff. At 1550 hours they broke through the clouds and fired 11 torpedoes. Unfortunately the supposed enemy was HMS Sheffield which managed to avoid all torpedoes. The Bismarck at that time was some 15 nautical miles to the southward. The striking force then returned an all aircraft had landed on by 1720/26.
At 1740/26, HMS Sheffield, sighted the Bismarck in position 48°30'N, 17°20'W and took station about 10 nautical miles astern and commenced shadowing the enemy.
Ark Royal's second attack, 2047/26.
The first striking force on its way back sighted the 4th Destroyer Flotilla 20 nautical miles west of Force H. As soon as the aircraft from the first strike had landed they were refuelled and rearmed as fast as possible. Take off started at 1910/26, a total of 15 Swordfish were launched. Reports coming in from HMS Sheffield placed the Bismarck at 167°, 38 nautical miles from the Ark Royal. The striking force was ordered to contact HMS Sheffield who was told to use DF to guide them in.
At 1955/26 HMS Sheffield was sighted but soon lost in the bad weather conditions. She was found again at 2035 hours, she guided the Swordfish in and directed them by visual signal on the enemy bearing 110°, 12 nautical miles. The force took departure for the target in subflights in line astern at 2040/26.
At 2047/26 no.1 subflight of three Swordfish dived through the clouds and sighted the Bismarck 4 nautical miles off to the south-east. One Swordfish of no.3 subflight was with them. Approaching again just inside the cloud they made their final dive at 2053/26 on the port beam under a very intense and accurate fire from the enemy. They dropped four torpedoes of which one was seen to hit. No.2 subflight, made up of two Swordfish, lost touch with no.1 subflight in the clouds, climed to 9000 feet, then dived on a bearing obtained by radar and then attacked from the starboard beam, again under heavy and intense fire. They dropped two torpedoes for one possible hit. The third plane of this subflight had lost touch with the other two and had returned to HMS Sheffield to obtained another range and bearing to the enemy. It then flew ahead of the enemy and carried out a determined attack from his port bow under heavy fire and obtained a torpedo hit on the port side amidships.
Subflight no.4 followed subflight no.3 into the clouds but got iced up at 6600 feet. It then dived through the clouds and was joined by no.2 aircraft from subflight no.3. The Bismarck was then sighted engaging subflight no.2 to starboard. The four aircraft then went into the clouds and cicled the German battleships stern and then dived out of the clouds again and attack simultaneously from the port side firing four torpedoes. All however missed the Bismarck. They came under a very heavy and fierce fire from the enemy and one of the aircraft was heavily damaged, the pilot and air gunner being wounded.
The two aircraft of subflight no.5 lost contact with the other subflights and then with each other in the cloud. They climbed to 7000 feet where ice began to form. When coming out of the cloud at 1000 feet aircraft 4K sighted the Bismarck down wind, she then went back into the cloud under fire from the enemy. She saw a torpedo hit on the enemy's starboard side, reached a position on the starboard bow, withdrew to 5 miles, then came in just above the sea and just outside 1000 yards fired a torpedo which did not hit. The second plane of this flight lost his leader diving through the cloud, found himself on the starboard quarter and after two attempts to attack under heavy fire was forced to jettison his torpedo.
Of the two Swordfish of subflight no.6 one attacked the Bismarck on the starboard beam and dropped his torpedo at 2000 yards without success. The second plane lost the enemy, returned to the Sheffield for a new range and bearing and after searching at sea level attacked on the starboard beam but was driven off by intense fire. The attack was over by 2125/26. Thirteen torpedoes had been fired and it was thought two hits and one probable hit had been obtained. Two torpedoes were jettisoned. The severe nature and full effect of the damage done was at first not fully realised. Actually the Bismarck had received a deadly blow. The last of the shadowing aircraft to return had seen her make two complete circles. One torpedo had struck her on the port side amidships doing little damage but th other torpedo that hit was on the starboard quarter damaging her propellors, wrecking her steering gear and jambing her rudders, it was this torpedo hit that sealed her fate.
HMS Sheffield was still shadowing astern when at 2140/26 the Bismarck turned to port and fired six accurate salvoes of 15". None actually hit Sheffield but a near miss killed three men and seriously injured two. HMS Sheffield turned away and while doing so she sighted HMS Cossack and the other destroyers from the 4th DF approaching from the westward. She then gave them the approximate position of the Bismarck. At 2155/26, HMS Sheffield lost touch with the Bismarck. The destroyers continued to shadow and eventually attack. Meanwhile HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal shaped course for the southward to keep the road clear for the Commander-in-Chief in HMS King George V and for HMS Rodney. Also in the Ark Royal aircraft were being got ready for an attack on the Bismarck at dawn.
Bismarck, 26 May 1941.
The Bismarck could no longer steer after the torpedo hit aft. The steering motor room was flooded up to the main deck and the rudders were jambed. Divers went down to the steering room and managed to centre one rudder but the other remained immovable. She was by this time urgently in need of fuel. It was hoped by the Germans that while she was nearing the French coast strong forces of aircraft and submarines would come to her assistance.
At 2242/26, Bismarck sighted the British destroyers. A heavy fire was opened on them. Their appearence greatly complicated the situation. Before their arrival however, Admiral Lütjens seems to have made up his mind as one hour earlier he had signalled to Berlin 'ship out of control. We shall fight to the last shell. Long live the Führer.'
The fourth Destroyer Flotilla makes contact, 26 May 1941.
Just as the sun was setting, Captain Vian (D.4) in HMS Cossack with HMS Maori, HMS Sikh, HMS Zulu and the Polish destroyer ORP Piorun arrived on the scene.
Shortly after 1900/26 HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal were sighted to the northward. Ark Royal was just about to fly off the second striking force. The destroyers continued on the the south-east. At 2152/26 HMS Sheffield was sighted and from her Captain Vian obtained the approximate position of the enemy.
The destroyers were spread 2.5 nautical miles apart on a line bearing 250° - 070° in the order from north-east to south-west, Piorun, Maori, Cossack, Sikh, Zulu. During the latter stages of the approach speed was reduced and the flotilla manoeuvred so as to avoid making a high speed end-on contact.
At 2238/26, ORP Piorun on the port wing reported the Bismarck 9 nautical miles distant, bearing 145° and steering to the south-eastward.
Destroyers shadowing, late on 26 May 1941.
At the time the Piorun reported being in contact with the Bismarck the destroyers were steering 120°. All were at once ordered to take up shadowing positions. Four minutes later the Bismarck opened a heavy fire with her main and secondary armaments on the Piorun and Maori. Two attempts were made by these ships to work round to the northward of the enemy but they were silhouetted against the north-western horizon making them easy to spot. The Bismarck's fire was unpleasantly accurate, through neither destroyer was actually hit. The Commanding Officer of the Maori then decided to work round to the southward and altered course accordingly.
The Piorun closed the range and herself opened fire from 13500 yards but after firing three salvoes, she was straddled by a salvo which fell about 20 yards from the ships side. She then ceased fire and turned away to port while making smoke. During this engagement she lost touch with the other destroyers and later also with the Bismarck. She remained under fire for about one hour but was not hit. She worked round to the north-east of the Bismarck but eventually lost touch with her prey at 2355/26.
The other destroyers, meanwhile, had been working round to the southward of the enemy to take up shadowing positions to the eastward of him. Soon after the initial contact it was evident the the Bismarck's speed had been so seriously reduced that interception by the battlefleet was certain, provided that contact could be held. In these circumstances Captain Vian defined his object at firstly, to deliver the enemy to the Commander-in-Chief at the time he desired, and secondly, to sink or immoblise her with torpedoes during the night but not with to great a risk for the destroyers. Accordingly at 2248/26 as signal was made to all ordering them to shadow and this operation was carried out through the night, though torpedo attacks were carried out later under the cover of darkness.
As darkness came on, the weather deteriorated and heavy rain squalls became frequent. Visibility varied between 2.5 nautical miles and half a mile but the Bismarck, presumably using radar, frequently opened up accurate fire outside these ranges.
About half an hour after sunset, the destroyers were ordered at 2324/26 to take up stations prepartory to carrying out a synchronised torpedo attack. This was subsequently cancelled on account of the adverse weather conditions and they were ordered to attack independently as opportunity offered. At about 2300 hours the Bismarck altered course to the north-westward.
At this time HMS Zulu was in touch with her and kept her under observation from the southward. At 2342 hours the Bismarck opened fire on HMS Cossack, then about 4 miles to the south-south-west and shot away her aerials. The Cossack turned away under the cover of smoke, shortly afterwards resuming her course to the eastward.
A few minutes later, at 2350 hours, HMS Zulu came under heavy fire from the Bismarck's 15" guns. The first three salvoes straddled wounding an officer and two ratings. Drastic avoiding action was taken as a result of which Zulu lost touch. HMS Sikh, however, who had lost sight of the enemy half an hour previously, had observed her firing at HMS Cossack and now succeeded in shadowing from astern until 0020/27 when the enemy made a large alteration to port and commenced firing at her. HMS Sikh altered course to port, intending to fire torpedoes, but the view of the Torpedo Control Officer was obscured by shell splashes and Sikh then withdrew to the southward.
Destroyer night torpedo attacks, 26/27 May 1941.
HMS Zulu, after her escape at 2345/26, had steered to the northward and at 0030/27 fell in with HMS Cossack. Shortly afterwards she sighted ORP Piorun. On receipt of a signal from Captain Vian, timed 0040/27, to take any opporunity to fire torpedoes, HMS Zulu altered course to the westward,and at 0100/27 sighted the Bismarck steering 340°.
Positions of the destroyers was now as follows; to the north-eastward of the enemy, HMS Cossack was working round to the north and west. HMS Maori, since losing touch, had been making to the westward. She was now to the south-west of the Bismarck. HMS Sikh was some distance to the southward, not having received any information regarding the position of the Bismarck since 0025/27. HMS Zulu was astern of the enemy and in contact. Range was only 5000 yards. Bismarck finally spotted Zulu and at once opened fire with her main and secondary armament and straddled Zulu. She fired four torpedoes at 0121/27 but no hits were observed and they are believed to have missed ahead. Zulu then ran out to the northward in order to be clear of the other destroyers. Shortly afterwards they widnessed a successful attack by HMS Maori.
HMS Maori had seen the Bismarck opening fire on the Zulu at 0107/27. Maori then closed to 4000 yards on Bismarck's port quarter apparently undetected. When abeam of the enemy, who then appeared to be altering course to starboard Maori fired a star shell to see what he was about. Two minutes later, at 0137/27, two torpedoes were fired and course was altered towards the Bismarck with the intention of attacking again from her starboard bow once the enemy had steadied on her new course. Whilst Maori was turning a torpedo hit was observed on the enemy. A bright glow illuminated the waterline of the enemy battleship from stem to stern. Shortly afterwards there appeared between the bridge and the stem a glare that might have been a second hit. The enemy immediately opened up a very heavy fire with both main and secondairy armaments and quick firing guns. As the Maori was being straddled, she turned away, and increased to full speed. Shots continued to fall on both sides of the ship until the range had been opened up to 10000 yards. Maori was not actually hit. Meanwhile HMS Cossack had been creeping up from the north-eastward and at 0140/27, only three minutes after Maori had fired two torpedoes, Cossack launched three torpedoes from 6000 yards. Bismarck stood out plainly, silhoutted by the broadsides she was firing at the Maori. One torpedo was seen to hit. Flames blazed on the forecastle of the Bismarck after this hit but they were quickly extinguished. Probably as a consequence of the torpedo hits the Bismarck stopped dead in the water, this was reported by HMS Zulu at 0148/27. After about one hour the Bismarck got underway again. On receipt of this report, HMS Sikh, who was closing the scene of the action from the southward, made an attack. Four torpedoes were fired at 0218/27 at the stopped battleship. It is believed that one hit was obtained. After this attack Sikh remained in radar contact with the enemy until 0359/27 when contact was lost.
Around 0240/27 the Bismarck was underway again, proceeding very slowly to the north-westward. At 0335/27, HMS Cossack made another attack firing her last remaining torpedo from a range of 4000 yards. It missed. HMS Cossack then came under a heavy fire. She withdrew to the northward under the cover of smoke, altering to a westerly course shortly afterwards.
At 0400/27 all destroyers had lost touch with the enemy. HMS Cossack was then to the north-west and HMS Sikh, HMS Zulu and HMS Maori were between the south-west and south-east of the Bismarck. All destroyers now endeavoured to regain contact.
Touch with the enemy was not regained until shortly before 0600 hours. By that time ORP Piorun, which was running short of fuel, had been ordered to proceed to Plymouth.
Destroyers shadowing, morning twilight, 27 May 1941, final attack.
Touch was regained by HMS Maori at 0550/27 when she sighted the Bismarck zigzagging slowly on a base course of 340° at about 7 knots. Maori commenced shadowing until daylight. At 0625 hours, HMS Sikh was also in contact when the Bismarck emerged from a rain squal 7000 yards on her starboard bow. By then it was nearly full daylight but to the surprise of the crew of the Sikh she got away with it without being fired at.
Shortly before sunrise a final torpedo attack was carried out by HMS Maori, which fired two torpedoes at 0656/27 from 9000 yards. Both missed. The Bismarck opened fire and straddled Maori which escaped at 28 knots.
At daylight the destroyers were stationed in four sectors from which they were able to keep the enemy under continuous observation until the arrival of the Battle Fleet at 0845 hours.
Force H, 26/27 May 1941.
While the destroyers were shadowing the Bismarck, the pursuing forces were drawing steadily closer. To the north was the Commander-in-Chief with the King George V and the Rodney with the Norfolk closing on them. In the south HMS Dorsetshire (Capt. B.C.S. Martin, RN) was coming up, while Force H was waiting for the dawn. When Captain Vian's destroyers got in touch at 2251/26 the Renown and Ark Royal were north-west of the enemy. It was not possible to attack with aircraft during the night
but all preparations were made to attack at dawn with 12 Swordfish. Course was shaped to the northward and then to the west for a time and at 0115/27 Force H turned south. Shortly afterwards instructions were received from the Commander-in-Chief to keep not less then 20 miles to the southward of the Bismarck so as to leave a clear approach for the Battle Fleet. Force H accordingly continued to the southward during the night. Bursts of starshell and gunfire could be seen during the night while the destroyers attacked. At 0509/27 an aircraft was flown off from HMS Ark Royal to act as a spotter for HMS King George V but it failed to find the Bismarck in the bad weather. The striking of force of 12 Swordfish was ready but due to the bad weather to strike was cancelled.
At 0810/27, HMS Maori was sighted. She reported the Bismarck 11 miles to the north of her. The made the enemy 17 miles to the north of HMS Renown so course was shaped to the south-west. At 0915/27 heavy gunfire could be heard and the striking force was flown off. They found the Bismarck at 1016/27. By then the battle was almost over, her guns were silenced and she was on fire. They saw her sink. At 1115/27 they had all landed back on HMS Ark Royal. A German Heinkel aircraft dropped a couple of bombs near HMS Ark Royal when they were landing on.
HMS Norfolk, 26/27 May 1941.
When the Catalina report (1030/26) came in, HMS Norfolk altered course to the south-west and increased speed to 27 knots. At 2130/26 the Bismarck was still some 160 nautical miles to the southward and speed was increased to 30 knots. At 2228/26 the report on the torpedo hit by the aircraft from Ark Royal came in and the Norfolk turned to the southward, continuing to close the enemy. At 0753/27 Norfolk sighted the Bismarck. She did not open fire and was lost to sight after ten minutes. At 0821/27, HMS King George V, was sighted to the westward, 12 nautical miles away. The position of the enemy was passed to the Commander-in-Chief. The action opened at 0847/27 at which time HMS Norfolk was then some 10 nautical miles from the Commander-in-Chief and due north of the Bismarck. HMS Norfolk had seen the beginning and was now to see the end.
HMS Dorsetshire, 26/27 May 1941.
On 26 May 1941, HMS Dorsetshire, was with convoy SL 74 proceeding from Freetown to the U.K. When she received the sighting report from the Catalina at 1056/26 she was some 360 nautical miles to the south of the Bismarck. She then left the protection of the convoy to the Armed Merchant Cruiser HMS Bulolo (Capt.(Retd.) R.L. Hamer, RN) and set course for the northward to take up the possible task of shadowing. By 2343/26 it became clear from reports that the Bismarck was making no ground to the eastward and that at 0230/27 she appeared to be laying stopped. Due to the heavy seas HMS Dorsetshire was forced to reduce speed to 25 knots and later even to 20 knots. At 0833/27 a destroyer was sighted ahead at a range of 8 nautical miles, it was HMS Cossack which reported the enemy at a range of 6 nautical miles. At 0850/27 the flashes of the Bismarck's guns could be seen to the westward. HMS Dorsetshire arrived at the scene of the action in the nick of time.
HMS King George V and HMS Rodney, 26/27 May 1941.
During 26 May 1941 the Commander-in-Chief in HMS King George V had been making hard to the south-east at 25 knots. He had been joined by HMS Rodney at 1806/26. They were then some 90 nautical miles north of the Bismarck. Fuel was a matter of grave anxiety. At noon on the 26th, HMS King George V, had only 32% remaining and HMS Rodney reported that she had to return at 0800/27. Speed had to be reduced on this account to 22 knots at 1705/26. In these circumstances it was no longer possible to hope to intercept the enemy, and the Commander-in-Chief decided that unless the enemy's speed had been reduced by 2400/26, he must turn at that hour. The only hope lay in the Bismarck being slowed up by the Swordfish attacking from HMS Ark Royal. A report came in that the striking force had left. Then at 2132/26, HMS Sheffield, reported that the enemy was steering 340° followed by 000° four minutes later. These reports indicated that the Bismarck was not able to hold her course and that her steering gear must have been damaged. It might still be possible to intercept her.
The Commander-in-Chief turned to the south at once hoping to make contact from the eastward in the failing light. Due to the bad weather conditions and visibility the Commander-in-Chief decided to haul off the the eastward and northward and then work round to engage from the westward at dawn. He turned eastward at 2306/26. During the night reports from Captain Vian's destroyers came in confirming the northerly course of the Bismarck. At 0236/27 the Commander-in-Chief ordered Captain Vian that the destroyers were to fire star-shell every half hour, but frequent rain squalls prevented these from being seen and they tended to attrack the enemy's fire. The Bismarck was still a formidable opponent for at 0353/27 Captain Vian reported that during the last hour she had done 8 nautical miles and that she was still capable of heavy and accurate fire. The Commander-in-Chief decided not to make a dawn approach but to wait until daylight while approaching from the west taking advantage of wind, sea and light. At 0529/27 HMS Rodney reported sighting HMS Norfolk to the eastward by DF. It was light at 0600 hours. At 0820 hours HMS Norfolk was sighted on the port bow of HMS King George V. She signalled 'enemy 130°, 16 nautical miles'. At 0843/27 looming on the starboard bow there emerges out of a rain squall the dark grey blot of a large ship. 'Enemy in sight'.
Bismarck 26/27 May 1941.
The Bismarck after altering course to the north-west had been labouring along with a jambed rudder, steering an erratic course at 8 knots. During the night the attacking destroyers were met with heavy and accurate salvoes. Sixteen torpedoes were fired at her. Early in the morning a glare of star-shell burst over her, lighting her up. Three torpedoes followed from a destroyer on the port bow (HMS Maori) of which one hit on the port side amidships. Three minutes later three more came from the starboard side (these were fired by HMS Cossack) of which one hit on the starboard bow. The damage that was sustained from these torpedo hits is not known. The Bismarck lay stopped for over one hour. At 0140/27 a message was received that a large number of Junkers bombers were coming to her aid as were U-boats but the Bismarck was beyond their help besides that the aircraft did not find her. One U-boat (U-556, which was out of torpedoes) on its way back from the Atlantic joined her and was within sight during the night. Another (U-74) arrived at 0600/27 but had been damaged in a depth charge attack and could do nothing as well. In the Bismarck the crew was exhausted and men were falling asleep at their posts. It was under these conditions that at 0840/27 two British battleships were seen to approach from the westward.
Situation before the action, 27 May 1941.
A north-westerly gale was blowing when dawn broke with a good light and clear horizon to the north-eastward. Reports received during the night indicated that, despite reduced speed and damaged rudders, Bismarck's armament was functioning effectively. Given the weather conditions the Commander-in-Chief decided to approach on a west-north-westerly bearing and, if the enemy continued his northerly course, to deploy to the southward on opposite course at a range of about 15000 yards. Further action was to be dictated by events.
Between 0600 and 0700 hours a series of enemy reports from HMS Maori which was herself located by DF bearings. This enabled HMS King George V to plot her position relatively to the Bismarck which had apparently settled down on a course of 330° at 10 knots. At 0708/27, HMS Rodney, was ordered to keep station 010° from the flagship. HMS Norfolk came in sight to the eastward at 0820/27 and provided a visual link between the Commander-in-Chief and the enemy. After the line of approach had been adjusted by two alterations of course, the Bismarck was sighted at 0843/27 bearing 118°, range about 25000 yards. Both British battleships was then steering 110° almost directly towards the enemy in line abreast formation, 8 cables apart.
Commencement of action 0847/27.
HMS Rodney opened fire at 0847/27, her first salvo sending a column of water 150 feet into the air. HMS King George V opened fire one minute later. Bismarck opened fire at 0850 hours after turning to open up A arcs. The first German salvo was short. The third and fourth salvoes straddled and nearly hit, but the Rodney manoeuvered succesfully to avoid them and the nearest fell 20 yards short. At 0854/27, HMS Norfolk joined in, but the target was not clearly visible and she opened fire without obtaining a range.
Observers state that the German gunnery was accurate at first, but commenced to deteriorate after 8 to 10 salvoes. The first hit on the Bismarck was believed to be scored by the Rodney at 0854 hours with her third salvo. Both British battleships made small alterations of course away from the enemy shortly after opening fire, the King George V to increase her distance from the Rodney and the latter to open her A arcs. From then onwards they manoeuvered independently although HMS Rodney conformed to the Flagship's general movements. The Bismarck's secondary armament came into action during this phase. HMS Rodney opened fire with her secondary armament at 0858 hours.
Run to the southward.
HMS King George V deployed to the southward at 0859/27 when the Bismarck was 16000 yards distant. HMS Rodney, 2.5 nautical miles to the northward, followed suit a minute or two later. Cordite smoke was hanging badly with the following wind and spotting was most difficult. Considerable smoke interference was therefore experienced on the southerly course which was partly overcome by radar. The Bismarck had transferred her fire to the King George V shortly after the turn but except for an occasional splash the latter hardly knew that she was under fire. At 0902/27, HMS Rodney saw a 16” shell hit the Bismarck on the upper deck forward, apparently putting the forward turrets out of action. At 0904 hours, HMS Dorsetshire joined in the firing from the eastwards from a range of 20000 yards but observation of the target was difficult and she had to check fire from 0913 to 0920 hours. Between 0910 and 0915 hours the range in King George V was more or less steady at 12000 yards.
The fate of the Bismarck was decided during this phase of the action although she did not sink until later. Around 0912 hours, the Bismarck was hit on her forward control position. During the run to the south HMS Rodney fired six torpedoes from 11000 yards and HMS Norfolk four from 16000 yards. No hits were obtained. The King George V’s secondary battery came into action at 0905 hours but this increased the smoke interference and was accordingly ordered to cease fire after two or three minutes.
Run to the northward.
At 0916/27 the Bismarck’s bearing was drawing rapidly aft and HMS Rodney turned 16 points to close and head her off. The King George V followed a minute or so later and both ships re-opened fire at ranges from 8600 and 12000 yards respectively. The Bismarck shifted her target to the Rodney about this time. A near miss damaged the sluice of her starboard torpedo tube. Most of the enemy’s guns had however been silenced at this time. Only one turret from her main armament was firing at this time as was part of her secondary armament. A fire was blazing amidships and she had a heavy list to port. During the run to the north HMS Rodney obtained a very favourable position on the Bismarck’s bow from which she poured in a heavy fire from close range. She also fired two torpedoes from 7500 yards but no hits were obtained.
HMS King George V’s position, further to leeward, was less favourable. Her view was obscured by smoke and splashes surrounding the target and her radar had temporarily broken down. Mechanical failures in the 14” turrets constituted, however, a more serious handicap at this stage. ‘A’, ‘X’ and ‘Y’ turrets were out of action for 30, 7 and a unspecified short period, respectively. This resulted in reduction of firepower of 80% for 7 minutes and 40% for 23 minutes which might have had serious effects under less favourable conditions. There were also several defects of individual guns in addition to those effecting the turrets.
At 0925/27, HMS King George V, altered outwards to 150° and reduced speed to avoid getting too far ahead of the Bismarck. She closed in again at 1005 hours, fired several salvoes from a range of only 3000 yards and then resumed her northerly course. Meanwhile HMS Rodney was zigzagging across the Bismarck’s line of advance at a range of about 4000 yards firing her main and secondary armaments. She also fired four torpedoes, one of which is thought to have hit. By 1015 hours the Bismarck was no more than a wreck. All her guns were silenced, her mast had been blown away, she was a black ruin, pouring high into the air a great cloud of smoke and flame. Men were seen jumping overboard at this time and the Captain of the King George V later remarked had he known it he would have ceased fire.
End of the action.
The Commander-in-Chief was confident that the enemy could never get back to harbour, and as both battleships were running short of fuel and as further gunfire was unlikely to hasten the Bismarck’s end, the Commander-in-Chief signalled the King George V and Rodney to steer 027° at 1015/27 in order to break off the action and return to base. At 1036/27 the Commander-in-Chief ordered HMS Dorsetshire to use her torpedoes, if she had any, on the enemy. In the meantime HMS Norfolk had been closing the target but due to the movements of the King George V and Rodney, had not fired her torpedoes until 1010 hours when she fired four torpedoes from 4000 yards and two possible hits were reported. The Dorsetshire was then approaching a mile or so to the southward, and anticipating the Commander-in-Chief’s signal at 1025 hours fired two torpedoes from 3600 yards into the enemy’s starboard side. She then steamed round the Bismarck’s bow and at 1036 hours fired another torpedo but now into her port side from 2600 yards. This was the final blow, the Bismarck heeled over quickly to port and commenced to sink by the stern. The hull turned over keel up and disappeared beneath the waves at 1040/27.
The Dorsetshire then closed and signalled to one of HMS Ark Royal’s aircraft to carry out a close A/S patrol while she was to pick up survivors assisted by HMS Maori. After 110 men had been picked up by both ships from the water both ships got underway again as a submarine was suspected to be in the area.
Damage to the Bismarck.
Survivors have told the story of terrible damage inflicted on her. The fore turrets seem to have been knocked out at 0902 hours. The fore control position was knocked out around 0912 hours. The after control position followed about 0915 hours. The after turrets were at that moment still in action. Then the aftermost gun turret was disabled by a direct hit on the left gun which burst sending a flash right through the turret. ‘C’ turret was the last one in action.
One survivor stated that around 0930 hours a shell penetrated the turbine room and another one entered a boiler room. A hit in the after dressing station killed all the medical staff and wounded that were in there at that moment. The upper deck was crowded with killed and wounded men and the seas surging in washed them overboard. Conditions below were even more terrible. Hatches and doors were jammed by concussion and blocked with wreckage. The air was thick with smoke and even more smoke was coming in from great holes in the upper deck. By 1000 hours all heavy guns were out of action and 10 minutes later the all secondary guns were also silent.
Commander-in-Chief returns.
As HMS King George V and HMS Rodney turned northwards they were joined by HMS Cossack, HMS Sikh and HMS Zulu at by 1600/28 more detroyers had joined the screen (HMS Maori, HMS Jupiter, HMS Somali, HMS Eskimo, HMS Punjabi, HMAS Nestor, HMS Inglefield, HMS Lance, HMS Vanquisher (Cdr. N.V. Dickinson, DSC, RN), HMCS St. Clair (Lt.Cdr. D.C. Wallace, RCNR), HMCS Columbia (Lt.Cdr. (Retd.) S.W. Davis, RN) and HMS Ripley (Lt.Cdr. J.A. Agnew, RN). Heavy air attacks were expected that day, but only four enemy aircraft appeared, one of which bombed the screen while another one jettisoned her bombs on being attacked by a Blenheim fighter. The destroyers HMS Mashona and HMS Tartar, 100 nautical miles to the southward, were not so furtunate. They were attacked in position 52°58’N, 11°36’W at 0955/28 by German aircraft. HMS Mashona was hit and sank at noon with the loss of 1 officer and 45 men. The Commander-in-Chief reached Loch Ewe at 1230/29. Vice-Admiral Somerville with Force H was on his way back to Gibraltar. HMS Renown, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Sheffield made rendezvous at 0800/29 with the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) and HMS Wishart (Cdr. E.T. Cooper, RN). At 1605/29, HMS Forester and HMS Fury were detached to hunt a submarine further to the west. Force H, minus the two destroyers that had been detached, arrived at Gibraltar around 2030/29.
End of ‘Operation Rheinübung’.
The Bismarck’s consort, heavy cruiser Prinz Eugen, was not heard off until 4 June 1941 when aircraft reported her having arrived at Brest. After leaving the Bismarck at 1914/24, the Prinz Eugen’s primary need was to replenish her fuel stock. She set course for a rendez-vous with two tankers, the Spichern (9323 GRT, built 1935, former Norwegian Krossfonn) and the Esso Hamburg (9849 GRT, built 1939) which were position to the north-west of the Azores. All next day the German cruiser made her way southwards, and at 0906/26 , some 600 nautical miles west-north-west of the Azores she sighted the Spichern and refuelled. Two reconnaissance ships had also been ordered into this area, the Gonzenheim and the Kota Pinang. On the 28th Prinz Eugen fuelled from the Esso Hamburg. She then proceeded southwards to carry out cruiser warfare against independently routed ships in the area to the north and west of the Cape Verde Islands but an inspection of her engines the next day showed that an extensive overhaul was needed. Her Commanding Officer then decided to break off the action and course was set for Brest, France where she arrived at 2030/1 June.
A German reconnaissance ship, a supply vessel and two tankers were intercepted by Royal Navy warships and sunk by their own crew or sunk with gunfire. Also two tankers were captured. These were in chronological order; tanker Belchen (6367 GRT, built 1932, former Norwegian Sysla) by gunfire from HMS Kenya and HMS Aurora on 3 June 1941 in the Greenland area in approximate position 59°00'N, 47°00'W. On 4 June the tanker Esso Hamburg by HMS London and HMS Brilliant (Lt.Cdr. F.C. Brodrick, RN) in position 07°35'N, 31°25'W, tanker Gedania (8966 GRT, built 1920) was captured in the North Atlantic in position 43°38'N, 28°15'W by naval auxiliary (Ocean Boarding Vessel) HMS Marsdale (Lt.Cdr. D.H.F. Armstrong, RNR), she was put into service with the MOWT as Empire Garden, reconnaissance vessel Gonzenheim (4000 GRT, built 1937, former Norwegian Kongsfjord) was scuttled by her own crew after being sighted by HMS Esperance Bay ((Capt.(ret) G.S. Holden, RN) and intercepted by HMS Nelson (Capt. G.J.A. Miles, RN) and finally ordered to be boarded by HMS Neptune in position 43°29'N, 24°04'W. The next day (5 June) supply vessel Egerland (10040 GRT, built 1940) was intercepted by HMS London and HMS Brilliant in approximate position 07°00'N, 31°00'W. On 12 June, HMS Sheffield, intercepted tanker Friedrich Breme (10397 GRT, built 1936) in position 49°48'N, 22°20'W and finally on 15 June, HMS Dunedin (Capt. R.S. Lovatt, RN), captured the tanker Lothringen (10746 GRT, built 1940, former Dutch Papendrecht) in position 19°49'N, 38°30'W which had first been sighted by an aircraft from HMS Eagle (Capt. E.G.N. Rushbrooke, DSC, RN). The Lothringen was sent to Bermuda and was put into service by the MOWT as Empire Salvage. (59) 19 May 1941 Fighter aircraft to be flown off to Malta.
Around 0330A/19, ' Force H ', made up of the battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN), light cruiser HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN) and the destroyers HMS Harvester (Lt.Cdr. M. Thornton, DSC, RN), HMS Havelock (Cdr. E.H. Thomas, DSC, RN) and HMS Hesperus (Lt.Cdr. A.A. Tait, RN) departed Gibraltar to the westward.
At 1500A/19, the aircraft carrier HMS Furious (Capt. A.G. Talbot, DSO, RN), heavy cruiser HMS London (Capt. R.M. Servaes, CBE, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Foxhound (Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN) and HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) departed Gibraltar to the westward to make rendezvous with ' Force H '.
At 1445A/19, ' Force H ' had altered course to the eastward to pass through position 35°40'N, 07°05'W at 1900A/19.
At 1920A/19, HMS Furious, HMS London and the four destroyers were sighted. HMS London, HMS Harvester and HMS Havelock were then detached to briefly provide cover for the dummy battleship HMS Centurion (resembling HMS Anson, King George V-class, Lt.Cdr.(Retd.) R.W.J. Martin, RN) which had departed Gibraltar for Freetown. HMS London, HMS Harvester and HMS Havelock returned to Gibraltar around 2300A/20.
At 2130A/19, the destroyer HMS Brilliant (Lt.Cdr. F.C. Brodrick, RN) departed Gibraltar to the eastward to make rendezvous with ' Force H ' after dawn.
At 2245A/19, ' Force H ' entered the Straits of Gibraltar. It was a bright starlit night and it was thought to be almost impossible to pass the Straits without being observed by fishing vessels.
At 0720B/20, HMS Brilliant joined ' Force H '. A section of fighters was kept ranged in HMS Ark Royal to be flown off if shadowers appeared.
An aircraft was detected by RDF at 1128B/20 passing along the African coast from west to east. It did not approach neared than 38 miles, a distance greater than existing visibility, and finally faded from the screen at a range of 48 miles.
At 1215B/20, when 70 miles north fo Oran, ' Force H ' passed through a very straggling and unescorted northbound Vichy French convoy. Given the loose formation of this convoy there was no way of avoiding detection but no ships were heard making a report though.
At 1350B/20, an aircraft was detected by RDF passing rapidly down the port beam of ' Force H ' at a range of ten miles and was held between bearings of 020° and 220°. The aircraft was nog sighted. As a precauteionary measure course was altered towards Ibiza.
At 1515B/20, a favourable weather report was received from the Naval Officer in Charge, Malta. This indicated that a westerly wind of not less than ten miles per hour might be expected and HMS Ark Royal reported that a flying off position of 06°00'E would be acceptavle. Speed was then reduced to 20 knots.
Further favourable weather reports from the Naval Officer in Charge, Malta were received at 2000B/20 as also from the Vice-Admiral Commanding North Atlantic Station at 1520B/20.
Three groups of aircraft were detected at 2135B/20, 18 miles to the southward, steering 080° at 160 knots. It was thought that these aircraft were Wellingtons proceeding from Gibraltar to Malta.
At 2215B/20, course was altered to 097° and speed increased to 22 knots so as to arrive in appoximate position 37°50'N, 06°00'E at dawn the following morning for flying off the fighters to Malta. Visibility inceased to 14 miles in the evening. There was so far no indication that ' Force H ' had been reported by aircraft or shipping.
At 2300B/20, when in position 38°05'N, 03°10'E, three lighted merchant vessels were sighted to the southward steering approximately 225°.
At 0200B/21, when in position 37°56'N, 04°29'E, a lighted merchant ship passed ahead of ' Force H ' northbound, evidently from Bougie. Weather reports indicating westerly winds of 10 miles an hour or over were received from the Naval Officer in Charge, Malta at 0200B/21 and 0430B/21, and from the Vice-Admiral Commanding North Atlantic Station at 0330B/21. Information was also received from the Naval Officer in Command, Malta that only two Glenn-Martin bombers would be available to guide the first two flights of Hurricanes in.
At 0535B/21, an all-round screen was formed and 15 minutes later, course was altered to 300° into the wind for flying-off. The first aircraft took off at 0600B/21 in position 37°47'N, 06°08'E. The Fulmar flown off by HMS Furious to lead the first flight of Hurricanes was unable to retract its undercarriage. The stand-by Fulmar was then flown-off by HMS Furious at 0617B/21 as a relief. However the Hurricanes had already formed up on the defective aircraft and the Hurricanes could not be persuaded to follow the relief aircraft so finally both Fulmars went off in company, each leading a portion of the Hurricane flight.
The complete flying-off programme was as follows;
0600 - First Hurricane flew off from HMS Furious.
0605 - First Hurricane flew off from HMS Ark Royal..
0608 - First flight of 9 Hurricanes from HMS Furious was airborne.
0610 - First flight of 11 Hurricane from HMS Ark Royal was airborne.
0635 - Second flight of 10 Hurricanes was airborne from HMS Ark Royal.
0650 - Second flight of 9 Hurricanes from HMS Furious was airborne.
0729 - Third flight of 9 Hurricanes from HMS Furious was airborne.
The Hurricanes took off very well, the take-off distance being between 300 feet and 380 feet with a wind speed of 30 knots over the deck and with auxiliary tanks full.
When all Hurricanes had left HMS Ark Royal flew off a section of two Fulmars to patrol over the fleet and transferred a Fulmar crew by Swordfish to HMS Furious, who had four Fulmars on board wit only three trained crews. Each of the carriers then ranged four Fulmars on deck.
At 0750B/21, HMS Ark Royal's second flight returned and the escorting Fulmar made an emergency landing due to heavy oil leakage. It was decided that HMS Ark Royal was to fly off another Fulmar instead and at 0815B/21, the Hurricanes departed for Malta again now with their new leader.
An Italian signal was intercepted at 0824B/21, reporting that 9 aircraft had been sighted at 0750 hours steering 150°. At 0900B/21, a Cant floatplane was sighed low down 10 miles to the southward, shadowing the fleet which was then retiring to the westward. HMS Renown fired a few salvoes of 4.5" to indicate the enemy to the Fulmars, but these were unable to intercept. At 0930 hours and Italian signal was intercepted revealing the correct composition of ' Force H '. These two sightings must have revealed the whole operation to the enemy.
At 0940B/21, HMS Ark Royal flew off a second section of Fulmars. The visibility was 20 miles from 2000 feet at 15 miles from 1000 feet, with cloud base at this height.
Information was received from the Naval Officer in Charge, Malta at 1015B/21 that the first formation had landed and the second was in sight. This was followed at 1100B/21 by a report that the fourth formation had landed and that the fifth was approaching. Information of the delayed third flight was not received until 1400B/21 when the Naval Officer in Charge, Malta reported that 5 Fulmars and 47 Hurricanes had arrived, and that one Hurricane had been seen to dive into the sea off Cape Bon. One Fulmar was therefore missing and the Naval Officer in Charge Malta was informed accordingly. Weather conditions for the flight had been favourable, the average wind at 2000 feet being 15 miles an hour from the north-west. Visibility had been 10 to 15 miles.
A further Italian signal was intercepted at 1230B/21 indicating that ' Force H ' had been reported at 1100 hours. At 1310B/21, a formation of aircraft was sighted low down 15 miles to the southward on an easterly course. These were probably Blenheims on passage from Gibraltar to Malta. At 1320B/21, a single aircraft, probably a Vichy-French plane bound for Algiers, was detected by RDF bearing 345°, distant 26 miles.
Information was received from the Vice-Admiral Commanding North Atlantic Station at 1321B/21 that an SOS had been heard from one of the Blenheims en-route for Malta and that its estimated position was approximately 02°00'E and 04°00'E. Four TSR aircraft were at once flown off from position 37°57'N, 02°56'E to carry out a search over the area indicated. The visibility was 40 miles to the north and east but rain persisted to the southward with visibility down to half a mile. These aircraft landed on at 1800B/21 having sighted nothing.
At 1855B/21, the A/S patrol reported a dinghy with one occupant bearing 290°, distant 12 miles from ' Force H ' (37°22'N, 01°13'E). HMS Hesperus was detached and picked up one officer, which was the navigator of the aircraft that had sent out the SOS.
At 0045B/22, course was altered briefly to avoid a merchant vessel steering approximately 300°.
At 0530B/22, HMS Ark Royal flew off seven Swordfish to carry out exercises with ' Force H '.
At 0544B/22, a signal was received from the Naval Officer in Command, Malta that the destroyer HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN) had departed from there for Gibraltar at 2030B/21 and that her estimated time of arrival at Gibraltar was 1600A/23.
HMS Furious, escorted by HMS Brilliant and HMS Hesperus, was detached at 0800B/22 to proceed at best speed towards Gibraltar for a quick docking. They arrived at Gibraltar around 1215A/22.
During the forenoon more exercises were carried out by ' Force H '.
At 1038A/22, an intercepted Italian signal indicated that HMS Foresight was being shadowed by enemy aircraft. Her estimated position was midway between Galita Island and Bougie. ' Force H ' therefore altered course to the west to close and instructed HMS Foresight to report immediately in case she was being attacked by enemy bombers and the result of such attacks.
No report had been received from HMS Foresight by 1600A/22 and as it was though that by now she would be (almost) out of range of enemy bombers, ' Force H ' revised course to the west and increased speed to 25 knots.
' Force H ' arrived at Gibraltar around 2245A/22. (60) 24 May 1941 At 0800A/25, the destroyers parted company.
[For more information see the events ' Chase and sinking of the German battleship Bismarck,
18 to 27 May 1941, Part I and Part II ' both for 18 May 1941.] (60) 29 May 1941 5 Jun 1941 Fighter aircraft to be flown off to Malta.
At 1030A/5, the light cruiser HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN) departed Gibraltar to the eastwards to serve as target for the defences of Gibraltar.
Around 1200A/5, the remainder of ' Force H ', made up of the battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carriers HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN), HMS Furious (Capt. A.G. Talbot, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN (Capt. D.8)), HMS Fearless (Cdr. A.F. Pugsley, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Foxhound (Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN) and HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) also departed Gibraltar and proceeded eastwards where they were joined by HMS Sheffield. During the afternoon some exercises were carried out while on passage eastwards.
The weather was fine and calm, with fair visibility. At 1742A/5 an aircraft was detected by RDF, bearing 190°, distant 11 miles. Eight minutes later it was sighted bearing 180°, apparently shadowing ' Force H '. The aircraft was thought to be Vichy-French.
At 1810A/5, a Catalina, which was carrying out an A/S patrol ahead of ' Force H ' sighted an object which might have been the conning tower of a submarine some 15 miles to the southward. She closed to investigate but saw nothing further. Whilst rejoining she was followed in by an unidentified aircraft which shadowed ' Force H ' from 1915A/5 to 1945A/5. This aircraft was aloso thought to be Vichy-French. At 2115A/5 a lighted merchant vessel was passed on opposite courses.
At dawn on 6 June the weather was fair, with a calm sea, clear sky, fair visibility, and a north-easterly wind, force 2. A favourable weather report was received from Malta at 0640A/6, which indicated a northwesterly wind from 10 to 27 miles an hour in the Malta area. Information was received at 0855A/6 that the first pair of Blenheim aircraft detailed to lead the Hurricanes to Malta had left Gibraltar at 0715A/6 and should arrive at the flying off position at 1015A/6.
At 0900A/6, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Sheffield, HMS Fearless and HMS Fury were detached to act independently to the southward of the other ships.
At 0930A/6, the first Blenheims was detected by RDF bearing 255°, distant 22 miles from HMS Sheffield. Eight minutes later it commenced to circle HMS Ark Royal. This was half an our earlier then expected. HMS Ark Royal at once started up her Hurricanes and worked up to speed for flying off.
The first Hurricane took off at 0958A/6 and the whole flight of twelve was airborne by 1004A/6. As this flight took its departure at 1013A/6, second Blenheim of the first pair arrived and circled HMS Furious which then flew off her first Hurricane at 1024 and the last of the first flight of ten at 1028A/6 at which time the second pair of Blenheims was seen approaching. Four minutes later the first flight of HMS Furious took its departure.
Position where the aircraft were launched was approximately 37°25'N, 03°26'E.
At 1041A/6, a Blenheim was one again circling each carrier. At 1049A/6 the first Hurricane of Ark Royal's second flight took off, followed two minutes later by the first one of the second flight of HMS Furious. The twelfth and last from Ark Royal's second flight took off at 1054A/6 and the tenth and last from Furious at 1055A/6. At 1100A/6 both these flights took their departure.
At 1108A/6, the two remaining Blenheims (spare) arrived and one Hurricane from Ark Royal's second flight returned with engine trouble. The Blenheims were ordered to proceed to Malta while the Hurricane landed on HMS Furious. HMS Ark Royal meanwhile flew of a fighter patrol of two Fulmars.
Course was altered to 260° at 1130A/6 and withdrawal to the eastward was made at 24 knots. Each carrier kept a section of fighters ranged.
At 1255A/6 RDF detected an aircraft bearing 070° distant 31 miles. Touch was lost at 1303A/6. Two minutes later this aircraft was seen bearing 120° and was thought to be a Vichy-French aircraft bound for Algiers.
The fighter patrol was landed on at 1330A/6 and an A/S patrol was flown off. Another aircraft was detected by RDF at 1455A/6, 18 miles to the south-eastward. Contact was lost after ten minutes.
A signal was received from Malta at 1852A/6 stating that 43 Hurricanes and 8 Blenheims had arrived safely at Malta.
At 1930A/6, the A/S patrol reported a Vichy-French merchant vessel bearing 245° distant 30 miles from HMS Renown steering 020° at 8 knots. No action was taken in regard to this ship.
At 2030A/6, information was received that the Vichy-French battlecruiser Dunkerque had left Mers-el-Kebir. At 2100A/6, one aircraft was then flown off to carry out a reconnaissance of the port by moonlight. This aircraft returned at 2230A/6 reporting the the Dunkerque was still in her usual berth at Mers-el-Kebir. This information was passed on to the Admiralty and the Vice-Admiral Commanding North Atlantic Station.
Having passed to the southward of Alboran Island, course was altered to 275° at 0200A/7 and HMS Ark Royal flew off ten Fulmars to land at Gibraltar to afford protection to the Fortress in case of bombing attack.
At 0730A/7 an exercise was started with the shore defences at Gibraltar. ' Force H ' entered harbour at 0845A/7. (60) 7 Jun 1941 At 2230A/7, ' Force H ', made up of HMS Renown (Capt. R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN), HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN), HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN (Capt. D.8)), HMS Fearless (Cdr. A.F. Pugsley, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Foxhound (Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN) and HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) departed Gibraltar to the westward to be clear of the harbour as Vichy-French reprisals (air attacks) were expected after the start of the Syrian campaign. The aircraft carrier HMS Furious (Capt. A.G. Talbot, DSO, RN) was also with ' Force H '. Also rendezvous was to be made with the aircraft carrier HMS Victorious (Capt. H.C. Bovell, RN) coming from the UK.
A speed of 17 knots was maintained, with the object of economising fuel in the destroyers and of ensuring efficient Asdic operating.
HMS Victorious was ordered to remain outside the submarine danger area and to pass through position 37°05'N, 13°48'W, at 0700A/9 steering 155° making good 16 knots.
Two outer and one inner A/S patrols were flown off at dawn on the 8th and maintained throughout the day. During the day a westerly wind enabled HMS Ark Royal to carry out deck landing training from inside the screen and full advantage was taken of this.
At 1800A/8, when in position 35°10'N, 11°08'W, a signal was received from a Catalina that she had unsuccessfully attacked a submarine at 1615A/8 in position 35°50'N, 13°00'W. Two relief A/S patrols were being ranged at tis time and these were flown off to search for and attack this submarine if she surfaced after the Catalina's attack. At 1845A/8 the Catalina, who returned to base after the attack, signalled that the submarine dived in position 36°02'N, 11°50'W. This latter position was based on a fix obtained at 1800A/8, presumably from the land and was some 60 miles further eastward then initially reported. The A/S striking force landed on at 1925 having sighted northing.
The submarine attacked was the Italian Velella. The bombs were close but caused no damage.
At 2030A/8, ' HMS Force H ' entered a patch of very low visibility which lased for about an hour. Course was altered to 330° at 2200A/8 when in position 35°00'N, 12°21'W to make rendzvous with HMS Victorious at dawn.
Throughout the day HMS Sheffield kept RDF watch, and fighters were kept at short notice in both HMS Furious and HMS Ark Royal in case Vichy-French aircraft should take offensive action. No aircraft were seen or detected.
At 0600A/9 HMS Ark Royal flew off two outer and one inner A/S patrol with instructions to locate HMS Victorious. At 0630A/9 one of these aircraft reported HMS Victorious to the northward and course was altered to close. HMS Victorous, screened by HMS Vansittart (Lt.Cdr. R.L.S. Gaisford, RN), HMS Wild Swan (Lt.Cdr. C.E.L. Sclater, RN), HMS Wivern (Cdr. M.D.C. Meyrick, RN) and HMS Wrestler (Lt. E.L. Jones, DSC, RN) was sighted at 0650A/9 and HMS Furious, HMS Sheffield and HMS Fury were detached to join her and form ' Group II '. The remaining ships of ' Force H ' formed ' Group I '.
HMS Victorious then transferred 5 Fulmars to HMS Ark Royal who flew off 6 Swordfish to ferry the Hurricane erecting personnel from HMS Furious to HMS Victorious.
HMS Wivern, who was short of fuel and had a leaking fuel tank was detached at 1030A/9 to return to Gibraltar.
The transfer of 75 members of the Hurricane ercting party was completed by noon under somewhat unfavourable weather conditions. HMS Furious, escorted by HMS Sheffield, was detached to overtake and rendezvous with HMS Argus (Capt. T.O. Bulteel, RN) in position 47°00'N, 24°00'W, at 1200A/11. HMS Sheffield was ordered to part company from HMS Furious in latitude 45°N and patrol an area between that latitue and 44°N, and between longitudes 23°W and 25°W, till dusk on the 14th with the object of intercepting enemy shipping. She was also with convoy SL 76 between 1130Z/14 and 2200Z/16.
Around noon, HMS Vansittart, HMS Wild Swan and HMS Wrestler were detached to return to Gibraltar.
HMS Renown, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Victorious screened by the six 'F'-class destroyers, steered to the south-west at 16 knots, to keep clear of the submarine concentration to the eastward. At 1500A/9, HMS Ark Royal flew off a reconnaissance of six aircraft from position 37°06'N, 15°06'W, to search from 130° through south to 310° to a depth of 80 miles to locate enemy shipping and submarines. These aircraft landed on at 1730A/9 having sighted nothing.
At 0100A/10, Admiralty's instructions were received that the next ferry trip of fighter aircraft to Malta was to be carried out as soon as possible. Course was therefore altered to 090° and speed increased to 20 knots and an hour later to 26 knots. Two out and one inner A/S patrols were flown off at dawn.
At 0750A/10 one of the outer A/S patrols flying at 800 feet sighted a submarine breaking surface heading south-west about 1500 yards distant. The aircraft attacked and dropped a stick of 6 100lb. A/S bombs from a height of 150 feet. All bombs missed over and failed to explode, the low height being insufficient for aiming. The submarine was submerged by the time the bombs were released. This incident occurred in position 35°31'N, 14°12'W. On receipt of the W/T report from the aircraft the course of the Fleet was altered to clear. This was probably the Italian submarine Veniero which was operating in the area but did not report being attacked though although she did report sighting an aircraft at 0850A/10 (Rome time) an also at 1050A/10 (Rome time) during which he dived.
At 1000A/10, information was received that ' Force H ' had been sighted at 0038 by an enemy submarine.
At 1610A/10, four corvettes were sighted in position 35°50'N, 10°30'W, carrying out an A/S sweep in conjunction with five ML's who were working 30 miles to the southward.
' Force H ' arrived in Gibraltar Bay at 0330A/11 and then entered harbour. (60) 13 Jun 1941 Fighter aircraft to be flown off to Malta.
' Force H ', comprising HMS Renown (Capt. R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN), HMS Victorious (Capt. H.C. Bovell, RN), HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN (Capt. D.8)), HMS Fearless (Cdr. A.F. Pugsley, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Foxhound (Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN), HMS Hesperus (Lt.Cdr. A.A. Tait, RN) and HMS Wishart (Cdr. E.T. Cooper, RN), sailed from Gibraltar at 1130A/13, shaping course to the eastward on co course 075° at 21 knots. In the afternoon some exercises were carried out.
Before leaving harbour a favourable weather report was received from Vice-Admiral, Malta, indicating fair weather and westerly winds. A further report was received at 2030A/13, indicating fair weather with a light south-easterly surfce wind but westerly above 5000 feet. As the weather forecast by HMS Renown indicated that easterly winds were anticipated in the vicinity of the flying off position, speed was increased to 23 knots at 1930A/13 to allow the flying off position to be transferred to the eastward should this to be found necessary. Course 057° was shaped from 2000A/13.
A weather report received from the Vice-Admiral Commanding, North Atlantic Station, at 0440A/14 forcast thundery conditions and westerly winds in the vicinity of the Balearics and Sardinia with light variable winds along the North African coast. Vice-Admiral, Malta's report received at 0620A/14 continued to forecast westerly winds in the vicinity of Malta. Vice-Admiral Somerville decided that it was not needed to proceed further to the east than had been planned and speed was accordingly reduced to 17 knots at 0620A/14. At this time there was a light easterly wind and slight sea. The sky was completely overcast and the visibility moderate and variable.
HMS Ark Royal, screerned by three of the destroyers, was detached at 0900A/14 to operate independently 5 miles to the southward of HMS Renown, HMS Victorious and the remaining destroyers. During the approach of the Hudsons, HMS Victorious obtained several rangs and bearings by RDF but these were inconsistent and very variable. It became evident during the operation that owing to the inexperience and possible defective apparatus the accuracy and reliability of Victorious' RDF fell far short of the standard of efficiency reached by HMS Sheffield.
The first three Hudsons left Gibraltar at 0652A/14. They were detected by the RDF of HMS Victorious bearing 258°, range 80 miles at 0946A/14. They were sighted at 1030A/14. Course was then altered to 080° into the wind and speed was increased to 25 knots. The first Hurricane left HMS Victorious at 1045A/14 followed two minutes later by the first one from HMS Ark Royal. The last one left each ship at 1050A/14 and 1054A/14 respectively taking final departure shortly afterwards (1056A/14 and 1058A/14). One of the Hurricanes from HMS Victorious left with its undercarriage down.
The second flight of Hudsons which left Gibraltar at 0723A/14 was sighted at 1121A/14. One Hurricane in HMS Victorious was defective and was not ranged. The first aircraft took off from HMS Victorious at 1131A/14 and from HMS Ark Royal at 1133A/14. The last aircraft of the second flight took off at 1134A/14 and 1138A/14 respectively. Both flights took their deparure at 1141A/14. The two reserve Hudsons were ordered to return to Gibraltar.
The mean position for flying off was 38°56'N, 03°00'E appoximately 20 miles east of the position originally intended.
At 1140A/14, course was altered to 220° HMS Ark Royal and her three escorting destroyers rejoined the other ships and speed was increased to 25 knots. HMS Ark Royal flew off a section of fighters and HMS Victorious and A/S patrol. Course was altered to 246° to pass north of Alboran Island. The fighters were landed on at 1815A/14 and the A/S patrol at 2030A/14.
Information was received from the Admiralty that ' Force H ' had been reported leaving Gibraltar, probably to supply aircraft to Malta. No enemy aircraft had so far been detected and no enemy reports were intercepted.
A signal was received from the Vice-Admiral, Malta, at 1542A/14 that the first flight had arrived safely and the the second flight was in sight. No further information was received until 1742A/14 when it was reported that a total of 35 Hurricanes and 3 Hudsons had arrived. Later this was amended to 43 Hurricanes and 4 Hudsons. One Hurricane was seen to make for the North African coast, one was seen to crash into the sea of Malta, the pilot being saved, and two which crashed on landing, the pilot of one being killed.
An A/S patrol was flown off at 0530A/15, being relieved by a Catalina from Gibraltar at 0800A/15. Four Fulmars were flown off to land at North Front. On approaching the Roch a range and inclination exercises was carried out for the benfit of the shore defences. Before entering harbour at 1030A/15 both carriers ranges all available aircraft on deck with the object of suggesting to enemy observeers that no aircraft had been flown off. (60) 15 Jun 1941 On departure from Gibraltar all available aircraft were ranged on deck in both carriers to mislead enemy observers. Course was shaped to the eastward at 18 knots.
At 2010/15, HMS Victorious transferred two Fulmars to HMS Ark Royal and flew off to North Front five Fulmars and one Hurricane. This was the Hurricane that had been unable to fly to Malta during operation Tracer. Some AA gunnery exercises were carried out during the evening.
Course was altered to the westward at 2050/15 and the force passed through the Straits under cover of darkness.
At 0200/16, Vice-Admiral Somerville was informed that two unidentified ships had been sighted by aircraft leaving Brest at 2100/15. Shortly afterwards he was instructed to act on the assumption that these were warships. Course was about to be altered to reach a favourable position for a reconnaissance when information was received that photographs had identified the two ships as merchant vessels.
Course was adjusted to pass 25 miles to the northward of convoy OG 64 in order to provide A/S protection for the convoy which was probably being shadowed by an enemy submarine. Visibility from 1000 feet was only 6 miles and reconnaissances flown off at 1420/16 from position 35°50'N, 09°36'W and at 1740/16 from position 35°57'N, 10°24'W both failed to locate the convoy.
During the day the wind was easterly involving a reversal of course for all flying operations. An A/S patrol of three aircraft was maintained from dawn till dusk and HMS Victorious tansferred six Swordfish to HMS Ark Royal.
At 1905/16, the escort destroyers HMS Avon Vale (Lt.Cdr. P.A.R. Withers, DSO, RN), HMS Eridge (Lt.Cdr. W.F.N. Gregory-Smith, RN) and HMS Farndale (Cdr. S.H. Carlill, RN) were sighted. They were on passage to Gibraltar.
Course was altered to 304° at 2230 for the rendezvous in position 49°00'N, 29°30'W.
Fog was encountered between 0400 and 0600/17 but cleared by sunrise when an A/S patrol of three aircraft was flown off. HMS Hesperus oiled from HMS Repulse during the forenoon taking 95 tons and thereby completing to full stowage. Whilst this was in progress HMS Faulknor obtained an A/S contact and attacked it but it was considered non-sub.
HMS Ark Royal flew off a reconnaissance of six aircraft from position 38°16'N, 15°32'W at 1130/17 to search to a depth of 70 miles from 215° through north to 035°. These aircraft sighted nothing more than a school of 13 whales. Visibility was reported as 8 miles.
The five 'F-class' destroyers were detached at 1140/16 in position 38°22'N, 15°22'W to return to Gibraltar.
A reconnassance of six aircraft took off at 1700/17 in position 39°20'N, 17°20'W and searched from 215° through north to 035° to a depth of 70 miles in visibility 17 miles. They sighted a Portugese ship who was circling round a large red buoy in position 40°30'N, 17°16'W at 1753/17.
Throughout the day there was a northerly wind force 3-4, and flying operations could be taken without large alterations fom the mean line of advance. All fighters and newly joined observers in HMS Ark Royal received training and 21 pilots made a total of 35 training flights.
At midnight speed was increased to 23.5 knots. The heavy ships were zig-zagging astern of HMS Hesperus who maintained a steady course at 22 knots.
At 0200/18, information was received that the latest intelligence of enemy submarines indicated the safest route for ' Force H ' lay through position 45°00'N, 18°00'W to 51°00'N, 20°00'W. Course was therefore altered to 025°.
At 0440 HMS Victorious reported reception of strong RDF transmissions from right ahead. Course was altered to 340° till daylight, when 035° was steered for the rendezvous. Subsequent investigation suggested that the transmissions heard by HMS Victorious was caused by the ASV gear in HMS Hesperus.
A very welcome signal was intercepted at 1130/18 stating that the five 'F-class' destroyers returning to Gibraltar had sunk a German submarine (this was U-138).
A reconnaissance of six aircraft was flown off at 0930/18 from position 43°31'N, 19°29'W. They returned at 1130/18 having searched to a depth of 65 miles from 305° trough north to 035°. The visibility had been around 17 miles. They had sighted nothing.
At 1510 the inner A/S patrol dropped depth charges on a coloured patch of water in position 45°15'N, 18°03'W. HMS Hesperus was ordered to investigate but no contact was obtained. On passing through the patch she fired a pattern of depth charges, mainly to provide an opportunity to exercise rapid reloading.
Throughout the day the wind was northerly, force 4. Some exercises were carried out throughout the day.
The evening reconnaissance was carried out by six Fulmars. They took off at 1735/18 in position 45°45'N, 18°15'W and searched to a depth of 65 miles from 257° through north to 077°. Visibility was reported as being 20 miles. They sighted nothing.
The final A/S patrol landed on at dusk just after midnight.
At 0710/19 six aircraft flew off in position 50°06'N, 19°47'W, to search from 257° through north to 077° wth instructions to inform Captain (D), 4th Destroyer Flotilla, of Renown's position, course and speed. The visibility from the air was only 8 miles and the reconnaissance flew to a depth of 75 miles. They sghte the destoyers of the 4th Destroyer Flottila and the corvettes Coreopsis and Fleur de Lys some 48 miles to the eastward returning to Gibraltar after escort duty with convoy SL 76.
HMS Cossack (Capt. E.L. Berthon, DSC and Bar, RN, (Capt. D.8)) and HMS Sikh (Cdr. G.H. Stokes, RN), joined at 0900/19 in position 50°04'N, 19°45'W. At 0937/19, HMS Victorious was detached for the UK, escorted by HMS Cossack, HMS Sikh and HMS Hesperus. HMS Renown and HMS Ark Royal then turned to 155°, 24 knots, to return to Gibraltar.
The wind had now conveniently shifted to the south-south-west, force 4. Various flying practices were therefore carried out including close range aiming practice at fighters simulating dive bombing attacks.
At 1800/19, a reconnaissance of nine aircraft was flown off in position 47°52'N, 18°12'W, to search from 065° though south to 245° to a depth of 95 miles. Visibility was 35 miles decreasing to 10 miles to the southward. Nothing was sighted.
Speed was decreased to 23 knots at 2000/19 owing to boiler defects in HMS Renown. The last A/S patrol landed on at 2320/19.
At 0100/20, course was altered to south and the first A/S patrol flew off at 0655/20. The wind was north-north-west, force 3. A full flying training programme was carried out, which involved a loss of advance of some 50 miles during the day.
Six Fulmars flew off at 0915/20 in position 42°45'N, 16°46'W, so search from east through south to west to a depth of 115 miles. The visibility was 30 miles to the south-west but only 10 miles to the south and south-east. The reconnaissance only sighted a Spanish merchant vessel.
The evening reconnaissance of six Swordfish flew off at 1745/20 in position 40°14'N, 16°24'W, to carry out a similar search. The aircraft penetrated to a depth of 95 miles with visibility 20 miles. The only ship sighted was a Greek one, on Swiss charter.
Clocks were put back one hour at 1830/20 to zone -1. Course was altered at 1925/20 to 1925/20. The last A/S patrol was landed on at 2200/20.
An A/S and fighter patrol were flown off at daylight and maintained during the day, the latter in case German Focke Wulf aircraft should be sighted.
HMS Faulknor, HMS Fearless, HMS Forester, HMS Foxhound and HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) joined at 0800/21 in position 36°05'N, 12°58'E. Course was then altered to 095° for Gibraltar. The wind was north-north-westerly, force 2, increasing to force 4 in the evening.
At 0930, 16 Swordfish aircraft armed with depth charges were flown off in position 36°02'N, 12°25'W, to carry out an A/S patrol sweep ahead of the fleet. Aircraft flew on tracks 8 miles apart to a depth of 115 miles but sighted nothing.
A similar sweep was flown of at 1630/21 with 14 Swordfish from position 35°57'N, 09°48'W, to a depth of 90 miles, but again nothing was sighted.
At 2005/21 speed was reduced to 18.5 knots to arrive at Gibraltar at daylight. The last A/S patrol was landed on at 2105/21.
HMS Renown enterned harbour at 0600/21 and HMS Ark Royal, screened by the five destroyers, proceeded to the eastward to carry out exercises. They entered harbour at 1000/21. (60) 26 Jun 1941Operation Tender.
Operations Dunlop and Salient.
HrMs O 21 (Lt.Cdr. J.F. van Dulm, RNN) carries out exercises off Gibraltar with HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN) and HMS Azalea (Lt. G.C. Geddes, RNR). Later exercises are carried out with aircraft from HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN). (57)Operation Tiger, supply convoy from Gibraltar to Alexandria and reinforcements for the Mediterranean Fleet and Operation MD 4, supply convoy from Alexandria to Malta and taking up the reinforcements for the Mediterranean Fleet.
Around 2000A/16, HMS Renown (Capt. R.R. McGrigor, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN, temporary flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN), HMS Wrestler (Lt. E.L. Jones, DSC, RN), HMS Fearless (Cdr. A.F. Pugsley, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN) and HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) departed Gibraltar westwards for exercises.
Chase and sinking of the German battleship Bismarck, 18 to 27 May 1941.
Chase and sinking of the German battleship Bismarck, 18 to 27 May 1941.
Operation Splice.
Around 0245A/24, ' Force H ', made up of the battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN), light cruiser HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, RN), HMS Foxhound (Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) and HMS Hesperus (Lt.Cdr. A.A. Tait, RN) departed Gibraltar for operation in the Atlantic to try to intercept the German battleship Bismarck and heavy cruiser Prinz Eugen.
Around 2030A/29, ' Force H ', HMS Renown (Capt. R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN) and HMS Sheffield (Capt. C.A.A. Larcom, RN) made rendezvous at 0800A/29 with the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) and HMS Wishart (Cdr. E.T. Cooper, RN). At 1605A/29, HMS Forester and HMS Fury were detached to hunt a submarine that had been reported further to the west. ' Force H ', minus the two destroyers that had been detached, arrived at Gibraltar around 2030A/29. (60)Operation Rocket.
Operation Tracer.
At 1800/15, ' Force H ' departed Gibraltar to the eastward. ' Force H ' was made up of the battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN (Capt. D.8)), HMS Fearless (Cdr. A.F. Pugsley, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Foxhound (Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN) and HMS Wishart (Cdr. E.T. Cooper, RN). The aircraft carrier HMS Victorious (Capt. H.C. Bovell, RN) and the destroyer HMS Hesperus (Lt.Cdr. A.A. Tait, RN) sailed with ' Force H '. These two ships were to return to the UK.
Operation Railway (phase 1).
Fighter aircraft to be flown off to Malta.
Arpund 0400A/26, the battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN), light cruiser HMS Hermione (Capt. G.N. Oliver, RN) and the destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN), HMS Lance (Lt.Cdr. R.W.F. Northcott, RN) and HMS Legion (Cdr. R.F. Jessel, RN) departed Gibraltar to proceed to the eastwards.
On board HMS Ark Royal there were 12 erected and10 unerected Hurricanes. The latter were erected during the day, the operation being completed and and all aircraft satisfactorily tested before dusk.
Speed was increased to 22 knots at 0630A/26 and course was altered to 060° at 1245A/26. One Catalina provided A/S patrol ahead of the fleet during the day and a second carried out RDF exercises with HMS Hermione.
Weather forecasts fom the Vice-Admiral Commanding, North Atlantic and Vice-Admiral, Malta, indicated that wind would probably be light but would be easterly at the lower altitudes in the vicinity of Malta and that the visibility would be moderate but not good for part of the passage. In view of this, HMS Ark Royal reported at 1420A/26 that it would be desirable but not essential, to move the flying off position 30 miles further to the eastward than planned. Vice-Admiral Somerville decided to do this and speed was accordingly increased to 24.5 knots from 1800A/28 to 2200A/28 and then reduced to 22.5 knots for the night. A signal was passed to the Catalina to inform 200 Group at Gibraltar of the change of rendezvous.
As far as is known the force was not sighted by hostile aircraft during the day. No enemy reports were intercepthed and the only suspicious RDF contact was at 1730A/26, 85 miles north of Oran, when an aircraft was detected 15 miles to the southward, waiting. After ten minutes it faded from the srceen. The visibility was moderate with a calm se and low lying haze and it is quite possible this aircraft did not sight the force.
Information was received at 0220A/27 that the first pair of Bleneims was airborne at 0140A/27 and was expected at the rendezvous at 0520A/27.
At 0300A/27, the force ran into variable patchy fog which persisted till shortly before the flying off position was reached. At 0456, HMS Hermione reported two aircraft bearing 230°, 21 miles. HMS Ark Royal was instructed to D/F these aircraft in and searchlights and black smoke were used as additional airds. The first pair of Blenheims was sighted at 0516A/27 when course was altered to 300° and speed increased to 25 knots for flying off.
The first Hurricane took off at 0526A/27, the 11th at 0531A/27, and the flight took departure at 0537A/27. One of these Hurricanes left with undercarriage down.
Course was altered to 090° at 0532A/27 and to 285° at 0558A/27. The second pair of Blenheims made contact at 0608A/27 and course was altered to 320° for flying off. The 12th Hurricane took off at 0619A/27, the 22nd at 0623A/27 and the flight took departure at 0627A/27.
The mean flying off position for the two flights was 37°34'Nm 04°55'W.
As soon as the last Hurricane had flown off course was altered to 271° and the force withdrew at 25 knots. A fighter patrol and an A/S patrol was flown off and maintained throughout the day. Course was altered to 250° at 0900A/27.
At 0950A/27, a signal was received from Vice-Admiral, Malta that the first flight was in touch, an hour later the second formation was reported in sight.
Shortly afterwards, at 1115A/27, Vice-Admiral, Malta reported that the first formation was incomplete, ad asked if any of the Hurricanes had retuned. W/T silence was broken to reply in the negative.
As no further information was received i again broke W/T silence at 1430A/27 to request a report from Malta.
Meanwhile at 1215A/27, when 56 miles north-north-west of Algiers, HMS Hermione detected an aircraft bearing 040°, 48 miles. It closed to 38 miles before fading on bearing 135°, 58 miles. This aircraft was probably bound for Algiers.
Information was eventually received from the Vice-Admiral, Malta, at 1510A/27 that all aircraft had arrived safely at Malta, but that one had crashed on landing, the pilot being safe.
Six Swordfish carried out flying exercises in the afternoon. At 1630A/27, HMS Hermione opened out on the port beam for a range and inclination exercise.
At 1700A/27, HMS Ark Royal reported that a Fulmar which was due to land on, had failed to return and that W/T communication could not be established on M/F. Attempts to D/F on R.T. failed owing to limitations of ship-intalled H/F - D/F. In order to clear the radar screen fighter and A/S patrols were ordered to circle over the fleet. HMS Hermione then located the lost aircraft 55 miles to the southwardd. The aircraft was given a course to ster and landed on successfully at 1820. It was then ascertained that the beacon was out of adjustement and the W/T set ha a defective valve.
The last fighter patol landed on at 1900A/27 and the A/S patrol at 2034A/27. There was a low haze and the surface visibility never exceeded five miles.
A speed of 25 knots was maintained till 0300A/28 when speed was reduced to 18 knots. Eight fighters and eight Swordfish were flown off at 0600A/28 for exercises. One Swordfish crashed after dropping its torpedo but the crew was picked up by HMS Lance who was acting as picking up destroyer.
' Force H' entered harbour at 0930A/28. (60)
28 Jun 1941
Operation Railway (phase 2).
Fighter aircraft to be flown off to Malta.
Around 1800A/28 hours, ' Force A', made up of the aircraft carrier HMS Furious (Capt. A.G. Talbot, DSO, RN), light cruiser HMS Hermione (Capt. G.N. Oliver, RN) and the destroyers HMS Fearless (Cdr. A.F. Pugsley, RN), HMS Foxhound (Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN), HMS Lance (Lt.Cdr. R.W.F. Northcott, RN) and HMS Legion (Cdr. R.F. Jessel, RN) departed Gibraltar to the west. This was a diversion and they turned to the east after dark.
Around 0130A/29, ' Force B ', made up of the battlecruiser HMS Renown (Capt. R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN), destroyers HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN), HMS Wishart (Cdr. E.T. Cooper, RN), and the escort destroyer HMS Avon Vale (Lt.Cdr. P.A.R. Withers, DSO, RN) departed at 0130A/29. HMS Wishart and HMS Avonvale were however soon detached to return to Gibraltar.
The two groups joined at 0700A/29 in position 36°12'N, 03°33'W. Course was altered to 061° at 1105A/29. Throughout the forenoon the weather was clear with maximum visibility but after noon visibility decreased considerably.
At 1240A/29, in position 36°30'N, 01°40'W, HMS Foxhound, on the port side of the screen, investigated a contact. The force turned away and whilst doing so HMS Forester, on the starboard side of the screen, also investigated a contact and fired a pattern of depth charges. Neither these contacts was confirmed and it is probable that vlack fish were responsible, several of these being seen in the vicinity.
No suspicious RDF contacts were reported by HMS Hermione and it is improbable that ' Force H ' had been sighted.
Weather reports received from the Vice-Admiral Commanding, North Atlantic Station and Vice-Admiral, Malta, did not necessitate any alteration in the flying off position that had been arranged. Information was received at 0230A/30 that the first formation of three Blenheims had left Gibraltar at 0220A/30 and expected to arrive at the rendezvous at 0520A/30.
Group II, consisting of HMS Furious, HMS Fearless, HMS Lance and HMS Legion, was detached at 0430A/30 to take station 5 miles to the southward of Group I consisting of HMS Renown, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Hermione and the remaining destroyers.
The first Blenheim was detected by HMS Hermione at 0515A/30 bearing 247°, 54 miles. This aircraft was sighted at 0535A/30 and Ark Royal's first flight of Hurricanes was started up.
The wind was light and sone delay ensued in finding the best course for flying off. The first Hurricane was flown off Ark Royal at 0557A/30 and the 14th at 0604A/30. The first flight took departure five minutes later.
The Blenheim detailed to lead the first flight from HMS Furious was sighted by that ship at 0605A/30. Engines were at once warmed and flying off commenced. Almost immediately a large flash and cloud of black some was seen to rise from HMS Furious, who was now some 8 miles to the southward. Course was altered to close but 5 miles later the second flight of Blenheims was sighted and it became necessary for Group I to turn into the wind to fly off the remaining 12 Hurricanes from HMS Ark Royal.
The 15th Hurricane was flown off at 0633A/30 ad the 25th at 0637A/30, the formation taking departure at 0639A/30.
The two flights from HMS Ark Royal were flown off from a mean position 38°43'N, 03°29'E. During the latter part of the operation a Vichy-French liner approached from the northward on a southerly course and probably observed the 2nd flight taking off and taking departure.
HMS Furious now reported flying completed, Groups I and II closed and withdrawal was made to the west-south-west at 25 knots. it was then ascertained that after the first Hurricane had taken off successfully from HMS Furious the second swerved when half way along the deck and hit the port navigating position. A long range tank was wrenched off and the aircraft crashed over the side. Burning petrol enveloped the port side of the bridge, the port navigating and signalling position and the look-out huts.
As the bridge was burning furiously the ship was turned out of the wind and the engines stopped. As soon as the fire was under control flying off was resumed and the fist flight was airborne by 0623A/30. The formation of nine led by the Blenheim then proceeded to Malta.
Among the personnel in the positions which caught fire wee the Headquarters flying staf, all the RAF pilots of the second flight, the pilots of the Sea Hurricanes, communication ratings, submarine look-outs, port medical party and the port fire party.
HMS Fearless closed HMS Furious at once when the Hurricane crashed and picked up the pilot who as suffering from minor injuries, and also another pilot was had been seen to jump overboard in flames. This officer was severely burnt and later died on board HMS Fearless. Two officers and one rating died at once in Furious and by midnight the total casualty list was: 4 Naval Officers (FAA), 1 RAF Officer, 4 Naval ratings. Seriously injured were: 2 Naval Officers (1 FAA, both have since died), 3 RAF Officers, 7 Naval ratings (2 have since died), 4 RAF ratings (1 has since died). Also 1 Naval officer was injured as was 1 RAF rating.
As one of Furious' doctors was a casualty Ark Royal flew over two doctors to assist.
The seagoing efficiency of the ship is not affected except for the destruction of the communications to the port navigating position. The fighting efficiency is affected to the extent that various gun cummunication and control instruments are destroyed. The six Hurricanes of the second flight were not damaged but could not be flown off as all their pilots were casualties.
An A/S patrol was maintained all day and a fighter patrol of four aircraft till 1700A/30.
At 1425A/30 information was received that all the six Blenheims and 35 Hurricanes had arrived safely at Malta.
During the afternoon (flying) exercises were carried out. Before dark six Swordfish of 818 Squadron were transferred from HMS Ark Royal to HMS Furious.
At 0600A/1 when off Europa Point HMS Furious flew off three Sea Hurricanes to North Point and then screened by HMS Faulknor and HMS Fearless proceeded into harbour. The remainder of the force turned back to the eastward for exercises. HMS Hermione was detached to act as target. Both destroyers that had escorted Furious into harbour also rejoined.
On completion of the exercises ' Force H ' arrived in harbour at 1030A/1. (60)
11 Jul 1941
The aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN, with Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN on board) departed Gibraltar at 0730/11 for exercises and flying training. She was being escorted by the destroyers HMS Fearless (Cdr. A.F. Pugsley, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Foxhound (Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN) and the escort destroyer HMS Eridge (Lt.Cdr. W.F.N. Gregory-Smith, RN). The light cruiser HMS Hermione (Capt. G.N. Oliver, RN) departed Gibraltar at 1020A/11 to join the exercises. The Admiral later returned to Gibraltar in an aircraft.
At 0815A/12, HMS Renown (Rear-Admiral R.R. McGrigor, RN) sailed from Gibraltar to join the exercises. All ships returned to harbour around 1700/12. (60)
21 Jul 1941
Operation Substance, convoys to and from Malta
Passage through the Straits of Gibraltar of the eastbound convoy and sailing from Gibraltar of the remaining ships involved in the operation.
Around 0130B/21 convoy WS 9C passed the Straits of Gibraltar. The convoy at that moment consisted of six merchant ships; City of Pretoria (8049 GRT, built 1937), Deucalion (7516 GRT, built 1930), Durham (10893 GRT, built 1934), Melbourne Star (11076 GRT, built 1936), Port Chalmers (8535 GRT, built 1933) and Sydney Star (11095 GRT, built 1936).
At the time they passed through the Straits they were escorted by HMS Nelson (Capt. T.H. Troubridge, RN), HMS Edinburgh (Capt. H.W. Faulkner, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral E.N. Syfret, RN), HMS Manxman (Capt. R.K. Dickson, RN), HMS Lightning (Cdr. R.G. Stewart, RN), HMAS Nestor (Cdr. A.S. Rosenthal, RAN), HMS Avon Vale (Lt.Cdr. P.A.R. Withers, RN), HMS Eridge (Lt.Cdr. W.F.N. Gregory-Smith, RN) and HMS Farndale (Cdr. S.H. Carlill, RN).
HMS Manchester (Capt. H. Drew, DSC, RN), HMS Arethusa (Capt. A.C. Chapman, RN), HMS Cossack (Capt. E.L. Berthon, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Maori (Cdr. R.E. Courage, DSO, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Sikh (Cdr. G.H. Stokes, RN) departed Gibraltar around 0200B/21 escorting troopship Leinster (4302 GRT, built 1937) which was to join the convoy. However Leinster grounded while leaving Gibraltar and had to left behind. The small fleet tanker RFA Brown Ranger (3417 GRT, built 1941, master D.B.C. Ralph) left Gibraltar around the same time escorted by the destroyer HMS Beverley (Lt.Cdr. J. Grant, RN).
About one hour later, around 0300B/21, HMS Renown (Rear-Admiral R.R. McGrigor, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN), HMS Hermione (Capt. G.N. Oliver, RN), HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Fearless (Cdr. A.F. Pugsley, RN), HMS Firedrake (Lt.Cdr. S.H. Norris, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Foxhound (Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) and HMS Duncan (Lt.Cdr. A.N. Rowell, RN) departed Gibraltar to give convoy for the convoy during the passage to Malta.
At sea the forces were redistributed; Force H, the cover force HMS Renown, HMS Nelson, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Hermione, HMS Faulknor, HMS Foresight, HMS Forester, HMS Fury, HMS Lightning and HMS Duncan.
Force X, the close escort for the convoy HMS Edinburgh, HMS Manchester, HMS Arethusa, HMS Manxman, HMS Cossack, HMS Maori, HMS Sikh, HMAS Nestor, HMS Fearless, HMS Firedrake, HMS Foxhound, HMS Avon Vale, HMS Eridge and HMS Farndale.
Plan for the operation
Force H was to cover the convoy until it reached the narrows between Sicily and Tunisia. Force X was to escort the convoy all the way to Malta. Ships of Force X also had troops for Malta on board that had been taken to Gibraltar by troopship Pasteur. On 23 July 1941, the day the eastbound convoy would reach ‘the narrows’ five empty transports and two tankers would depart Malta for Gibraltar (Convoy MG 1) The seven empty transports were; Group 1 (speed 17 knots) HMS Breconshire (9776 GRT, built 1939), Talabot (6798 GRT, built 1936),
Group 2 (speed 14 knots) Thermopylae (6655 GRT, built 1930), Amerika (10218 GRT, built 1930),
Group 3 (speed 12 knots) Settler (6202 GRT, built 1939), Tanker Svenor (7616 GRT, built 1931) and Tanker Hoegh Hood (9351 GRT, built 1936) These were escorted by the destroyer HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St J. Morgan, RN) which had been repairing and refitting at Malta.
Through intelligence it was known that the Italian Navy had five battleships operational (three of them at Taranto) and about ten cruisers divided between Taranto, Palermo and Messina. The Italian Air Force had about 50 torpedo planes and 150 bombers (30 of which were dive bombers) stationed in Sardinia and Sicily, roughly half of each type on both islands.
The Royal Air Force was able to be of more help than during the previous convoy trip from Gibraltar to Malta last January. Aircraft from Gibraltar conducted A/S patrols for the fleet during the first two days of the passage to the east. Also patrols were flown between Sardinia and the coast of Africa, while aircraft from Malta conducted reconnaissance between Sardinia and Sicily, besides watching the Italian ports. Malta would also provide fighter escort for Force X and the convoy after Force H would part with them and HMS Ark Royal could no longer provide fighter cover for them.
During the operation eight submarines (HMS Olympus (Lt.Cdr. H.G. Dymott, RN), HMS Unique (Lt. A.F. Collett, RN), HMS Upholder (Lt.Cdr. M.D. Wanklyn, RN), HMS Upright (Lt. J.S. Wraith, DSC, RN), HMS Urge (Lt. E.P. Tomkinson, RN), HMS Utmost (Lt.Cdr. R.D. Cayley, DSO, RN), HMS P 32 (Lt. D.A.B. Abdy, RN) and HrMs O 21 (Lt.Cdr. J.F. van Dulm, RNN)) were on patrol to report and attack Italian warships that might be sailed to intercept the convoy.
The passage East, 22 July 1941
On 22 July the destroyers from Force X oiled from the Brown Ranger two at a time. A task that took about 10 hours. Having completed the oiling of the destroyers the Brown Ranger and her escort returned to Gibraltar. An Italian aircraft had reported Force H in the morning but the convoy and Force X, at that moment about 100 nautical miles to the south-westward, appeared not to have been sighed. At 2317B/22 the Italian submarine Diaspro missed HMS Renown with torpedoes. HMAS Nestor sighted the torpedo tracks and was able to warn HMS Renown which was then able to avoid the torpedoes by doing an emergency turn to port.
The passage East and attacks by the Italian Air Force, 23 July 1941
Force H rejoined the convoy around 0800B/23 as the British were now approaching the danger area. Shadowing aircraft had already reported the position of the fleet that morning and heavy air attacks soon followed.
The first came at 0945 hours, a well times combination of nine high level bombers and six or seven torpedo planes approaching from the north-east. HMS Ark Royal had eleven fighters up, which met the bombers about 20 miles from the fleet. They managed to down two of the nine bombers but unfortunately three Fulmars were shot down by the enemy. The other seven bombers came on working round the head of the screen of destroyers to attack the convoy from the starboard beam at a height of 10000 feet. Their bombs fell harmlessly amongst the leading ships as they altered course to avoid the attack. The torpedo planes however were more successful. They came from ahead out of the sun, flying low, and as the destroyers opened fire they divided into groups of two or three and to attack the convoy on both sides. Two aircraft attacked HMS Fearless, stationed ahead in the screen, dropping their torpedoes at ranges of 1500 and 800 yards from a height of 70 feet. The destroyer avoided the first torpedo, but was hit by the second, set on fire, and completely disabled. Other aircraft went to press on their attacks on the convoy itself. One of them, dropping its torpedo between two merchant vessels hit HMS Manchester as she was turning to regain her station after avoiding two torpedoes fired earlier. She reversed helm once more but to no avail. During the attacks three enemy torpedo bombers were shot down by AA fire from the ships.
HMS Manchester was badly damaged and could only use one engine out of four. At first she could steam only 8 knots. She was ordered to make for Gibraltar with HMS Avon Vale as escort. That evening, further to the westward, they were attacked again by three enemy torpedo planes but their AA gunfire kept the enemy at a distance. Both ships successfully reached Gibraltar on the 26th.
At 1010B/23 five more bombers tried to attack the convoy crossing this time from north to south. Fighters from HMS Ark Royal forced them to drop their bombs from great height and mostly outside the screen.
At 1645B/23 five more torpedo planes led by a seaplane came in from the northward. Three Fulmars caught them about 20 miles away. They managed to shoot down two planes and drove the remainder away.
Soon afterwards the fleet arrived off the entrance to the Skerki Channel. There HMS Hermione was transferred to Force X to take the place of HMS Manchester. Six destroyers were assigned to Force H and eight to Force X. At 1713 hours Vice-Admiral Somerville hauled round to the westward. HMS Ark Royal kept her Fulmars up until RAF Beaufighters had arrived from Malta to take over.
The convoy was attacked again around 1900B/23. Four torpedo planes arrived from the eastward, flying low and and working round from ahead to the starboard side of the convoy. They approached in pairs in line abreast. They kept HMS Sikh (on the starboard bow of the screen) between them and their target until nearly the moment for attack, thereby hampering the AA fire from the other ships. They dropped their torpedoes from long range from a height of 50 feet and nearly hit HMS Hermione, sternmost ship in the starboard column. To avoid the attack each column of the convoy turned 90° outwards and all warships opened barrage fire from all guns that would bear. The barrage however fell short but it caused the Italians to drop their torpedoes early. Also one of the enemy was possibly shot down.
This attack scattered the convoy and it took some time to reform. At 1945B/23 about seven bombers appeared from ahead at a height of about 14000 feet to attack the convoy from the port side. The convoy altered 40° to port together and the escort opened up a controlled fire with some hesitation as the Italian aircraft looked a lot like Beaufighters. The bombing was extremely accurate. Several bombs fell near HMS Edinburgh which was leading the port column, and a near miss abreast a boiler room disabled HMS Firedrake which had been sweeping ahead of the convoy. She could no longer steam so Rear-Admiral Syfret ordered her back to Gibraltar in tow of HMS Eridge. They had an anxious passage, being shadowed by aircraft continuously during daylight hours, but were not again attacked. On the 25th HMS Firedrake managed to lit one boiler so the tow was slipped. Both destroyers entered Gibraltar harbour on the 27th.
Soon after leaving the Skerki Channel in the evening of the 23th the convoy hauled up to the north-east towards the coast of Sicily. This was to lessen the danger of mines. The Italians did not shadow the convoy after the attack at 1945 hours and missed this alteration of course which they clearly did not expect. Around 2100 hours, as it was getting dark, enemy aircraft were seen searching along its old line of advance. During the evening the convoy sighted flares several times about 20 miles to the south.
Continued passage to the east and enemy attacks, 24 July 1941
Between 0250 and 0315 hours the convoy was however attacked by the Italian MAS boats MAS 532 and MAS 533. The managed to torpedo and damaged the Sydney Star. HMAS Nestor went alongside and took off almost 500 soldiers. Sydney Star was however able to continue her passage as staggler escorted initially by HMAS Nestor. Admiral Syfret however sent back HMS Hermione. At 1000B/24 eight German dive bombers and two high level bombers attacked. Their bombs fell close the escorting ships. HMS Hermione shot down one dive bomber. The three ships arrived at Malta early in the afternoon.
The main body of the convoy meanwhile continued on its way unhindered after the attacks of the motor torpedo boats except for an attempt by three torpedo planes around 0700 hours. They dropped their torpedoes at a safe distance when fired on by the destroyers in the screen ahead. According to the orders Rear-Admiral Syfret was to leave the convoy now, if there was no threat from Italian surface forces, and go on to Malta with the cruisers and some of the destroyers. They were to land the passengers and stores, complete with fuel and return to Force H as soon as possible. The remaining destroyers were to accompany the transports to Malta. They too were to join Force H as soon as possible. Rear-Admiral Syfret felt easy about the surface danger as all Italian ships were reported in harbour the day before, but he was anxious about the threat to the convoy from the air. He decided to go ahead with the cruiser but leave all destroyers with the convoy so at 0745B/24, HMS Edinburgh, HMS Arethusa and HMS Manxman left the convoy and pressed ahead at high speed to Malta where they arrived at noon the same day. The transports and the destroyers arrived about four hours later. They had been attacked only once by a torpedo plane since the cruisers separated.
Return passage of the warships of force X to make rendez-vous with Force H.
In the evening HMS Edinburgh, HMS Arethusa, HMS Hermione and HMS Manxman sailed together followed by five destroyers; HMS Cossack, HMS Maori, HMS Sikh, HMAS Nestor, HMS Foxhound, later the same evening. The destroyers overtook the cruisers in the morning of the 25th. The sixth destroyer, HMS Farndale, had to be left at Malta due to defects (condenser problems). All ships made rendez-vous with Force H to the north-west of Galita Island at 0800B/25.
Movements of Force H after it parted from the convoy.
After parting with the convoy in the evening of the 23rd, Vice-Admiral Somerville had taken force H westward at 18 knots until the afternoon of the 24th going as far west as 03°30’E. He then turned back to meet Admiral Syfret, also sending from HMS Ark Royal six Swordfish aircraft which left her in position 37°42’N, 07°17’E at 1000B/25. After their junction Forces H and X made the best of way towards Gibraltar. Fighter patrols of HMS Ark Royal shot down a shadowing aircraft soon after the fleet had shaped course to the westward, losing a Fulmar in doing so. However another aircraft had meanwhile reported the fleet.
High level bombers appeared from the east and torpedo bombers from the north at 1100 hours. HMS Ark Royal at that moment had four fighters in the air and sent up six more. They prevented the bombing attack shooting down three aircraft out of eight at a cost of two Fulmars, while the ships watched the enemy jettison their bombs 15 miles away. The torpedo attack came to nothing too for the enemy gave up the attempt and retired while still several miles from the fleet. Two days later, on the 27th, the fleet reached Gibraltar.
The movements of the seven empty ships coming from Malta.
Six of the transports / tankers left Malta for Gibraltar in the morning of the 23rd, escorted by HMS Encounter. The seventh ship, tanker Svenor grounded while leaving harbour and was held up for some hours. At dusk, when a few miles from Pantelleria, the six ships devided into pairs according to their speed. HMS Encounter initially escorted the middle pair but joined the leading ships in the evening of the 24th when past the Galita Bank.
Italian aircraft, both high level bombers and torpedo planes, attacked all these ships on the 24th to the southward of Sardinia. They made their first attempt on the second pair of transports and HMS Encounter. Four torpedo planes attacked at 1230B/24 and four bombers at 1250B/24. No ships were hit though the bombs fell close. Next came the turn for the leading pair, which were attacked further westwards by two bombers that came singly at 1330B/24 and 1400B/24. The second plane nearly hit HMS Breconshire. Finally when the third pair of ships reached about the same position in the evening they were attacked by torpedo planes and the Hoegh Hood was damaged but she managed to arrive at Gibraltar only a few hours after her consort on the 27th. The last ship, the one that had been delayed at Malta, arrived on the 28th. (61)
30 Jul 1941
Operation Style.
Ferrying of troops and supplies to Malta and diversery attack on Sardinia.
' Force X ', made up of the light cruisers HMS Hermione (Capt. G.N. Oliver, RN) and HMS Arethusa (Capt. A.C. Chapman, RN), fast minelayer HMS Manxman (Capt. R.K. Dickson, RN) and escorted by the destroyers HMS Sikh (Cdr. G.H. Stokes, RN) and HMS Lightning (Cdr. R.G. Stewart, RN) departed Gibraltar on the 31 July 1941 carrying the troops and supplies that had been on the troopship Leinster and the light cruiser HMS Manchester which had not reached Malta during Operation Substance.
To cover ' Force X ', ' Force H ' departed Gibraltar around 0600A/30 and it was made up of the battleship HMS Nelson (Capt. T.H. Troubridge, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), battlecruiser HMS Renown (Rear-Admiral R.R. McGrigor, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN). They were escorted by the destroyers HMS Cossack (Capt. E.L. Berthon, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Maori (Cdr. R.E. Courage, DSO, DSC and Bar, RN), HMAS Nestor (Cdr. A.S. Rosenthal, RAN), HMS Faulknor (Capt. A.F. de Salis, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Foxhound (Cdr. G.H. Peters, DSC, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN), HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St J. Morgan, RN) and the escort destroyer HMS Eridge (Lt.Cdr. W.F.N. Gregory-Smith, RN). They were also ordered to create a diversion for the operation.
An then these was also ' Force S ' which was made up of the Royal Fleet Auxiliary tanker Brown Ranger (3417 GRT, built 1941, master D.B.C. Ralph) escorted by the escort destroyer HMS Avon Vale (Lt.Cdr. P.A.R. Withers, RN). This force also departed Gibraltar on 30 July 1941.
At 1630B/31, the destroyers HMS Cossack and HMS Maori were detached to bombard the harbours of Alghero and Port Conte on Sardinia and fire star shells for a night raid by aircraft from the aircraft carrier Ark Royal. Also the seaplane base at Porte Conte was to be attacked.
The destroyers at first proceeded as of making for the Straits of Bonifacio altering course after dark.
At 0130B/1, HMS Maori parted company with HMS Cossack and proceeded toward Porte Conte while Cossack went towards Maddalena Island where she switched on her searchlight at 0220B/1 to search the bay and the harbour. Cossack also fired starshell on various bearings from north to south-east and moved right into Alghero Roads. They harbour and roads were completely emptry and no targets could be found. One starshell started a fire in a building about 2 miles north of the town.
Meanwhile Maori had opened fire with starshell at 0210B/1 in the entrance to Port Conte and steamed up the bay at 12 knots. The whole bay was illuminated and seen to be empty. Buildings on the hill to the east of the harbour were illuminated by searchlight and the Customs house and one other official looking building were demolished by gunfire at a range decreasing from 4000 to 2000 yards. A church between these two targets was not fired at. Maori detected a large number of sharp asdic contacts ahead and thinking they might be possibly caused by a line of mines, stopped engines and turned round.
At 0235B/1, Cossack sighted a plane flying up the coast from the south and passing over Alghero. As there were no targets to be engaged and as he considered a sufficient diversion had been caused in the vicinity, Capt. Berthon ordered both destroyers to withdraw which they then did to the south-west. When clear of the 50 fathom line speed was increased to 32 knots and course was shaped to rejoin ' Force H ' after daylight.
At 0310B/1, ' Force H ' alterered course together and HMS Ark Royal flew off 9 Swordfish from position 40°43'N, 06°35'E, for a bombing attack on Alghero airodrome. On completion of flying off the fleet withdrew on course 255° at 20 knots.
The aircraft, which were armed with four 250lb G.P. bombs, 40lb G.P. bombs and 20lb H.E. bombs abd flares were ordered to attack aircraft on the ground and the aerodrome buildings and hangars.
When they attacked two direct hits were observed on the equipment shop where a fire broke out. The eastern and western hangars and the living quarters were also hit and fired were caused in the two latter targets.
As soon as the flares illuminated the aerodrome considerable light AA fire was experienced but no aircraft was hit. No enemy aircraft were observed. A fire was burning in a two storey building just to the north of the town of Alghero which was probably that started by the starshell from HMS Cossack.
All aircraft returned to the carrier. Landing on began at 0621B/1. As the third aircraft landed a 40lb G.P. bomb exploded which had probably hung up on the racks, exploded setting the aircraft on fire, blowing a hole in the deck and killing four officers and three ratings. One rating was wounded. The remaining aircraft now could not be landed before the remains of the burnt aircraft had been hauled aft and the flight deck was repaired. Also the arrestor gear was damaged by the explosion and had to be repaired. Repairs were completed at 0715B/1 after the remaining six aircraft landed on. Course was continued to the westward and HMS Cossack and HMS Maori rejoined at 0800B/1.
At 0812B/1, an Italian aircraft was sighted but the fighters could not intercept as it hid in the low cloud.
Another aircraft was reported to the southward at 0852B/1 but again the fighters failed to make contact. The aircraft was however believed to be a Spanish flying boat.
All aircraft were landed on by noon owing to low visibility and approaching heavy rain.
Attempts to refuel destroyers in the afternoon from Brown Ranger did not succeed owing to the weather and the tanker with its escort were ordered to proceed further to the south. HMS Cossack and HMS Maori went with them as they were the first that had to refuel. They were ordered to try to refuel during the night if possible ad make rendezvous with ' Force H ' at 0630B/2.
At 1807B/1, HMS Renown reported that her port bulge wa coming away and that she would require docking on arrival at Gibraltar and that high speed was undesirable except in an emergency.
Meanwhile ' Force X ' had proceeded to the eastward some 35 nautical miles from the African coast. They streamed paravanes at 0700B/1 and then proceeded at 25 knots increasing to 26 knots at noon. At 2000B/1 speed was increased to 28 knots which was Arethusa's best speed with paravanes streamed.
While ' Force X ' was passing south of Sardinia, ' Force H ' proceeded down the western side of the Balearics to make rendezvous with Brown Ranger the following morning.
At 0025B/2, ' Force X ' intercepted an enemy report which might have emanated from a submarine sighting the force while it passed the Cani Rocks. Cape Bon was passed 1.5 nautical miles abeam to starboard at 0145B/2.
At 0510B/2 the light cruiser Hermione rammed and sank Italian submarine Tembien between Pantelleria and Linosa in position 36°21'N, 12°40'E. The light cruiser sustained only light damage. HMS Lightning was then briefly detached to search the area but soon rejoined having sighted nothing.
' Force X ' arrived safely at Malta at 0900B/2.
Meanwhile ' Force H ', having passed to the westward of the Balearics during the night, made rendezvous with the Brown Ranger at 0630 some 40 nautical miles south-east of Ibiza. HMS Cossack and HMS Avon Vale had topped off with fuel ad HMS Maori who made an unsuccesful attempt before dark was completing with fuel as ' Force H ' approached.
There was a north-westerly wind force 4 and a slight south-west swell. Brown Ranger steamed to and fro south of te islands on courses either directly with or against the prevailing south-westerly swell whilst ' Force H ' cruised within visibility distance changing destroyers as necessary for fuelling. Problems with the gear on board the Brown Ranger caused some delays. All destroyers were however able to refuel and at 1900B/2 Brown Ranger was ordered to return to Gibraltar now escorted by HMS Eridge.
While oiling was tanking place and A/S patrol was kept up over the area while a fighter patrol was kept ready on the deck of HMS Ark Royal.
At 1900B/2, after the last destroyers had just completed fuelling, ' Force H ' altered course to 102° at 18 knots. Speed was increased to 20 knots at 2200B/2 to rendezvous with ' Force X ' about 0830B/3 in position 38°05'N, 07°28'E.
While ' Force H ' had been spending the day south of the Balearics, ' Force X ' was unloading troops and stores and fuelling at Malta. ' Force X ' sailed at 1600B/2 augumented by the escort destroyer HMS Farndale (Cdr. S.H. Carlill, RN) who had completed repairs at Malta. The force proceeded at 24 knots, this being HMS Farndale's best speed. When north of Gozo, HMS Farndale reported that she could not maintain a higher speed than 18 knots. She was then ordered by HMS Hermione to return to Malta.
' Force X ' then increased speed to 26 knots and returned by the same route which they had followed successfully on the eastward passage through Tunisian territorial waters. Owing to loss of paravanes HMS Hermione was stationed astern of the line, which was led by HMS Arethusa.
At 2215B/2, RDF indicated a low flying aircraft 20 miles to the southward and up moon. The aircraft came straight in, unseen, and passing about 1000 feet overhead, opened 8 miles to the northward and faded. It was though the aircraft had failed to sight the force but a little later it returned and appeared to circle ahead.
At 2225B/2 when in position 36°28'N, 12°00'E, the aircraft approached at right angles on HMS Hermione's port beam and dropped one torpedo at a range of 100 yards abreast Hermione's stern. The aircraft was engaged by pom-pom and seen to jink just before dropping it's torpedo which missed well astern. The speed of ' Force X ' was evidently considerably underestimated. The aircraft which did not appear to be hit was held by RDF as far as Pantellaria before it faded. Twenty minutes later a shore station was heard apparently homing an aircraft but no enemy report was intercepted.
At 0027B/3, ' Force X ' was turning to starboard to approach Kelibia a small darkeneded vesel was sighted at about 5000 yards on the port beam. Guns and searchlights were trained on but as the vessel drew into the path of the moon it was identified as a small schooner. The order was passed to 'revert to normal' but Hermione's pom-pom opened fire at about 4000 yards. HMS Manxman and HMS Arethusa both joining in. Cease fire was immediately ordered by W/T. No hits were observed.
' Force X ' proceeded without further incident to rendezvous with ' Force H '. A low layer of misty cloud and reduced visibility probably accounted for the abence of enemy air reconnaissance.
At 0612B/3, HMS Ark Royal, flew off a reconnaissance of three aircraft along tracks 080°, 093° and 106° to a depth of 80 miles to locate ' Force X ' and any enemy forces that might be to the northward and between forces ' X ' and ' H '.
At 0640B/3, HMS Foresight sighted a floating mine and sank it with small arms fire. HMS Foresight was then stationed 3 miles 160° from HMS Nelson to asist in homing in the reconnaissance aircraft.
The first fighter patrol was flown off at 0700B/3. An hour later the reconnaissance aircraft returned reporting ' Force X ' bearing 117°, 33 nautical miles from HMS Nelson. No enemy forces had been sighted. HMS Foresight was then ordered to rejoin the destroyer screen.
at 0835B/3, when ' Force H ' was 75 nautical miles west-north-west of Galita, ' Force X ' was sighted 6 nautical miles to the eastward.
' Force H ' altered course to 270° as ' Force X ' joined and the whole fleet withdrew to the westward at 20 knots. Visibility gradually improved.
At 0927B/3, while the visibility was still low, an enemy aircraft was sighted and one section of fighters was sent to investigate. The enemy only entered the visibility circle to the north-west for a very short period before making off at high speed on a course of 250°. The fighters were not able to intercept the enemy.
At 1006B/3, a shadower was detected by RDF and four fighters in the air were sent to intercept. The enemy was engaged by one of the Fulmars but was able to take cover in the clouds and disappeared to the north-east.
An enemy report was intercepted at 1045B/3 indicating that this aircraft reported the position of the fleet at 1010B/3. No further enemy aircraft were sighted.
Course was altered to 260° at 1515B/3 and speed was reduced to 18 knots as by this time HMS Repulse's port bulge had started to fold back. At 1917B/3 course was altered to 250°.
Low visibility probably persised in the vicinity of Cagliari during the forenoon and early afternoon may have been partly responsible for the enemy's lack of enterprise.
At 0400 when in position 37°22'N, 01°01'E, look-outs in HMS Avon Vale heard shouts and after investigating picked up an RAF sergeant pilot from a rubber dinghy. He was the sole survivor of a Wellington aircraft whichhad force landed on the night of 31 July when en-route from Gibraltar to Malta.
At daylight the fleetwas divided into three groups to facilitate berthing arrangements at Gibraltar. Group one comprising HMS Ark Royal, HMS Hermione, HMS Lightning, HMS Sikh, HMS Encounter and HMS Forester proceeded ahead at 27 knots and entered harbour at 2030B/4.
Group two, comprising HMS Nelson, HMS Arethusa, HMS Manxman, HMS Faulknor, HMS Foresight, HMS Foxhound and HMS Fury proceeded at 20 knots and entered harbour at 2230B/4.
And finally, Group three, comprising HMS Renown, HMS Cossack, HMS Maori, HMAS Nestor and HMS Avon Vale proceeded at 18 knots and entered harbour at midnight. (60)
14 Aug 1941
At 2230A/14 the following ships departed Gibraltar for exercises; battleship HMS Nelson (Capt. T.H. Troubridge, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN), light cruiser HMS Hermione (Capt. G.N. Oliver, RN) and the destroyers HMAS Nestor (Cdr. A.S. Rosenthal, RAN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St J. Morgan, RN) and HMS Vimy (Lt.Cdr. H.G.D. de Chair, RN).
At 0930A/16, HMS Nelson and HMS Vimy returned to harbour. HMS Hermione returned at 1610A/16.
HMS Ark Royal returned to harbour at 1130A/17 after having completed flying training. The destroyers HMAS Nestor, HMS Fury, HMS Forester, HMS Foresight and HMS Encounter which had been screening the carrier only returned at 1400A/17 after having conducted torpedo firings. (60)
21 Aug 1941
Operation Mincemeat.
Air attacks on Sardinia and minelaying in the Gulf of Genoa.
At 2200A/21, ' Force H ', departed Gibraltar and set course to the eastward. It was made up of the battleship HMS Nelson (Capt. T.H. Troubridge, RN, now flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN) and light cruiser HMS Hermione (Capt. G.N. Oliver, RN). They were escorted by the destroyers HMAS Nestor (Cdr. A.S. Rosenthal, RAN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) and HMS Encounter (Lt.Cdr. E.V.St J. Morgan, RN).
The fast minelayer HMS Manxman (Capt. R.K. Dickson, RN) departed Gibraltar at 0210A/22 and also set course to the eastward.
' Force H ' passed 9 miles south of Alboran Island at 0530A/22 and shaped course 080° at 17 knots altering course to 065° at 1400A/22 when 28 miles north of Oran.
An east-north-east wind persisted all day, rising to force 6 by 1800A/22 after which it fell to a light breeze. The visibility throughout the day was approximately 10 miles from 1000 feet and there is no reason to suppose that the force was sighted by enemy aircraft.
Several exercises had been carried out during the day. At 2200A/22, ' Force H ' was in position 37°00'N, 01°32'E, steering 070°.
At 0600A/23, when ' Force H ' was in position 37°48'N, 04°07'E course was altered to 300° to avoid being too far to the eastward before dark.
The first RDF report was at 0810A/23 when the fleet was 80 nautical miles north-north-east of Algiers. An aircraft was detected bearing 020°, 30 miles. It pased from east to west some 25 miles north of the fleet. A section of fighters was then flown off from HMS Ark Royal.
An aircraft was sighted by HMS Ark Royal at 0850A/23 and the fighters were directed on. The shadower, a Cant 506B, was attacked nine times fom astern before all ammunition was expended. The rear gunner was put out of action and one wing was damaged, but the aircraft escaped. Whilst returning to the carrier the fighters reported a second enemy aircraft ten miles to the southward and a relief section of fighters was flown off at 0915A/23 and made contact ten minutes later with another Cant 506B. Seven attacks were carried out before all ammunition was expended. Although some of these attacks were made from close range, the enemy escaped with his rear gunner out of action. It appears that the pilots and engines in these aircraft are now well armoured.
At 1230A/23, ' Force H ' altered course to 055° when in position 38°23'N, 02°45'E. Speed was increased to 18.5 knots to reach the required position for flying off the night striking force.
During the afternoon there were various RDF reports but the aircraft were all considered to be civil machines bound to or from North Africa. At 1722A/23 when in position 38°58'N, 04°17'E an aircraft was sighted low down bearing 300° passing from North to South. The fighters were vectored on and shortly afterwards reported they had shot down a Ju.52 with swastika markings on the tail.
Speed was increased to 19 knots at 2000A/23 and forty minutes later course was altered to 047° to reach the flying off position about 80 miles west of Port Conte.
At 0250A/24, ' Force H ' altered course to 115° into the wind and increased speed to 23 knots. Ten Swordfish were flown off from position 40°50'N, 06°59'E to attack the cork woods in the vicinity of Tempio. Immediately all aircraft had flown off course was altered to 235° and withdrawal was made at 20 knots.
Flying conditions were good and navigation was aided by a clear starlight night and a poor black out at Tempio. Woods to the west and south-east of the town were attacked with incendiaries and many large fires were started. A warehouse on the south-west outskirts of the town was also left well alight. It was unfortunate there was only a slight breeze in the target area or the conflagration might have been considerably assisted. Only light AA fire was encountered. All aircraft returned safely at 0615A/24 and all were landed on at 0645A/24.
At 0735A/24 an unknown aircraft was detected by RDF bearing 170° 32 miles and the fighter patrol was sent in to intercept. On reaching a position 28 miles from the fleet the unknown aircraft turned away and faded from the screen. The fighters were recalled.
At 0920A/24 two signals were intercepted from an aircraft from Malta reporting units of the Italian Fleet about 30 miles south of Cagliari at 0810A/24 steering 240° at 15 knots. The total enemy force at this time was reported as two battleships, four cruisers and nineteen destroyers.
At 1251A/24 a signal was intercepted from HMS Upholder (Lt.Cdr. M.D. Wanklyn, DSO, RN) reporting one battleship, two cruisers and six destroyers in position 38°30'N, 12°00'E, steering 215° at 25 knots at 1030A/24. This brought the total strenght of the enemy up to three battleships, six cruisers and twenty-five destroyers.
It was clear that ' Force H ' alone could not engage this concentration, but it hoped it might prove possible to launch a torpedo-bomber attack at dusk, provided the enemy were sufficiently far to the westward to reduce to a reasonable extent the chances of the torpedo-bombers being intercepted by enemy shore-based fighters. ' Force H ' steered 235° until 1340A/24, when ' Force H ' was 67 miles south-east of Palma when course was chenged to 170°.
Vice-Admiral Somerville however received no further information on the enemy and at 1420A/24 he broke W/T silence to ask the Vice-Admiral Malta if he could shadow then enemy between 1600A/24 and 2100A/24, providing they were west of Cagliari. At 1520A/24 when in position 38°28'N, 04°05'E, ' Force H ' altered course to 090°.
By 1600A/24 there was still no information on the enemy's whereabouts. As it was thought possible that the enemy was within 40 to 50 miles of ' Force H ' if he had continued a westerly course at high speed, ' Force H ' turned to the westward flying off an air reconnaissance from position 38°25'N, 04°14'E to search to a depth of 110 miles.
At 1705A/24 te RDF detected a hadower approaching from the eastward and the fighters were vectored on. Contact was made at 1720A/24 and the shadower, although engaged until all ammunition was expended after sixteen attacks, escaped with his rear gunner silenced. Some fourty minutes later an enemy report was intercepted from an Italian aircraft.
The reconnaissance, which had sighted nothing, was landed on at 1945A/24 when course was altered to 230° and speed reduced to 17 knots.
At 2012A/24 a signal was received from the Vice-Admiral, Malta stating the air reconnaisance had sighted two battleships and fourteen destroyers in position 38°38'N, 09°31'E, steering 140°, speed 15 knots at 1655A/24, and four cruisers and five destroyers in position 38°35'N, 09°25'E at 1700A/24 steering 070° at 15 knots. The signal added that ethe enemy were not being shadowed. This report indicated that an attack on the enemy was not feasable and it was clearly his intention to refuse action except under close cover of his shore-based air forces.
At 2230A/24, ' Force H ' altered course to pass between Ibiza and Majorca during the night.
At 0330A/25, course was altered to 290° to steer for Valencia, where it was intended ' Force H ' should make a demonstration with a large number of aircraft in the air. Paravanes were streamed at 0645A/25 before entering coastal waters.
At 0930A/25, HMS Ark Royal started flying off aircraft and ' Force H ' steamed down the coast from Sugunto to Valencia seven miles off shore. Fourteen Fulmars and seventeen Swordfish circling overhead. During this demonstration a Spanish submarine surfaced about four miles on the port bow and displayed two large Spanish ensigns. Several small craft were passed at close quarters.
All aircraft were landed on by 1200A/25 and the force proceeded to the southward at 17 knots. Various exercises were carried out during the afternoon and evening. One Swordfish, taking part in a navigation exercise, force landed due to oil-failure. HMS Hermione was despatched ahead at full speed and recovered the crew uninjured.
After dark a night-encounter exercise was carried out with HMS Hermione, star-shell and searchlights being used.
Various practices were carried out. Including an attack by aircraft during which nine torpedoes were dropped.
' Force H ' retuned to Gibraltar at 1430A/26.
Movements of HMS Manxman.
HMS Manxman passed between the Balearic Islands and the Spanish coast during the night of 22/23 August. At sunrise she was about 40 nautical miles to the north of Majorca and course was then set for Toulon with the French colours and pendant hoisted and the crew in similar disguise. Visibility was extreme as the ship made her way northwards. A flying boat, though to be a Donier, passed eight miles on her port beam without showing any interest.
By 1535A/23, the hills behind Toulon were in sight and course was altered to 090°. Three hours later course was altered towards Ajaccio to further emphasise her ' French ' character during the last hours of daylight. At 1845A/23, she entered a thick fog bank which cleared after about 15 minutes but from then on visibility was no longer extreme.
At 2015A/23, the mountain tops of Corsica were sighted at a distance of 60 miles and an hour later, after the sun had set the French coulours were replaced by the White Ensign. Also the French uniforms were discarded, the false bow dismantled and paravanes streamed. Speed was then increased to 30 knots and course set to pass close north of Corsica and then onwards to the laying area.
The minelay commenced at 0208A/24, and was completed, without a hitch by 0338A/24. A total of 140 mines and 16 obstructors were laid in four paralllel lines on a heading of 070° - 250°, within a rectangle contained by lines joining positions; A) 43°13'N, 10°12'E. B) 43°17'N, 10°12'E. C) 43°19'N, 10°19'E. D) 43°16'N, 10°21'E.
On completion of the minelay HMS Manxman retired on a course of 276° to pass six nautical miles to the south of Gorgona Island and so to obtain a final check on the position of the lay. As it was suspected hydrophones would be present at the island speed was reduced to 10 knots which also allowed the paravanes to be recovered and to refit the false bow. At 0414A/24, course was set to the westward at 37 knots in a race to get clear of the Gulf of Genoa before sunrise.
At 0648A/24, the full disguise was again assumed and speed reduced to 33 knots so as to ensure that no smoke was made. Having covered a further 150 miles to the west by 1100A/24 course was altered more to the southwards and speed reduced to 20 knots.
The Commanding Officer had decided to keep closer to the Spanish coast then on the outward passage and this turned out to be a wise move when shortly afterwards a warship was sighted hull down to the south-east on a north-easterly course. This was thought to be a Vichy French warship on passage from North Africa to Toulon.
During the night of 24/25 August, HMS Manxman passed to the west of the Balearic Islands and at 1200A/25 she assumed her own nationality. She arrived at Gibraltar around 2300A/25 and after fuelling left for the U.K. to be clear of land by daylight on the 26th.
The minefield was discovered by the Italians on 26 August 1941 after 22 mines had been sighted on the surface. The whole field was swept but the Italian auxiliary minesweeper G 28 / Carmelo Noli (109 GRT, built 1929) set off a magnetic mine and sank around 1330B on 21 September 1941.
Movements of the Italian Navy.
The Italians were aware of Force H leaving Gibraltar and sent the fleet to sea.
The battleships Littorio and Vittorio Veneto escorted by the destroyers Granatiere, Fuciliere, Bersagliere, Alpino, Aviere and Camicia Nera sailed from Taranto at 1450B/22-1610B/22 and crossed the Straits of Messina at 0730B/23-0800B/23. They operated in the Tyrrhenian Sea. At 1635B/23, they were reinforced by destroyers Nicoloso Da Recco, Lanzerotto Malocello and Ugolino Vivaldi. They had sailed from Naples at 1232B/23-1405B/23 (so did he destroyers Freccia, Folgore and Fulmine who sailed at 2030B/23-2045B/23 and then went to Palermo, arriving at 1000B/25-1110B/25). At 1845B/23, they sighted the cruisers of the Third Cruiser Division (see below). At 2035B/24-2216B/24, the destroyers Aviere, Camicia Nera, Alpino, Fuciliere, Granatiere, Bersagliere and Maestrale reached Cagliari to refuel and sailed again at 0350B/25-0530B/25. The two battleships, screened by Camicia Nera, Antoniotto Usodimare, Alpino, Ugolino Vivaldi, Antonio Da Noli, Nicoloso Da Recco and ? ), reached Naples at 0647B/26-0834B/26. Aviere reached Naples at 1230B/26. Emanuele Pessagno arrived at Naples at 1617B/26.
Other movements: The Third Cruiser Division departed from Messina at 0955B/23-1010B/23: heavy cruisers Trieste, Trento, Bolzano and Gorizia, screened by the destroyers Carabiniere and Corazziere. Ascari and Lanciere, sailed from Reggio (Calabria) at 0900B/23-0940B/23 to join them. We know they joined the Battle Squadron at 1845B/23 but it is not clear when they were detached. They returned to Messina at 0728B/26-0815B/26, with the following exceptions: as they approached their destination, Bolzano was torpedoed by HMS Triumph (Cdr. W.J.W. Woods, RN) at 0638B/26 and reached Messina at 1306B/26. Corazziere entered Messina at 1130B/26 and Carabiniere at 1220B/26, Ascari and Lanciere returned to Reggio at 1228B/26-1259B/26. The destroyers Antonio Pigafetta, Emanuele Pessagno, Giuseppe Da Verazzano, Antoniotto Usodimare and Antonio Da Noli sailed from Trapani at 1915-2020B/23. The destroyers Maestrale and Scirocco sailed from Palermo at 1240B/23-1330B/23. Maestrale and Scirocco returned to Palermo at 0130B/26 and 1831B/26 respectively. Da Verazzano, Pigafetta and Maloceloo arrived at La Spezia at 1400B/26, 1345B/26 and 1403B/26 respectively.
The Eighth Cruiser Division, made up of the light cruisers Luigi Di Savoia Duca Degli Abruzzi, Muzio Attendolo and Raimondo Montecuccoli, screened by five destroyers, including the Fulmine, departed from Palermo at 0530B/24-0630B/24. They returned to Palermo at 0830B/24-0940B/25.
The Italian squadrons reported six submarine sightings: 1. 1039B/24 by the destroyer Fulmine (318° - Marettimo – 30 miles) sighted two torpedo tracks and dropped depth charges (this was HMS Upholder). 2. 1745B/24 by the battleship Vittorio Veneto (off Cape Spartivento, Sardinia). 3. 1219B/25 by the destroyer Nicoloso Da Recco (off Cape Spartivento, Sardinia). 4. 1238B/25 by the destroyer Aviere (48 miles SSE of Cape Spartivento, Sardinia). 5. 1845B/25 by the destroyer Granatiere and the battleship Littorio (85 miles east of Cape Carbonara, Sardinia). 6. 1900B/25 by the battleship Vittorio Veneto (off Cape Carbonara, Sardinia). The last five sighting seems all to be bogus. (62)
2 Sep 1941
Around 0930A/2, the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN), light cruiser HMS Hermione (Capt. G.N. Oliver, RN) and the destroyers HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) and HMS Gurkha (Cdr. C.N. Lentaigne, RN) departed Gibraltar for exercises. HMS Hermione returned at 1630A/2 while HMS Ark Royal and the destroyers only returned at 1515A/3. (60)
7 Sep 1941
Operation Status (phase 1).
Fighter aircraft to be flown off to Malta.
At 1700A/7, HMS Hermione (Capt. G.N. Oliver, RN) departed Gibraltar and proceeded to the west with a view of promoting the idea that no operation was intended and that the subequent movements of HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN) were connected with local exercises. HMS Hermione was instructed to return through the Straits after dark and rendezvous with HMS Ark Royal to to east and out of sight of Gibraltar and Ceuta after daylight.
After dark, HMS Furious (Capt. A.G. Talbot, DSO, RN) was warped close up to HMS Ark Royal and 26 Hurricanes and 1 Swordfish were transferred by means of the ramp.
At 2300 hours Vice-Admiral Somerville embarked onboard HMS Ark Royal with certain members of his staff.
HMS Ark Royal slipped at 0540A/8 but owing to a westerly wind of 18 miles an hour and HMS Furious occupying the berth immediately astern, the three tugs available experienced great difficulty in hauling off and the harbour entrance was not passed until 0705A/8.
After flying off 1 Swordfish and 1 Fulmar to North Front course was shaped to the eastward with the destroyers HMS Gurkha (Cdr. C.N. Lentaigne, RN), HMS Lively (Lt.Cdr. W.F.E. Hussey, DSC, RN), HMS Lance (Lt.Cdr. R.W.F. Northcott, RN) and HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN) as A/S screen. One Catalina was patrolling overhead.
During the day all Hurricanes were W/T tested, engines run up and then ranged aft. The pilots were also given full instructions for the take off and passage to Malta.
So far as can be ascertained the force was not sighted during this day.
After leaving Gibraltar a moderate westerly wind was experienced until reaching the vicinity of Alboran Island when the wind fell to light airs and subsequently changed to moderate and at times freh north-easterly.
At dawn on the 9th, the weather was clear with some cloud and a light north-easterly wind.
The first pair of Blenheims were due at the rendezvous, 40 miles north-east of Algiers at 0620A/9 (sunrise), whilst the second pair were due at 0635A/9.
At 0550A/9, Hermione's RDF reported aircraft bearing 250° distant 35 miles. At 0551A/9 an aircraft of the first pair asked for a course. This was signalled and courses continued to be passed throughout the approach of this aircraft.
Owing to poor W/T conditions at this time and interference from a beam station at Algiers, communications were slow and unreliable.
At 0621A/9, requists for courses were received from other aircraft. Owing to the conditions referred to above, the first pair of Blenheims appeared to have passes to west and north of ' Force H ' without sighting and continued on a north easterly course as the result of confusion arising in the identifying the various Blenheims that were in the vicinity and unreliable communications.
At 0628A/9, a Blenheim was sighted and proved to be the standby aircraft of the second pair. This Blenheim failed to answer V/S signals and proceeded to a waiting position to the northward. It was subeqently acertained that the Aldis lamp of the aircraft had developed defects.
At 0637A/9, a second Blenheim was sighted to the southward. This proved to be the leader of the second pair ad as it crossed ahead of Ark Royal the first Hurricanes took off. Before the Blenheim had completed two circuits of the ship, the first flight of 14 Hurricanes had taken off and when formed on the Blenheim was given the order to proceed to Malta. The Hurricanes and their Bleinheims arrived at Malta at 1115A/9.
With the figures then available concerning the endurance of the Blenheims and the time occupied flying off owing to the light winds, Vice-Admiral Somerville did not consider it was advisable to retain the standby Blenheim until the second range of Hurricanes could be ranged up and flown off. This Blenheim wa therefore ordered to return to Gibraltar.
No contact either by RDF of W/T was obtained with the fouth Blenheim who returned to Gibraltar in due course.
The failure of the first pair of Blenheims to locate ' Force H ' is regrettable but was due to a considerable extent to the poor W/T conditions and the fact that these aircraft were not flying in company.
When it was clear that there could be no hope of either of the first pair of Blenheims making the rendezvous, the Force was turned to the west and proceeded at 19 knots.
A section of Fulmars was ranged on deck ahead of the remaining Hurricanes to deal with shadowers.
The RDF plot during the forenoon showed that a number of aircraft, possibly French, were in the vicinity and that in particular there were two shodowers waiting some 20 miles to the eastward.
In addition to these two shadowers, a Boston aircraft with French markings continued to circle the force just outside gun range. Two Fulmars were flown off to deal with the shadowers. One of the eastward shadowers was sighted for a few seconds by the Fulmars before disappearing in the clouds. The Fulmars were then vectored on the French Boston who waggled his wings when approached by the Fulmars but did not appear to be particularly disturbed by their presence.
As the Boston then made off to the north, the Fulmars were landed on at 1115A/9 with the Hurricanes ranged before the barrier. Shortly after the Fulmars were landed on, the Boston again appeared for a few minutes and finally disappeared in the direction of Algiers.
At 2000A/9, HMS Hermione was ordered to proceed at 26 knots and pas through the Straits during the dark hours returning to the eastward after daylight in ordered to maintain the impression that she had not proceeded to the east. From information subsequently available it does not appear that this rusa achieved its purpose.
HMS Ark Royal and the destroyers entered harbour at 0915A/10. Vice-Admiral Somerville then returned to HMS Nelson. HMS Hermione had returned shortly before HMS Ark Royal. (60)
10 Sep 1941
Operation Status (phase 2).
Fighter aircraft to be flown off to Malta.
After her return to Gibraltar HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN) took over 14 Hurricanes from HMS Furious (Capt. A.G. Talbot, DSO, RN).
At 1900A/10, the aircraft carrier HMS Furious departed Gibraltar to the westward. She was being escorted by the destroyers HMS Legion (Cdr. R.F. Jessel, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN) and HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN).
The remainder of ' Force H ', battleship HMS Nelson (Capt. T.H. Troubridge, RN, now flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal, light cruiser HMS Hermione (Capt. G.N. Oliver, RN) and the destroyers HMS Gurkha (Cdr. C.N. Lentaigne, RN), HMS Lance (Lt.Cdr. R.W.F. Northcott, RN), HMS Lively (Lt.Cdr. W.F.E. Hussey, DSC, RN) and HMS Zulu (Cdr. H.R. Graham, DSO, RN) sailed to the eastward at 2130A/10. HMS Cossack (Capt. E.L. Berthon, DSC, RN) was also to have sailed with them but was unable to do so due to defects.
At 0632A/11, HMS Furious and her three escorting destroyers was sighted. She had passed through the Straits during the night. By 0700A/11 when 30 miles north-east of Alboran Island all ships were formed on HMS Nelson and ' Force H ' was proceeding east at 17 knots.
HMS Hermione left the screen during the forenoon to act as target for a range and inclination exercise. It was also learnt from the Vice-Admiral North Atlantic Station that the departure of ' Force H ' had probably been reported to the enemy.
A Catalina was provided by 200 Group as A/S patrol throughout the day. This aircraft left the fleet at 2000A/11. On it return flight to Gibraltar the Catalina experienced very bad weather conditions with frequent thunderstorm fromm Cape de Gata to Gibraltar.
During the night ' Force H ' proceeded eastward to reach approximate position 38°N, 04°E, at 0530A/12 preparatory to flying off Hurricanes.
At 0530A/12, HMS Furious screened by three destroyers proceeded 5 miles south of HMS Nelson. W/T communication with Gibraltar which commenced to be unreliable at midnight failed from 0100 to 0600 hours. No messages concerning the departure of the Blenheims an no weather forecast were received.
At 0625A/12 a Catalina was sighted. This aircraft should have been 60 miles further eastward carrying out a reconnaissance as a precaution against interference by enemy surface forces.
The flying off position 38°N, 04°E was reached at 0530A/12 but no Blenheims arrived and no information was available till 0730A/12 when communication with Gibraltar was established and a message received which stated that these aircraft had been delayed 24 hours on account of weather. The signal giving this information was timed 0320A/12 and the delay in its receiption was due to improvised arrangements whilst the main Gibraltar W/T transmitter was being shifted underground.
This postponement of the operation was disappointing as the weather conditions between ' Force H ' and Malta appeared to be ideal. It was subsequently learnt that the 24 hours delay was imposed as a result of the weather experienced by the Catalina referred to earlier.
At 0740A/12 course was altered to the westward at 19 knots. Between 0900 and 0935 hours when in position 77 miles 017° from Algiers two unidentified aircraft were detected by RDF in the vicinity of the Fleet, and one float plane was sighted. Later an enemy report was intercepted timed 0930A/12 which presumably originated from one of these aircraft. HMS Furious struck down her land Hurricanes and ranged three sea Hurricanes on deck to deal with any shadowers that offered a reasonable chance of interception.
A Catalina sent out from Gibraltar A/S patrol was detected by RDF at 0944A/12 and sighted ten minutes later.
Speed was reduced to 17 knots at noon. At 1500A/12 Vice-Admiral Somerville learnt that the force had been reported at 1010A/12 as well as at 0930A/12. There had been no indication of the presence of a shadowing aircraft at that time. Presumably the aircraft came in low below the RDF beam and was not sighted by lookouts. Again at 1655A/12 an enemy report was intercepted without any sighting or RDF indication of shadowing aircraft.
A range and inclination exercise was carried out with HMS Hermione from 1700 to 1730 hours. At 1900A/12 course was altered to 060°, speed 18 knots and a further alteration to 090° was made at 2200A/12 to reach the flying off position at 0530A/13.
A signal was received at 0450A/13 stating that the first three Blenheims had left Gibraltar at 0310A/13 and were expected to arrive over the fleet at 0635A/13. Weather reports were favourable and inicated moderate westerly winds.
At 0410A/13, when in position 38°04'N, 03°30'E, a merchant vesel northbound from Algiers passed about 4 miles from the fleet. HMS Furious screened by three destroyers was detached at 0550A/13 to operate 5 miles to the southward of HMS Nelson.
The Catalina carrying out the dawn security patrol to the eastward of the fleet was detected by RF bearing 315° at 45 miles at 0547A/13. A formation of friendly aircraft was detected at 0623A/13 bearing 210°, 68 miles and closing. Courses to steer were passed to these aircraft by HMS Ark Royal and they were sighted at 0649A/13.
The course for flying off was 050°. The extermely light wind rendered it necessary for Ark Royal to work up to 26 knots. Whilst in order to have sufficient deck space for taking off under these conditions HMS Furious was anly able to range a maximum of 7 Hurricanes instead of the required 10. This resulter in her flights being flown off in batches of 7 and 3. The figures for the first flight were as follows; HMS Furious, 1st off 0657A/13, 10th off 0709A/13, departure 0713A/13. HMS Ark Royal, 1st off 0706A/13, 14th off 0712A/13, departure 0717A/13 from position 38°04'N, 04°13'E.
The 3rd Hurricane to take off from HMS Furious crashed into the port bridge and was lost overboard together with its pilot (Sergeant W.R. Findlay, RCAF).
After the 7th aircraft took off there was a slight delay in ranging the remaining 3 of that flight due to the jambing of the fire curtains which had been lowered when the aircraft crashed.
At 0707A/13 the second formation of 4 Blenheims was detected by RDF bearing 205°, 71 miles. These aircraft were sighted at 0730A/13. Hurricanes were started up and flown off when ready, the figures being as follows; HMS Furious 11th off 0750A/13, 20th off 0803A/13, departure 0812A/13. HMS Ark Royal 15th off 0745A/13, 26th off 0750A/13, departure 0755A/13 from position 38°10'N, 04°20'E.
The homing of the Blenheims was greatly facilitated owing the flying in formation on this occasion. Hitherto objection has been raised to flying in formation on the grounds that this would entail some additional ependiture of fuel and that as the Blenheims have to fly at 5000 feet for maximum ful economy cloud condition might render formation flying impracticable.
Immeddiately on completion of flying off all ships formed on HMS Nelson and course was shaped to the westward at 20 knots. At 0826A/13 HMS Ark Royal flew off an A/S patrol and one section of fighters. Before the fighters could take off HMS Hermione sighted an unidentified aircraft which faded from the RDF screen at a range of 16 miles at 0830A/13. HMS Hermione again obtained a fleeting glimpse of an aircraft low down at 0910A/13 but the fighters were unable to intecept. Later signals were recieved that the force had been reported at 0825 and 0843 hours.
It is clear that the enemy reconnaissance aircraft are taking full anti-RDF precautions. If the enemy aircraft do not attempt to gain height until out of RDF range they will enjoy a fair degree of immunity from fighter interception providing they restrict their obervation to a short sighting and then withdraw below the horizon.
At 1105A/13 an unidentified aircraft was detected bearing 128° 33 miles. It closed to 23 miles and then opened on a bearing 160°. Fighters were directed but failed to make contact and were recalled at 35 miles.
News was recieved at 1130 and 1218 hours that the 1st and 2nd flights respectively had arrived at Malta. Confirmation that seven Blenheims and 45 Hurricanes had arrived was recieved at 1428A/13. During the afternoon the fighter patrol was increased to give more pilots training. HMS Furious also exercised her Sea Hurricanes.
At 1615A/13, HMS Hermione reported an aircraft in sight low down and later a signal was intercepted showing that this shadower had reported the force. Again lack of RDF results rendered fighter direction impossible.
The passage back to Gibraltar was uneventful and the 14th was devoted to various practices. One Fulmar crashed in the sea when attempting to land on buth both crewmembers were saved.
At 1310A/14, HMS Nelson, HMS Furious, HMS Hermione with four destroyers (HMS Foresight, HMS Forester, HMS Lively and HMS Gurkha) proceeded ahead and entered harbour at 1630A/14.
HMS Ark Royal and the remaining three destroyers (HMS Zulu, HMS Lance and HMS Legion) remained out for exercises upon completion of which no. 812 Squadron was landed on coming from North Front. They entered harbour at 1915A/14. (60)
16 Sep 1941
Around 0800A/16, the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN) and the destroyers HMS Gurkha (Cdr. C.N. Lentaigne, RN), HMS Legion (Cdr. R.F. Jessel, RN) and HMS Lance (Lt.Cdr. R.W.F. Northcott, RN) departed Gibraltar for exercises to the east of Gibraltar.
They were followed around 1100A/16 by the battleship HMS Nelson (Capt. T.H. Troubridge, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN) and the destroyers HMS Cossack (Capt. E.L. Berthon, DSC, RN), HMS Zulu (Cdr. H.R. Graham, DSO, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) and HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN).
HMS Nelson, HMS Cossack, HMS Gurkha, HMS Legion and HMS Lance returned to harbour around 2330A/16.
HMS Ark Royal, HMS Zulu, HMS Fury and HMS Foresight returned to harbour around 1330A/17. (60)
25 Sep 1941
Operation Halberd Supply convoy to Malta.
Continuation of the events of 17 September 1941, convoy WS 11X.
Situation at 1800 hours on 24 September 1941.
At 1800B/24 the situation was as follows; Convoy WS 11X was to the west of Gibraltar escorted at that moment by the British battleship HMS Prince of Wales (Capt. J.C. Leach, MVO, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral A.T.B. Curteis, CB, RN), the British light cruisers HMS Edinburgh (Capt. H.W. Faulkner, RN, flying the flag of Rear-Admiral E.N. Syfret, RN), HMS Kenya (Capt. M.M. Denny, CB, RN), HMS Euryalus (Capt. E.W. Bush, DSO, DSC, RN), HMS Sheffield (Capt. A.W. Clarke, RN), the British destroyers HMS Laforey (Capt. R.M.J. Hutton, DSO, RN), HMS Lightning (Cdr. R.G. Stewart, RN), HMS Oribi (Lt.Cdr. J.E.H. McBeath, DSO, RN), HMS Cossack (Capt. E.L. Berthon, DSC, RN), HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN), the British escort destroyers HMS Farndale (Cdr. S.H. Carlill, RN) and HMS Heythrop (Lt.Cdr R.S. Stafford, RN).
At Gibraltar were the British battleships HMS Nelson (Capt. T.H. Troubridge, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), HMS Rodney (Capt. J.W. Rivett-Carnac, DSC, RN), the British aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN), the British light cruiser HMS Hermione (Capt. G.N. Oliver, RN), the British destroyers HMS Duncan (Lt.Cdr. A.N. Rowell, RN with Capt. D.(13) Capt. H.W. Williams, RN, on board), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN), HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN), HMS Lively (Lt.Cdr. W.F.E. Hussey, DSC, RN), HMS Legion (Cdr. R.F. Jessel, RN), the Polish destroyers ORP Piorun (Kmdr.por. (Cdr.) E.J.S. Plawski), ORP Garland (Kmdr.por. (Cdr.) K.F. Namiesniowski) and the Dutch destroyer HrMs Isaac Sweers (Cdr. J. Houtsmuller, RNethN). Also at Gibraltar was the RFA oiler Brown Ranger (3417 GRT, built 1941) and the British corvette HMS Fleur de Lys (Lt.(Retd.) A. Collins, RNR).
Approaching Gibraltar from the west were the British destroyers HMS Zulu (Cdr. H.R. Graham, DSO, RN), HMS Gurkha (Cdr. C.N. Lentaigne, RN) and HMS Lance (Lt.Cdr. R.W.F. Northcott, RN).
Movement of forces on the night of 24/25 September.
At 1815 hours, HMS Nelson departed Gibraltar and after passing farewell messages to HMS Rodney she proceeded westwards screened by HrMs Isaac Sweers, ORP Piorun and ORP Garland. These ships reversed course at 2130 hours and proceeded eastwards.
Shortly after HMS Nelson and her three escorting destroyers had departed Gibraltar harbour HMS Gurkha, HMS Zulu and HMS Lance, wich had been sent ahead to fuel aft Gibraltar, entered harbour.
At 2030B/24 RFA Brown Ranger and her escort, corvette HMS Fleur de Lys departed Gibraltar to take up a position eastwards to fuel the destroyers that were to protect the Halberd convoy.
At 2300B/24 HMS Rodney, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Hermione escorted by HMS Duncan, HMS Foresight, HMS Forester, HMS Lively, HMS Zulu, HMS Gurkha, HMS Legion and HMS Lance departed from Gibraltar eastwards to simulate a normal sortie by 'Force H' and to rendezvous with the convoy to the eastward of Gibraltar at 0800B/25.
'Force Z', consisting of, HMS Princess Beatrix (4136 GRT, built 1939) (Cdr.(ret.) T.B. Brunton, RN), HMS Queen Emma (4136 GRT, built 1939) (Capt.(ret.) G.L.D. Gibbs, DSO, RN), HMS Royal Scotsman (3288 GRT, built 1936) (T/Cdr. J.W. Peters, RNR) (whose ultimate destination was Freetown), HMS Ulster Monarch (3791 GRT, built 1929) (T/Cdr. J. Wilson, RNR) and Leinster (4302 GRT, built 1937) escorted by the British corvettes HMS Jonquil (Lt.Cdr. R.E.H. Partington, RD, RNR), HMS Spiraea (T/Lt. L.C. Head, RNVR) and HMS Azalea (Lt. G.C. Geddes, RNR) had been stationed behind the main convoy at dusk was ordered to proceed into Gibraltar Bay. It was hoped that the presence of these ships in the Bay would lay suspicion in the event of the convoy having been sighted and reported while passing through the Straits.
The remainder of convoy WS 11X, made up of transport ships Ajax (7797 GRT, built 1931), City of Calcutta (8063 GRT, built 1940), City of Lincoln (8039 GRT, built 1938), Clan Ferguson (7347 GRT, built 1938), Clan Macdonald (9653 GRT, built 1939), Dunedin Star (11168 GRT, built 1936), Imperial Star (12427 GRT, built 1934), Rowallan Castle (7801 GRT, built 1939) and HMS Breconshire (9776 GRT, built 1939) (Capt.(ret.) C.A.G. Hutchison, RN), with the escort, organised in two groups one mile apart, and led by the Vice Admiral, 2nd in Command, Home Fleet in HMS Prince of Wales, and the Rear Admiral commanding 18th Cruiser Squadron in HMS Edinburgh respectively, passed south of Europa Point at 0130B/25. This disposition was adopted to reduce the frontage of the convoy during its passage through the Straits.
At 0730B/25 HMS Rodney, HMS Ark Royal and their screening destroyers were sighted from HMS Nelson at a range of about 10 nautical miles. Half an hour later the convoy and its escort was sighted.
The escorting force was now reorganised into two groups; Group 1: HMS Nelson, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Hermione, HMS Cossack, HMS Zulu, HMS Foresight, HMS Forester, HMS Laforey and HMS Lightning.
Group 2: HMS Prince of Wales, HMS Rodney, HMS Kenya, HMS Edinburgh, HMS Sheffield, HMS Euryalus, HMS Duncan, HMS Gurkha, HMS Legion, HMS Lance, HMS Lively, HMS Oribi, HrMs Iscaac Sweers, ORP Piorun, ORP Garland, HMS Fury, HMS Farndale and HMS Heytrop and the entire convoy.
Events of group 1 and group 2 during 25 September
At 1700B/25 (time zone -2) HMS Duncan obtained an Asdic contact in position 36°36'N, 01°58'W and attacked with a pattern of four depth charges (more were intended but the starboard thrower failed to fire. Another depth charge attack was carried out by HMS Grukha at 1716 hours. She dropped a pattern of fourteen depth charges. HMS Duncan attacked again at 1750 hours with a second depth charge pattern. Both destroyers then proceeded to rejoin the screen at 1758 hours. Both ships sighted bubbles rising to the surface possibly from a damaged submarine.
Meanwhile on the 25th all destroyers of group 2 were fuelled by RFA Brown Ranger but not without delay as Brown Rangers speed was slower then anticipated and she was therefore further to the west then anticipated. This resulted in that not all destroyers were back in position at dusk. HMS Oribi was unable to find group 2 during the night and joined up with group 1 until daylight of the 26th when she rejoined group 1.
Events of group 1 and group 2 during 26 September
At 0932B/26 lookouts on HMS Nelson spotted an Italian aircraft shadowing group 1 at a range of 10 miles. The aircraft was flying very low and had not been picked up by RDF. The fighters from HMS Ark Royal that were in the air failed to intercept this aircraft due to failure of the R/T equipment in the flight leaders aircraft. An enemy report from the aircraft was intercepted at 0935 hours. A re-broadcast of this signal by an Italian shore station was picked up 20 minutes later.
At 1300 hours Group 1 reversed course to close the distance to group 2 and HMS Hermione was stationed astern of HMS Ark Royal for RDF purposes and to give additional AA protection to the carrier.
At 1537 hours two aircraft were sighted low down to the eastward by HMS Zulu, HMS Nelson and HMS Hermione. These aircraft were at first thought to be Hudsons but turned out to be enemy when a signal they made was intercepted. By now it was too late to vector fighters towards them.
Movements of group 1 and group 2 and enemy air attacks during 27 September.
Around 0730B/27 group 1 and 2 joined. HMS Ark Royal was now protected by HMS Euryalus (ahead) and HMS Hermione (astern) as close escort. Four Fulmar fighters were flown off at 0800 hours. This number was increased to ten at 1000 hours and twelve at 1100 hours and finally to sixteen at 1200 hours when it was though most likely air attacks might develop due to the fact the the forcehad been shadowed and reported by enemy aircraft from at least 0810 hours.
At 1255 hours RDF picked up enemy aircraft formations closing in on the convoy, one from the north and one from the east, both 30 miles distant. Position was 37°48'N, 08°50'E. Fighters were vertored towards these formations and one enemy aircraft was shot down at 1300 hours. Six enemy torpedo bombers approached from the port bow and beam of the convoy. Two were shot down at 1302 hours, most likely by AA fire from HMS Rodney and HMS Prince of Wales. An unknown number of torpedoes were dropped by the other aircraft. No hits were obtained but HMS Lance was narrowly missed by two of these torpedoes. HrMs Isaac Sweers was missed with one torpedo by 30 yards and HMS Rodney by one torpedo by 100 yards. One of the attacking aircraft was shot down by the destroyers while another torpedo bomber meanwhile was shot down by the Fulmars from the Ark Royal. Finally at 1310 hours a Fulmar was accidentaly shot down by HMS Prince of Wales. The first attack was was now over.
At 1327B/27 RDF reported a group of aircraft splitting into two formations and approaching from the east. Destroyers on the starboard wing of the screen opened fire at 1329 hours when six or seven torpedo bombers (BR 20's) were seen approaching very low from the starboard bow and beam. Position was 37°49'N, 08°58'E.
Three of these aircraft pressed on through the barrage put up by the destroyers and made a most determined attack on HMS Nelson who was swinging to starboard to comb the tracks. On aircraft dropped its torpedo out 450 yards 20° on Nelson's starboard bow passing over the ship at a height of 200 feet. This aircraft was almost certainly shot down astern of HMS Nelson by HMS Sheffield and HMS Prince of Wales. The track of the torpedo was not seen until about 150 yards ahead of the ship and no avoiding action was possible and the torpedo hit HMS Nelson on the port bow 10 feet below the waterline. The speed of HMS Nelson was reduced to 18 knots.
The second aircraft of this formation missed HMS Nelson with its torpedo by about 100 yards while the third aircraft was claimed to have been shot down by HMS Laforey. It's W/T operator, the only one of the crew alive but wounded, was picked up by HMS Forester.
Three or four aircraft from this group attacked from the starboard quarted but without result.
One torpedo bomber was shot down by the Fulmars at 1336 hours. One of the Fulmars was now shot down by mistake by pompom fire from HMS Rodney but the crew was rescued by HMS Duncan.
At 1345 hours the third attack started. RDF reported a group coming in from the south-west. Ten or eleven S.79's split into two groups and were seen coming in low over the water and were taken under fire from the escorting ships on the starboard side of the convoy. Seven or eight of the attackers then retired to the south-west and disappeared but three others tried to work round the starboard bow of the convoy which then turned ay 60° to port. The three attackers were then driven off by gunfire from the destroyer screen and dropped their torpedoes at long range but one torpedo narrowly missed HMS Lightning. One of these aircraft was shot down by a Fulmar as it retired. Position of this attack was 37°50'N, 09°06'E.
At 1354 hours three of the aircraft that had initialy turned away returned from astern. Two of these retired again on being fired at but the third pressed on to attack HMS Ark Royal but it was shot down by AA fire from that ship and HMS Nelson before it had dropped it's torpedo.
At 1358 hours one aircraft, seen right ahead of HMS Nelson, dropped a torpedo outside the screen. HMS Cossack was able to avoid this torpedo by the HE of this torpedo being picked up by her Asdic set.
Attempt to intercept the Italian battlefleet
While the third air attack was still in progress at 1404 hours an emergency report was received from an aircraft operating from Malta that it had sighted two Italian battleships and eight destroyers in position 38°20'N, 10°40'E steering a course of 190° at 20 knots at 1340 hours. The position of HMS Nelson when this report was received was 37°46'N, 09°04'E so the enemy was only 70-75 miles away. At this time HMS Nelson, with it's gun armament unimpaired was thought to be capable of 18 knots or more. Admiral Somerville decided to proceed towards the enemy at best speed with HMS Nelson, HMS Prince of Wales, HMS Rodney and the destroyers HMS Duncan, HMS Gurkha, HMS Lance, HMS Lively, HrMs Isaac Sweers and ORP Garland, leaving HMS Kenya, HMS Edinburgh, HMS Sheffield and ten destroyers with the convoy. HMS Euryalus, HMS Hermione and the destoyers HMS Piorun and HMS Legion remained with the Ark Royal.
It was also decided to fly off two Swordfish aircraft from the Ark Royal to take over shadowing duties from the aircraft operating out of Malta and to arm and fly off air striking force as soon as possible.
Ark Royal launched the two Swordfish at 1448 hours. It was intended to have launched them earlier but the launch was delayed due to the main armamant of HMS Ark Royal being in action and the recovery of two Fulmar fighters which were short on fuel.
In the meantime, at 1425 hours, the aircraft that was in contact with the Italians now also reported four cruisers and eight destroyers 15 nautical miles west-south-west of the enemy battlefleet. They were steering the same course and speed.
Meanwhile, at 1417 hours, the battleships had been ordered to form on HMS Nelson who had increased speed and proceeded ahead of the convoy. However at 1433 hours it became necessary for HMS Nelson to reduce speed to avoid further flooding due to the damage sustained. The Vice Admiral, 2nd in Command, Home Fleet in HMS Prince of Wales was now ordered to proceed with his flagship, HMS Rodney, HMS Edinburgh, HMS Sheffield and six destroyers to close the enemy at best speed. HMS Nelson meanwhile took station astern of the convoy.
While these instructions were carried out a report was received that the enemy had reversed course to 360°. This was followed by a further report that the enemy was steering 060°. Also a report was received that the battleships were of the Littorio class and not Cavour's as was previously believed. It was now clear that the enemy tried to avoid contact. It was still hoped that a striking force from HMS Ark Royal would be able to inflict damage to the enemy and reduced his speed allowing our battleships to overtake him before dark.
At 1530 hours a Fulmar fighter which was short of fuel force landed on the water astern of the Ark Royal. The crew was picked up by ORP Piorun.
At 1540 hours, HMS Ark Royal launched her stiking force of twelve Swordfish and four Fulmars. These aircraft did not find the enemy force and all aircraft returned to HMS Ark Royal around 1900 hours.
Between 1620 and 1645 hours, Fulmars from the CAP drove off an air attack threatening from the port side of the convoy. Later a shadowing enemy aircraft was shot down by Fulmars.
At 1658 hours, the Vice Admiral, second in Command Home Fleet, was ordered to reverse course and rejoin the convoy which was done at 1851 hours. No further reports of the enemy had been received for almost two hours and even if the striking force from HMS Ark Royal was able to inflict damage on the enemy these could not be intercepted before dark.
Detachment of Force X and the convoy.
At 1855 hours, on reaching the Skerki Channel, the escort of the convoy was split up into two forces, Force A, made up of HMS Nelson, HMS Prince of Wales, HMS Rodney, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Duncan, HMS Gurkha, HMS Legion, HMS Lively, HMS Lance, HMS Fury, HrMs Isaac Sweers, ORP Piorun and ORP Garland split off from the convoy while Force X, made up of HMS Kenya, HMS Edinburg, HMS Sheffield, HMS Hermione, HMS Euryalus, HMS Cossack, HMS Zulu, HMS Foresight, HMS Forester, HMS Laforey, HMS Lightning, HMS Oribi, HMS Farndale and HMS Heythrop remained with the convoy.
Between 1915 and 1930 hours enemy aircraft twice approached the convoy but turned away after fire had been opened on them. They were probably CR.42 fighters.
Night T/B attack on Force X and the convoy and loss of the Imperial Star.
Between 2000 and 2040 hours four torpedo bomber attacks were made on the convoy and Force X from the port beam, two or three aircraft taking part in each attack. The first two attacks had no result for the Italians.
During the third attack the two rear ships in the port column of the convoy collided with each other, these were the Rowallan Castle and the City of Calcutta. No serious damage was sustained and both were able to proceed on their way.
During the fourth attack, at 2032 hours, in position 37°31'N, 10°46'E the Imperial Star was struck by a torpedo on her port side aft. HMS Oribi was also attacked and narrowly missed by a torpedo four minutes later. She was able to shoot down the aircraft that had dropped this torpedo with her pompom and oerlikons.
When the Imperial Star was torpedoed it is probable that the explosion blew away both propellers and her rudder. In addition no.6 hold and the after engine room were both flooded.
HMS Heythrop, the rear ship of the port screen, proceeded alongside, but did not attempt to take Imperial Star in tow as she did not consider she was a suitable vessel to do so.
About 2045 hours HMS Oribi was ordered by HMS Euryalus to go to the assistance of the Imperial Star. When Oribi closed Heythrop was already standing by, and while Heythtop took off the passengers of the Imperial Star, HMS Oribi proceeded alongside to receive a report of the damage. It was decided to attempt to tow her to Malta.
For two hours the most determined attemps were made by HMS Oribi to tow the Imperial Star to Malta and although a speed of 8 knots was obtained nothing could be done to prevent her steering in circles. At is thought that her damaged stern was now acting as rudder.
Eventually, at 0120B/28, HMS Oribi found herself being dragged stern first by her tow sheering off and she was forced to slip the tow. Oribi went alongside to consult again and it was reluctantly decided that there was no other choice then to scuttle the ship. Three depth charges were placed lashed together abreast a bulkhead and these were fired by a safety fuse.
HMS Oribi cast off 0340B/28 and the depth charges were fired eleven minutes later, starting a large fire aft. As this did not spread quickly, Oribi shelled Imperial Star with 4.7" S.A.P. shells. Oribi finally left her at 0452 hours. Imperial Star was by that time heavily on fire fore and aft and listing badly. Aircraft from Malta could not find the wreck of the Imperial Star so there is no doubt that she sank.
HMS Oribi then made off from the scene along the convoy route at 32 knots and came with them near Malta 1215B/28 having passed unmolested within 7 nautical miles from the Sicilian coast in daylight.
Passage of the convoy and Force X through the narrows.
In the meantime the convoy and Force X had proceeded through the narrows along the south coast of Sicily.
In the meantime. at 2030B/27, HMS Hermione had departed the convoy to carry out a bombardment of Pantellaria harbour. Having completed the bombardment HMS Hermione rejoined Force X at 0615B/28. At daylight HMS Farndale and HMS Heythrop were detached to fuel at Malta.
Although several formations of enemy aircraft were detected between dawn and the arrival of the convoy at Malta, the excellent protection given by shore based fighters from Malta prevented any attack from developing.
At 0800B/28 a report was received that no enemy surface forces were reported near the convoy. The cruisers HMS Kenya, HMS Sheffield, HMS Euryalus and HMS Hermione then proceeded ahead to Malta to fuel where they arrived at 1130 hours. The remainder of Force X and the entire convoy, with the exception of the Imperial Star, arrived later in the afternoon.
Movements of Force A during 28 September.
While Force X and the convoy continued on to Malta, Force A proceeded to the west at 14 knots, which was the best speed of HMS Nelson at that time.
At 0725B/28 HMS Ark Royal flew off one A/S patrol and three fighters. At 0812 hours one enemy shadower was seen but it escaped into a cloud.
At 1025 hours HMS Nelson sighted a Cant. 506 aircraft very low down and fighters were vectored in. After a chase to the south-east this aircraft was shot down near Cape de Fer, Algeria.
Shadowers were again reported at 1640 hours and again one hour later but due to a failure of the R/T transmitter in Ark Royal it was not possible to vector fighters in time to intercept. An enemy report made by Italian aircraft was intercepted at 1720 hours.
At 1942B/28 one of the destroyers of the screen, HMS Duncan, obtained an Asdic contact in position 37°30'N, 03°45'E. She carried out two depth charge attacks but with no apparent result. HMS Legion closed to co-operate but did not gain contact. Both ships left the area at 2012 hours to rejoin the screen.
At 2020 hours speed was reduced to 12 knots to reduce the strain on bulkheads and decks of HMS Nelson. At this time Nelson was about 8 feet down by the bows and it was estimated that 3500 tons of water had entered the ship.
At 2100B/28, HMS Prince of Wales, HMS Rodney, HMS Ark Royal, HMS Gurkha, HMS Lance, HMS Legion, HMS Lively, HMS Fury and HrMs Isaac Sweers were detached to proceed to the eastward and rendezvous with Force X. HMS Nelson, escorted by HMS Duncan, ORP Piorun and ORP Garland, continued on to Gibraltar.
At 0555B/29, in position 37°30'N, 06°25'E, HMS Prince of Wales obtained an RDF surface echo ahead, and an emergency turn of 40° to port was carried out with all ships at 0609 hours. Three minutes after this turn HMS Gurkha sighted a torpedo track approaching. It was too late to alter course to avoid. A second torpedo track followed a few seconds later. Both torpedoes appeared to pass underneath the ship. HMS Gurkha then turned to port in the direction from which the torpedoes had approached and HrMs Isaac Sweers also joined to hunt the submarine. No A/S contacts were obtained and no depth charges were dropped. HMS Gurkha and HrMs Isaac Sweers rejoined the screen at 0700B/29. The attacker was the Italian submarine Diaspro which managed to escape unharmed.
At 0810B/29 HMS Gurkha obtained an A/S contact in position 37°26'N, 07°14'E. At 0815 hours a pattern of fourteen depth charges was dropped. Six minutes later a heavy underwater explosion was heard. At 0841 hours HMS Gurkha was ordered to rejoin screen and the hunt was abandoned.
Movements of Force X during 28/29 September on the return trip from Malta.
In the meantime the ships that are part of Force X had all fuelled at Malta and at 1500B/28 the escort destroyers HMS Farndale and HMS Heythrop were sailed followed at 1615 hours by HMS Kenya, HMS Edinburgh and HMS Oribi. The remainder of Force X sailed at 1830 hours. HMS Farndale and HMS Heythrop joined Force A at 0835B/29. The remainder of Force X joined Force A at 1030B/29.
Movements of HMS Nelson and passage to Gibraltar.
In the meantime HMS Nelson and her three escorting destroyers were still proceeding to the west. They were joined by aircraft to provide additional A/S protection from 0730B/29 onwards.
At 1110B/29, ORP Piorun obtained a doubtful A/S contact and dropped one depth charge.
At 1909B/29, HMS Duncan also obtained A/S contact and dropped one depth charge.
At 1945B/29 the A/S screen was reinforced by the destroyer HMS Rockingham (Lt.Cdr. A.H.T. Johns, RN) coming from Gibraltar. Later in the evening four corvettes also joined for additional A/S protection of the damaged battleship, HMS Samphire (Lt.Cdr. F.T. Renny, DSC, RNR) joined at 2120B/29, HMS Jonquil (Lt.Cdr. R.E.H. Partington, RD, RNR) at 2140B/29, HMS Fleur de Lys at 2150B/29 and finally HMS Arbutus (T/Lt. A.L.W. Warren, DSC, RNR) at 2340B/29. Nelson's screen now consisted of four destroyers and four corvettes.
At 0130B/30 HMS Samphire and HMS Arbutus obtained an A/S contact and dropped depth charges without result, the contact was probably non-sub.
At 1200B/30 HMS Nelson entered Gibraltar Harbour.
Movements of Force A and Force X as of 1030 hours on 29 September.
Meanwhile after all ships of Force X had joined up with force A at 1030B/29 course was shaped to the westward, keeping 40 nautical miles clear of the African coast.
At 1645B/29, in position 37°26'N, 04°37'E, HMS Lively, sighted an object resembling a ship's lifeboat with mast at a range of 1000 yards. This was soon identified as the conning tower and periscope of a submarine momentarily breaking surface. Two torpedo tracks were sighted shortly afterwards. Lively immediately attacked with a pattern of fourteen depth charges at 1650 hours. HMS Legion, which was next to Lively in the destroyer screen, had already dropped a pattern of five depth charges about a minute and a half earlier. HMS Legion then joined up with HMS Lively to hunt this submarine.
At 1700 hours HMS Lively obtained a definate A/S contact and attacked with another pattern of fourteen depth charges five minutes later. After having dropped this pattern contact was regained at 1715 hours. Contact was however soon lost at and not regained. The hunt was abandoned at 1745 hours.
At 1930B/29, HMS Prince of Wales, HMS Kenya, HMS Sheffield, HMS Laforey, HMS Lightning, HMS Oribi, HMS Foresight, HMS Forester and HMS Fury parted company with the rest of the force and proceeded ahead to arrive at Gibraltar p.m. 30 September 1941. They arrived at Gibraltar at 1800B/30.
At 0928B/30, in position 37°10'N, 00°56'E, HMS Gurkha, obtained Asdic contact wich was confirmed as a submarine. She immediately attacked and fired a pattern if fourteen depth charges at 0935 hours. A black circular buoy with electric cable attached to it came to the surface after this attack. At 0945 hours a loud underwater explosion was heard and felt and oil started to come to the surface. Gurkha was unable to gain contact on the submarine from now on. HMS Legion who was by now assisting Gurkha in the hunt obtained contact and attacked with a fourteen depth charge pattern at 0955 hours. A second fourteen depth charge pattern was fired at 1009 hours. During Legion's second attack wreckage and oil came to the surface. Among the wreckage picked up was an Italian dictionary, a mattess, a pillow, numerous pieces of wood, some with bright screws and a piece of human scalp attached to a piece of wood by a splinter of metal. The interiors of the dictionary, the mattress and the pillow were dry. There was now no doubt that an Italian submarine was sunk by HMS Gurkha and HMS Legion.
All ships in this force entered Gibraltar harbour between 0700 and 0900 hours on 1 October.
Convoy MG 2, passage of three merchant vessels from Malta to Gibraltar.
At noon on the 26th the first out of three empty transports, the Melbourne Star (11076 GRT, built 1936), departed Malta for Gibraltar. At 1030B/27 the other two ships Port Chalmers (8535 GRT, built 1933) and City of Pretoria (8049 GRT, built 1937). These last two ships were escorted by the corvette HMS Gloxinia (Lt.Cdr. A.J.C. Pomeroy, RNVR) until 1930B/27. After an uneventful passage the Melbourne Star arrived at Gibraltar at 0700B/29. The Port Chalmers and City of Pretoria were spotted and reported by Italian aircraft at 1200B/27, shortly after leaving Malta. No enemy surface craft were seen until 2320B/27 when it was believed that an E-boat was sighted by the Port Chalmers which was following in the wake of the City of Pretoria. The Port Chalmers opened fire on the E-boats bow wave with it's 4" gun. The enemy then returned fire with a machine gun. After six rounds of 4" the enemy crossed the stern of the Port Chalmers and was not seen again. The City of Pretoria had not seen the enemy at all. The action had taken place about 15 nautical miles south-south-west of Pantelleria.
At 0535B/28 the Commodore of the convoy ordered he Port Chalmers to part company. Port Chalmers then proceeded at full speed, wearing French colours.
At 0915B/28 an Italian Cant. 506 seaplane approached from the direction of the French north African coast and circled the City of Pretoria. This aircraft then made off to the westward and gave the Port Chalmers the same attention. Both ships were wearing French colours and had taken care to keep all service personnel out of sight. Both ships were fully ready for action, but did not open fire as the aircraft took no offensive action.
At 1015B/28 the City of Pretoria was circled several times by a large three-engine seaplane, with distinct French markings, which approached from the direction of Bizerta.
At 1145B/28 the City of Pretoria sighted a twin-engined Italian seaplane stopped on the water, five nautical miles to the north. She lost sight of this aircraft at 1215 hours.
The Port Chalmers was circled by an Italian aircraft at 1555B/28. The aircraft did not attack.
At 1725B/28 the City of Pretoria was attacked by three Italian torpedo bombers. As the aircraft approached with obviously hostile intentions the British colours were hoised and fire was opened as soon as the leader came in range. By skilful handling all three torpedoes were avoided. A submarine periscope was then reported on the starboard quarter by two independent lookouts. Three smoke floats and a depth charge set to 150 feet were dropped and under the cover of the smoke the City of Pretoria turned away.
When the City of Pretoria was approaching Cape de Gata at 0200B/30 an unidentified vessel, possibly a submarine, was seen to be following. Two or three rapid shots, followed by a dull explosion, were heard. City of Pretoria made smoke and dropped smoke floats and then made close in Almeira Bay, into territorial waters, thus shaking off her pursuer.
The Port Chalmers arrived at Gibraltar at 0900B/30. City of Pretoria followed during the afternoon. (63)
7 Oct 1941
HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN), HMS Hermione (Capt. G.N. Oliver, RN), HMS Legion (Cdr. R.F. Jessel, RN), HMS Lance (Lt.Cdr. R.W.F. Northcott, RN) and HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) departed Gibraltar at 0630 hours. Upon completion of the exercises they returned to harbour at 1915 hours. (60)
13 Oct 1941
Around 0700A/13, the aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN) departed Gibraltar for exercises to the east of Gibraltar. She was escorted by the destroyers HMS Cossack (Capt. E.L. Berthon, DSC, RN), HMS Sikh (Cdr. G.H. Stokes, DSC, RN), HMS Lance (Lt.Cdr. R.W.F. Northcott, RN) and the escort destroyer HMS Croome (Lt.Cdr. J.D. Hayes, RN).
They returned to Gibraltar around 1845A/13. (60)
16 Oct 1941
Operation Callboy.
Aircraft to be flown off to Malta and the transfer of ' Force K ' to Malta.
At 1100/16, ' Force H ' made up of the battleship HMS Rodney (Capt. J.W. Rivett-Carnac, DSC, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, DSO, RN), aircraft carrier HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, RN), light cruiser HMS Hermione (Capt. G.N. Oliver, RN) and the destroyers HMS Cossack (Capt. E.L. Berthon, DSC, RN), HMS Sikh (Cdr. G.H. Stokes, DSC, RN), HMS Zulu (Cdr. H.R. Graham, DSO, RN), HMS Legion (Cdr. R.F. Jessel, RN), HMS Foresight (Cdr. J.S.C. Salter, RN) HMS Forester (Lt.Cdr. E.B. Tancock, DSC and Bar, RN) and HMS Fury (Lt.Cdr. T.C. Robinson, RN) departed Gibraltar and proceeded eastwards.
Some exercises were carried out during the afternoon and early evening.
At 0640/17, two Swordfish were flown off from HMS Ark Royal for A/S patrol. These patrols were maintained throughout the day. A section of fighers was kept ranged until 0850/17 when they were flown off. During daylight always one section of fighters was kept in the air.
At 0710/17 the fleet made an emergeny turn after HMS Legion had obtained an A/S contact. The contact turned out to be non-sub.
Another non-sub contact was obtained by HMS Cossack about an hour later and again the fleet made an emergency turn. Two whales were sighted shortly afterwards which were the source of the A/S contact.
During the forenoon two more Fulmars were flown off for exercises (heightfinding and plotting). Also trials were carried out with the close range weapons in all ships.
At 1120/17 an unidentified aircraft was detected by RDF. It passed about 12 miles ahead of the fleet, steering a southerly course. It was not sighted.
Half an hour later HMS Ark Royal reported severe interference with fighter R/T from RDF transmissions. The interference proved to be coming from HMS Hermione and she was stationed further away from HMS Ark Royal.
At noon on the 17th ' Force H ' was in position 38°01'N, 02°26'E.
At 1350/17, a low flying Cant. 506 enemy aircraft was seen by HMS Ark Royal. This aircraft had not been picked up on RDF. One section of fighters was vectored towards it. The enemy was shot down after a chase of about 20 miles.
Around an hour later the fighters were vectored against an aircraft first detected by RDF and subsequently sighted to the north-west of the fleet. It proved to be a four-engined flying boat with French markings.
As ' Force H ' was ahead of time for arrival at the flying off position course was reversed at 1600/17 for one hour.
At 0130/18, course was altered to 050° for flying off. The destroyers took station in a circular screen around HMS Rodney and HMS Ark Royal. 11 Albacores and 2 Swordfish aircraft wee flown off between 0135 and 0145/18. One Albacore had been unable to take off due to a defect. On completion of flying off, the fleet formed up again and set course to 270°.
At 0547/18 the fleet had to make an emergency turn when HMS Forester reported a contact but it was soon reported to be non-sub and the fleet resumed its mean course.
At daylight, 0650/18, a fighter patrol of two Fulmars was flown off by HMS Ark Royal. Also two Swordfish for A/S patrol were flown off.
Fighters were vectored towards an aircraft reported by RDF as 25 miles ahead of the fleet at 0825/18 but they did not intercept. The aircraft which was on a northerly course was probably French on passage from Algiers to Merseilles.
A signal reporting the arrival at Malta of 11 Albacores was received at 0849/18. Later a further signal announced that one Swordfish had arrived. No news of the second Swordfish was recieved. No reason is known why this second Swordfish failed to arrive at Malta.
An aircraft was sighted from HMS Sikh south-west of the fleet at 0958/18. Fighters were vectored towards and they soon sighted an Italian BR.20. After a chase of 45 miles to the south-east the enemy was shot down about 10 miles from Cape Bengut.
Later another aircraft was detected by HMS Hermione. It was seen to be a Cant.506 but the fighters failed to intercept it.
At noon ' Force H ' was in position 37°20'N, 02°49'E. At 1400/18 course was altered to 245° to pass south of Alboran Island.
At 1450/18, HMS Hermione sighted a floating mine in position 37°25'N, 01°46'E but failed to sink it. She was then stationed ahead of the fleet for execises.
A/S and fighter patrol were withdrawn at 1825/18 and then landed on HMS Ark Royal.
At 2323/18, HMS Forester obtained an A/S contact which was thought to be a submarine. A pattern of five depth charges was dropped. The fleet turned 90° to starboard on the first report but when contact was not regained after the depth charge attack the fleet resumed the mean course.
The fleet altered course to 280° at 0645/19 and a few minutes later an A/S patrol of 2 Swordfish aircraft were flown off. This patrol was maintained until 1315/19 when it was reduced to one aircraft.
During the day an exercises programme was carried out. At 1000/19 ' Force K ' was sighted by HMS Hermione and also by the aircraft from HMS Ark Royal.
Ten Swordfish aircraft landed on HMS Ark Royal at 1120/19. They had come from North Front aerordrome.
The fleet entered Gibraltar Bay at 1619/19 and then entered harbour.
Meanwhile the cruisers of ' Force K ', HMS Aurora (Capt. W.G. Agnew, RN) and HMS Penelope (Capt. A.D. Nicholl, RN) departed Gibraltar and joined up at 0800/19 some 40 miles from Europa Point with the destroyers HMS Lance (Lt.Cdr. R.W.F. Northcott, RN) and HMS Lively (Lt.Cdr. W.F.E. Hussey, DSC, RN) which had been already out for exercises since 1715/18.
' Force K ' arrived at Malta umolested at 0915/21. (60)
7 Nov 1941
HrMs O 21 (Lt.Cdr. J.F. van Dulm, RNN) conducted exercises off Gibraltar with HMS Wishart (Cdr. H.G. Scott, RN) and aircraft from HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, CBE, RN) and HMS Malaya (Capt. C. Coppinger, DSC, RN). (64)
10 Nov 1941
Operation Perpetual and the sinking of HMS Ark Royal
Transfer of Hurrican fighters (from aircraft carriers) and Blenheim bombers (from Gibraltar) to Malta.
10 November 1941.
At 0235 hours (zone -1) on 10 November 1941, Force H departed Gibraltar for operation Perpetual. Force H was made up of the battleship HMS Malaya (Capt. C. Coppinger, DSC, RN, flying the flag of Vice-Admiral J.F. Somerville, KCB, KBE, DSO, RN), aircraft carriers HMS Ark Royal (Capt. L.E.H. Maund, CBE, RN), HMS Argus (Capt. G.T. Philip, DSC, RN) and the light cruiser HMS Hermione (Capt. G.N. Oliver, DSO, RN). They were escorted by seven destroyers; HMS Laforey (Capt. R.M.J. Hutton, RN), HMS Lightning (Cdr. R.G. Stewart, RN), HMS Legion (Cdr. R.F. Jessel, RN), HMS Gurkha (Cdr. C.N. Lentaigne, RN), HMS Sikh (Cdr. G.H. Stokes, DSC, RN), HMS Zulu (Cdr. H.R. Graham, DSO, DSC, RN) and HrMs Isaac Sweers (Cdr. J. Houtsmuller, RNN).
At 0800 hours, HMS Argus flew off one aircraft for A/S patrol and a Catalina aircraft joined from Gibraltar at 0930 hours. The force passed to the north of Alboran Island. A French merchant vessel was sighted ahead at 1526 hours. She was north bound. During the afternoon AA firing exercises were carried out.
11 November 1941.
Force H continued to the eastward during the night. As the takeoff of the Blenheim bombers from Gibraltar was delayed due to unsuitable weather conditions it was decided that Force H would withdraw to the westward for a while, with the dual object of increasing the distance to the enemy air bases in Sardinia and to give the impression to possible enemy shadowers that the fly off of the Hurricanes had already taken place, and that Force H was already retiring.
At 0935 two aircraft were reported by RDF to the southward. Later the echo faded, but they were sighted flying very low over the Algerian coast. They were too far to be identified and were thought to be possibly French. However a report timed 0935 by an Italian reconnaissance aircraft was intercrypted shortly afterward and it became clear that the two aircraft were in fact Italian.
As hurricanes were range on Ark Royal’s flight deck, making it impossible for her to operate her own fighters. Argus had two Sea Hurricanes ranged, but the enemy aircraft disappeared before these could be launched.
Between 1835 and 1910 hours Vice-Admiral Somerville had a message transmitted that unless the Hurricanes could be flown off the following morning he intended to return to Gibraltar, as he did not consider it desirable to remain in this area without A/S air and fighter patrols.
At 2130 hours, Force H turned to the eastward again towards the flying off position.
12 November 1941.
Shortly after midnight a signal was received that it was intended that the carriers could launch their Hurricanes for Malta at 1000 hours.
At 0743 hours a signal was received that the firt group of Blenheim bombers was airborn at that they would be near the takeoff position of the Hurricanes shortly after 1000 hours.
Between this time and the completion of flying off of all the land Hurricanes, no fighters were available for the interception of enemy aircraft.
Two aircraft, presumed hostile, were detected by RDF to the north-eastward at 0907 hours, but they were not sighted. Later a report from an Italian reconnaissance aircraft time 0907 hours was intercripted, and this no doubt originated from one of these two aircraft.
At 1004 hours four Blenheim bombers were sighted and by 1021 hours 13 Hurricanes had been launched by Ark Royal and 6 by Argus. One of the Hurricanes that was to be launched from Ark Royal had troubles with the engine and was, after repairs, included in the second batch that was to be launched.
At 1048 hours, two more Blenheims were sighted, and within five minutes Ark Royal had flown off the first of the Hurricanes for her second batch. By 1112 hours all Hurricanes had been launched by the carriers and they made off with the Blenheims for Malta.
By 1130 hours all ships were back in position after the flying off operations and course was set to the west. From Ark Royal one Swordfish was flown off for A/S duties and four Fulmars for fighter patrol. These patrols were maintained until dusk.
At 1425 hours HMS Ark Royal reported an aircraft in sight low down to the southward. The four Fulmar fighters were vectored but a section of two Fulmars only sighted the enemy until on the return trip from the chase. One of the Fulmars was able to fire one good burst of gunfire from 300 yards before the enemy aircraft escaped into the clouds. Both wings of this Fulmar were damaged by enemy gunfire. Two sighting reports from this aircraft were intercepted.
Between 1500 and 1515 hours RDF reported that enemy aircraft were shadowing the fleet but by now weather had deteriorated and there was much low rain cloud. Although fighters were vectored no interceptions were made.
At 1625 hours hours Malta reported the arrival of 34 Hurricanes and 7 Blenheims. One Blenheim had returned to Gibraltar with engine trouble. Also a report on U-boat sightings in the Western Mediterranean was received.
Late in the evening speed had to be reduced in the bad weather to avoid weather damage to the escorting destroyers.
13 November 1941
At 0140 hours, weather had improved at bit and speed was increased by one knot to 17 knots but by 0500 hous weather had worsened even further then earlier and speed was reduced to 15 knots. This was only temporary though and at 0630 hours speed was increased to 17 knots and by 0800 hours (daylight) even to 19 knots.
An underwater explosion was observed by HMS Legion in her wake at 0413 hours. This was also heard be several of the other ships. Legion at that time was the starboard wing destroyer. This was thought to be a torpedo exploding at the end of its run.
This might well be correct as according to German sources the German submarine U-205, at 0506 hours (Berlin time), made a torpedo attack on a force of enemy warships but no hits were obtained.
At 0645 hours, Ark Royal flew of an AS patrol of six Swordfish for a dawn A/S patrol. They sighted nothing. They returned at 0850 hours. More A/S patrol were maintained throughout the day.
At 0817 hours a report was received that submarine were to be expected to be in the area. Course was now altered to approach Gibraltar directly from the east and not as was usually the case along the Spanish or Maroccan coast.
Later in the morning HMS Laforey and later HMS Lightning both reports A/S contacts and the fleet evaded these.
The fleet conducted exercises in the afternoon. HMS Laforey reported another A/S contact and the fleet once again made an emergency turn. The contact was however soon classified as ‘non sub’ and the main course was promptly resumed.
At 1541 hours, while in position 36°03’N, 04°40’W HMS Ark Royal was hit by a torpedo on the starboard side. Following this HMS Malaya immediately altered course to port and increased speed. HMS Legion and HMS Gurkha, the rear destroyers on the starboard wing at once turned outwards and started an A/S search to the north and east of the Ark Royal, the most probable area where the attacker must have been.
At this time HMS Ark Royal was still going ahead at considerable speed, listing to starboard and apparently under port wheel. A number of her aircraft were still circling overhead as she had been conducting aircraft operations when she was hit.
At 1549 hours, HMS Laforey and HMS Lightning were ordered to join HMS Ark Royal who appeared to be loosing speed. Signals were also made to require tugs to be sent out from Gibraltar and all available A/S craft to be sent out to patrol the area. HMS Hermione was ordered to stand by HMS Ark Royal The remaining three destroyers, HMS Sikh, HMS Zulu and HrMs Isaac Sweers were ordered to screen HMS Malaya.
By 1610 hours, HMS Ark Royal was laying stopped and listing heavily to starboard but she reported she had steam on her port engine. HMS Laforey, HMS Lightning and HMS Gurkha had closed her and were circling Ark Royal. HMS Legion was alongside Ark Royal. HMS Hermione was still closing. HMS Malaya and her three escorting destroyers were about 5 miles off and proceeding to Gibraltar at 18 knots as was HMS Argus who was some distance astern of her but catching up on Malaya. At 1615 hours Argus flew off two Swordfish aircraft for A/S patrol.
At 1710 hours, when 8 nautical miles eastwards of Europa Point, HMS Malaya was passed by units coming out of Gibraltar to assist. These were the destroyer HMS Wild Swan (Lt.Cdr. C.E.L. Sclater, RN), motor launches ML 121, ML 130, ML 132, ML 135, ML 170, ML 172, ML 176 and the tugs St. Omar and Thames. Shortly before the tug St. Day had also been sighted proceeding eastwards. Besides these ships the destroyer HMS Vidette (Lt.Cdr. E.N. Walmsley, RN) had also been ordered to proceed to the east.
HMS Malaya and HMS Argus entered harbour around 1820 hours and before she was berthed Vice-Admiral Somerville had transferred to HMS Sikh and went out again to proceed to HMS Ark Royal. Shortly before Sikh left the harbour the destroyer HMS Wishart (Cdr. H.G. Scott, RN) had also left the harbour to assist. Sikh, Zulu, Isaac Sweers and Wishart joined the patrol near Ark Royal for the night.
At 1900 hours, three corvettes departed Gibaltar to assist. These were; HMS Rhododendron (Lt. H.I. Davis, RNVR), HMS Marigold (T/Lt. J. Renwick, RNR), HMS Pentstemon (Lt.Cdr. J. Byron, RNR). This last corvette had a large 6” portable pump on board
The trawlers HMS St. Nectan (T/Lt.Cdr. H.B. Phillips, RNR) and HMS Lady Shirley (Lt.Cdr. A.H. Callaway, RANVR) had also been sailed around 1715 hours to patrol the area. They had not been very near to Ark Royal during the coming night.
Around 2040 hours the situation was as follows. Ark Royal was being towed by Thames and St. Day. The tow was proceeding at 2 knots. It was hoped that Ark Royal was able to raise steam shortly.
At 2224 hours, the Capt. (D) 19th Destroyer Flotilla on board Laforey reported that Ark Royal had her own steam and power and that flooding was apparently under contral and that no more tugs would be required until off the harbour. Shortly afterwards Vice-Admiral Somerville therefore ordered the three corvettes to establish A/S patrol astern of the Ark Royal and to close her only by daylight.
At 2355 hours, HMS Legion arrived at Gibraltar packed with crew of HMS Ark Royal which were not needed in the rescue effort. After landing these she proceeded back to sea.
14 November 1941
At 0221 hours, the Capt. (D) 19th Destroyer Flotilla reported that Ark Royal had lost steam (and power) and that a powerful pump would be required. Another signal at 0242 hours stated that another tug would be required. This indicated that the situation was deteriorating. Vice-Admiral Somerville therefore ordered HMS Sikh to close. HMS Pentstemon, the corvette with the portable pump on board, was also ordered to close. From Gibraltar the tug Rollicker was also sent out to assist.
On approaching HMS Laforey, which was alongside Ark Royal together with St. Day, signaled to Sikh that Vice-Admiral Somerville could better transfer to an ML which he did. At 0430 hours Vice-Admiral Somerville boarded Laforey to find she was on the point of casting off from HMS Ark Royal. Capt. Maund was also on board Laforey with the last of the steaming party. Ark Royal now had a list of 35° and was listing still further judging by the straining and parting of wires securing the ships alongside her. The situation was reported by signal to the Admiralty at 0446 hours.
After getting clear in HMS Laforey, Vice-Admiral Somerville, ordered St. Day to go ahead of Thames but at 0600 hours Thames reported that she had cast off the tow as Ark Royal was sinking. The carrier turned over at 0613 hours and remained bottom up for a few minutes after which she disappeared from sight. This was reported by signal to the Admiralty at 0623 hours.
Vice-Admiral Somerville then ordered the Capt. (D) 19th Destroyer Flotilla to take all destroyers in the area under his command and to commence an A/S sweep to the eastward. He was instructed to return to Gibraltar by dark. In the end HMS Laforey, HMS Lightning, HMS Gurkha, HMS Legion and HMS Zulu returned to Gibraltar at 1535/14 followed about 15 minutes later by HMS Wild Swan.
Vice-Admiral Somerville himself returned to Gibraltar in HMS Sikh arriving at 0830 hours as did HrMs Isaac Sweers at 0900 hours. (60)
Media links
|
|
Sources
- ADM 199/393
- ADM 53/107522 + ADM 53/107725 + ADM 53/108563 + ADM 53/108656 + ADM 53/108667 + ADM 53/108689 + ADM 53/108736 + ADM 53/108757 + ADM 53/108783 + ADM 53/108830 + ADM 53/110128 + ADM 53/110779
- ADM 53/107522 + ADM 53/108667 + ADM 53/108736 + ADM 53/108757 + ADM 53/108830 + ADM 53/109748 + ADM 53/110651
- ADM 186/794
- ADM 53/107523 + ADM 53/110180
- ADM 53/110180
- ADM 199/380
- ADM 53/110180 + ADM 199/380
- ADM 53/110181 + ADM 199/380
- ADM 53/110731
- ADM 53/110182 + ADM 199/380
- ADM 53/110182
- ADM 53/109074
- ADM 53/111429 + ADM 53/112868 + ADM 199/380
- ADM 53/111429 + ADM 53/111919 + ADM 53/112968
- ADM 53/111919
- ADM 53/113068 + ADM 199/380
- ADM 53/112868 + ADM 53/113068 + ADM 199/380
- ADM 53/111320
- ADM 53/112031
- ADM 53/112194
- ADM 53/111429
- ADM 53/111430
- ADM 53/111431
- ADM 53/111431 + ADM 199/654
- ADM 53/111431 + ADM 53/111432 + ADM 53/122339
- ADM 53/111432 + ADM 53/111963
- ADM 53/111432
- ADM 53/111432 + ADM 199/654 + Report of proceedings from HMAS Stuart
- ADM 199/376
- ADM 199/376 (+ ADM 53/111432 and ADM 53/111433)
- ADM 53/112008 + ADM 199/388
- ADM 53/111433 + ADM 53/112269
- ADM 53/111433
- ADM 53/111434
- ADM 234/318
- ADM 186/797
- ADM 53/111435 + ADM 199/391
- ADM 199/386 + ADM 199/391
- ADM 199/391
- ADM 199/386 + ADM 199/387 + ADM 199/391
- ADM 53/111437
- ADM 199/392
- ADM 53/111437 + ADM 53/111438 + Reports of proceedings of HMAS Australia for September and October 1940
- ADM 53/111438
- ADM 53/111438 + ADM 53/111439 + ADM 53/111568 + ADM 53/112300 + ADM 53/112301
- ADM 199/387 + ADM 199/392
- ADM 53/111439 + ADM 53/113078
- ADM 234/325 + ADM 234/326
- ADM 53/111440 + ADM 199/392
- ADM 199/414 + ADM 199/656 + ADM 223/679 + ADM 234/335
- ADM 199/656
- ADM 199/1136
- ADM 53/114964 + ADM 199/656
- ADM 53/113627
- ADM 53/114965 + ADM 199/656
- File 2.12.03.6404 (Dutch Archives, The Hague, Netherlands)
- ADM 199/414 + ADM 199/656
- ADM 234/322
- ADM 199/657
- ADM 53/114626 + ADM 234/335
- ADM 199/657 + ADM 234/560 + ADM 234/561 + Official Italian naval history (USMM) volume 3
- ADM 199/831
- File 2.12.03.6410 (Dutch Archives, The Hague, Netherlands)
ADM numbers indicate documents at the British National Archives at Kew, London.
As an Amazon Associate uboat.net earns a commission from qualifying purchases.